Lecture 6 - Hematology/Liver/GI Lab Values
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
what is complete blood count (CBC) used for
evaluate symptoms (non-specific - fever, fatigue, bruising)
diagnose condition (anemia, infection, leukemia)
determine stage of disease (leukemia)
what does a CBC count provide
info on number of platelets, RBCs, WBCs
what does a Differential CBC provide
more detailed information on the number of different types of WBCs
what does a RBC indices provide
informaiton on RBC morphology(size, shape, colour) → classify type of anemia
hemoglobin (Hgb)
hematocrit (Hct)
what is mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
average size of RBCs
what is mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
average weight/amount of hemoglobin in a RBC
what is mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
average concentration of hemoglobin per volime of RBC
what is red blood cell distribution width (RDW)
measure of cell size distribution
how are levels of mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) classified
hyperchromic (high concentration)
normochromic
hypochromic (low concentration)
how is mean corpuscular volume (MCV) classified
macrocytic (large)
normocytic
microcytic (small)
what condition is associated with microcytic MCV
Iron deficiency anemia
what condition is associated with macrocytic MCV
vitamin B deficiency
what condition is associated with hypochromic MCHC
iron deficiency anemia
thalassemia
what condition is associated with hyperchromic MCHC
hemolytic anemia
what are additional lab tests for anemia
ferritin
vitamin B12
folic acid
reticulocyte count
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
C-reactive protein (CRP)
what does ferritin measure
how much iron is stored in the body
(iron deficiency produces microcytic anemia)
what does a vitamin B12 deficiency result in
macrocytic normochromic anemia
what does a lab test for folic acid indicate
involved in maturation of RBCs
can accompany vitamin B12 deficiency
what is reticulocyte count measure
immature red blood cells
reflects erythropoietic activity of bone marrow → useful for anemia diagnosis and monitoring to medication therapy
what does erythrocyte sedimentation rate measure
presence/level of inflammation in the body
usually a slow process
what does C-reactive protein measure
inflammation in the body, preferred over erythrocyte sedimentation rate
can indicate viral/bacterial infection, vasculitis, severe arthritis
what are the 3 types of granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
what are the 2 types of agranulocytes
lymphocytes, monocytes
what is neutrophilia
increased neutrophils
can indicate bacterial infection, trauma, MI
can be caused by medications - corticosteroids, lithium, epinephrine
what is neutropenia
decreased neutrophils
can indicate vitamin B12/folate deficiency
can be caused by medications - ganciclovir, clozapine, ticlopidine, cytotoxic meds
what is eosinophilia
increased eosinophils
can indicate allergic/acute reactions, parasitic infections
can be caused by medications - antibiotics (penicillins), ACEI, anticonvulsants (carbamezepine)
what is monocytosis
increased monocytes
can indicate recovery from bacterial infection, tuberculosis, endocarditis, leukemia
what is lymphocytosis
increased lymphocytes
can indicate infectious mononucleosis, viral infections, tuberculosis, syphilis, lymphoma
what is lymphopenia
decreased lymphocytes
can indicate HIV, radiation exposure, lymphoma (Hodgkins)
can be caused by medications (corticosteroids)
what does the liver produce
clotting factors, bile, albumin
what does the liver regulate and store
carbohydrates, fats, proteins
what does the liver metabolize and eliminate
medications, bilirubin
what can liver laboratory values be used to assess
determine what is happening with the liver
detect the presence of disease
differentiate different types of liver disease
measure extent of liver damage
evaluate response to treatments
monitor side effects of certain medications
how is liver function assessed
measure ability to synthesize
measured by albumin, clotting factors
how is liver injury assessed
measure aminotransferases → ALT, AST
how is cholestasis assessed
measure abnormal bile flow
measured by alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
