Sexually Transmitted Infections and Urinary Tract Infections (Quiz 2)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
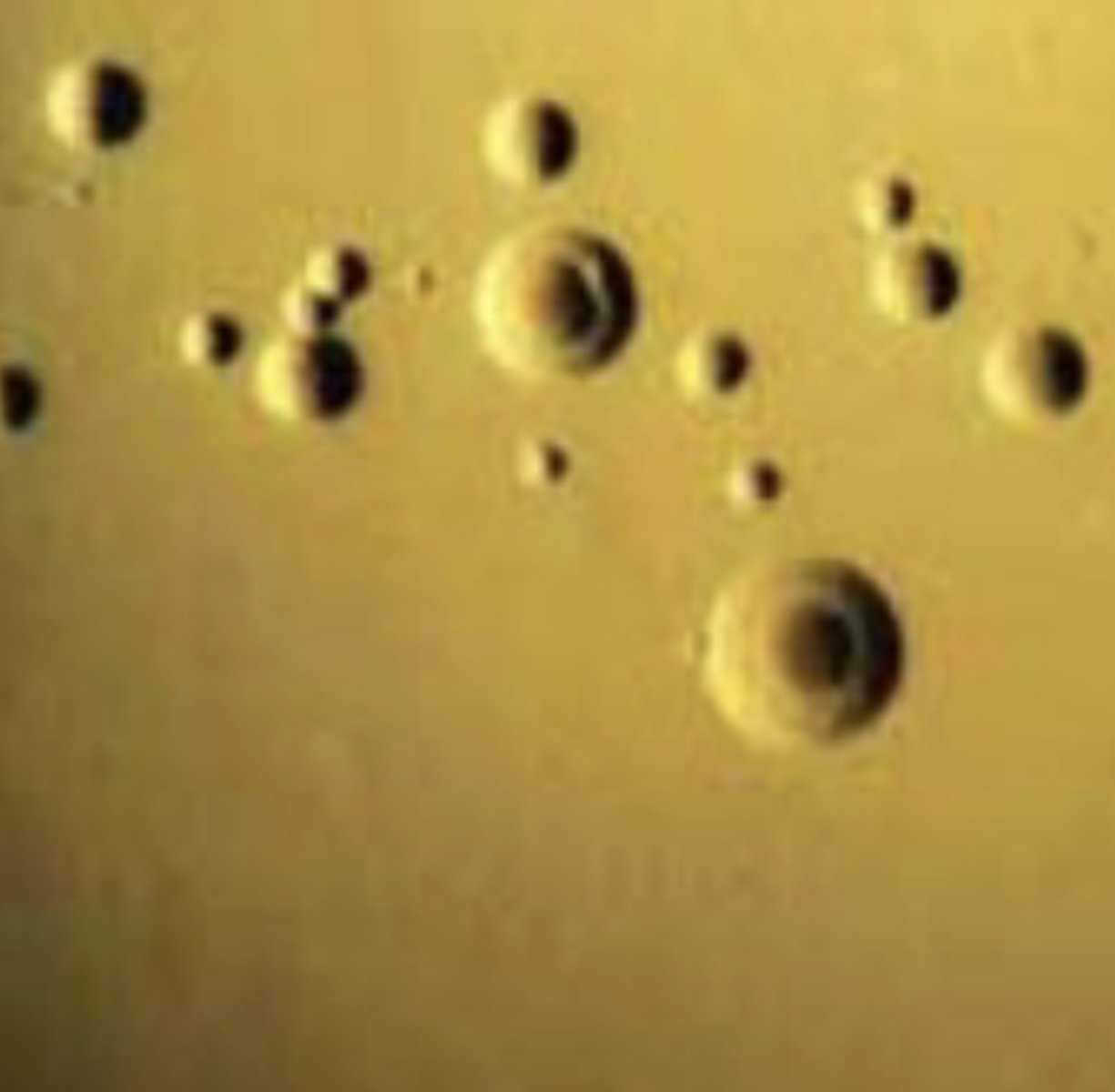
1. Mycoplasma
General Characteristics
-> Lack rigid ___ ___
-> Not affected by ________
-> Can be treated with __________
-> Small: 125 - 250nm
-> Pleomorphic (occur in various forms)
-> Require _________ for growth
Have sterols in their membrane but cannot synthesize it
-> Colonies have a “_____ ____” appearance
cell wall
Penicillin
Tetracyclines
cholesterol
Fried egg
1. Mycoplasma
Diagnosis
Best diagnosis is by _____ _____, reinforced by serological tests and or PCR assays
clinical signs
Chlamydia
-> Energy parasites; requiring living cells for ______
-> Small round to ovoid organism
-> Have 2 lipid bilayers and very little peptidoglycan
-> Three species commonly infect humans
1. Chlamydia _______
2. Chlamydia _______
3. Chlamydia _______
growth
trachomatis
psittaci
pneumoniae
Chlamydia
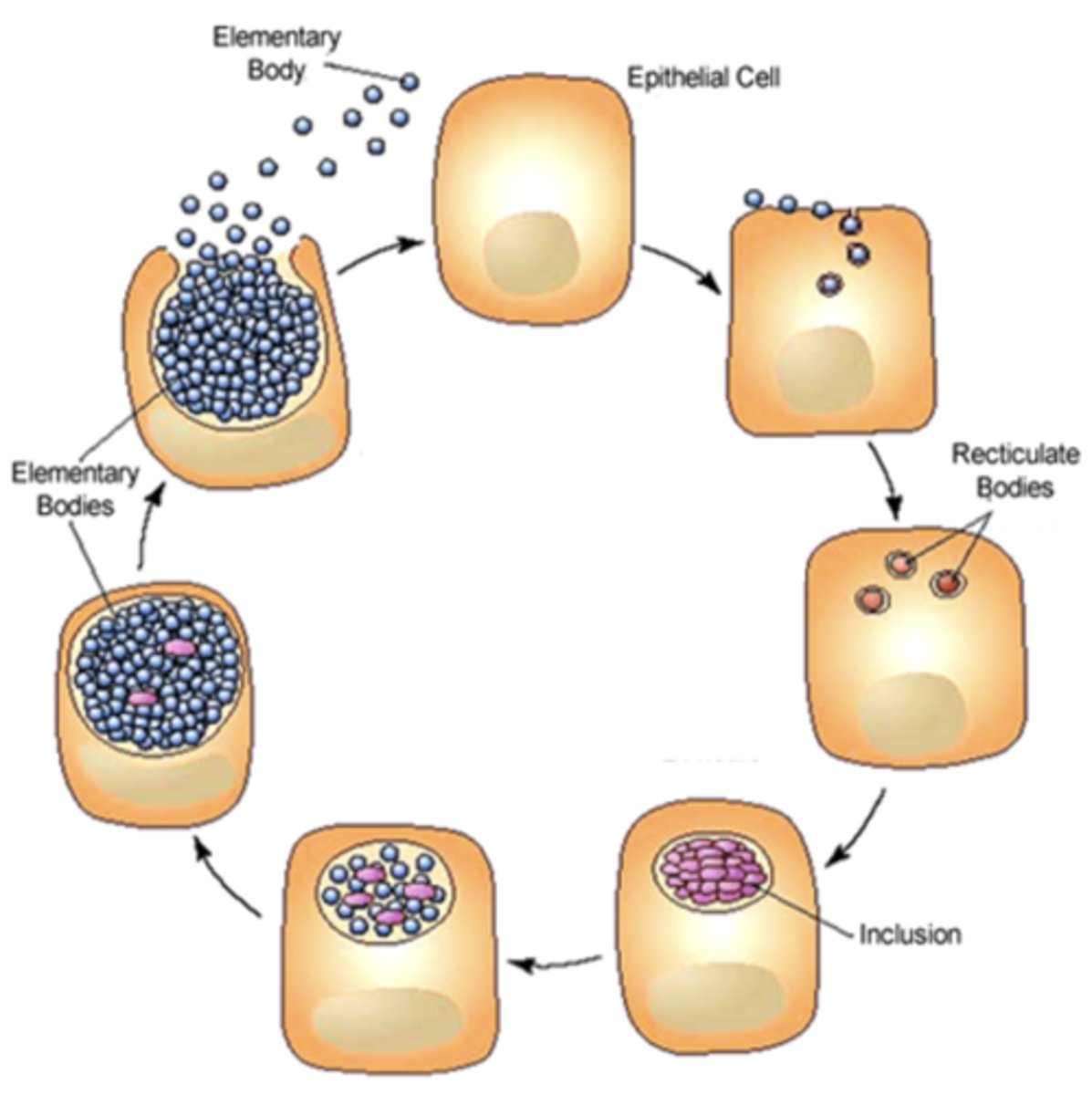
Intracellular Development Cycle
-> Infectious particle is called an “______ body” (EB) which is metabolically _______
-> Within hours (6-8), EB reorganizes into a larger metabolically _______ body called “______ body”
elementary
inactive
active
reticulate
