m4 tuts pcol p1
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Pharmacology
Study of uses and efforts of drugs
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
Nervous System | Preganglionic NT (Receptor) | Postganglionic NT (Receptor) | Response |
|---|---|---|---|
Parasympathetic | Longer Acetylcholine (Nn ACh receptor) | Acetylcholine (Cholinoceptor) | M-AChR: SM, heart, glands
Nm-AChR: Skeletal muscles (neuromuscular junction) - DEPOLARIZATION
|
Sympathetic | Shorter Acetylcholine (Nn ACh receptor) | Norepinephrine (Adrenoceptor) | a, B
|
Parasympathetic (Cholinergic)
Neurotransmitters:
Preganglionic NT: Acetylcholine
Postganglionic NT: Acetylcholine
Receptor: Cholinoceptor
Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes
Subtype | Location/Effect |
|---|---|
M1 - Gq | Mind, gastric mucosa |
M2 - Gi | Heart – ↓ heart rate |
M3 - Gq | Most dominant and most common - smooth muscle |
M4 - Gi | CNS modulation |
M5 - Gq | CNS modulation |
Parasympathetic Peripheral Effects
M1, M2, M3
Diarrhea: ↑ peristalsis
Urination: contraction of detrusor muscle (relax or dilate of sphincter)
Miosis (pupil constriction)
Bradycardia: ↓ heart rate, inotropy, dromotropy
Bronchoconstriction
Emesis, erection
Lacrimation
Salivation
↑ Secretion
Parasympathetic in the Brain
Brain: M1, M4, M5 – modulation of neurotransmission
Nn-ACh receptor
Modulation of dopamine release in the brain
ANS ganglia
Inhibited by ganglionic blockers
Nm-ACh receptor
Muscular depolarization (contraction)
Direct-acting Cholinergic Agonists
Muscarinic receptor agonists:
Bethanechol
Pilocarpine
Muscarine
Analog: Cevimeline
BET MUSCle PIoLO
Nicotinic receptor agonists:
Nicotine ⭐
Lobeline
Cytisine
Analog: Varenicline ⭐
Muscarinic & Nicotinic receptors: Nonselective
Carbachol
Acetylcholine
Methacholine
Arecholine
Muscarinic receptor agonists
Bethanechol
Pilocarpine
Muscarine
Analog: Cevimeline
Nicotinic receptor agonists
Nicotine
Lobeline
Cytisine
Analog: Varenicline
Muscarinic & Nicotinic receptors
Carbachol
Acetylcholine
Methacholine
Arecholine
Drugs for Sjogren Syndrome
For saliivary gland destruction (dry eyes, dry mouth):
Pilocarpine
Cevimeline
Treatment of atonic bladder
For acontractile bladder - like postpartum & postoperative urinary retention
Bethanechol - Bladder emptier (BE)
It helps to cause urination and emptying of the bladder
Metacholine
Diagnosis of asthma
Smoking deterrents
Quit smoking aid
Alkaloid: Nicotine (FULL AGONIST) ⭐
Non-nicotine: Varenicline (PARTIAL AGONIST) ⭐
Others:
Antidepressant: Bupropion ⭐
Ganglionic blocker: Mecamylamine (under study)
Indirect-Acting Cholinergic Agonists
Also known as an anticholinesterase or cholinesterase inhibitor
Enhances cholinergic activity by blocking the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) enzyme, which normally breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to Choline + Acetate
Inhibition of AChE = ↑ ACh
Spectrum: Both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
Reversible AChE inhibitors
Carbamates:
Neostigmine - 4° POLAR
Pyridostigmine - 4° POLAR
Physostigmine - 3° NONPOLAR (Periphery and Centrally)
Reversible AChE inhibitors
Quaternary ammonium compounds: POLAR
Ambenonium
Demecarium
Edrophonium
Centrally-acting Reversible AChE inhibitors
LIPOPHILIC - for Alzheimer's Disease
Donepezil
Galantamine
Rivastigmine
Irreversible AChE inhibitors (Organophosphates)
LIPOPHILIC - central and peripheral effects
Malathion
Parathion
Echothiophate
Isoflurophate
Myasthenia gravis
long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness.
