Mechanical Waves Review
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Waves
Transfer energy without transferring mass
Mechanical Waves
Waves that exist as an vibration of a physical medium (e.g. water, sound)
Electromagnetic Waves
Consist of electric and magnetic fields; can travel through a vacuum (do NOT require a medium)
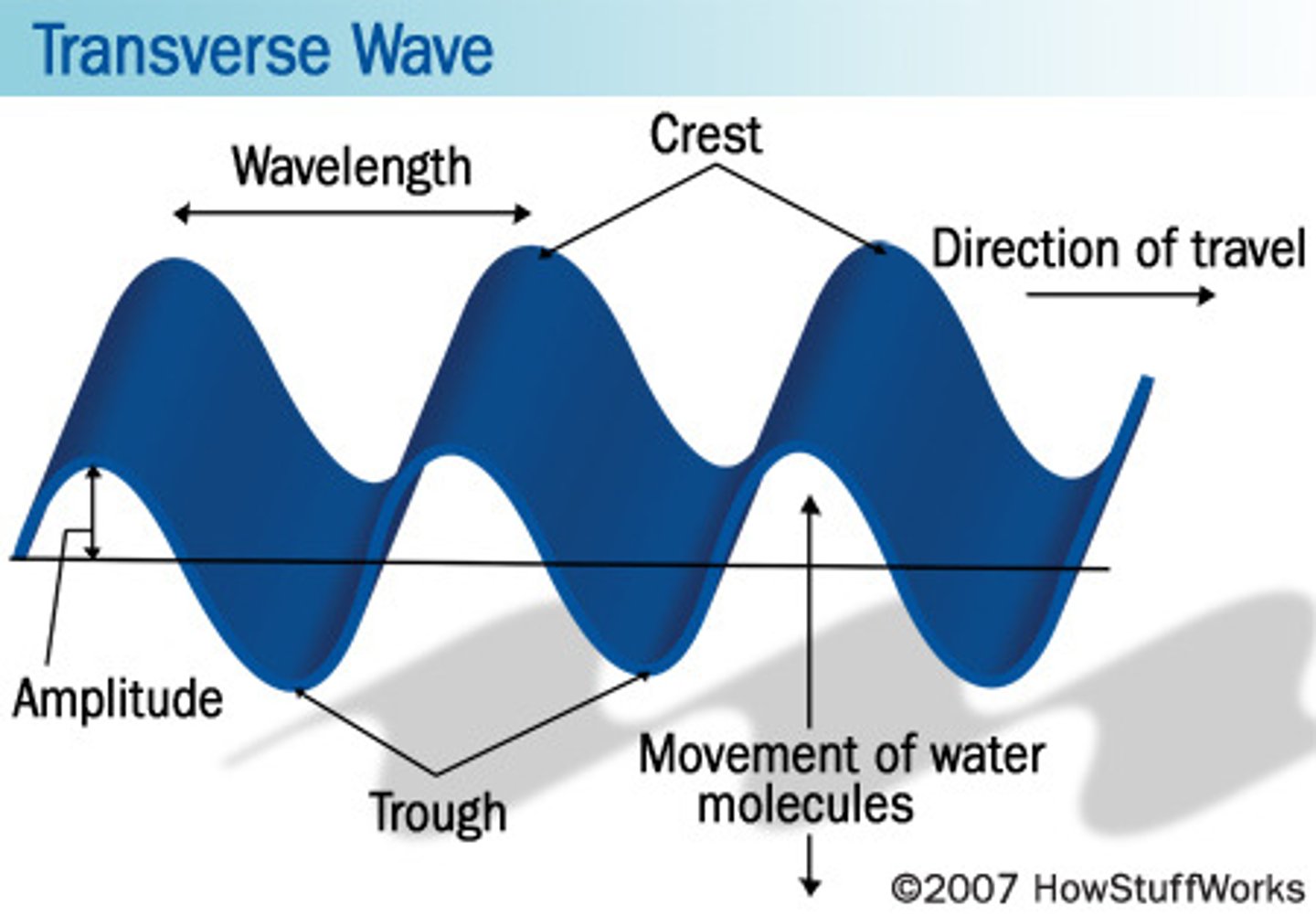
Transverse Waves
A wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate PERPENDICULAR to the direction the wave is traveling.
Longitudinal Waves
A wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate PARALLEL to the direction the wave is traveling.
