Near East quiz #1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Protoliterate Period
4200-3000 BC
Early Dynastic Period
2900-2334 BC

title, date, material, findspot
White Temple and Anu Ziggurat
c. 3300 BC, Protoliterate Period (4200-3000 BC)
Mudbrick
Uruk, Iraq

title, date, material, findspot
Uruk Vase
c. 3300 BC, Protoliterate Period (4200-3000 BC)
Carved alabaster
Eanna Precinct, Uruk, Iraq

title, date, material, findspot
Head of a Woman — Goddess Inanna?
3300 BC, Protoliterate Period (4200-3000 BC)
Marble
Eanna Precinct, Uruk, Iraq

title, date, material, findspot
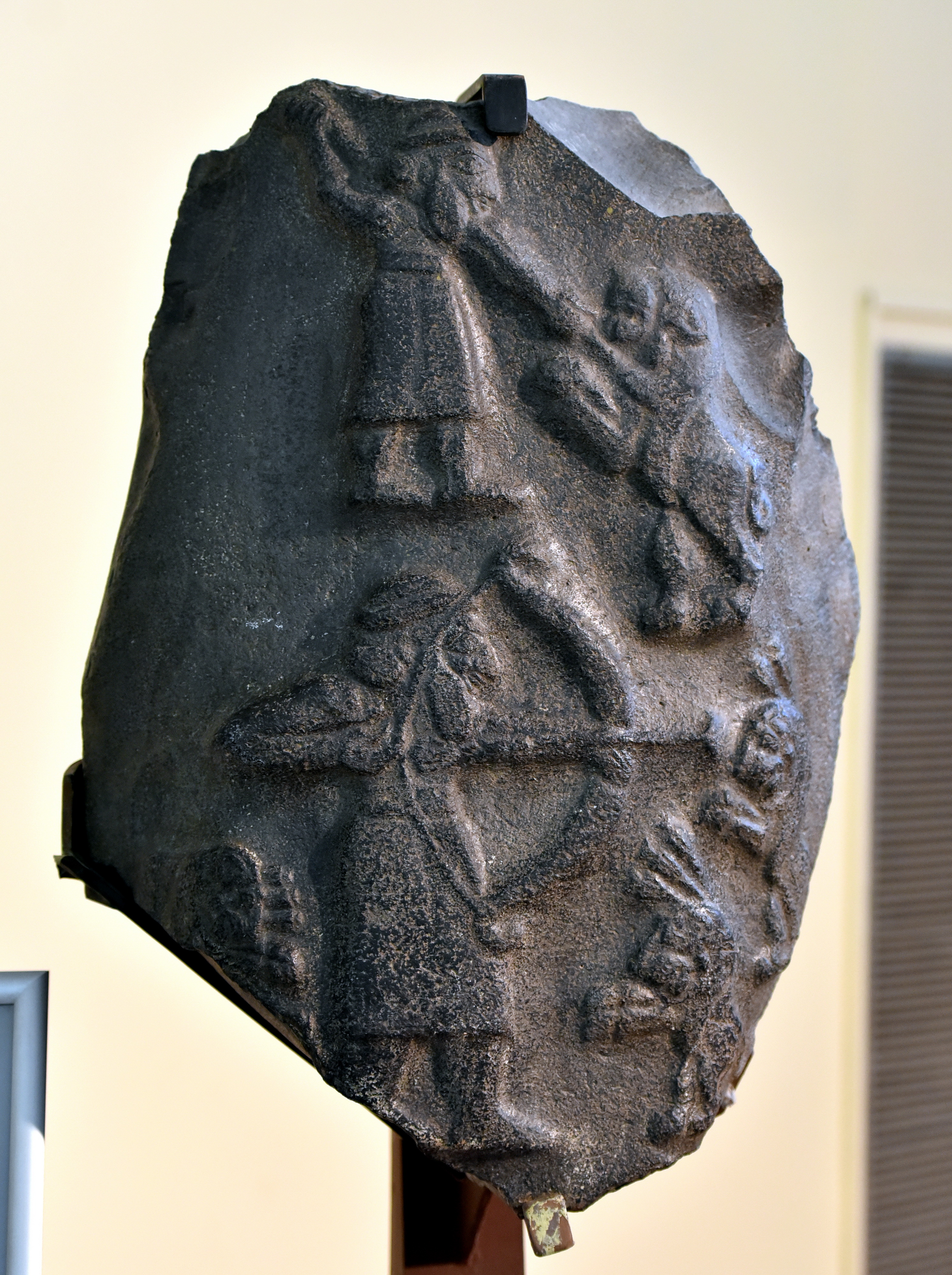
Lion Hunt Stele
c. 3300 BC, Protoliterate Period (4200-3000 BC)
Basalt
Eanna sanctuary, Uruk, Iraq