Edrophonium
Diagnosis of Myasthenia gravis (Tensilon test)
Treatment of Myasthenia gravis
Extreme fatigue in muscles so choose quaternary amines
1. Pyridostigmine (first line; (+) corticosteroids if poor response)
2. Neostigmine
Methacholine
Diagnosis of bronchial hyperreactivity
Alzheimer’s disease
↓ Low ACh = suffering from retrograde amnesia (past events)
First-line drugs: Centrally Acting Reversible AChE blockers
Rivastigmine
Donepezil
Galantamine
Tacrine* (obsolete - toxic in liver, inferior effect)
Physostigmine
DOC for atropine poisoning
Atropine is a tertiary amine = antidote should be tertiary amine
Treatment of pesticide poisoning
Pesticide poisoning (i.e., organophosphates)
1. Atropine (MOA: Cholinoceptor blocker)
2. Pralidoxime (MOA: regenerates AChE)
Organophosphate poisoning (cholinergic crisis)
Mechanism:
Organophosphates bind to acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Inhibition can be irreversible after a process called aging
Aging:
Time-dependent process where the organophosphate-AChE complex becomes permanently bound = irreversible
Makes reactivation of the enzyme impossible
Treatment:
Pralidoxime (2-PAM)
Reactivates AChE only if given before aging occurs
Atropine
Competitive antagonist at muscarinic receptors (Cholinoceptor blocker)
Relieves muscarinic symptoms such as salivation, bronchorrhea, and bradycardia
Open-angle glaucoma
Most common type
Decreased aqueous humor reabsorption
Painless visual loss
Angle-closure glaucoma
Blockade of the canal of Schlemm (normally held open by trabecular meshwork)
Can be acute (painful) or chronic (genetic)
Chemical warfare agents
Sarin, Soman, Tabun
True
Condition / Use | Drug / Notes |
|---|---|
Diagnosis of Myasthenia gravis | Edrophonium |
Treatment of Myasthenia gravis | 1. Pyridostigmine (first line; (+) corticosteroids if poor response) 2. Neostigmine |
Diagnosis of bronchial hyper-reactivity | Methacholine |
Alzheimer’s disease | First-line drugs: Reversible AChE blockers |
DOC for atropine poisoning | Physostigmine |
Treatment of pesticide poisoning | (i.e., organophosphates) |
1. Atropine (MOA: muscarinic receptor blocker) | |
2. Pralidoxime (MOA: regenerates AChE) | |
Chemical warfare agents | Sarin, Soman, Tabun |
Open-angle glaucoma
Most common type
Decreased aqueous humor reabsorption
Painless visual loss
Angle-closure glaucoma
Blockade of the canal of Schlemm (held open by trabecular meshwork)
Acute (painful) or chronic (genetic)
True
Glaucoma treatment goal
Primary goal: Decrease intraocular pressure (IOP)
Methods to achieve:
↓ Aqueous humor production
↑ Aqueous humor outflow
Drugs: PBAC
P - prostaglandins analogues
B - beta blockers
A - alpha 2 agonists
C - carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Decrease aqueous humor production
Beta Blockers:
Timolol
Betaxolol
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Acetazolamide
