ch 1-4 - f300
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Define economics
How people make decisions about production, distribution, and consumption, all while inhabiting a world with limited resources
What purposes does money serve?
1) Medium of exchange
2) Imperfect store of value (the amt doesn’t change but the prices of goods do)
3) Unit of account (can measure things we value)
Commodity vs Fiat money
Commodity- HAS intrinsic value (e.g. gold)
Fiat - DOES NOT have intrinisc value (e.g. US dollars)
Define Finance
Subfield within economics that examines how people use markets and money to achieve their goals
Define Corporate Finance
How BUSINESSES allocate their scarce capital when facing an uncertain future
What is a corporation?
Legal arrangement of the business’ affairs chosen by the owners
What is capital?
The set of resources available to the business to produce whatever goods/services it sells (can be non-physical; think education)
Does a contract have to explicit or can it be an implicit agreemnt between two parties?
It can be implicit
Who are capital providers?
Owners and lenders
What are the 4 primary forms of business organizations?
1) Sole Proprietorships
2) Partnerships
3) Corporations
4) Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Who are the residual clamiants (lowest priority claim on the biz’s cash flows)?
Owners
Define a sole proprietorship
Business organization where the owner is a single person and is solely responsible for controlling the business
Advantages of a sole proprietorship
Simpliest type of business to start
Lowest regulation
Owner gets to keep all the profits
Since personal assets and business assets are the same, the gov taxes the business’ profits as personal income (no double taxing)
Disadvantages of sole proprietorships
No specialization
Unlimited liability for business debts (creditos can look beyond the biz’s assets to the personal assets of the propreitor to satisfy debts)
When sole proprietor dies, business is sold or liquidated (no forever life)
Can’t raise a lot of capital
Assymetric information can use illiquidity
What is liquidity?
The degree to which one can quickly convert an asset to cash at the asset’s fair market value
What is a partnership agreement and why is it important?
It explains the clear set of rules the partners will follow.
Without it, the partnership will DISOLVE when a partner leaves the firm or dies
What is a general partnership?
All the partners typically have a say in the critical biz decisions and then share in the resulting gains or losses
The partners face UNLIMITED liability (if you provide 25% of capital, you are still responsible for 100% of the creditor’s claims)
Explain what a limited partnership is
There are two types of partners: general and limited
General - run the biz, make all the significant decisions, UNLIMITED liability
Limited - provide capital, do not run the firm, max loss possible is hte money they invested into the partnership **BUT if they become too involved, they will face unlimited liability
What are some benefits of partnerships?
Specialization
More longevity than SP
NO double tax: gov only taxes the profits of the firm ONCE as the partners’ personal income
What are some negative aspects of a partnership?
Agency costs
Unlimited liability (but limited partnerships can mitigate this)
Not as much capital raised compared to corps
What is an agency relationship?
A relationship where the owner (principal) hires another person (agent) to represent their interests
What is the principal-agent conflict (aka agency problem)?
When in an agency relationship, there is a conflict of interest between a principal and the agent.
What is the difference between direct and indirect agency costs?
Direct costs - easily assign a dollar value (employee steals 100 dollars, you need to install 5k security cameras)
Indirect costs- not quantifiable (manager doesn’t share potentially big money-making idea in fear of losing job)
What is a corporation?
A business and legal entity that is ENTIRELY SEPARATE and distinct from its owners
T/F: In the eyes of the law, a corporation IS a fictional person who can enter contracts?
True
How does a corporation pursue its business goals?
By creating a nexus of contracts
In what state do most large corporations live in and why?
Delaware
It has a Court of Chancery that specializes in corporate issues and uses judges instead of juries
What are the articles of incorporation? And what is it also commonly called?
AKA: charter
Articles of incoporation: the document used to form a corporation that contains basic info on the corporation, intended life, purpose, number of shares the corporation can issue, and info about the person setting up the corporation
What are bylaws?
The owners must draw up a corporation’s bylaws (rules and procedures used to govern the business)
Includes the process to amend the artices of incorporation and the bylaws in the future
Spell out what kind of stock gets issued and voting rights
Procedure the shareholders will follow to select the board of directors
What is the responsibility of the board of directors?
Hiring managers and overseeing the direction of the firm’s operations
Acts in the best interests of shareholders
Difference between S and C Corporations
IRS:
S Corp: 100 or fewer owners; owners can elect to have biz profits taxed ONCE at the personal level
C Corp: More than 100, IRS treats the owners as separate from the corp (therefore taxing both), C-Corps are fictional people who need to pay taxes (corporate income tax)
The after-tax profits to shareholders (dividends) are taxed at the personal income tax level
Does the IRS apply a lower tax rate on dividends/capital gains OR wage income?