title, date, material, findspot
Cylinder Seal
3500-3100 BC, Protoliterate Period (4200-3000 BC)
Green Jasper
Provenance unknown
acquired by Louvre in 1877

title, date, material, findspot
Administrative Text
c. 3400 BC, Protoliterate Period (4200-3000 BC)
Baked clay with early cuneiform writing
Uruk, level IV, Iraq

title, date, material, findspot
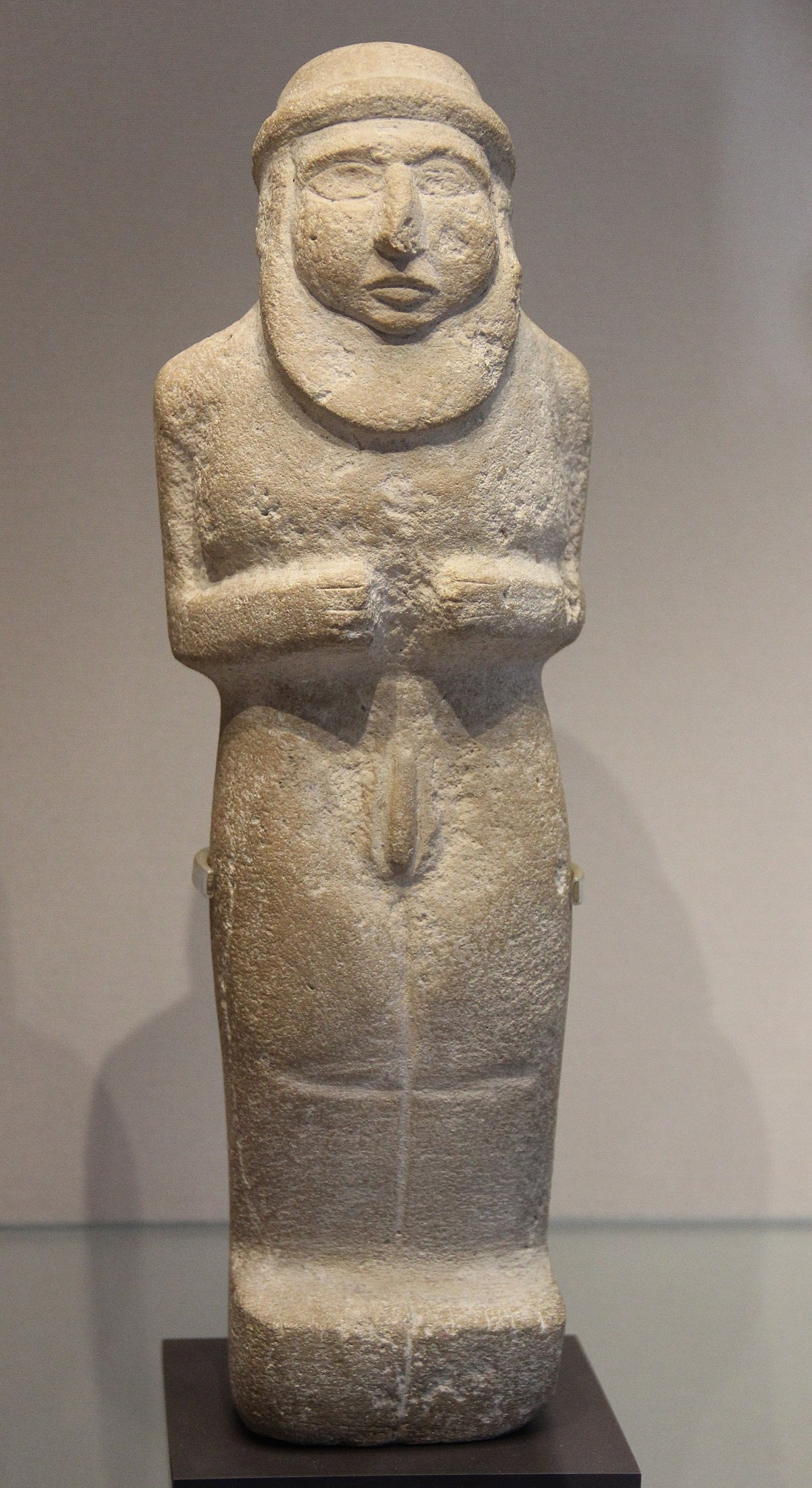
Priest King Statues
c. 3300 BC, Protoliterate Period (4200-3000 BC)
Limestone
Provenance unknown, probably from Uruk

