AICE Enviro Unit 5
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Food Security
Exists when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life
Food Wheel: Components of Food Security
Availability
Access
Utilization
Stability
Availability
Availability: Food availability means that sufficient quantities of appropriate and quality food is available from domestic production, commercial imports, food assistance or food reserves on a consistent base
Accessibility
Accessibility: People have adequate income or other resources to access appropriate food domestically through home production, buying in local markets or as exchange, gifts, borrowing or as food aid
Utilization
Utilization: People utilize food properly through food storing and processing practices while have sufficient knowledge where they apply nutritional, health, sanitation, socio-cultural as well spiritual parameters of food.
Stability
Stability: Stability of food refers to availability of adequate food all the time, thus, certain that access and utilization of appropriate food is not curtailed by any hindrance, shortages or by emergencies or sudden crises.
Food homogeneity
the lack of diversity in food we eat
It has a dangerous impact on climate change, food security, and human health
Despite having 14,000 edible and nutritious plant species to choose from, 75% of the food we eat comes from just 12 plants and five animal species
Causes of Food Insecurity
Population growth
Unsustainable production, increase in homogeneity in global food supply
Price setting
Land degradation
Agricultural disease
Diverting crops for biofuels
Climate change
Water shortages
Poverty
Impacts of Food insecurity
regional food scarcity
nutritional deficiency and malnutrition
poverty
forced migration
conflict
famine
death
Price setting
The government sets the price for certain commodities which makes it easier to subsidize them.
ex. corn has a set price. Corn is used for humans, livestock, and biofuel. Farmers cannot charge a higher amount for when they sell it as a fuel.
Subsidy
Money from the government that is intended to keep the price of a commodity low.
Subsidized loans
offers a six-month grace period after graduation, during which the federal government pays the interest. Lower Interest rate.
Unsubsidized Loans
six-month grace period but interest occurs during this time.
Land degradation
soil erosion and depletion
affects 24% land area globally
Affects 40% of land in Europe
80% caused by agriculture
Biofuels
increases monocultures (one oil type produced)
releases CO2 but considered carbon neutral b/c the plants absorb it again as they grow
Climate Change
increasing temp
weather vulnerability
shifting agroecosystem boundaries
invasive crops and pests
more frequent extreme weather events
reducing crop yields
reducing nutritional quality
lowering livestock productivity
Urban Gardens
Input
Money: Material (seeds, irrigation, fencing, equipment)
Labor: maintenance ($), people
Resource - land, water, soil
Output
Crop yield - varies seasonally
dietary diversity
less imports, higher utilization
Developed countries found to be more effective at producing high value crops, such as vegetable.
How to reduce food waste
shop smart
buy “ugly produce”
know your dates
save leftovers
organize the fridge
compost
donate
smaller portions
Food recovery hierarchy
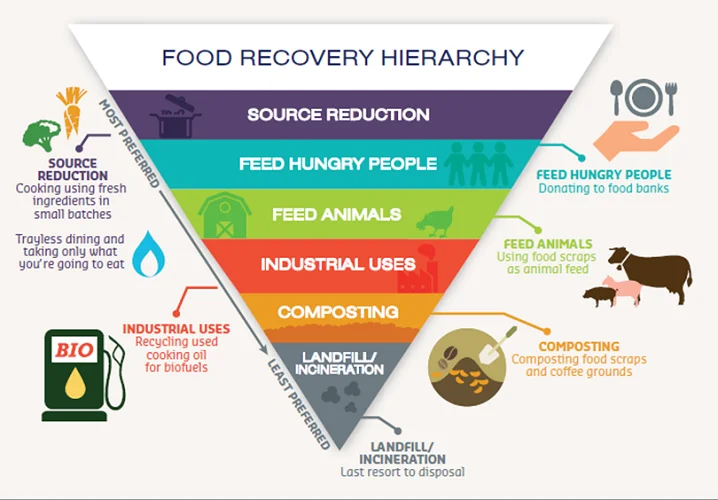
Managing food security
subsistence agriculture
increase food production by intensification and extensification
improved agriculture techniques and efficiency
reduction in livestock and increase in growing crops
reduce food waste
large scale food stock poling
improve transportation of food
protect pollinating insects
World Food Programme and food aid
rationing
Intensification and extensification
use more land for agriculture purposes and produce a higher crop yield from the land
agricultural intensification ensure sufficient food is grown to meet population demands.