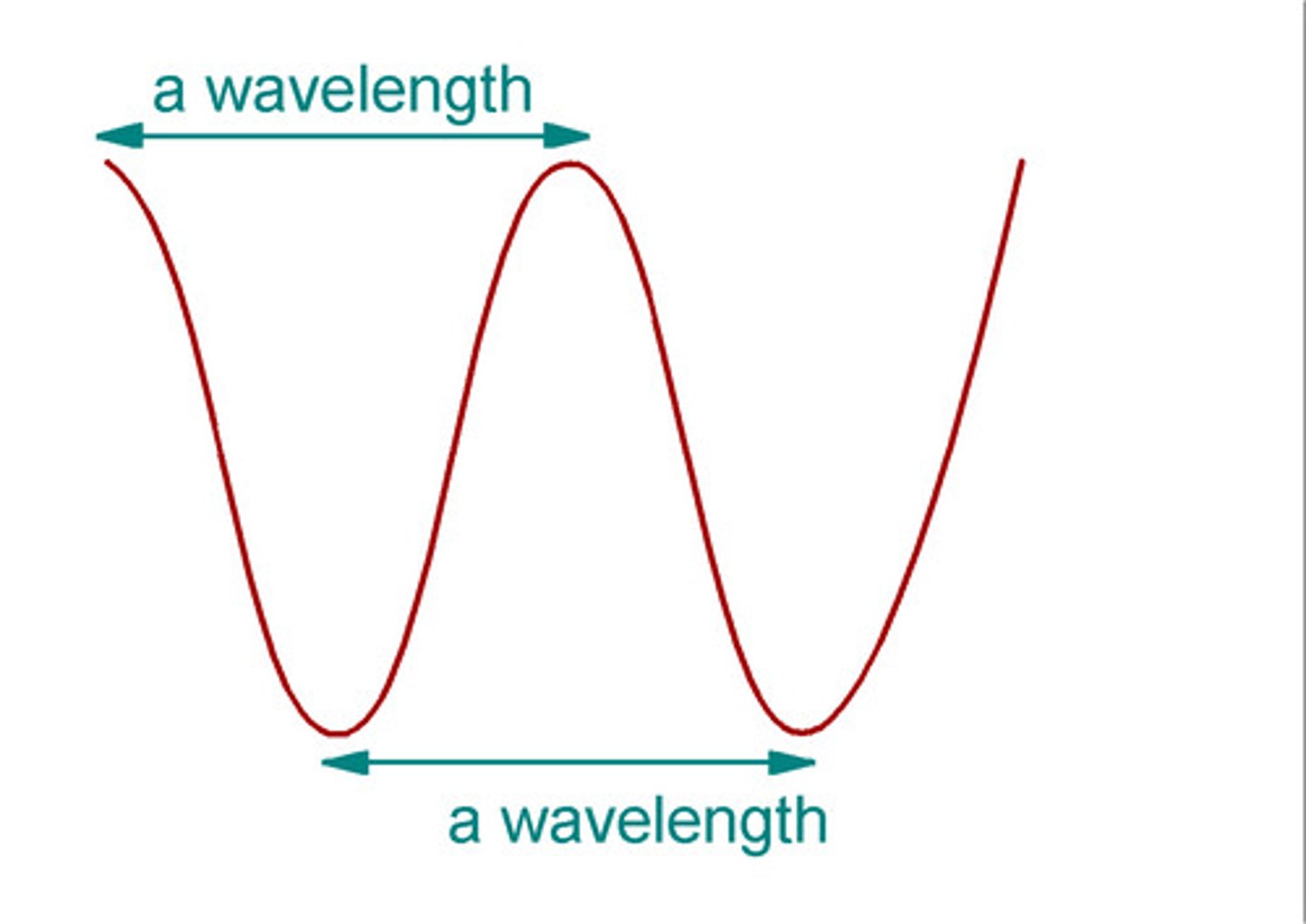
Wavelength
The distance between consecutive, corresponding points (e.g. peak of crest to peak of crest, beginning of crest to beginning of the next crest)
Frequency
The number of complete waves per second. Frequency = (# of waves)/time
Period
The time for one complete wave. Period = time/(# of waves)
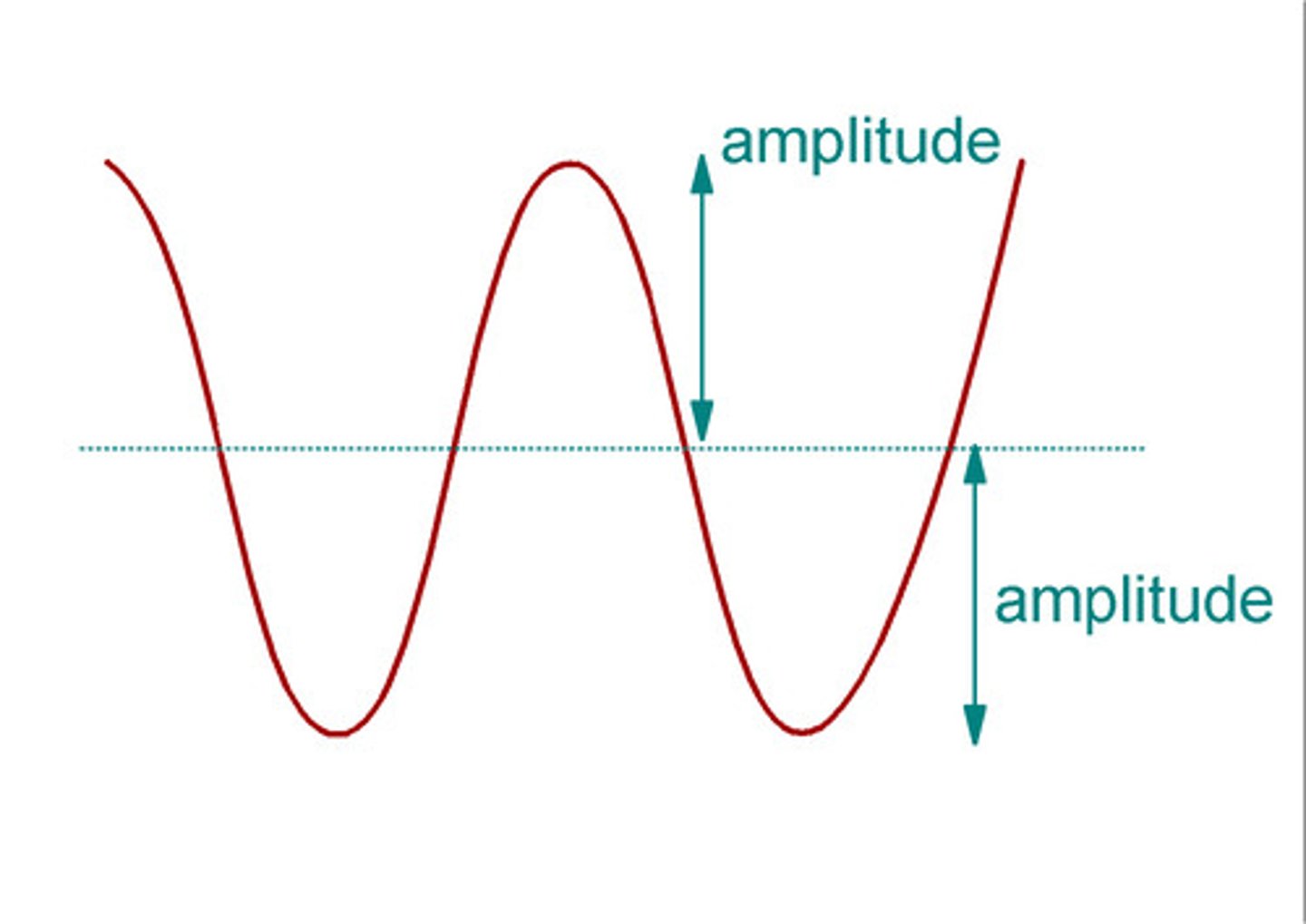
Amplitude
The height of a wave, measured from the mid-line up to the crest OR down to the trough.