title, date, material, findspot
Vase of Entemena
Early Dynastic Period, 3000-2300 BC
Silver of a copper foot
Telloh (Lagash)

title, date, material, findspot
Group of Statuettes
Early Dynastic Period, 3000-2300 BC
Stone, shell, lapis, lazuli
Tell Asmar

title, date, material, findspot
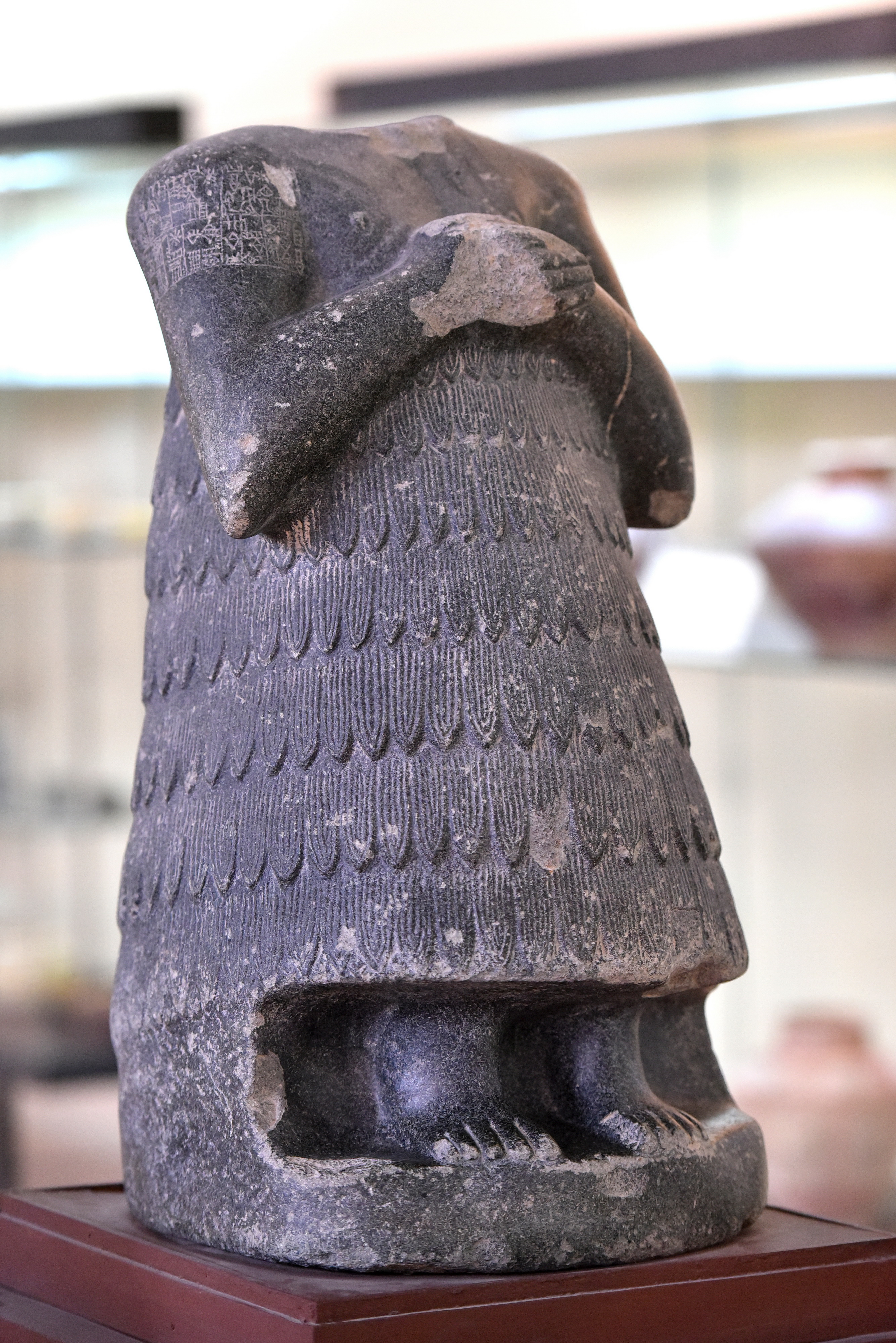
Entemena of Lagash
c. 2400 BC, Early Dynastic Period 2900-2334 BC
Black Diorite
Ur (approx. 3 feet tall)