"Elementary Body"
infectious or not infectious?
Infectious
"Reticulate Body"
infectious or not infectious?
not infectious
Life cycle of Chlamydia is about __ hours/_ days -> to start seeing clinical signs
48
2
Chlamydia
Life cycle of Chlamydia Summary
The __________ body (EB) is the infectious form of Chlamydia that attaches to a host cell __________ and enters the cell. Once inside, the EB reorganizes into the __________ body (RB), which is metabolically __________ but non-infectious. The RB replicates by __________ __________ within a membrane-bound structure called an __________. During replication, host DNA synthesis __________, and the RB produces its own __________, __________, and __________. The RBs then reorganize back into __________ bodies (EBs), causing __________ to increase. Finally, the host cell undergoes cell __________ or releases EBs, allowing infection of neighboring cells.
Elementary
receptor
Reticulate
active
binary fission
inclusion
declines
DNA
RNA
protein
Elementary
infectivity
lysis
Chlamydia
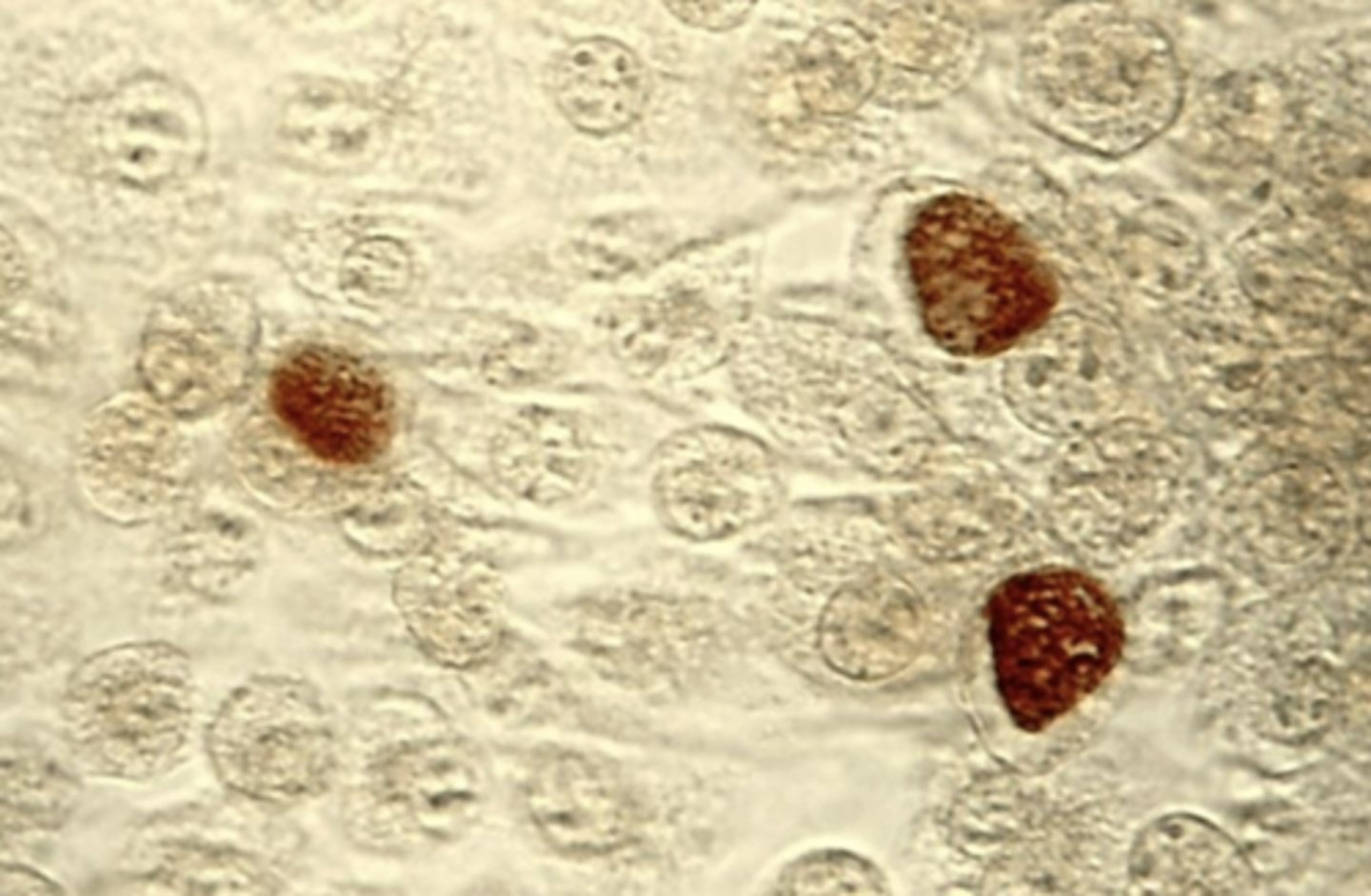
Life cycle of Chlamydia Summary
- Intracellular ______ are diagnostic of chlamydial infections
- Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies (brown) in a McCoy cell (mouse) culture.