Mechanical Wave Energy
Directly proportional to amplitude
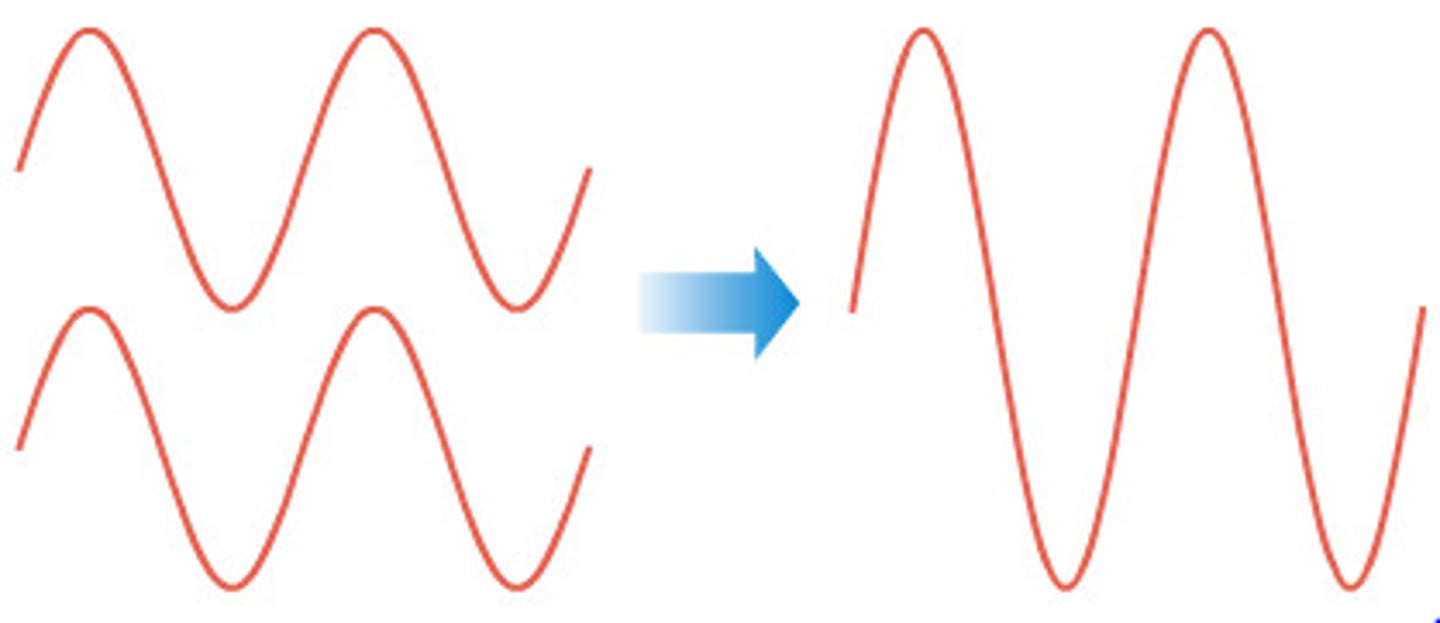
Constructive Interference
Maximum at 0 degree phase difference (e.g. crest lined up with crest, trough lined up with trough)
Destructive Interference
Maximum at 180 degree phase difference (e.g. crest lined up with trough)
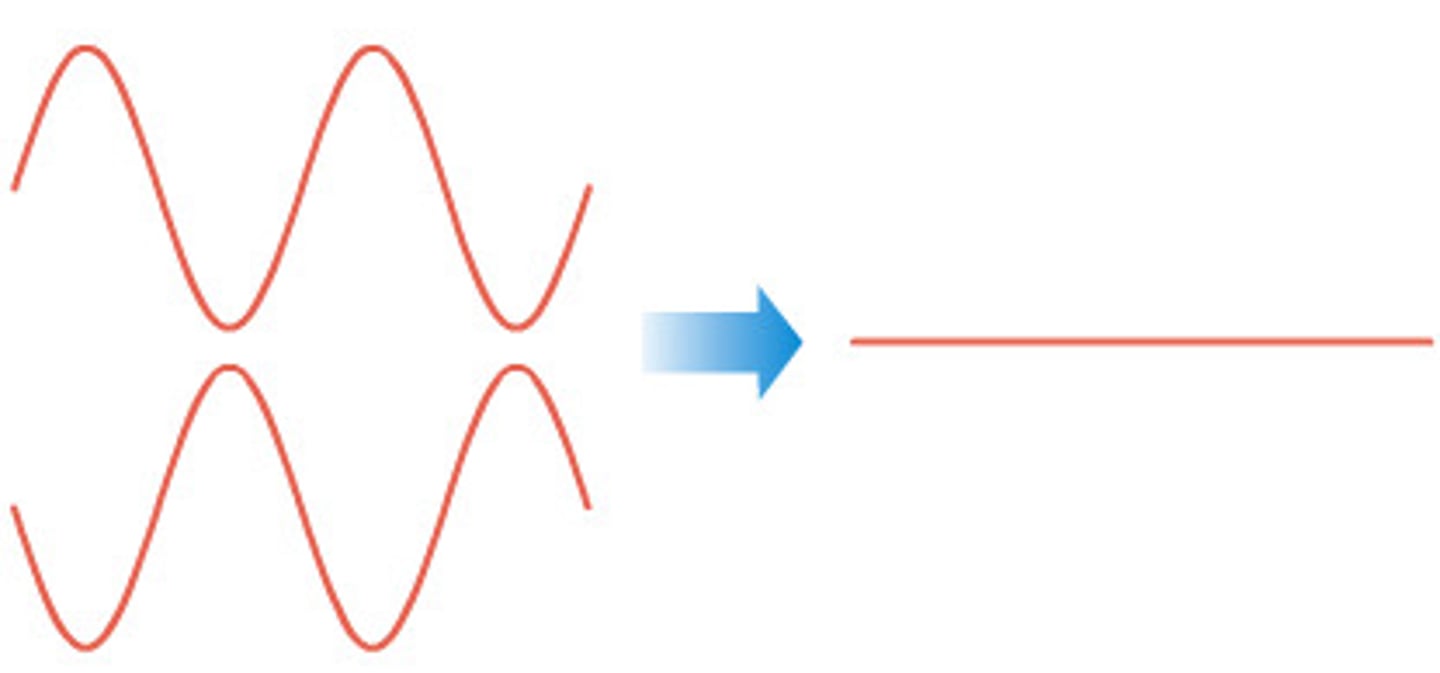
Standing Wave
A pattern of wave crests and troughs that appear to remain stationary. Caused by two identical waves traveling in opposite directions.