title, date, material, findspot
Dudu the Scribe
2500-2450 BC, Early Dynastic Period 2900-2334 BC
Basalt
Girsu, Iraq (17.5 inches tall)
title, date, material, findspot
Ibgal of Inanna built by Urnanshe
c. 2450 BC, Early Dynastic Period 2900-2334 BC
Mudbrick and stone
Lagash

title, date, material, findspot
Anzu Relief
Early Dynastic Period, 3000-2300 BC
Copper on wooden core
Al ‘Ubaid

title, date, material, findspot
Stele of Urnanshe
Early Dynastic Period, 3000-2300 BC
Limestone
Telloh

title, date, material, findspot
Jewellery Of Queen Puabi
Early Dynastic Period, 2550-2400 BC
Gold, lapis lazuli, carnelian
Ur

title, date, material, findspot
Helmet of Meskalamdug
Early Dynastic Period, 2550-2400 BC
Gold
Ur

title, date, material, findspot
Dagger and sheath of Meskalamdug
Early Dynastic Period, 2550-2400 BC
Gold with lapis lazuli handle
Ur

title, date, material, findspot
Offering Stand
Early Dynastic Period, 2500 BC
Wood, silver, shell, red limestone, lapis lazuli, gold-foil
Ur

title, date, material, findspot
Harp from Ur
Early Dynastic Period, 2550-2400 BC
gold, silver, lapis lazuli, bitumen, wood
Ur

title, date, material, findspot
Royal “Standard” from Ur
Early Dynastic Period, 2550-2400 BC
Lapis Lazuli, red limestone
Ur

title, date, material, findspot
Stele of Eannatum
Early Dynastic Period, 2450 BC
Limestone
Girsu, Iraq