Subsistence Agriculture
food grown is used for the farmer and their family
it cuts cost of shipping and ensures local food availability
Improved techniques
hydroponics
use of selectively breeding and genetically modified crops to develop pest resistant crops with a higher yield
controlling limiting factors (ex. fertilizer for areas short of nutrients)
increasing productivity by removing competition and reducing pests through biological control
Renewable energy resources
Biofuels (wood, biogas, bioethanol)
geothermal energy
wind energy
solar energy
tidal energy
wave energy
hydroelectric dams
Hydroelectric dams
provides place to convert the potential of kinetic energy of water to electrical of kinetic energy of water to electrical energy by using a turbine or generator.
Disadvantages: environmental impacts, high initial costs, and the potential for water scarcity and displacement of communities.
Solar energy
energy from the sun that is converted into thermal electric energy
Disadvantages: dependence on weather, high initial costs, storage challenges, and environmental concerns
Wind energy
the process by which the wind is used to generate mechanical power or electricity
can be used for grain grinding or pumping water
Disadvantages: intermittency (reliance on wind), noise pollution, visual impact, potential harm to wildlife (especially birds and bats), and land use requirements
Wave energy
transport and capture of energy by ocean surface waves
used for electrical/generation, water desalination, and pumping water.
Disadvantages: high costs for initial installation and ongoing maintenance, potential disruption of marine ecosystems, and the difficulty of efficiently transmitting energy to land
Tidal energy
produced by natural rise and fall of tides caused by gravitational interaction between sun and moo
converted into electricity
Disadvantages: it costs a lot of money to get all those turbines and cables underwater. and they could have negative effects on the environment – confusing or even injuring sea-life
Non-renewable energy
Fossil Fuels (oil, natural gas, coal)
Nuclear energy
Generations of biofuels
1st Generation Biofuel
It has High Carbon Content
Made from Edible Items.
Sugar, Corn, Starch, etc.
2nd Generation Biofuel
Greenhouse Gas content less than 1st Generation Biofuel
Made from leftover of Food Crops
Rice, Husk, Wood Chips, etc.
3rd Generation Biofuel
It is Carbon Neutral in (CO2 Emitted = Co2 Sequestrated)
Produced using microorganisms
Algae
4th Generation Biofuel
Made from ‘Genetically Engineered Crops’
They are Carbon Negative
Biogas
renewable fuel produced by breakdown of organic matter such as food scraps and animal waste.
used for vehicle fuel, and heating and electricity generation
Geothermal energy
heat from earth’s subsurface
used for heating and cooling, generate clean electricity
Oil
from ground, drilled and pumped out
found in underground reservoirs or by strip mining
Natural Gas
composed of methane
common/conventional located in porous or permeable rock or mixed in oil reservoirs
unconventional any form of gas too difficult or expensive to regularly drill instead requiring fracking (harmful)
Coal
Carbon heavy rock
most carbon extensive fossil fuel
Nuclear energy
nuclear fission, mostly uranium, to generate energy
uranium rods can only be used ONCE
Energy security
reliable availability of energy sources at an affordable price with consideration of the environment.
Long-term energy
supply of energy in line with economic development and environmental needs.
Short-term energy
systems that react promptly to sudden changes in the supply demand balance.
Short-term vs Long-term security
Short-Term Energy Security
Ensuring immediate energy supply despite disruptions (e.g., natural disasters, political conflicts).