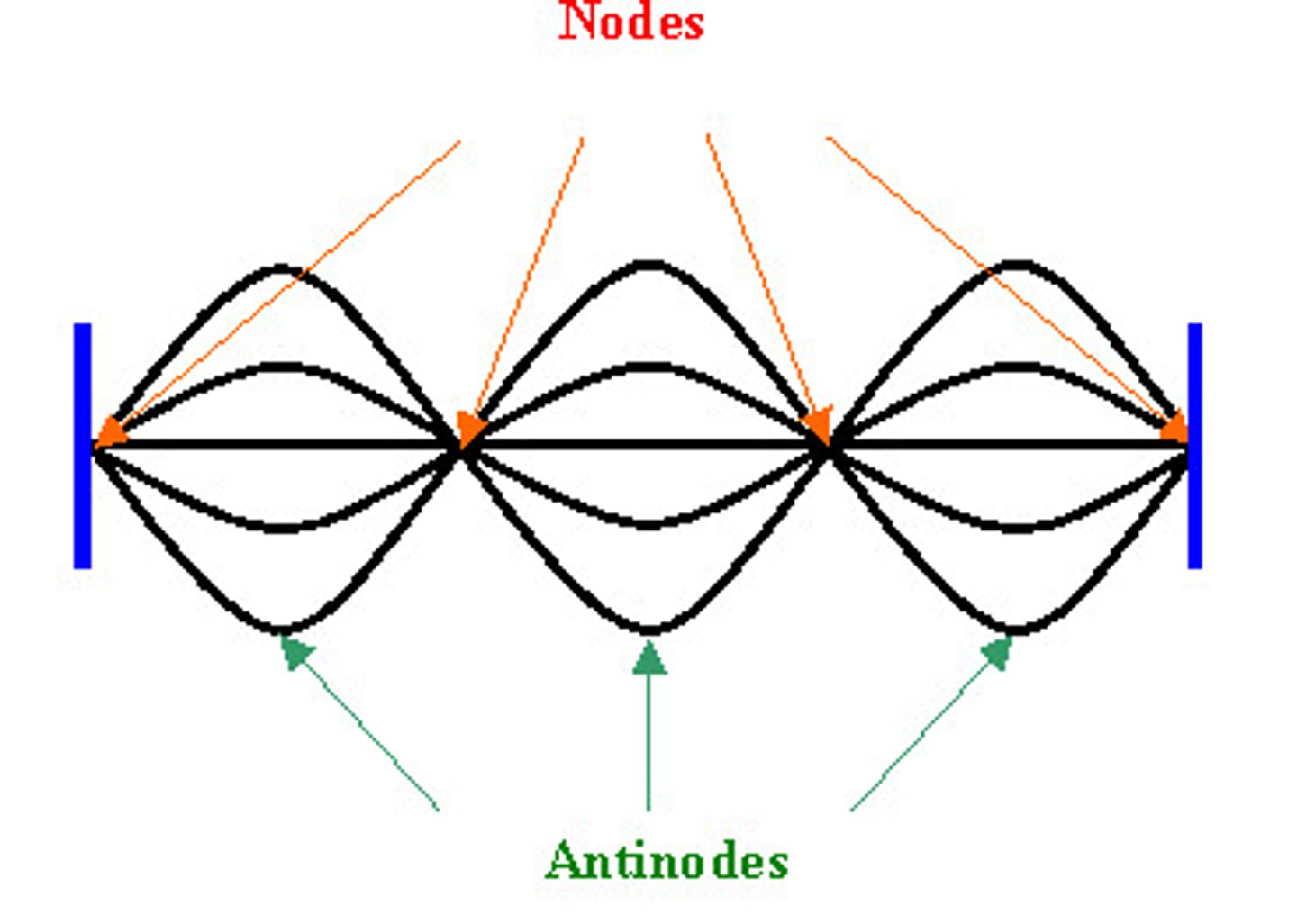
Node
The part of a standing wave where destructive interference occurs
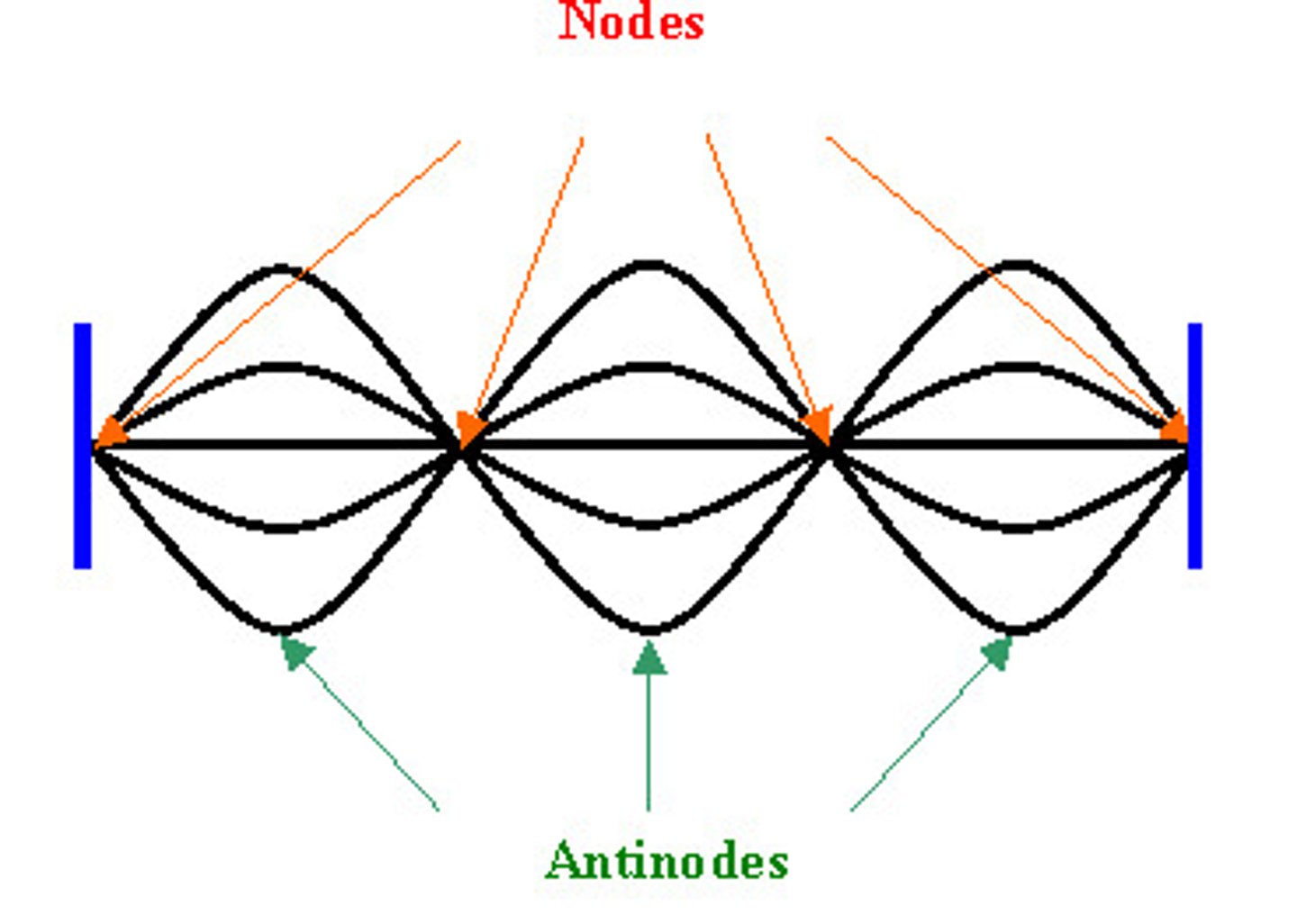
Antinode
The part of a standing wave where constructive interference occurs