what are non-specific markers for liver lab values
bilirubin, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
what is albumin liver function test
major plasma protein that contributes to osmotic pressure, transport of hormones/medications
concentration decreases in chronic liver diseases (e.g. cirrhosis)
hypoalbuminemia → decreases osmotic pressure → peripheral edema, ascites
what is clotting factors liver function test
vitamin K dependent factors: I, II, V, VII, IX, X (synthesized/stored in liver)
low factors = clotting abnormality → excessive bleeding, easy bruising
monitor by INR measurement
main causes of liver injury
medications, alcohol, hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
what are aminotransferases
used to assess liver injury
involved in metabolic processes, highest concentrations found in liver
(also found in cardiac/skeletal muscles, brain, kidney, lung, pancreas, blood cells)
what is alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
type of aminotransferase to assess liver injury
more specific for liver disease
what is aspatate aminotransferase (AST)
type of aminotransferase to assess liver injury
less specific for liver
what to look for when assessing liver injury
magnitude of increase of aminotransferases
mild = 5x ULN
moderate = 5-10x ULN
severe = >10x ULN
rate in change of enzyme levels (over days/months/years)
what is cholestasis
reduction of stoppage of bile flow
can be from impaired secretion from hepatocytes/obstruction of bile flow through intra-extra-hepatic bile ducts
what are symptoms of cholestasis
jaundice, pruritis, xanthomas (lipid deposition in skin), malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamine (ADEK), anorexia
what are the lab tests to identify cholestasis
elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (remember not specific to liver)
elevated gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) (not very specific to liver)
concurrent rise in both indicates underlying hepatobiliary disease
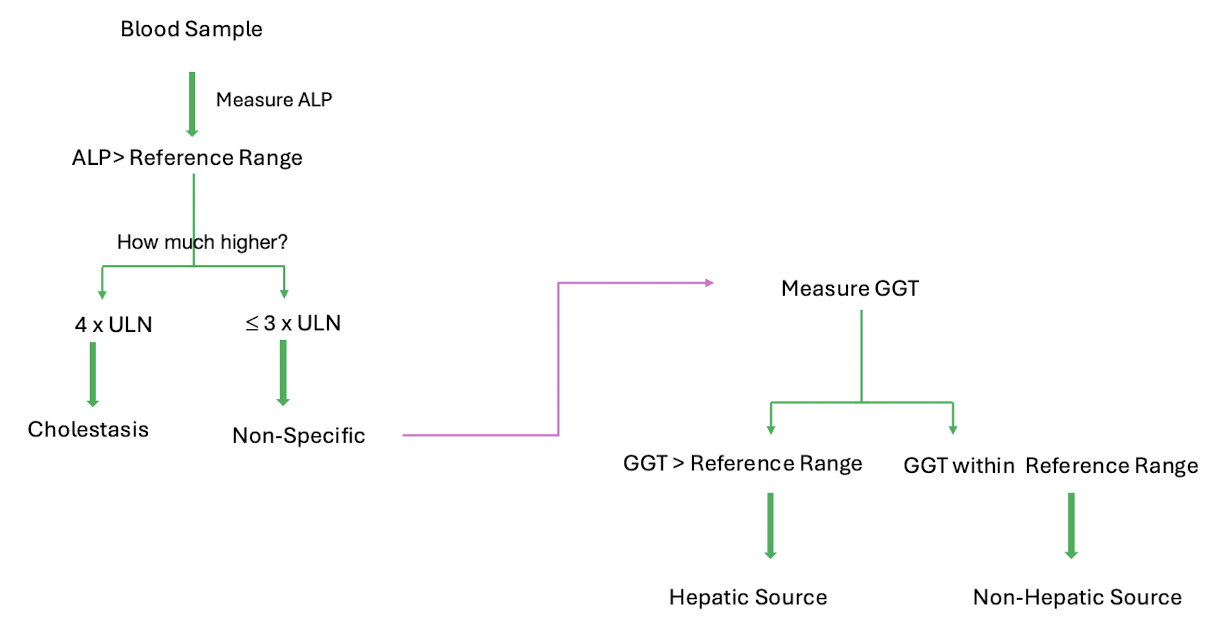
what is another cause of elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
skeletal disease, extrahepatic biliary obstruction
what is another cause of elevated gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
alcohol abuse
what are the 2 non-specific markers of liver laboratory values
bilirubin
lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
what do bilirubin levels indicate
bilirubin = product of hemoglobin metabolism in liver (RBC breakdown)
elevated associated with jaundice
measured as total and conjugated only (conjugated with glucuronide in liver to increase solubility)
some medications cause hemolytic anemia related to elevated bilirubin: antimalarials, benzos, sulfonamides, cytotoxic medications
what do lactate dehydrogenase levels indicate
LDH = enzyme present in every tissue
elevated = indicate cell damage (non-specific)
what is the Child Pugh Score in liver disease
predict mortality in cirrhosis patients
3 categories: A = good hepatic function, B = moderately impaired, C = advanced hepatic dysfunction
scoring based on: ascites, bilirubin concentration, albumin concentration, prothrombin time, encephalopathy
medications that may require surveillance of liver functions
HIV medications
statins
isotretinoin
tuberculosis medications (e.g. isoniazid)
rheumatoid arthritis medications (e.g. methotrexate)
how might doses need to be changed in patients with liver dysfunction
reduce dose of drugs that undergo first pass metabolism in the liver
increase dose of prodrugs
liver lab values in patients with lipid abnormalities
start statins
baseline monitoring to assess liver function → ALT
monitor after 3 months and compare to baseline
what are the 2 main lab tests used to assess the gastrointestinal system
amylase
lipase
both secreted by pancreas and salivary glands
what does an elevation of amylase and lipase indicate
problem with exocrine function in pancreas (pancreatitis)
problem with gallbladder/bile duct blockage
inflammation or blockage of salivary gland
CKD (enzymes not cleared)
2 other common miscellaneous lab tests
serum creatinine → used to assess GFT
waste product of creatine breakdown
blood urea nitrogen (BUN) → used to assess kidney function
urea = end product of protein metabolism (concentration depends on protein intake, nitrogen metabolism)