Dividends/capital gains — reduces impact of double taxation
Benefits of corporation
Limited liability- if you buy stocks, you just lose the money you invested (not your personal assets)
Access to lots of capital (thanks to standardized ownership claims they issue in large number: aka stocks)
IF PUBLIC: less asymmetric information bc of SEC regulation and reliable info on NYSE/NASDAQ
Specialization
Doesn’t die unless it financially dies
Negatives about corporations
Regulations by SEC (securities and exchange commission)
Sarbanes-oxley (SOX): independent auditors are needed, regualtes financial reporting and omissions reporting
What makes a company a “public company”?
The company has shares traded on AT LEAST ONE of the stock exchanges (NASDAQ, NYSE)
What does it mean to “go dark”
Public company goes private (usually bc of compliance costs)
What is a limited liability company (LLC)?
New business enetity
Hybrid between proprietorships/parternships and corporations
All the advantages and disadvantages of SP and Partnerships BUT owners have limited liability like Corps
Do not have bylaws, articles of incorp, shares of stock, board of directors, annual meetings like Corps (so way simplier than Corps)
They CAN have large market capitalizations but most are small biz
What is the PRIMARY goal for every for-profit business REGARDLESS of its form?
MAXIMIZE THE VALUE OF THE FIRM!!!
Value: highest price a buyer would pay to buy the business
What is the total value of a corporation called?
Market cap = current price for one share of stock multiplied by # of shares OUTSTANDING (P*Q)
When considering the total value of US stocks, which size of cap company (large, mid, small) constitute the majority?
Large-cap
What is capital budgeting?
Process of identifying, evaluating, and managing long-term assets of the business
Compare what something is worth to its price
What is capital structure?
Mixture of funding sources management chooses
Debt and equity
CHOOSE the mix of debt/equity that maximizes value
What is leverage?
Extent to which the company uses debt to finance its asset purchase
What does it mean to lever up vs lever down
Lever up- increases the proportion of debt to equity (debt-equity ratio increases)
Level down- opposite
What does it mean when a firm is choosing to be unlevered?
It uses 100% equity financing
Advantage of using equity financing?
Company does not contractually have to pay the owners, ever BECAUSE owners are residual claimants who only get leftover cash
Does the source and use of cash matter in capital structure?
Yes! If you tell a bank that you need to pay off your gambling debt (lol not good)…high risk —bank will be mean with the loan
What is Working Capital Management?
How the firm manages day-to-day activiites involving short-term assets and short-term liabilites
Working capital = short term assets - short term liabilities
Deciding to sell to customers on credit is a WCM problem NOT Capital Structure bc of short horizons
If working capital is high, then opportunity cost…
Is high — capital can be used for something else more productive
What is commerical paper and why would a company chose it?
Commerical Paper: unsecured promissory note issued by banks and corporations with short-term borrowing needs (usually less than 9 mo)
If you need short-term financing
What are the 3 parts of value maximization?
Cash flow size
Cash flow timing
Cash flow riskiness
What is the typical corporate organizational structure?
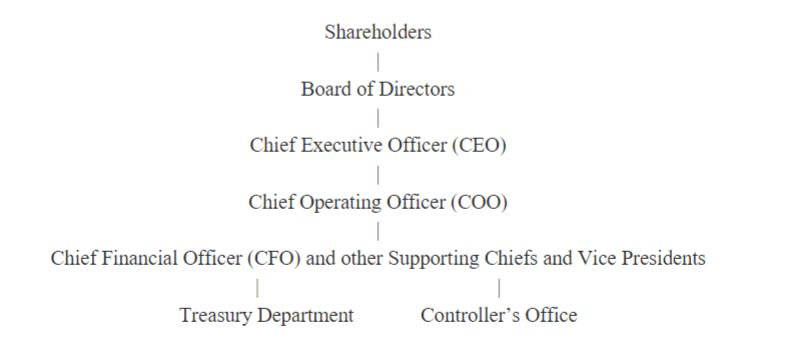
What is the CEO?
Leader and face of company, has the vision for the company
COO’s role?
Actual day-to-day management
CFO role?
Financial planning, financial reporting, managing cash flows, in charge of controller’s office and treasure dept
What does the controller’s office do?
Handle the firm’s financial, managerial, and tax acct
AKA: accounting (cat!)
What does the treasury dept do?
Financial planning, evaluates CAPEX, manages the credit to customers, handles cash dlows, raises necessary capital, protect firm from financial risks
*Essentially: capital budgeting, capital structure, and WCM
Label the following as principal or agent:
Shareholders
Board of Directors
C-Suite
Shareholders: principals
Board: agents
C-Suite: agents
T/F: The C-Suite often suggests which board candidates the shareholders should elect
True
OPM stands for…
Other people’s money
What are the 2 factors that determine whether managers will act in the stockholders’ best interests?