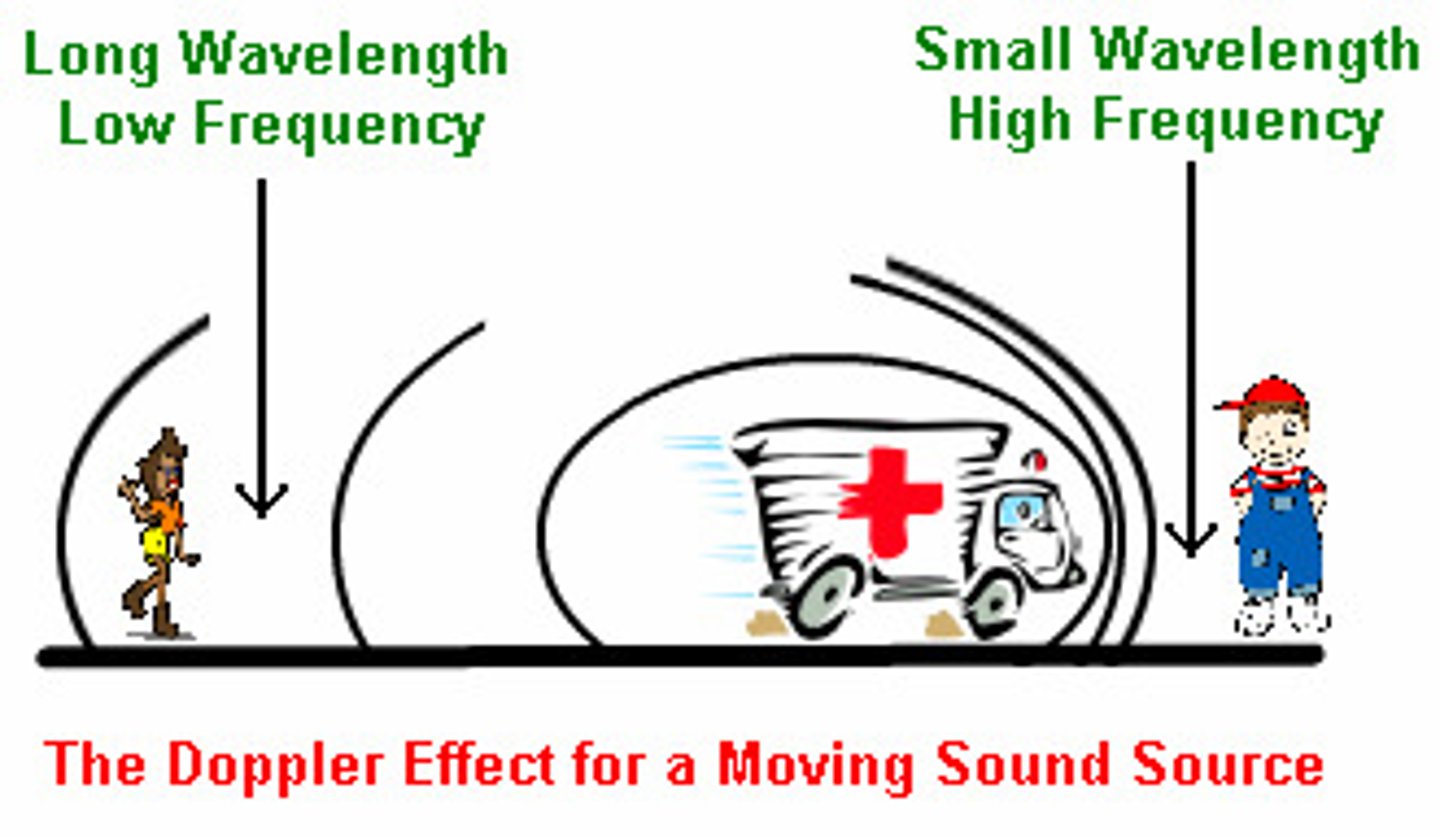
Doppler Effect
The apparent shift in a wave's frequency/pitch due to relative motion between the source and observer
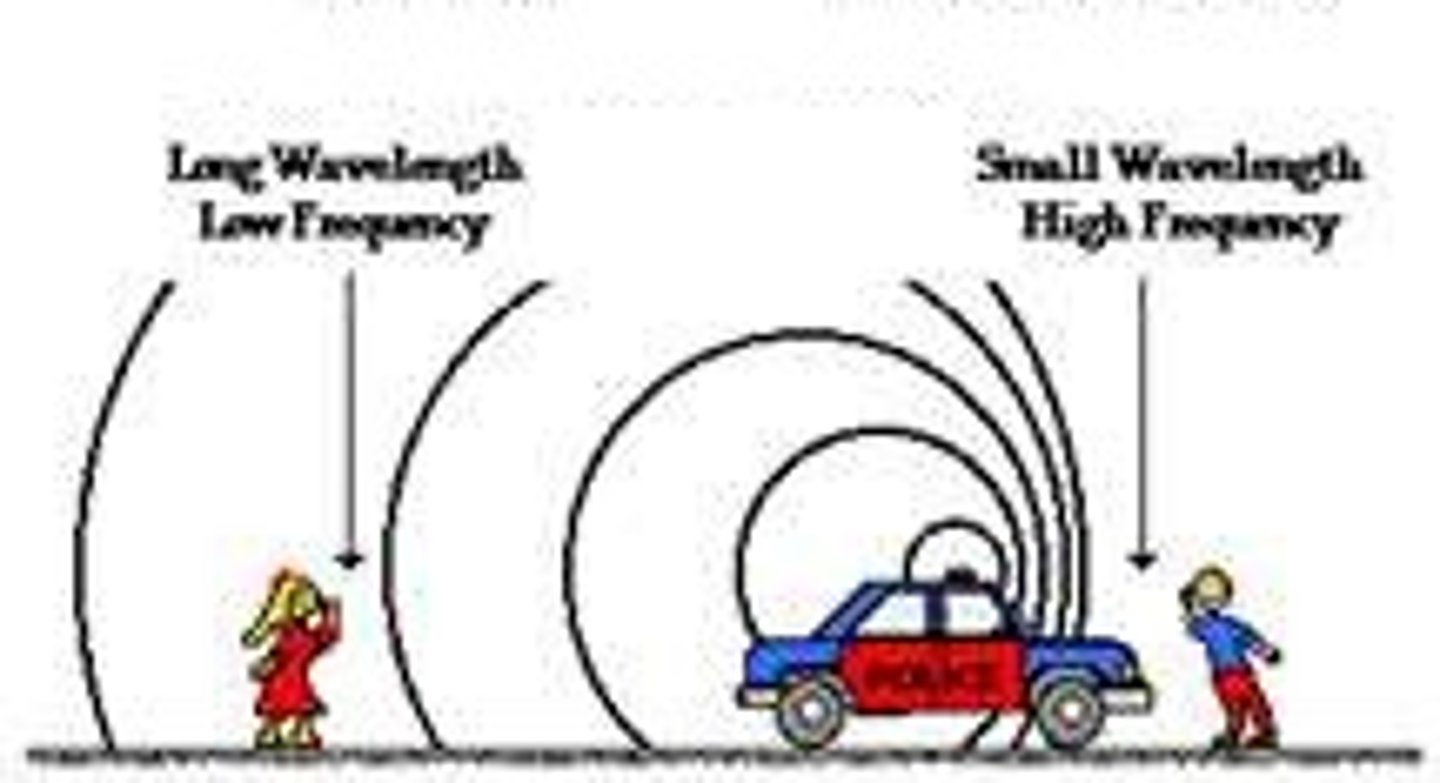