Dorzolamide
Increase aqueous humor outflow
PGF2α analogs:
Latanoprost
Bimatoprost
Miotics: e.g., Pilocarpine
Non-selective alpha agonist: Dipivefrin → Epinephrine
Decrease production & increase outflow aqueous humor
Alpha-2 agonists:
Brimonidine
Apraclonidine
Synthesis of Acetylcholine
Choline Uptake - rate limiting step
Blocked by: Hemicholinium
ACh Synthesis (Choline + Acetyl CoA)
Enzyme: Choline Acetyltransferase (ChAT)
Product: Acetylcholine (ACh)
Vesicular Storage
Blocked by: Vesamicol
Release via Exocytosis
Inhibited by: Botulinum Toxin
Stimulated by: α-latrotoxin (black widow spider)
Facilitated by: High Ca²⁺ influx
Neurotransmitter Binding → Response
Occurs at muscarinic or nicotinic receptors
Inhibited by: Anti-cholinergics (atropine)
Enzymatic Metabolism
Enzyme: Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Products: Choline + Acetate
AChE Blockers (↑ ACh)
Neostigmine, Physostigmine (reversible), Organophosphates (irreversible)
Cholinoceptor Blockers: Anti-cholinergics
Atropine (muscarinic)
Tubocurarine (nicotinic)
Choline Recycling
Choline is reabsorbed for reuse in ACh synthesis
True
Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
1. Blocks the uptake of choline | A. Hemicholinium |
2. Blocks the release of ACh | C. Botulinum toxin |
3. Stimulates the release of ACh | D. Latrotoxin |
4. Blocks the receptor of ACh | E. Atropine (anticholinergics) |
5. Blocks the storage of ACh | B. Vesamicol |
Choline Acetyltransferase (ChAT)
Enzyme responsible in synthesis of ACh:
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) / Cholinesterase
Enzyme hydrolyzing ACh
Parasympathetic (Cholinergic) Blockers
Block cholinergic receptor = Parasympatholytic effect = Anti-DUMBBELLS
A/E: mydriasis - blurred vision, ↓ secretion - dry mouth & eyes
Nonselective Parasympathetic (Cholinergic) Blockers
Atropine ⭐
Homatropine ⭐
Benztropine ⭐
Trospium
Ipratropium ⭐
Tiotropium ⭐
Scopolamine
Dicyclomine
Cyclopentolate
Oxybutynin
Flavoxate
Propantheline
Selective Parasympathetic (Cholinergic) Blockers
M3-Selective (for management of OA bladder) ⭐
Darifenacin
Solifenacin
Tolterodine
Fesoterodine
M1-Selective ⭐ (management of ulcer disease)
Pirenzepine
Telenzepine
Natural alkaloids
Drug | Use / Notes |
|---|---|
Atropine | Antidote for cholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor |
a. Physostigmine toxicity (reversible) | |
(+) Pralidoxime | b. Organophosphate poisoning (irreversible) |
Scopolamine | Aka Hyoscine |
Treatment of motion sickness (via transdermal patch & postoperative nausea & vomiting) |
Atropine
Antidote for cholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor
a. Physostigmine toxicity (reversible)
b. Organophosphate poisoning (irreversible) (+) pralidoxime
Scopolamine
Aka Hyoscine
Treatment of motion sickness (via transdermal patch & postoperative nausea & vomiting)