- Within a eukaryotic cell, Chlamydia resides in a membrane-bound vacuole known as the _______
- Inclusion contains _______
- ______ can be used as an energy source
inclusion
inclusions
glycogen
Chlamydia
1. Chlamydia trachomatis -> Associated with ___
2. Chlamydia psittaci -> Associated with ___
3. Chlamydia pneumoniae -> Associated with ___
Causes a range of _____ (GU) and _____ infections
STI
Respiratory Tract
Respiratory Tract
genitourinary
eye
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> A, B, C
Clinical Syndrome(s): _________
Trachoma
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> D - K
Clinical Syndrome(s): _________
Cervicitis
Endometritis
Epididymitis
Infant pneumonia syndrome
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> L1, L2, L3
Clinical Syndrome(s): _________
Lymphogranuloma venereum
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> D - K
Most common ______ STD in the USA
bacterial
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> D - K
Adult males -> urethritis, epididymitis, proctitis (anal and rectal inflammation)
Adult women -> cervicitis, salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tube), vaginitis, infertility
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> D - K
Causes: Inclusion ________
- Named for the inclusion bodies seen in the infected conjunctiva epithelial cells
-> Newborn - conjunctivitis from genitally infected ______. Approximately 10% of infected infants will present with or develop _________
-> Adults – conjunctivitis from ______ infection
-> Does not lead to ________
conjunctivitis
mothers
pneumonia
genital
blindness
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> D - K
Does this serotype lead to blindness?
No
Chlamydia trachomatis
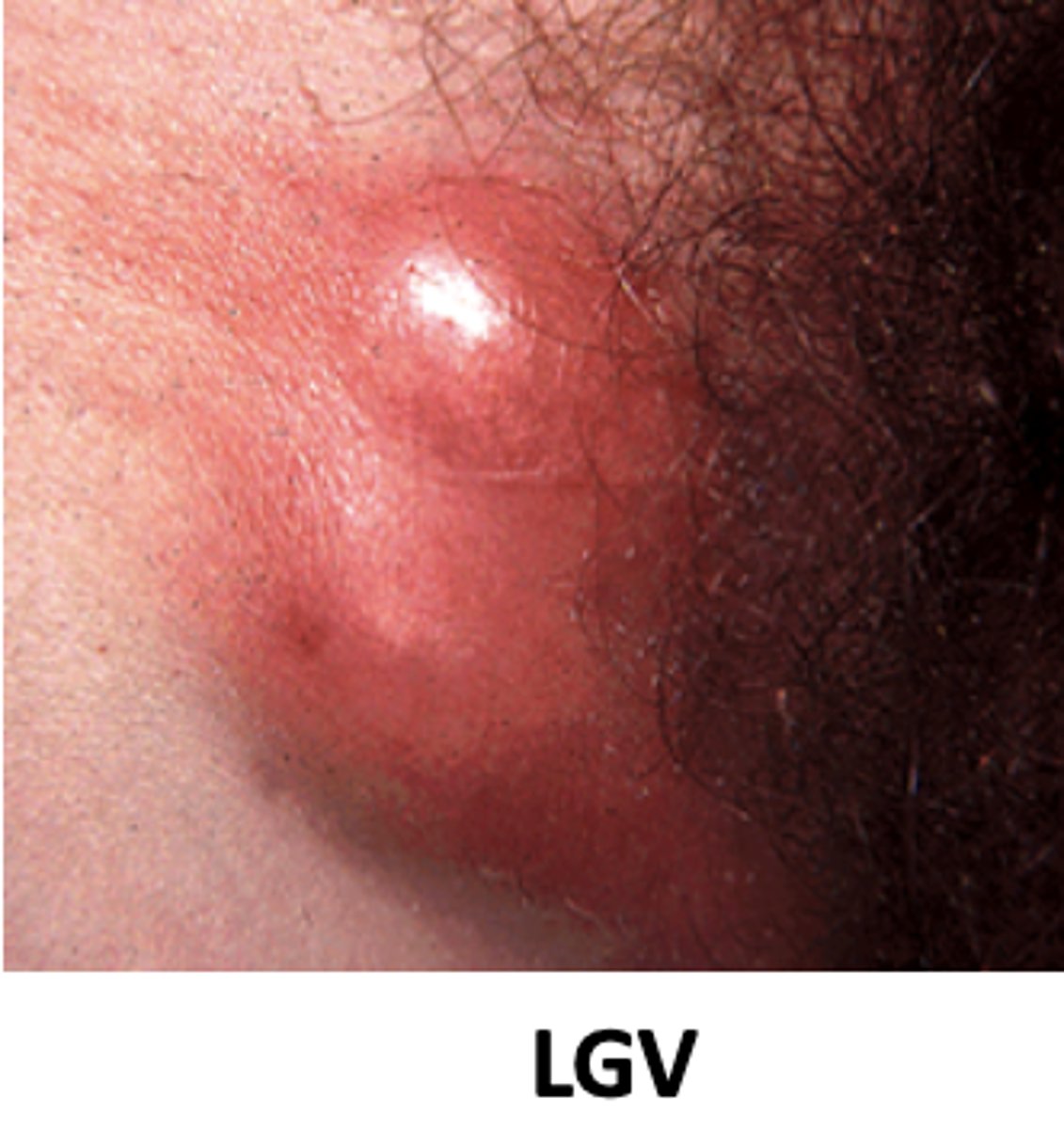
Serotype -> L1, L2, L3
Causes: _____________ Venereum (LGV)
More ______ STD than serotypes D-K
_______ in the USA
Lymphogranuloma
invasive
Uncommon
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> L1, L2, L3
____ infection (Primary stage): Painless primary lesion(s), fever, headache and myalgia (muscle pain)
_________ (Secondary stage): Infection spreads to lymph nodes. Symptoms include inflammation and swelling of inguinal and perirectal lymph nodes
______ ______ _____ (Tertiary stage): Ulcers, fistulas and genital elephantiasis (due to obstruction of the lymphatics)
Local
Dissemination
Progressive tissue damage
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> A, B, C
Causes: _______
- Major cause of ________ in Asia and Africa
- Chlamydia invades the epithelium of the conjunctiva
Modes of transmission:
- _____ to _____
- Flies
- Linen, towels
Trachoma
blindness
Finger to eye
Chlamydia trachomatis
Serotype -> A, B, C
Does this serotype lead to blindness?