Wave Source and Observer Get Closer
Observed frequency is higher than emitted
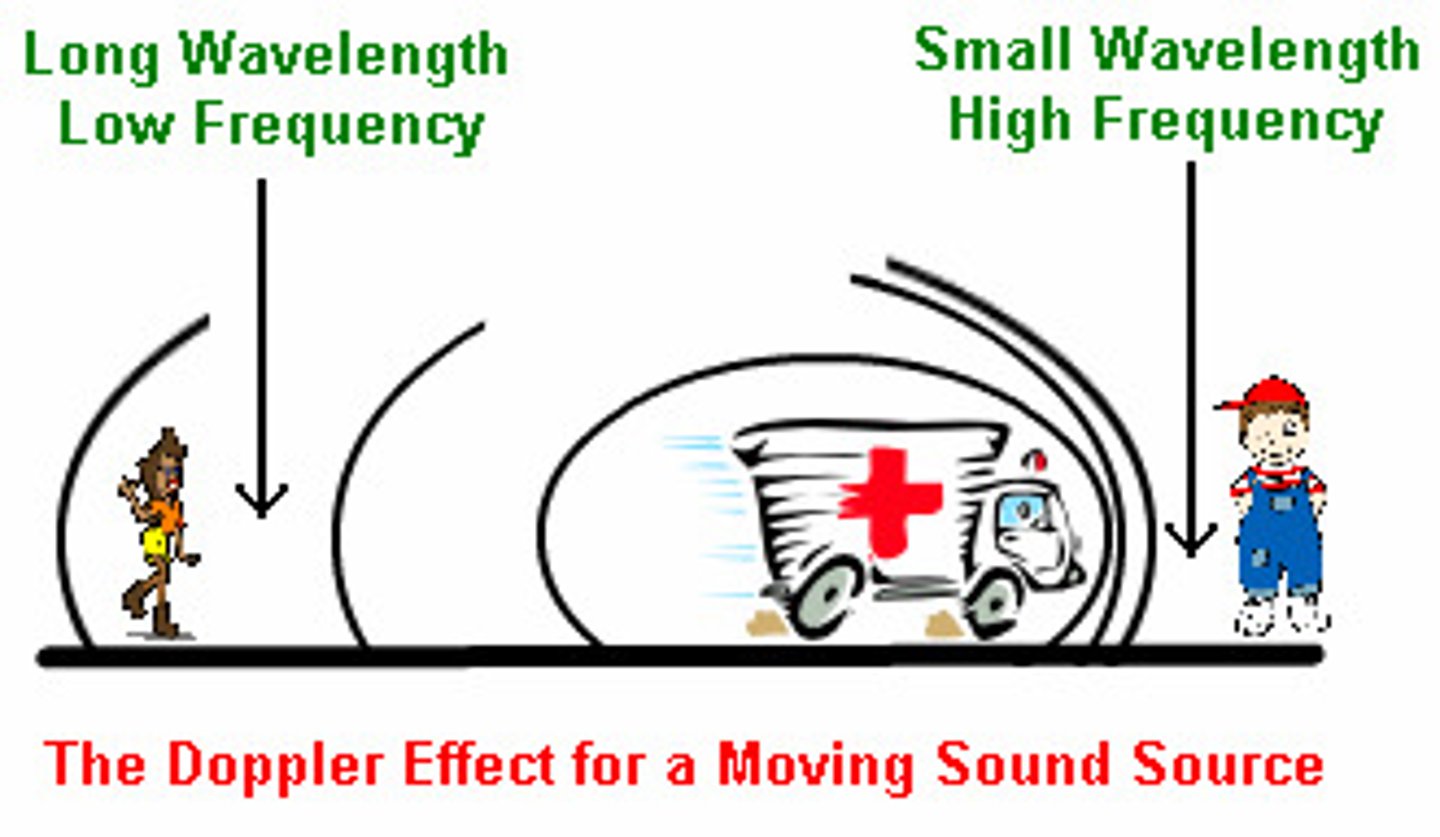
Wave Source and Observer Get Farther Away
Observed frequency is lower than emitted
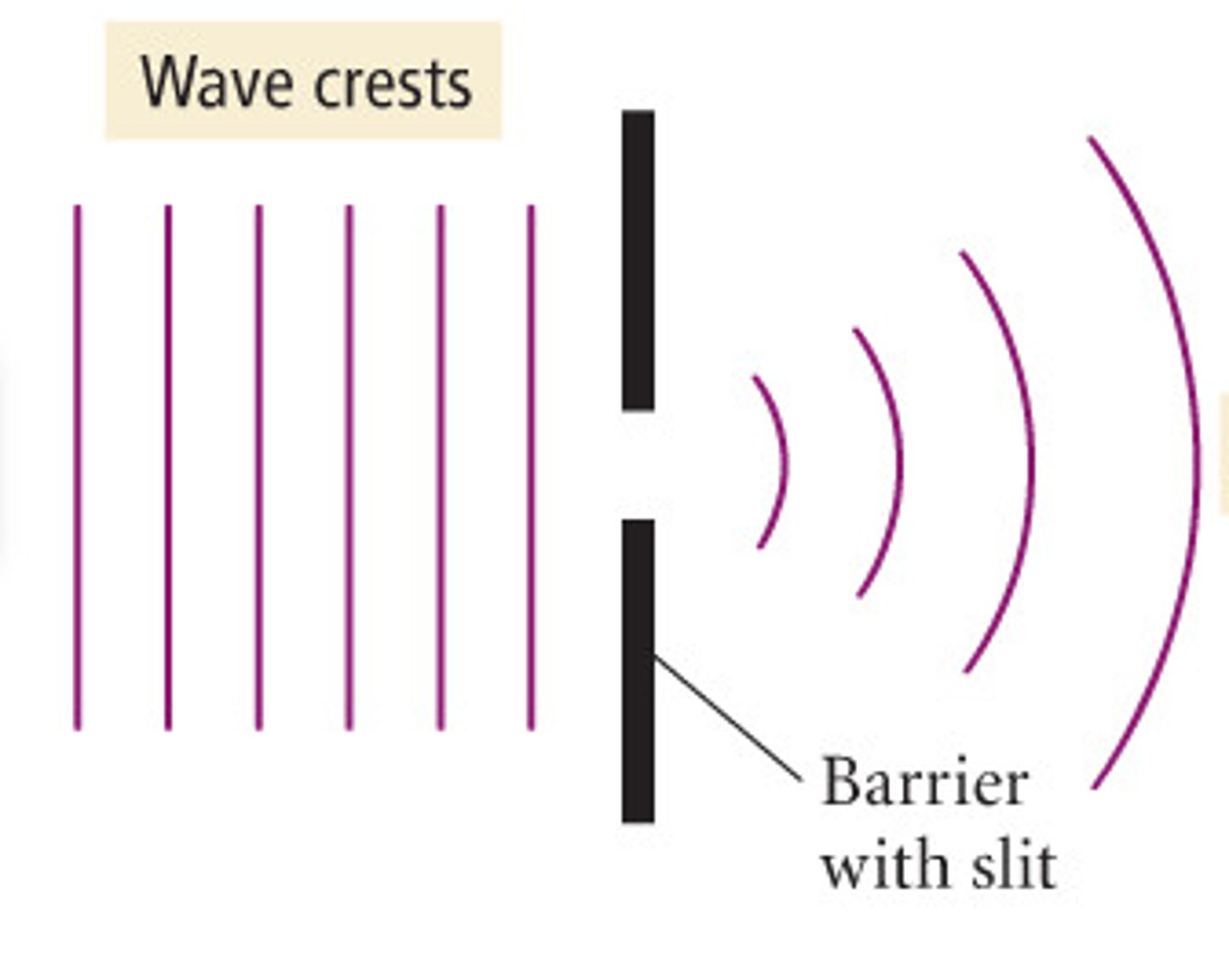