Anti-Parkinson drug
Pseudoparkinsonism - by using haloperidol
EPS
↑ Acetylcholine = lead to tremors
Tx: anticholinergics (3 BiBe)
Benztropine - Treatment of extrapyramidal symptoms (e.g., acute dystonia and Parkinson-like symptoms) ⭐
Biperiden
Trihexyphenidyl
Mydriatic, cycloplegic drugs
Atropine
Homatropine
Tropicamide
Cyclopentolate
COPD and asthma
Tx: Inhibit M3 = bronchodilation
Ipratropium and Tiotropium
Treatment of overactive bladder
Tx for Urinary frequency, urgency, and incontinence
Inhibits M3 (detrusor muscle ) = ↓ contraction (urinary retention)
Drugs / Suffix |
|---|
1. -fenacin |
2. -terodine |
3. -butynin |
4. Trospium |
5. Propantheline |
Antispasmodic agent
To relieve GIT spasm caused by IBS
Dicyclomine (dicycloverine)
Propantheline
Sympathetic (Adrenergic)
Neurotransmitters
Preganglionic NT: Acetylcholine
Postganglionic NT: Norepinephrine
Receptor: Adrenoceptor (a, B)
Opposite of DUMBBELLS
Sympathetic (Adrenergic) Receptors
Receptor | Response |
|---|---|
Alpha 1 |
|
Alpha 2 |
|
Beta 1 ❤ | ↑ Heart rate/chronotropy, ↑ contractility/inotropy, ↑ dromotropy |
Beta 2 Baga Bahay bata Bladder | Relaxation of
|
Beta 3 |
|
Sympathetic (Adrenergic) Receptors
Alpha 1
Vasoconstriction
Mydriasis
Contraction of bladder neck (closed sphincter) → urinary retention
Alpha 2
Central: ↓ NE release → vasodilation
Peripheral: vasoconstriction
NET effect: Vasodilation
Example: Clonidine → transient increase in BP
↓ Intraocular pressure
Beta 1 ❤
↑ Heart rate / chronotropy
↑ Contractility / inotropy
↑ Dromotropy
Beta 2
Lungs: bronchodilation
Bladder detrusor: relaxation → urinary retention
Uterus: tocolysis (pampakapit)
Beta 3
↑ Lipolysis
Relaxation of bladder (detrusor muscle)
True
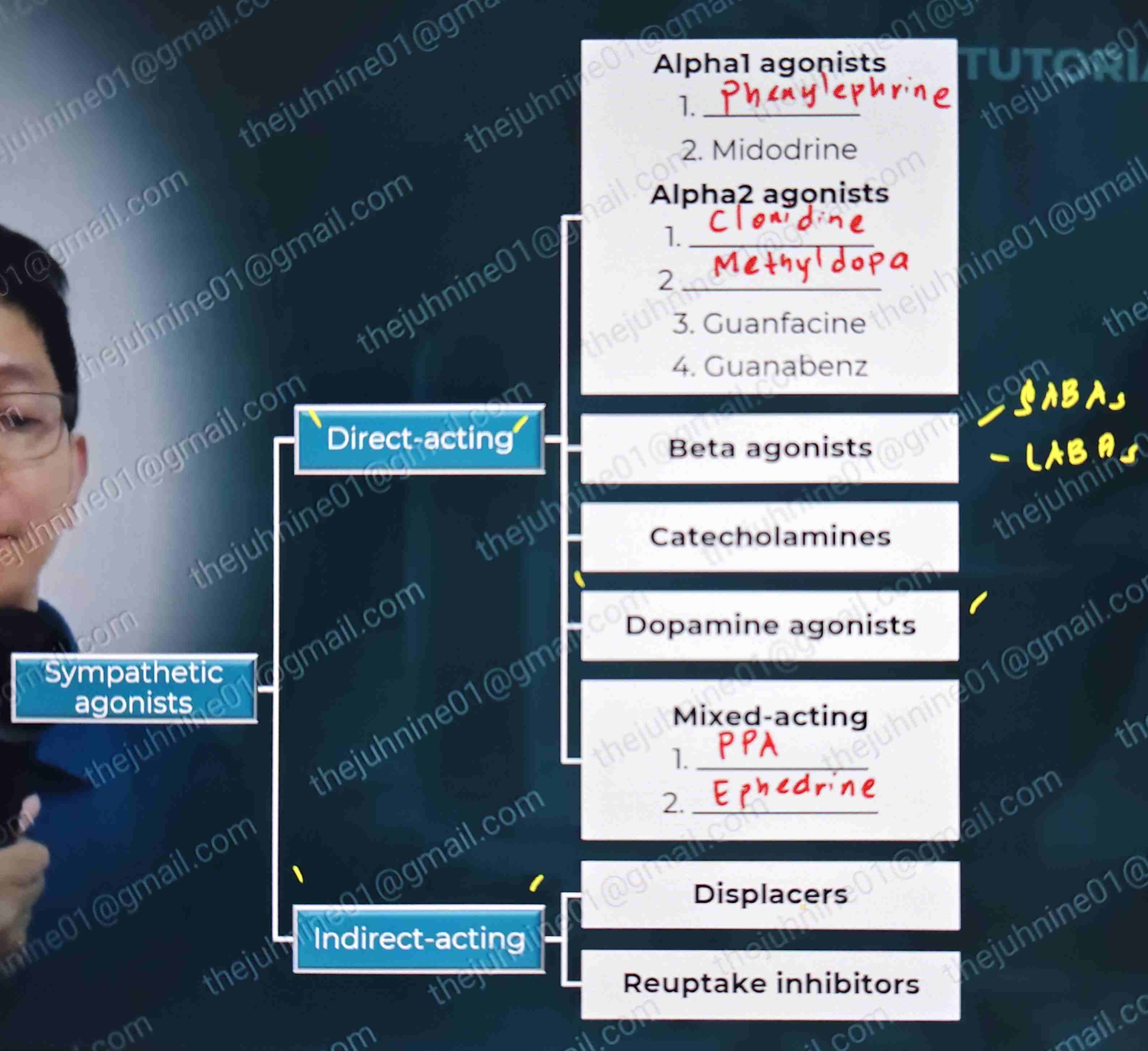
Sympathetic agonists:
Direct Acting
Alpha 1 agonist
Alpha 2 agonist
Beta agonists
Catecholamines
Dopamine agonists
Mixed acting
Indirect acting
Displacers
Reuptake inhibitors
Natural (endogenous) catecholamines
Catecholamine | Use / DOC |
|---|---|
Epinephrine | Adrenaline DOC for anaphylactic shock |
Norepinephrine | Noradrenaline DOC for septic shock |
Dopamine | Adv: Versatile
|
Epinephrine
Adrenaline
DOC for anaphylaxis/anaphylactic shock
Norepinephrine
Noradrenaline
DOC for septic shock
Dopamine
Adv: Versatile
Shock + hypotension
Shock with renal shutdown
Hypovolemic shock (fluid)
Synthetic (exogenous) catecholamines
Drug | Use |
|---|---|
Isoproterenol (Isoprenaline) |
|
Dobutamine |
|
Isoproterenol
Isoprenaline
Inhalation: Acute asthma
IV: refractory bradycardia and AV block
Dobutamine
Tx of shock without hypotension
Treatment of cardiogenic shock
Atropine
Symptomatic bradycardia DOC
Phenylephrine
4 uses
Nasal decongestant
IV: Tx of orthostatic hypotension
Injection: Priapism (prolonged & painful erection)
Topical: Mydriatic agent (retina exam)
Dexmedetomidine