Focuses on reserves, grid stability, and emergency responses.
Examples: Strategic petroleum reserves, backup power systems.
Long-Term Energy Security
Ensuring sustainable, stable, and affordable energy supply for the future.
Focuses on diversification, renewable energy, infrastructure investment.
Examples: Transition to renewables, energy efficiency policies.
Causes of Energy insecurity
fossil fuel depletion
inequality in global resources
population growth
differing energy needs in countries of different income groups
climate change
supply disruption
Natural disasters, piracy, terrorism
Impacts of energy insecurity
disrupted electricity supply to homes and industry
increasing prices for energy resources
increasing costs for industry
job losses, economic recession
increased levels of poverty and low standards of living
reliance on imported sources of energy
civil disruption and conflict
Eutrophication
a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water
Strategies to manage energy security
increasing energy efficiency
increasing energy production
reduce reliance of fossil fuels
invest in renewable resources and carbon neutral fuels
development of alternative energy techniques
investment in local projects
rationing
Waste Management Methods
Landfill sites
Incineration
Storage
Disposal at sea
Recycling
Exporting waste
Incineration
Advantages
Drastically reduced the amount of waste sent to landfill, minimizing the environmental impact of disposal.
Reclaimed valuable land that could have been used for landfills and turned into parks and recreational areas.
Electricity and heat produced helped meet energy needs of households and businesses
Better control over oder and noise
Prevents the production of methane gas
Eliminates harmful germs and chemicals
Reduced reliance on transportation
Disadvantages
High operating costs
Significant level of pollution(smoke from burning process can include acid gases)
Health and environment risk
Environmental racism
Does not contribute to waste reduction
Much of the waste can be recovered and recycled
Landfills
Advantages
relatively cheap method of dealing with waste because environmental costs are not taken into account
Landfill is a low technology method of waste disposal that countries at any level of development can use
occurs in specific location that can be chosen and monitored
waste going to well-designed landfills can be processed to remove recyclable materials before tipping
properly managed landfills can capture the methane produced by decomposition
Disadvantages
limit to the number of appropriate available sites in many regions
as sites become scarce, the cost of land increases
increasing public opposition to opening new landfill sites and expanding existing ones because of environmental and health concerns
land sites can generate considerable heavy vehicle traffic
Open Dumping
Advantages
Cost effective, does not require payment unlike other waste disposal methods
Easily accessible - Low effort and time to dispose waste
Disadvantages
May cause soil pollution, which could harm crop growth, productivity, and agriculture
Affects local ecology
Negative impact on health, exposing surrounding residents to the potential causes for cancer
Leached waste is likely to infiltrate groundwater causing water (ex.lake Malawi) and soil pollution
Strong winds can blow waste, causing air pollution
Increased levels of water pollution which affects species and overall, all marine ecosystems
Negative impact on tourism due to unpleasant views, especially around shorelines.
Impacts of waste disposal
contamination of soil leading to leaching and contamination of ground water
build up and release of methane with a danger of explosions
visual and noise pollution and unpleasant odor
risk of spread of disease
release toxic substances
bioaccumulation and biomagnification
plastics and microplastics
Infectious/ Biological waste
animal pathogens
biohazardous waste
bloodborne pathogens
infectious waste
sharps
plant pathogens
Threat: contamination of soil and water, the spread of infectious diseases, and exposure to harmful pathogens.
Toxin level and Trophic level
toxins can be introduced as early as the producer but can infect each trophic level after in the food chain, only becoming visible when a human is impacted.
Bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation
gradual accumulation of substances such as pesticides or other chemicals in an organism
Strategies to reduce impacts of waste
Three Rs
Biodegradeable plastics
food waste for animal feed
composting + fermentation
use to generate energy
education
financial incentives and legislation
Biomagnification
only concentration of a toxin, such as pesticides, in the tissue of tolerant organisms at successfully higher levels in a food chain.