Diffraction
The spreading out of a wave beyond a barrier
Natural Frequency
The particular frequency at which an object naturally vibrates when disturbed
Resonance
The spontaneous vibration of an object at its natural frequency due to an incident wave of the same frequency
Periodic Wave
A wave caused by a repetitive oscillation.
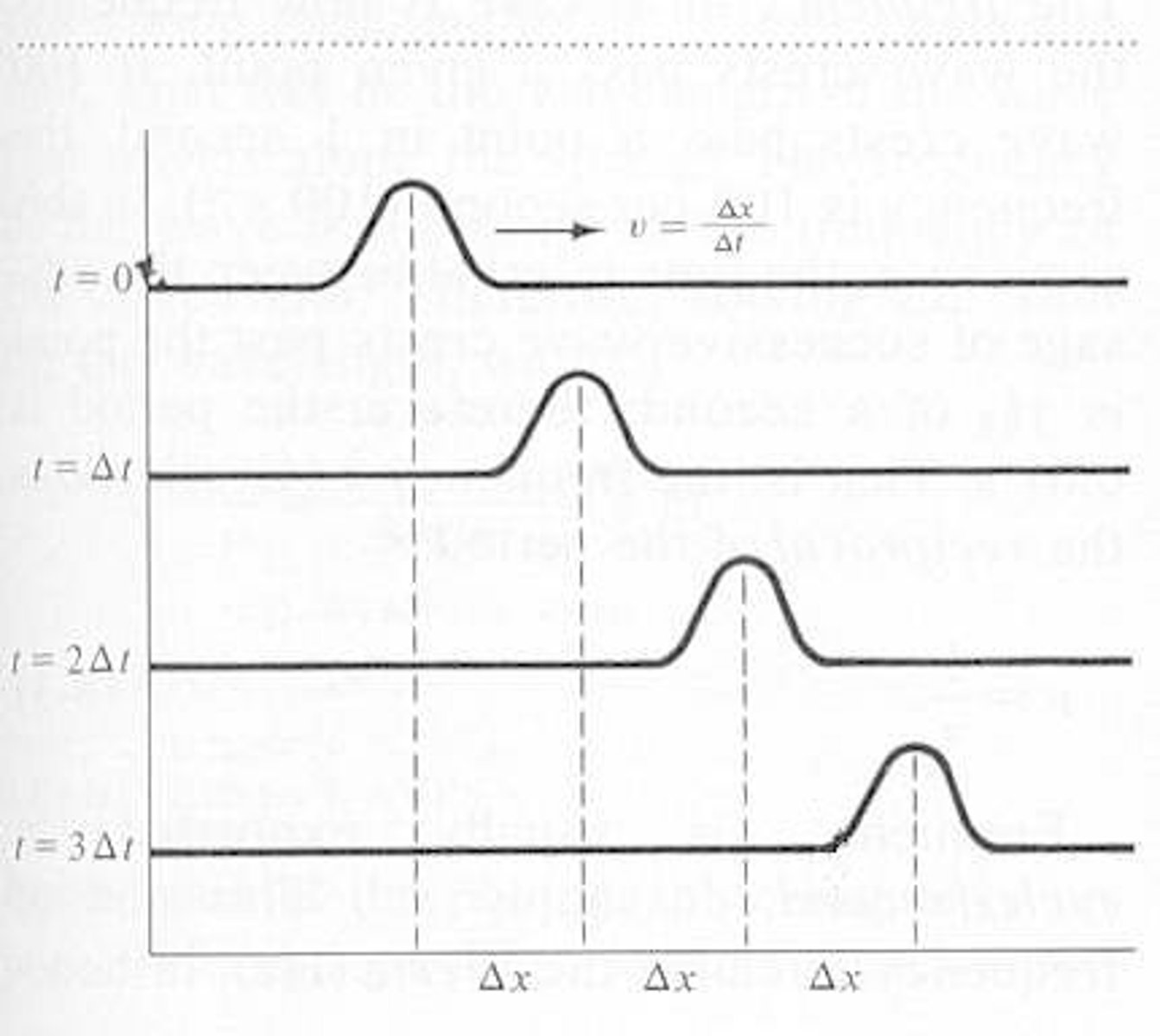
Pulse
A disturbance in a medium caused by a single oscillation.