Yes
Chlamydia trachomatis
Effects of Trachoma
- ______ inflammation of conjunctiva
- Scarring of ______
- Distortion of external portions of the eye
- Can lead to ________
Chronic
cornea
blindness
Chlamydia trachomatis
Diagnosis
____
NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test)
Chlamydia trachomatis
Gram (+) or (-)?
(-)
Chlamydia trachomatis
Treatment
Adults and adolescents?
Doxycycline (tetracycline)
Chlamydia trachomatis
Treatment
Small children and why?
Erythromycin or azithromycin for small children because of the effects of tetracyclines on teeth and bones. Tetracyclines discolor developing teeth by binding to Ca2+ ions in teeth which becomes yellow, then brown after eruption due to oxidation and exposure to light
- Tetracyclines negatively affects bone development
Chlamydia trachomatis
Treatment
Pregnant women?
Azithromycin
Chlamydia psittaci
- Many serotypes
- Zoonotic species of chlamydia (from birds)
- Affects the respiratory tract causing pneumonia (psittacosis)
KNOW -> _______ absent from inclusion
Glycogen
How are Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia pneumoniae different from Chlamydia trachomatis?
- Important
Chlamydia psittaci's inclusions lack glycogen
Chlamydia pneumoniae
- One serotype
- Human pathogen spread by _______ _______
- Infection is common but usually not severe
- Symptoms include bronchitis, pneumonia, sinusitis
KNOW -> _______ absent from inclusion
respiratory droplets
glycogen
Neisseria
Pathogens:
1. N. meningitidis (meningococcus) -> Commensal or Pathogen?
2. N. gonorrhoeae (gonococcus) -> Commensal or Pathogen?
Commensal
Pathogen
Neisseria
Morphology
- Gram ______ ______ (Important)
- N. gonorrhoeae: polysaccharide capsule _______ --> Vaccine or no?
- N. meningitidis: polysaccharide capsule _______ --> Vaccine or no?
negative
diplococci
absent
no
present
yes
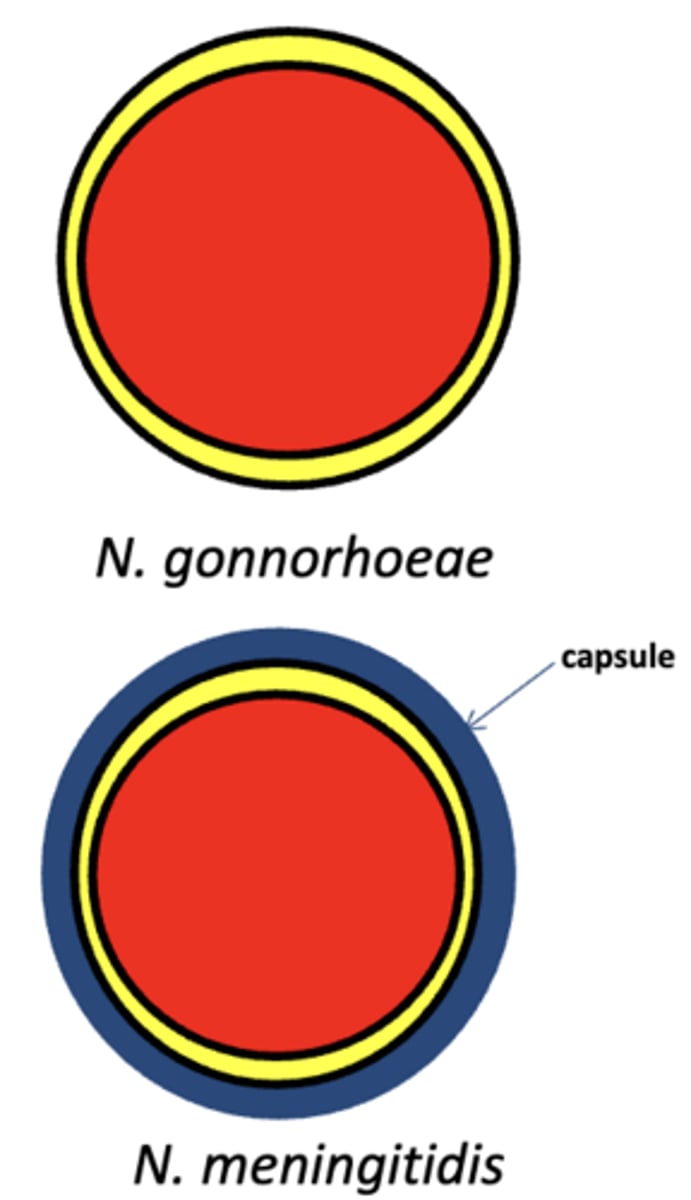
Which is more resistant to abtibiotics?
N. gonorrhoeae or N. meningitidis
N. gonorrhoeae
Neisseria
Cultivation
N. _________ → Chocolate agar
- It is usually isolated from sterile body fluids (blood or CSF).
- No normal flora are present to compete with or overgrow it.
- Therefore, a non-selective medium like chocolate agar is sufficient.
N. _________ → Thayer-Martin agar (Chocolate agar with antibiotics)
- It is collected from non-sterile sites (urethra, cervix, rectum, pharynx).
- These sites contain lots of normal bacteria and fungi.
- Selective antibiotics in Thayer-Martin suppress other organisms so N. gonorrhoeae can grow. (antibiotics are needed to kill the others)
meningitidis
gonorrhoeae
Neisseria
Cultivation
Neisseria gonorrhoeae → Thayer-Martin agar
Types:
a. Vancomycin – kills most gram _____
b. Colistin - kills most gram _____
c. Nystatin - kills most _____
positives
negatives
fungi
Neisseria
Virulence Factors of Meningococcus and Gonococcus:
A. Polysaccharide _______ - resists phagocytosis, only in _________ as a virulence factor
B. ___ - also resist phagocytosis, protein in nature, enhance attachment to host cells, important for both species, and particularly for __________
C. Lipo-oligosaccharide (LOS) – An LPS variant that triggers inflammatory cytokine release
capsule
meningococcus
Pili
gonococcus
Neisseria
Virulence Factors of Meningococcus and Gonococcus:
D. ______ proteins (Opa)- Outer membrane proteins; prevents phagocytosis
E. Porin _ - essential outer membrane protein present in ___________. It serves as the primary channel for nutrient uptake and plays a secondary role in host cell attachment and invasion.