title, date, material, findspot
Cylinder Seal of Queen Puabi
Early Dynastic Period, 2600 BC
Lapis lazuli
Ur
White Temple and Anu Ziggurat
Over 5,300 years old
Very old monument
Service of religion
Ziggurat → built entirely from mudbrick
Religious building → Temple
Anu (made for)
Ziggurat → to be high
Man made, mudbrick mound that is meant as a platform to build a temple on top of it
Mound between heaven and earth
Standard form:
Made of mudbrick (most available)
Corners of a Ziggurat → always oriented to the four most cardinal points
Trying to look like mountain sides
Sides of Ziggurat:
Recesses and buttresses → slant inward when go up
Shrines or temples on top of them
Temples on top:
The White Temple → famous temple
Generally rectangular in shape
Temples made of mudbrick
White painted plaster (outside)
Recessed and buttressed walls in the temple
Bent axis approach
Uruk Vase
3 ft vase
Found with another pair
Pairs of similarly shaped vases are shown in other pieces of art
Records the most famous religious festival in the Sumerian (found in temple)
Narrative going on
Fertility and control on nature
Sculptural style
New years festival
Based on agricultural cycles
Dedicated to two gods: the Great Mother and Tamus
Vase read from bottom to the top
Three areas/registers that are decorated
Lower Register:
Rippled water
Plants
Alternating grains and date palms
Animals with the water as well
Middle Register:
Great Mother and Tamus have been remarried and unified
Series of naked men carrying baskets of fruits
Spouted vessels
Top Register:
Baskets filled high with food
Female → perhaps goddess Inanna – next to gate posts
Gate posts → in a pair, Gate Posts of Inanna
Iconography: any feature of costume, posture, gesture, and attributes
Female: heavy thick robe, has one arm fully covered/other arm is bare, thumb almost in mouth (gesture of prayer)
Gate posts on the left
Baskets with fruit
Animals
Two statues standing on top of ram
Double line = possibly two rams
Vase is on the vase (behind the rams)
Pairing fertility
Registers get widder and widder when you get to the top of the vase
Shows progression
Directions change in each register
Moving in opposite directions
Feels like a procession
Hieratic scale!!!
Hierarchy = larger thing is more important/powerful
Figures are bulky/stocky
Eyes are shown frontal (not a profile eye)
Striding (balance, no one is falling over)
Many depictions of animals and plants
Even animals are bulky
Head of a Woman — Goddess Inanna?
Thought to depict a female/goddess
Early example of art made by humans to depict the invisible entity [god/goddess] (cult statue)
Naturalistic
Composite statue (made of many materials)
Eyes are in laid (either with shells or precious stones [lapis lazuli – comes from modern day Afghanistan])
Bitumen → black tar substance
Body may have been made out of wood? → no longer here
Probably dressed in clothing/linen
May of had some earrings
Waves of hair (depressions) → sheets of gold to make hair appear to have waves?
Lion Hunt Stele
Basalt is a dense, black, heavy, volcanic based stone
Hard to carve
Pretty durable