Used to reduce opioid requirement in pain control (ICU) - potency enhancer
Analgesic and sedative effect
Clonidine
Used to facilitate abstinence from opioid
INDIRECT-ACTING ADRENOCEPTOR AGONIST
Displacers
Amphetamines
Methylphenidate
Modafinil
Reuptake inhibitors
Cocaine
TCAs, SNRIs
Displacers (stimulants)
Drug | Use / Notes |
|---|---|
Amphetamine | Treatment of ADHD, narcolepsy & obesity |
Methylphenidate | Treatment of ADHD |
Modafinil | DOC for narcolepsy |
MOA: NE & DA displacers
Displace norepinephrine (NE) from storage vesicles
Result: Reverse transport of NE into the synapse through the norepinephrine transporter (NET) into the synaptic cleft, even without an action potential
↑ NE & DA in synaptic cleft
↑ Sympathetic stimulation (CNS stimulation, increased HR, alertness)
Amphetamine
Treatment of ADHD, narcolepsy & obesity ( ↑ DA, ↑ NE)
Methylphenidate
Treatment of ADHD
Modafinil
DOC for narcolepsy
Non-stimulants for ADHD
Atomoxetine ⭐
Clonidine
Guanabenz
Short-acting beta2 agonists (SABAs)
Examples:
Albuterol (Salbutamol)
Levalbuterol
Fenoterol
Terbutaline
Uses:
Acute asthma (reliever)
Treatment of Hyperkalemia
Side effect:
Hypokalemia
Long-acting beta2 agonists (LABAs)
Examples:
Salmeterol
Formoterol
Uses:
Chronic asthma (controller) + Inhaled Corticosteroids
Nocturnal asthma
Mirabegron
Beta-3 agonist for overactive bladder (promote urinary retention)
Fenoldopam
Dopamine-1 agonist for hypertensive crisis (outcome is vasodilation)
Vasopressors
(Vaso = vessel, Pressor = compress) = CONSTRICTORS
Used in shock, orthostatic hypotension
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Phenylephrine
Vasopressin
Inotropes
Used in acute HF (cannot be used in chronic) - stimulate contractility of 💖
Dobutamine (Vasodilator)
Milrinone
Vasopressor + inotrope
Dopamine (dose dependent)
mcg/mg/min
1 to 3 low dose = stimulate D receptor = VASODILATION
4 to 10 intermediate dose = Stimulate B-receptor = INOTROPIC
Grater than 10 high dose = Activate a-1 receptor = VASOCONSTRICTION (vaspressor)
SYMPATHETIC NT SYNTHESIS & DEGRADATION
Synthesis of Norepinephrine
Tyrosine enters the neuron
Tyrosine → DOPA via Tyrosine Hydroxylase
Inhibited by: Metyrosine → ↓ DOPA production → ↓ NE
DOPA → Dopamine via DOPA Decarboxylase
Dopamine enters vesicle
Dopamine → Norepinephrine (NE) via Dopamine β-Hydroxylase
Storage
NE is stored in vesicles inside the neuron until release
Inhibited by: Reserpine → blocks VMAT → prevents dopamine from entering vesicle → ↓ NE formation
Release
Action potential arrives → causes calcium influx
Calcium triggers exocytosis → NE is released into the synaptic cleft
Inhibited by: Guanethidine, Bretylium, Guanabenz → block NE release from neuron
Receptor Binding and Response
NE binds to adrenergic receptors (α and β)
Leads to sympathetic effects (opposite of DUMBBELS):
↑ heart rate
Bronchodilation
Vasoconstriction
Mydriasis, etc.