F. Ig_ protease - important for _______ species
Opacity
B
gonococcus
A
both
IgA protects what?
-Frequent boards question-
Mucosal surfaces
Neisseria
Gonococcus
Disease and Epidemiology
- Gonococci attack mucous membranes of genito-urinary tract, eye, rectum, and throat
1. Reservoir: An infected person
2. Transmission: ______ contact
sexual
Neisseria
Gonococcus
Clinical Forms:
a. Acute urethritis in the male: not so common in the female
b. Endocervicitis → Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
c. ______ _____ in sexually promiscuous individuals -> *Blood in Joints*
d. Eye infections
In adult: Auto-infection
In newborn: Ophthalmia neonatorum, acquired through passage of birth canal
- Most common manifestation in ______
- Treatment: ________ ophthalmic ointment
e. Proctitis: Inflammation of the _____ and _____
f. Pharyngitis
Pyogenic arthritis
infants
Erythromycin
anus
rectum
Neisseria
Gonococcus
Diagnosis
-> _____
-> _____ ______ : Gram _ _______
NAAT
Gram stain
(-) diplococci
Neisseria
Gonococcus
Treatment
a. ______ injection is first choice
b. ______ is added if coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis is not ruled out
- If testing for chlamydia has not been done, doxycycline is added to ensure both pathogens are treated and to prevent persistent infection or complications because Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections frequently occur alongside Chlamydia trachomatis
c. ______ is no longer used due to resistance
Ceftriaxone
Doxycycline
Penicillin
Neisseria
Meningitis - N. meningitidis
- Reservoir: Humans, in the ___________
- Transmission is by inhalation of ________ ________
nasopharynx
respiratory droplets
Neisseria
Meningitis - N. meningitidis
Clinical Forms
a. Respiratory symptoms may initially occur (mainly asymptomatic)
b. Septicemia (Meningococcemia): Bacteria cross the epithelial lining of the nasopharynx and enter the blood stream where they rapidly multiply
b. Meningitis: Bacteria can travel to meninges from the blood Inflammation occurs resulting in purulent meningitis
Neisseria
Meningitis - N. meningitidis
Main Symptoms:
sensitivity to ______ -> Important
headache
fever
_____ _____ -> Important
vomiting
rash
Can lead to coma and death
light
stiff neck
Neisseria
Meningitis - N. meningitidis
Diagnosis
- _____
- Culture on Chocolate agar
- _____ _____
NAAT
Gram stain
Neisseria
Meningitis - N. meningitidis
Treatment
___________ antibiotic
Ceftriaxone
Neisseria
Meningitis - N. meningitidis
Prevention?
Vaccination
Spirochetes
Three genera pathogenic to humans:
Treponema - syphilis, yaws, pinta
Borrelia - relapsing fever, Lyme disease
Leptospira - leptospirosis
Spirochetes
Borrelia recurrentis
Disease: ________ fever
Transmission: ______ and ______
Symptoms: Flu-like symptoms that resolves and ______
Relapsing
Ticks and lice (bite)
recurs
Spirochetes
Borrelia burgdorferi
Disease: _____ disease
Transmission: _____
Symptoms: Rash (______ migrans), flu-like symptoms, joint pain, neurological
problems
Lyme
Ticks
erythema
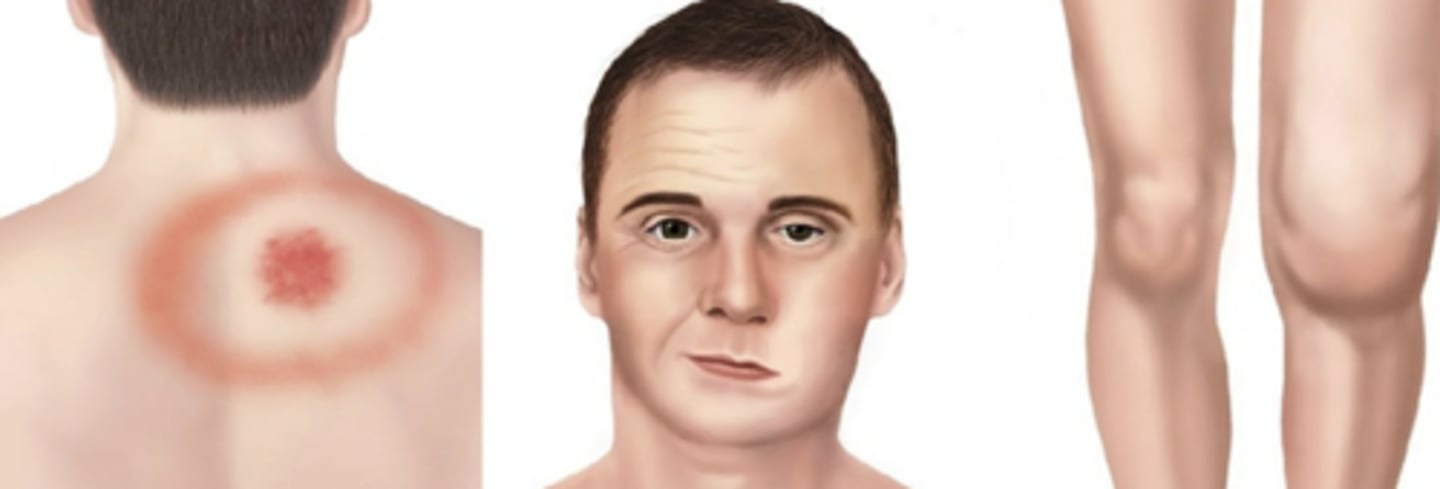
Spirochetes
Leptospira
Disease: Leptospirosis
Transmission: ______ of an infected animal e.g. rats and mice
Urine
Spirochetes
General Characteristics
A. _____ shaped gram _______ bacteria
B. Possess __________ (axial filaments underneath the outer membrane)- for motility
C. Chemical composition of cell wall and cell membrane is similar to other Gram negative bacteria, except the wall is not _____
= Does not stain well
Spiral
negative
endoflagella
rigid
Spirochetes
Morphology
1. Treponema - ____, regular coils
2. Borrelia - Coarse, ______ coils
3. Leptospira - Very ____ coils, end(s) ______
Tight
irregular
tight
hooked

Spirochetes
Treponema Species
A. T. pertenue - yaws in tropical
Infection of the skin, bone and joints
B. T. carateum - pinta in Central & South America
Skin disease
C. T. denticola - present in the mouth, implicated in gingivitis, periodontitis, acute ________ ________ ________
necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
Spirochetes
T. pertenue
Yaz affects what?
