Genetics Lab #8 - Forensic DNA Fingerprinting
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Real world application
Crime scene
Paternity
Human relatedness
Disease-causing organisms
Food identification
Human remains
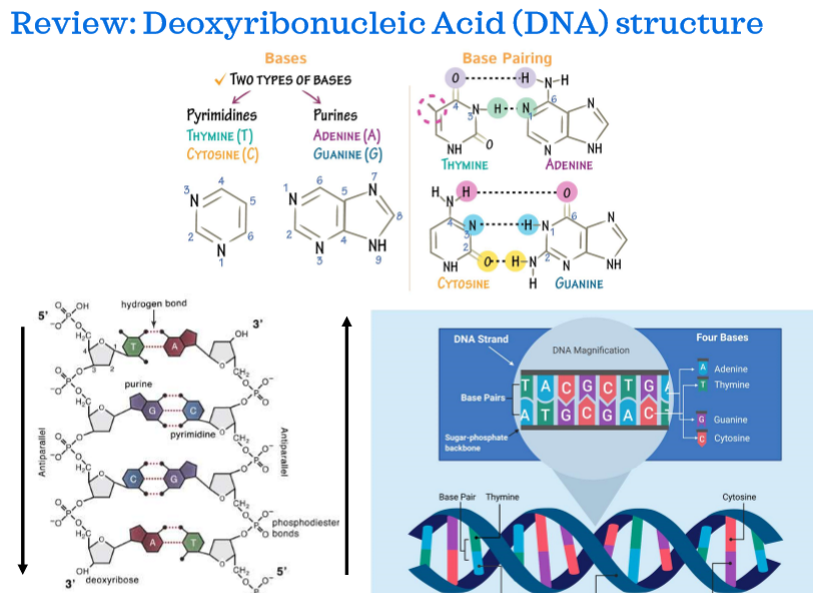
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) structure
DNA restriction enzymes
Enzymes that destroy DNA from invading bacteriophages. Defense mechanism evolved by bacteria.
Restriction Endonucleases
Another name for DNA restriction enzyme. Makes double stranded cuts to DNA at recognition sites.
Restriction site
specific sequence where each enzyme cuts DNA. Enzymes recognize 4-6 base pair palindromic sequence
2 restriction enzymes used in lab
EcoRI enzyme: In E. coli and contains a 5’ overhang
Pstl enzyme: In Providencia Stuartii and contains a 3’ overhang
How do multiple fragments arise
When a specific restriction site occurs in multiple locations, a restriction enzyme (restriction endonuclease) will cut at each site producing multiple fragments
Linear DNA fragment formula
#fragments = #restriction sites + 1
Circular DNA fragment formula
#fragments = #of restriction sites
Two types of DNA profiling
PCR
RFLP
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Lab technique used to increase number of DNA copies of a specific segment from a small sample
PCR is highly specific
Only produces copies of desired sequence
Uses primers designed to be complementary and are on each side of target DNA sequence
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
technique used to differentiate individuals by analysis of patterns derived from cleavage of DNA.
Compares fragment sizes cut by restriction enzymes.
Exploits variations between individuals
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) steps
1) Restriction enzymes cleave a region of known variability
2) Separating the fragments with agarose gel electrophoresis
3) Determining the number of fragments and relative sizes
What leads to differences in size or number of fragments
During RFLP mutations in nucleotide sequences within restriction sequences will lead to restriction enzymes cleaving differently.
DNA digestion reaction needs
restriction buffer
optimal temperature
What is within restriction buffer
NaCl: provides correct ionic strength
Tris-HCl: keeps pH at 8
Mg: an enzyme cofactor
optimal temperature
37 degrees Celsius or body temp is optimal for enzymes to survive
What happens of temperature is changed
Too Hot: enzyme will denature
Too cold: Enzyme activity is lowered and digestion is slowed
Gel electrophoresis
Separates DNA fragments on agarose gel and allows for fragment size determination when comapred to DNA standard
Gel electrophoresis components
Agarose Gel Has large pores for fragments to separate
buffer is placed in gel to allow for current
Samples are placed in wells with dye to track movement
DNA ladder or strands with known band sizes must be added to 1 lane per gel
Anodes color representation on gel electrophoresis chamber
Red is positive
Black is negative
Which side does DNA samples move towards and why
DNA fragments have a negative phosphate backbone which will be attracted to positive end (red end) of chamber when electric current is turned on.
Sample loading dyes use
Sample loading dyes do not stain the DNA itself but can still be used to monitor DNA movement across gel
Which fragments will move faster and farther
Smaller fragments will move faster and farther because they navigate through pores in gel better
Two different stains
Fast Blast DNA Stain: Dye molecules are positively charged and bind to negatively charged phosphate groups on DNA backbone. This is used to stain gel after electrophoresis has run
SYBR or Green Glow DNA dye: Insert themselves into DNA helix and appear as a green glow when under UV light. Added to stain gel before electrophoresis.
Gel analysis
Measure the distance in mm that each DNA fragment traveled from the well and match with known base pair size. A standard curve can then be created with distance on X axis and Bp on Y axis
DNA samples used for experiment
Crime scene
Suspects 1-5
DNA size standard
What is placed in each tube
Every tube gets EcoRI/Pstl restriction enzyme mix. The DNA size standard is left as is.
What do you do with samples after adding mix
Incubate in water bath at 37 degrees Celsius for 45 minutes
Setting on electrophoresis chamber after adding DNA samples to wells
100V for 30 minutes