1) How closely are management goals aligned with stockholder goals?
Can compensate with stock to help
2) Can managers be replaced if they do not pursue stockholder goals?
What is restricted stock?
The stock a manager will not own until a contractually specified number of years lapses (known as a vesting period)
What are options?
Firms give managers the option to buy the company’s stock at a bargain price.
Who ultimately controls the firm?
Stockholders — they elect the board who hire and fire managers
What is a proxy fight?
A way unhappy stockholders can act to replace existing management
The authority to vote someone’s stock
A group solicits proxies to replace the existing board and replace current managers
What is a takeover?
Poorly managed companies get acquired bc their share price is low (think Carl Icahn)
What is an advantage of debt?
The gov treats interest payments as business expenses and allows companies to deduct them when calculating income taxes
In contrast, profits disgorged as dividends to shareholders are not tax-deductible
What’s the benefit of equity as opposed to debt?
The firm has no contractual obligation to pay the owners
But with a loan, you have to pay them
What does a firm need to do to get the funding it needs from capital providers?
Convince capital providers that this project will make them better off than their next best investment will (aka their opportunity cost)
What is a subsidiary?
A company partially or wholly owned by another corporation, the parent or holding company
T/F: The interest rate is the rental rate
True
The interest rate is an equilibrium that results from the interaction between…
The providers and users of money
How does the use of funds determine the interest rate?
The bank will charge a higher interest rate for something more risky
When the collateral isn’t very liquid/high value, they will charge higher interest rates (shiatsu massage vs equipment)
What is the money market?
Instruments that span a year or less
Used by institutions for WCM
Explain what commercial paper and T-bills are
Money market instruments
Commercial paper: promissory note
T-Bills: issued by US Treasury (agency that collects tax revenues and pays its obligations); gov is borrower, ESSENTIAL component of money market
What types of assets form the capital market?
Long-lived financial assets
What is the longest-lived form of financing?
Stocks - ownership claims do not expire as long as the firm survives
Explain the differences between the private and public market
Private
Access to purchase securities is extremely limited to potentially just two counterparties
E.g. bank loan
No active and transparent market for private
Public
Anybody with money can participate
Instead of one loan with JPMorgan, you can create a million small loans (bonds)
A corporation will get a loan it needs (in the form of bonds) for a potentially lower interest rate through public markets than private ones
What are private equity firms?
Firms that buy large chunks of a company or the whole thing
What are unicorns?
Privately held copmanies with valuations of a billion dollars or more
Relative to public markets, private markets are…
Illiquid (cannot easily exchange ownership claims)
What is a floatation?
Attracting capital in public markets
What does private placement mean?
When a corporation enters a debt agreement with an institution that is not public
E.g. Google takes a loan from JPMorgan
T/F: Public debt and equity offerings must register with the SEC?
True
IPO stands for…
Initial public offering
What is an SEO?
Seasoned equity offering (aka seasoned issue)
Issuing more shares of stock
Can dilute the ownership stakes of the original shareholders
What are the two most important secondary equity markets in the US?
NYSE and NASDAQ
What makes public securities more attractive in comparison to private securities in the secondary market?
Public
Active and liquid secondary market
Purchasers of shares might be more willing to pay more for this feature
Due to SEC regulations, valuations and other info is more accurate than in private
Private
Opaque and illiquid secondary markets (if they exist at all)
Non-transparent reporting due to lack of SEC regulations
The success of the money-making idea often hinges on the producer’s ability…
to convince a consumer they need that thing
What is the most critical source of cash for a typical corporation?
Sales to customers
Who are stakeholders?
Economic agents who have claims on the biz’s cash flows but do NOT provide it capital
When the corporation is either sharing residual profits with the owners or reinvesting the profits in the biz to produce future earnings, it is…
spending internally generated equity
What are buybacks?
When a corp uses moeny it could’ve paid dividends with to instead purchase its own shares.
Steps of start-up funding
Own money
Friends and family
Crowdsourcing
Angel investor
Ventrue capitalists
Go private or public
What is an angel investor?
A successful entrepreneur who contributes capital and advice
Who are venture capitalists?
Pool money from investors, then seek out and buy stakes in promising start-ups with huge growth possibilities.
More hands on than Angel Investors
Can provide advice and highly skilled employees
If a firm decides to go the private path, then…
A private equity firm will purchase a significant chunk of shares and will oversee the acquisition process
What does an investment bank (aka underwriter) do?
Uses its experience, knowledge of market conditions, and relationships with wealthy clients to help the firm determine its value to the general public
Since the investment bank will typically guarantee the cient will get the money they need, how do they deal with the risk?
The bank will syndicate with other banks to spread out the risk
Investment bank’s fee is…
Up to 7% of the floatation value