Know!
Skin, bone, joints
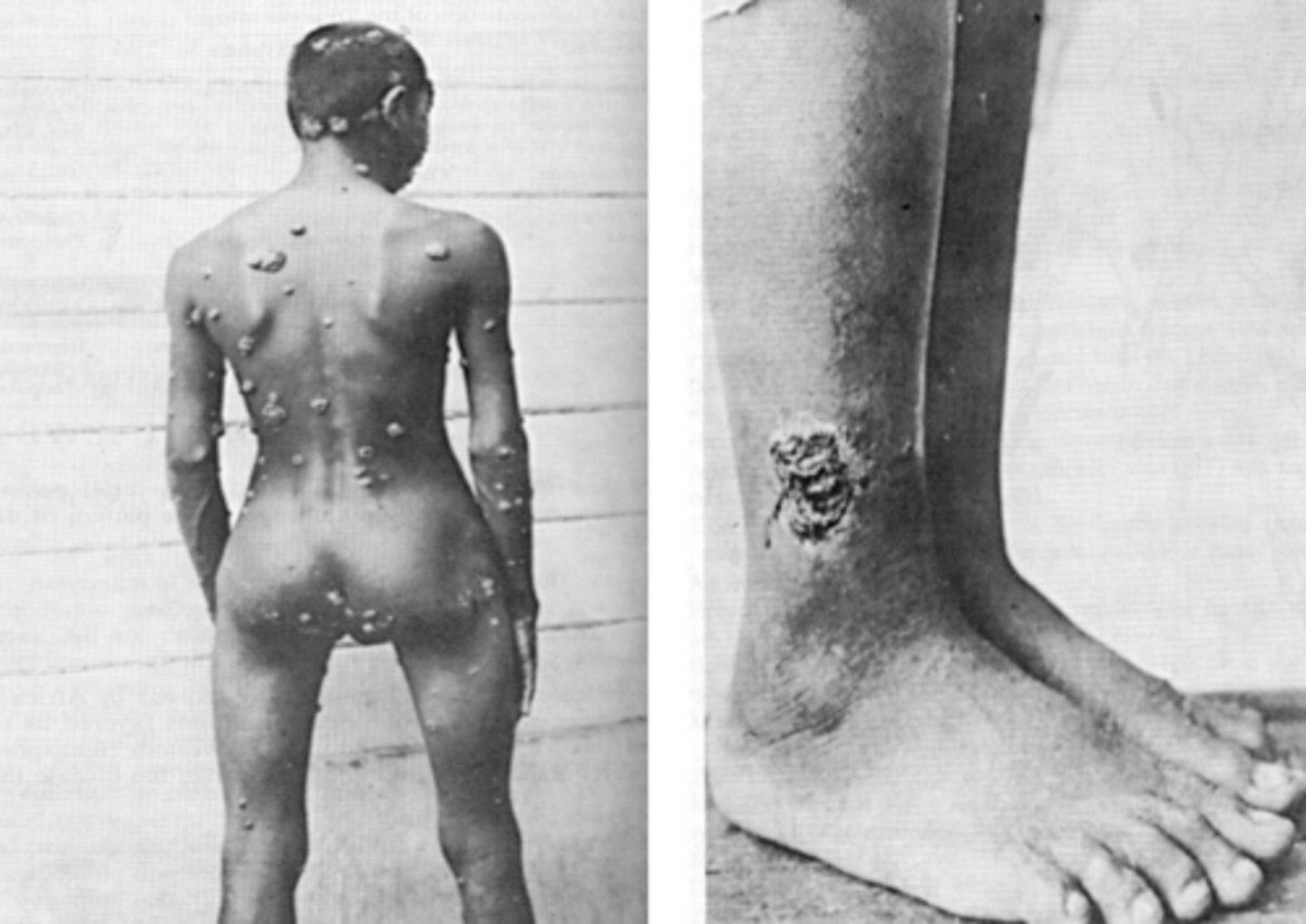
Spirochetes
T. carateum
Pinta affects what?
Know!
Skin only
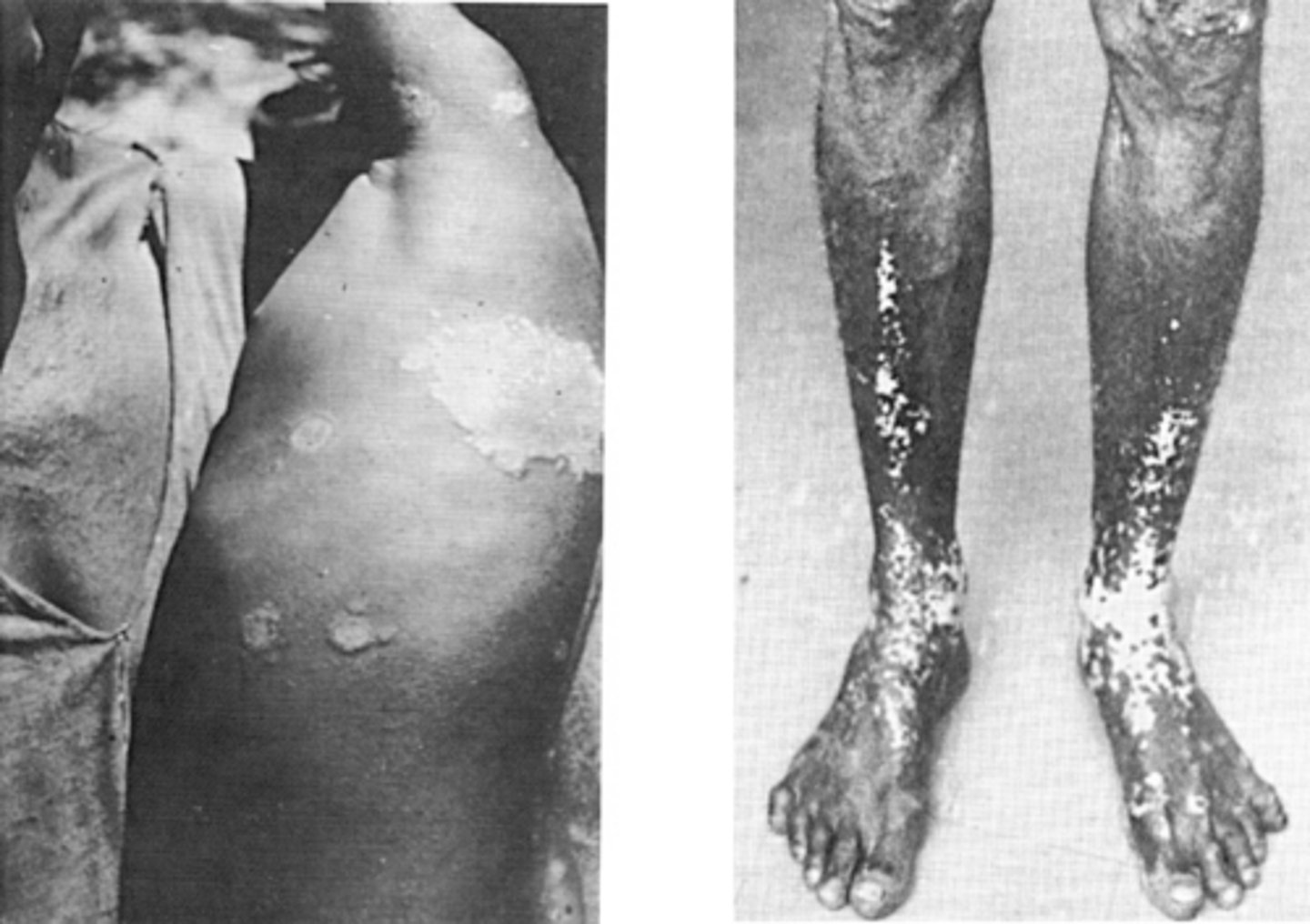
Spirochetes
T. denticola
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis main features?
