natural and artificial selection
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
definition of variation
differences between organisms of the same species
importance of variation
to provide adaptations so that organisms can survive in ever changing environment
is continuous variation quantitative or qualitative?
quantitative
is discontinuous variation quantitative or qualitative?
qualitative
describe/define continuous variation
individuals in a population show a gradation from one extreme to the other
describe/define discontinuous variation
individuals in a population shows no gradation from one extreme to the other
what variation that’s affected by environmental factor
continuous variation
how continuous variation differ from discontinuous variation
continuous variation has intermediate characteristics within the same species
what caused discontinuous variation
genetic factors
does discontinuous variation affected by environmental factor
no
what variation is height and weight
continuous variation
what variation is blood group
discontinuous variation
what variation is the skin colour
continuous variation
what can caused genetic variation
-sexual reproduction
-crossing-over
-chromosome mutation
-hybridisation
-etc
what is meant by selection
a process whereby one or more factors acting on phenotypes favour the transmission of particular alleles tothe following generation
types of selection
natural and artificial
what is natural selection
a biological theory that explains why organisms seem match their environmental niches so well.
natural selection acts directly on genotype or phenotype
phenotype
what are the types of selections
-stabilising selection
-discuptive selection
-directional selection
-sexual selection
-polymorphism
stabilising selection
genetic diversity decreases as the population stabilises on a particular trait
disruptive selection
Favours individuals and both extremes of a characteristic range
directional selection
Favours individuals at one end of the spectrum
sexual selection
Selection with respect to mating success
polymorphism
Refers to many different phenotypes found in population
What is artificial selection
A process of intentional or unintentional notification of a species/human action that encourages the breeding of certain traits over others.
What is a gene bank?
A type of biorepository which preserves genetic materials.
What type of selection that has its extreme values of character are selected against?
Stabilising selection.
What type of selection that has the emergence two distinct phenotypes?
Disruptive selection.
What type of selection that favours a single allele and allele people to shift to one direction?
Directional selection.
What type of selection that has some individuals are more successful than others in attracting mates?
Sexual selection.
What type of selection that has human interference involved?
Artificial selection.
What are the types of polymorphism?
Balance polymorphism and transient polymorphism.
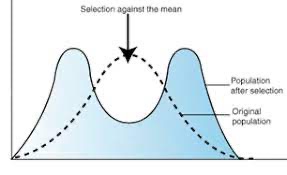
what type of selection is this?
disruptive selection
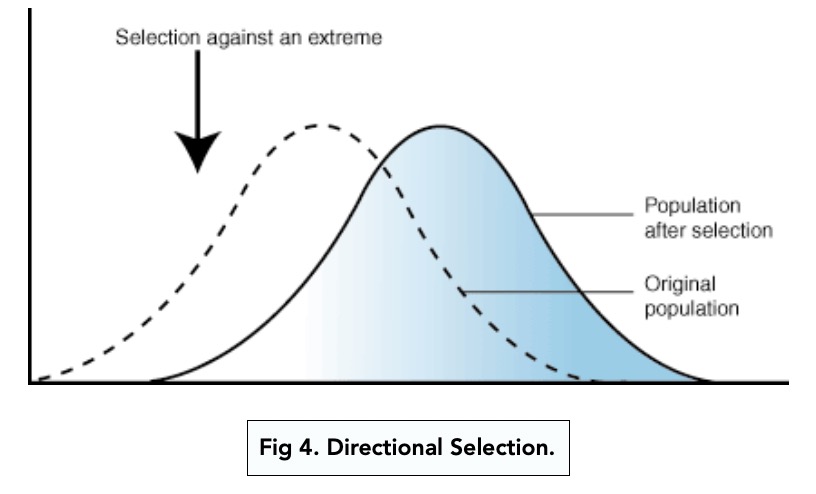
what type of selection is this?
directional selection
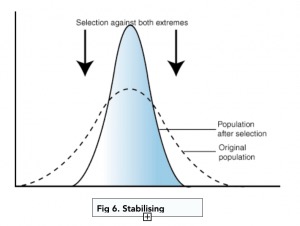
what type of selection is this?
stabilising selection
describe balanced polymorphism.
two or more alleles of a gene are maintained in am population because each is favoured by a separate environment force.
(two or more forms coexists in a stable ratio in a population)
describe transient polymorphism.
occurs when a morph is in the process of spreading through a population.
In an event of malaria infection do people with normal haemoglobin (HH) survive the disease?
no they die