Inhibited by sympatholytic agents
Termination of Action
Reuptake into the presynaptic neuron (main mechanism)
Inhibited by: Cocaine, TCAs, SNRIs (e.g., Venlafaxine, Duloxetine) → block NET → ↑ NE in synapse
NE is either recycled into vesicles or degraded
Metabolism
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) → degrades NE inside the neuron
Inhibited by: MAO inhibitors (e.g., Selegiline, Phenelzine, Tranylcypromine) → ↑ NE levels
Catechol-O-Methyl Transferase (COMT) → degrades NE in the synapse/periphery
Inhibited by: COMT inhibitors (e.g., Entacapone, Tolcapone) → ↑ NE levels
True
Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
1. Blocks the storage of dopamine | B. Reserpine |
2. Blocks the release of NE | C. Bretylium, Guanethidine, Guanadrel |
3. Stimulates the release of NE | F. Amphetamine |
4. Blocks tyrosine hydroxylase | A. Metyrosine |
5. Blocks NET transporter | D. TCAs and SNRIs (including cocaine) |
6. Blocks the metabolism of NE | E. MAO inhibitors |
B. Dobutamine
Which of the following is not a vasopressor?
A. Dopamine
B. Dobutamine
C. Isoproterenol
D. Phenylephrine
E. Epinephrine
D. Phenylephrine and Acetylcholine (ACh is not a catecholamine)
Which of the following are not catecholamines?
A. Dopamine and Dobutamine
B. Dobutamine and Isoprenaline
C. Isoproterenol and Adrenaline
D. Phenylephrine and Acetylcholine
E. Epinephrine and Noradrenaline
A. Acetylcholine (-) AChE = ↑ ACh
What neurotransmitter is increased by Rivastigmine in the CNS synapses?
A. Acetylcholine
B. Norepinephrine
C. Epinephrine
D. Dopamine
A. Methyldopa
Anti-HPN for pregnant women
A. Methyldopa
B. Aliskiren
C. Candesartan
D. Captopril
Aliskiren, ARBs, ACEi = renal dysgenesis
Sympathetic (Adrenergic) Blockers
Sympathoplegics/Sympatholytics = Inhibit adrenoceptor = ↑ DUMBBELLS (same effects with parasympathetic)
Non-selective alpha blockers
Selective alpha-1 blockers
Selective alpha-1A blockers
Selective beta blockers