Painful, bleeding gums, and ulceration of inter-dental papillae
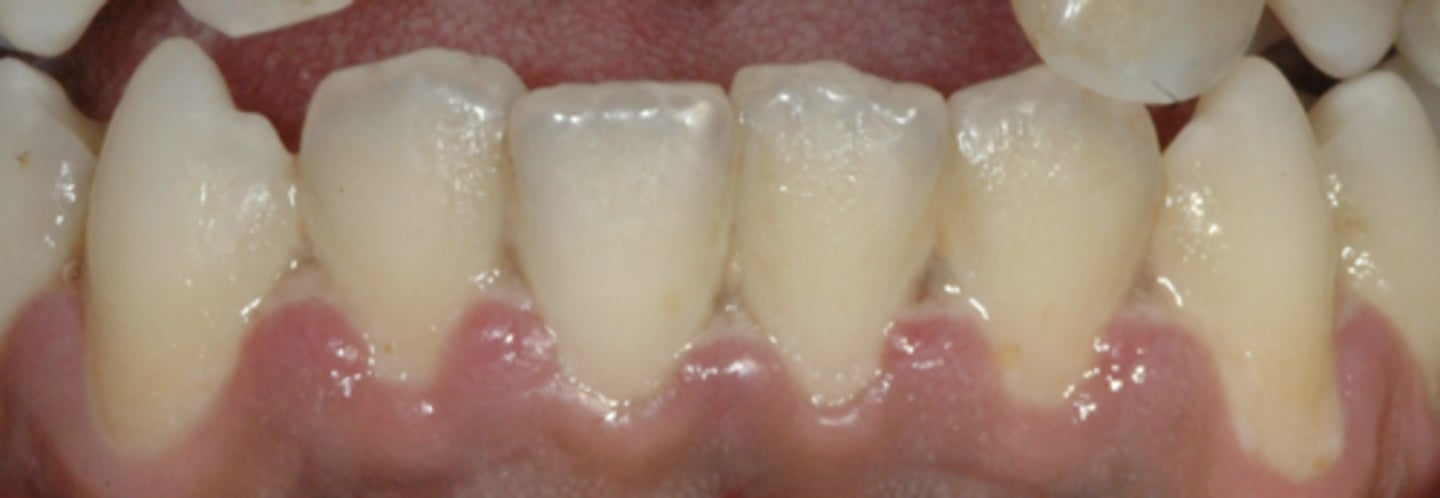
Spirochetes
General Features of Yaws and Pinta
1. _______ diseases - chronic skin lesions
2. Non-venereal
3. Associated with poor personal hygiene or insect vectors
4. Positive syphilitic serology (false (+) results)
5. Respond well to penicillin
Tropical
What is the incubation period for T. Pallidum (Syphilis)?
3 weeks
Spirochetes
T. Pallidum (Syphilis)
Clinical Manifestation:
a. _______ Stage:
- Non-tender, indurated ulcer (chancre)
- Highly ________ but heal spontaneously in 3 – 6 weeks
- Patients do not recall their primary lesions (chancre) because they are painless and inconspicuous (especially for females because it's inside the vagina)
- Usually not noticeable + a tiny sore
Primary
infectious
Spirochetes
T. Pallidum (Syphilis)
Clinical Manifestation:
b. ________ Stage:
- Organism spreads throughout the body via the _______ and _______
- ______ to ______ after Primary Stage
- Red maculopapular rash on body including palms and soles of feet
- Pale moist flat papules in the anogenital regions (called condylomata lata), armpits and mouth
Secondary
blood and lymph
Weeks to months
Spirochetes
T. Pallidum (Syphilis)
Clinical Manifestation:
c. ________ Syphilis
- ___________ but positive serology (antibodies in the serum)
Latent
Asymptomatic
Spirochetes
T. Pallidum (Syphilis)
Clinical Manifestation:
d. _____ (tertiary) Stage
- _ to __ years after Primary Stage
- Involves _________ system (aortitis)
- _______ ______ system (neurosyphilis)
- No organ of the body is immune
- _________ disease -> granulomatous- like lesions in the skin, bones and liver
Late
3 to 30
cardiovascular
Central nervous
Gummatous
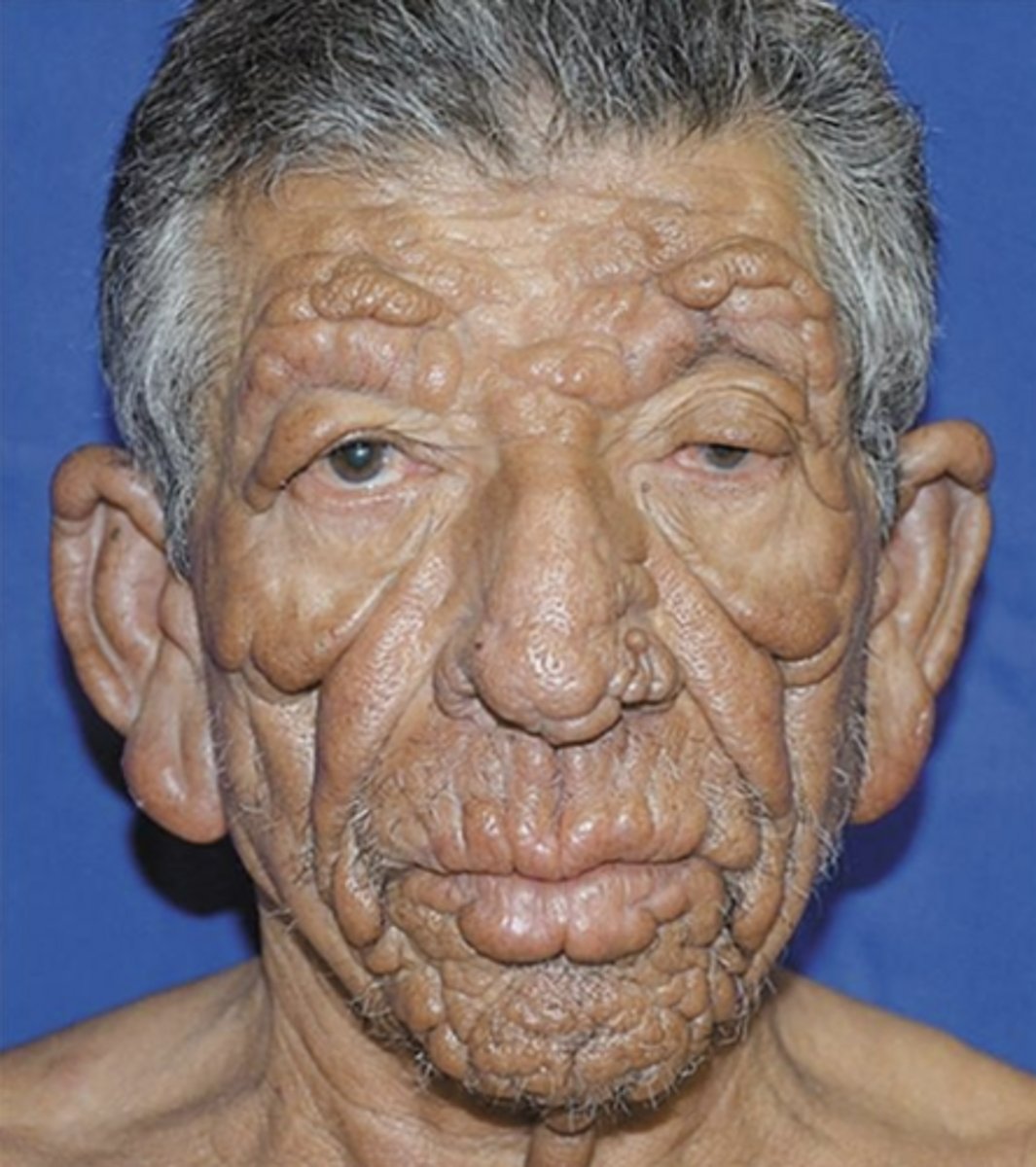
Which of the stages are infectious?
Primary and Secondary only.
Spirochetes
T. Pallidum (Syphilis)
Laboratory Diagnosis:
A. Direct visualization of organisms - for Primary & Secondary stages
(1) ________ microscopy
(2) Direct Fluorescent ________ Test
Darkfield
Antibody
Darkfield microscopy is looking for?
Organisms
Direct Fluorescent Antibody Test is looking for?
Antibodies
Spirochetes
T. Pallidum (Syphilis)
Laboratory Diagnosis:
B. Serology antibody tests
-->Detects 2 different antibodies
1. Anti-treponemal antibody test
- Looks for antibodies specific to treponemal ________ antigen (antibodies against bacteria)
OR
2. Non-treponemal antibody (reagin) test
- Looks for antibodies specific to _________ host cell phospholipid components (such as cardiolipin)
Antibody stimulated by cellular _______
surface
damaged
damage
Spirochetes