Depicts a hunter killing lions
Guy driving a spear into lions
Other dead lions with arrows in them
Hunter = preist king
Stele = slab of stone that is carved with either with inscription or with a visual scene
Has a function in some way
Stele function: used as grave markers, propaganda pieces, tell a story, record the names of kings (public), religious purposes
Boundary markers
Same guy shown twice
Guy is a priest king/ruler → “en”
Powerful person because he is a mighty hunter who is defeating these mighty beasts
Common theme of lions in Mesopotamian art
Links hunting and power
Priest king iconography in protoliterate style
Almost always have cap headdresses (rolled around the edges)
Hair is wrapped into a bun
Typically have a beard (false beards) → could be something that they added to their face
Naked torso
Skirts (belt or rolled up at waist)
Cylinder Seal
Glyptic art
Did have seals before cylinder seals
Seemed to occur → wanted to cover more surface
Validate documents
Writing in clay tablets
Every person has a tiny piece of stone that has some type of iconography (or writing) that is unique to them = their signature
Depict priest king in the center – feeding rams (flowers)
Rosettes of Inanna
Stone and ram is copper (cylinder)
Two gate posts (left side) and animal floating = cult statue → inside part of temple and dedicating two pairs of vases
Importance:
Cylinder seals show us trade patterns (by what stones were used/findspots)
Styles
Some seals have inscriptions of the owners
Often depict important mythological scenes, daily life scenes
Demise of a government and society (tracks downfall)
Even lower class people had and used cylinder seals
Cylinder seal in green jasper and modern clay impression
Administrative Text
seal on back side
cuneiform
oldest writing come from Uruk
Priest King Statue
rolled cap and beard
gesture of prayer and holding an offering between his hands
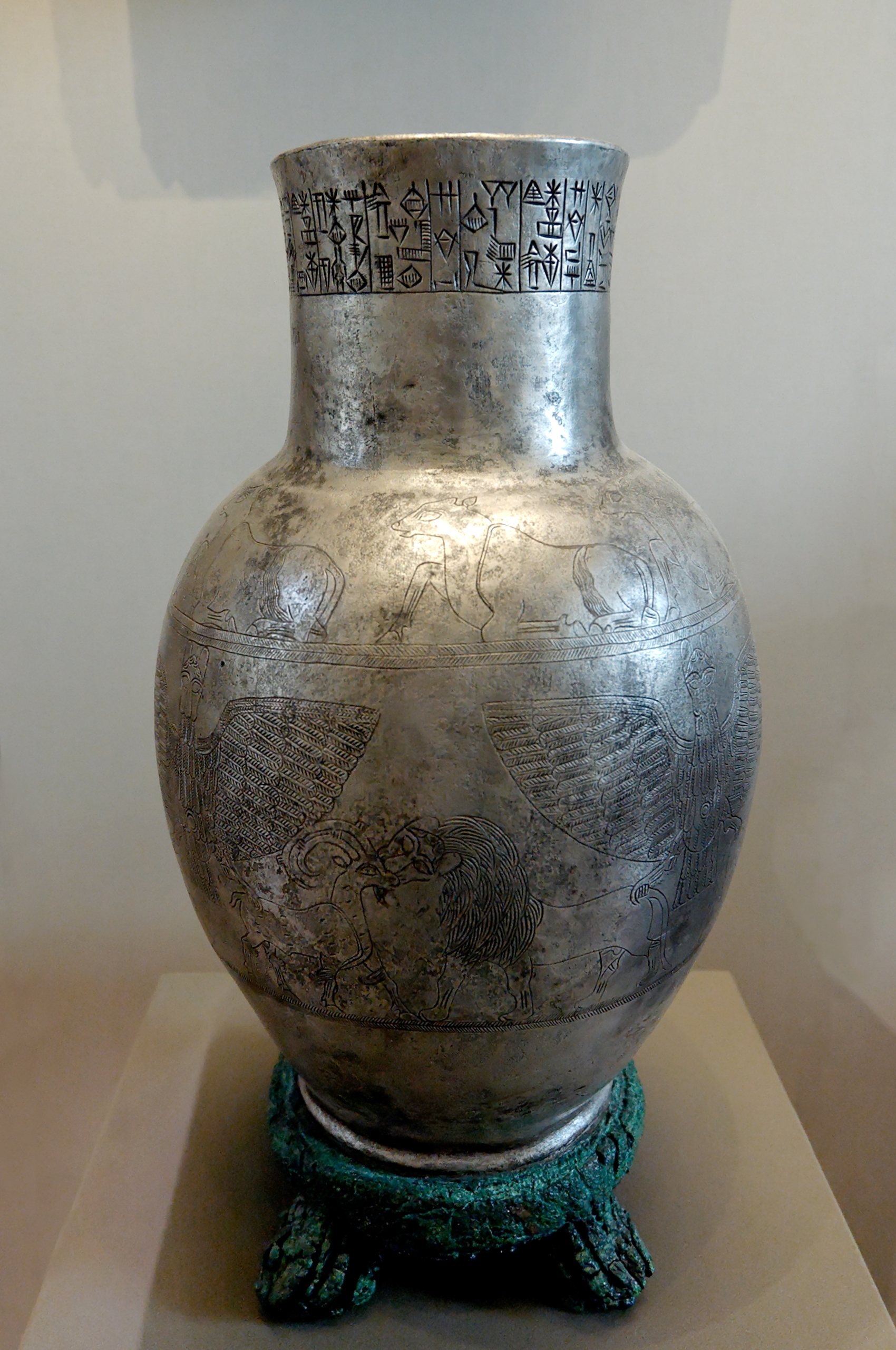
Vase of Entemena
Votive from early dynastic period
Votive offerings are the most common from the early dynastic period
Made of silver and has copper foot
Major part of relationships of humans and gods
do ut des → Latin for “I give so that you might give”
People gave gods votives (like statues, vases, textiles, animals, oils) expecting that the deities would give back to them
Found in a temple
Inscribed on top of the vessel
Material is interesting
Around 2500 BCE, metals like silver, copper, and gold became the rage → see an increase in votives made from these materials
Anzu (lion headed, eagle bodied) – earthly embodiment of Ningursi (god of Thunder)
God would have violent/war like characteristics
Two eagle legs out controlling rams (grabbing their backs)
“Domesticating animals”
Band of animals → animals look a little chunky (little bit of proto-literature style)
Name of ruler who is the dedication of this vase
What he is the ruler of and the connection to the deity
God also is connected to him because he is using the offerings
Group of Statuettes
Embodies the biggest change of votives during this period
Votives are no longer animals/vases → now are humans worshiping their deities