Non-selective beta blockers
Drugs for pheochromocytoma
Tumor in adrenal medulla = ↑↑EPI/NE = Hypertensive episodes
Treatment: Nonselective a-blockers
Reversible, competitive: PHENTOLAMINE
Irreversible, non-competitive: PHENOXYBENZAMINE (preferred)
A/E: reflex tachycardia (mx: B-blockers)
Nonselective a-blockers
For pheochromocytoma
Reversible, competitive: PHENTOLAMINE
Irreversible, non-competitive: PHENOXYBENZAMINE (preferred)
Phentolamine
Reverses the effect of EpiPen® after accidental injection to the finger
First line drugs for LUTS
First line drugs for LUTS (nocturia, urinary frequency, urgency, incomplete micturition) caused by BPH - Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (FDA-approved)
Tx:
a1 blockers (-zosins) = vasodilation = increased urinary flow = used for HTN + BPH (mx of LUTS - symptoms of BPH only)
Prazosin
Terazosin
Doxazosin
a1-a blockers = less amount in BV = lesser vasodilation tx of BPH only
Silodosin
Tamsulosin
Alfuzosin
Agent of choice for BPH to decrease prostate size
Finasteride
a1 blockers (-zosins)
= vasodilation = increased urinary flow = used for HTN + BPH (mx of LUTS - symptoms of BPH only)
Prazosin
Terazosin
Doxazosin
a1-a blockers
= less amount in BV = lesser vasodilation tx of BPH only
Silodosin
Tamsulosin
Alfuzosin
Finasteride
Agent of choice for BPH to decrease prostate size
First-dose phenomenon
Adverse effect of alpha blockers
Mx: start with low dose at bedtime, monitor BP
Prazosin
Treat HPN (non-first line - inferior)
Non-FDA (off-label)
Raynaud's phenomenon (nifedipine/CCBs - DOC)
Reduce nightmares in PTSD (SSRI - DOC)
Scorpion envenomation
Nicotinic Receptor Blockers
Type 1 - Nm: Blocked by:
Non-depolarizing Neuromuscular blockers (Paralytic agents)
Type 2 - Nn: Blocked by:
Ganglionic blockers
Nicotinic Receptor Blockers
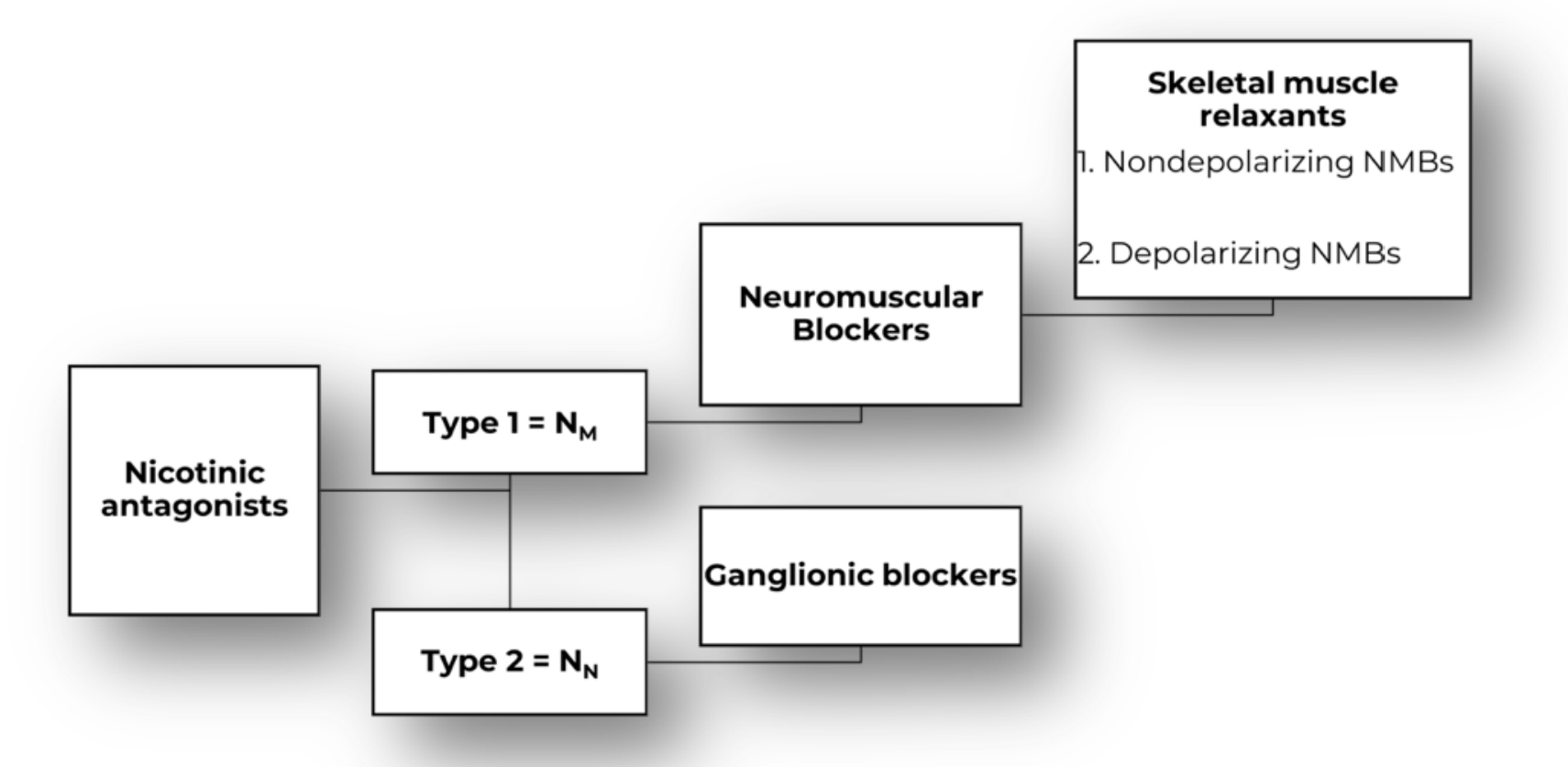
Ganglionic blockers
Malignant HTN (RARE)
Mecamylamine (used as smoking deterrent)
Trimethaphan