T. Pallidum (Syphilis)
Laboratory Diagnosis:
B. Serology antibody tests
1. Anti-treponemal antibody test
- Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody–Absorption (FTA-ABS) test
• This is a type of anti-treponemal antibody test
• Used in laboratory diagnosis of _______
• Detects antibodies specific to Treponema ________
syphilis
pallidum
Spirochetes
T. Pallidum (Syphilis)
Laboratory Diagnosis:
B. Serology antibody tests
(2) Non-treponemal (reagin) antibody tests
- Part of laboratory diagnosis of syphilis
- Detect antibodies against cellular __________ of products, not T. pallidum itself
- Target ______ (e.g., cardiolipin) released from damaged host cells
- Antibodies are produced due to cellular damage
Types:
(1) _____ test
- Detects agglutination microscopically
- Named after the lab that developed it
(2) _____ test
- Detects agglutination without a microscope
- Cardiolipin is linked to particles (e.g., carbon) to make results visually easier to see
breakdown
lipids
VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory)
RPR (Rapid Plasma Reagin)
Spirochetes
T. Pallidum (Syphilis)
Treatment?
Penicillin G
Other Urogenital Infections
Trichomoniasis
- Caused by _____ ____ protozoan parasite
• Spread by ______ contact
• Most infected persons have minimal or no symptoms
• Some infected men have symptoms of urethritis, epididymitis, or prostatitis, and some infected women have vaginal discharge that might be diffuse, malodorous, or yellow-green with or without vulvar irritation
Trichomonas vaginalis
sexual
Other Urogenital Infections
Trichomoniasis
Treatment?
Metronidazole
What is the most prevalent non-viral STD in the USA
Trichomoniasis
Other Urogenital Infections
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
• BV is a polymicrobial clinical syndrome resulting from replacement of the normal Lactobacillus sp. in the vagina with high concentrations of other bacteria such as _______.
• BV is associated with having multiple male or female partners, a new sex partner, douching, lack of condom use, and lack of vaginal lactobacilli; women who have never been sexually active are rarely affected
• BV is the most prevalent cause of vaginal discharge or ________ however most women are asymptomatic
- Essentially, the pH of the vagina becomes more alkaline rather than acidic
Gardnerella vaginalis
malodor
Other Urogenital Infections
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
Treatment?
Metronidazole
_______ ______ are responsible for 80 - 85% of UTIs
__________ _________ are responsible for 5 - 15% of UTIs
Know!
Escherichia coli
Staphylococcus saprophyticus