Found underneath the temples (buried)
Representing the worshippers
Posture is religious
Arms are bent (some holding cups) → gestures of prayer/offering
Early Dynastic: large eyes (usually inlaid with shells/lapis lazuli), geometric and abstracted, hands come together, gestures are similar, men have stylized beards/hair, looking up/not looking ahead, very broad shoulder/skinny waists, unrealistic shows of muscles, flounced skirts
Two figures that are different:
These two figures are different → size and dress
Fancy stuff on their bases
Abu (man’s base) → god of vegetation
Represent Abu, representation does not seem to be finished
Eagle in the center, two animals lying on either side with vegetation growing out of their backs
Woman had a figure standing next to her
Guy looks like a priest king → rolled skirt, hair and beard are longer, eyes are bigger
Woman has clothing that shows a shoulder, but covers her other shoulder
Entemena of Lagash
Priest King
Importance:
Subject – depicts ruler of Lagash (Entemena)
Earliest depictions of a Mesopotamian ruler
Material – diorite (black diorite), imported (used a lot in royal structures)
Inscription on the shoulder (early example of words/image working together)
Gods favor his rule
Building temples
Gives a name
Set up by ruler in temple in Ur, and it was a votive offering
Sumerian god of the sky
Same overarching cone shape, standard clasps hands in prayer, multi-layered flounced coat, broad shoulders
Dudu the Scribe
Votive statues also showed members of societies beyond rulers
Found in temple for the god of thunder
Not the ruler!!
Range of people
Ibgal of Inanna built by Urnanshe
Oval shaped temple
Oval temples → outer walls are oval shaped
Core central role that religion plays in
Cities usually have one god that protects each city
Functional, religion core of the city
The patron of the temple is important (as well as his grandson)
Built by Urnanshe, later got renovated by his grandson
Continuity of sacred space/conservation of sacred space
Anzu Relief
Found in a lot of debris
Decorative sculpture
Emblem → god of Thunder
Not sure where is would actually be placed, possibly on top of the door (lintel)
Complex sculptures
Style: playing with the plain of the relief → bodies (Anzu and innocent deer) are in relief
Heads are projecting out of the relief and become 3-dimensional
Anzu is so powerful that his head projects way above the rim of the relief
The antler spill over the frame
Lion headed eagle body → earthly representation of Ningursi
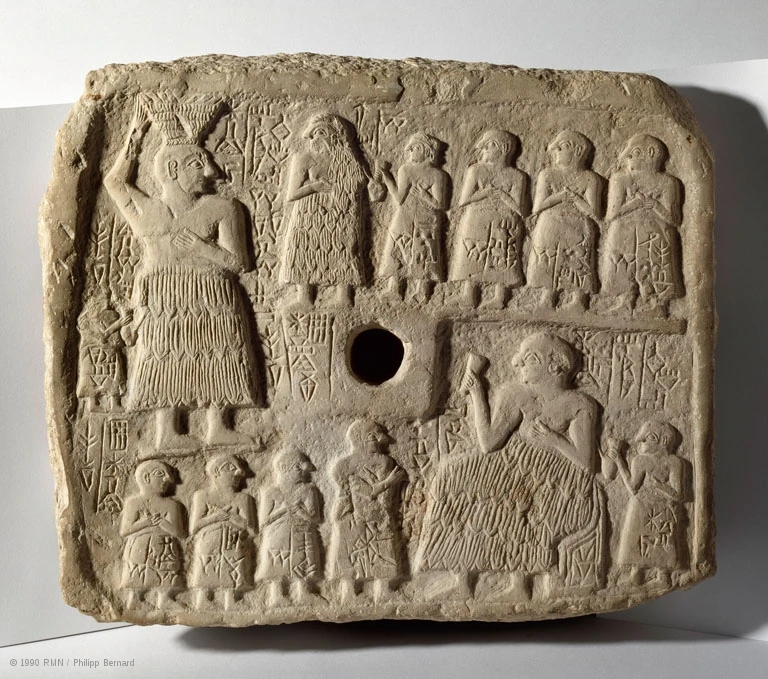
Stele of Urnanshe
More temple decoration
limestone plaque that was meant to decorate the wall of a temple
Wall in the middle → put giant nail in the middle to put in the wall
Beginning of a long tradition to decorate temple walls
Plaque shows ruler (biggest person [top left]) and is engaged in building a temple
Basket of mud on his head
Going to make the first mudbrick to build a temple that he is paying for
Approached by a line of family members (first figure may be daughter)
On the bottom, he is sitting down
He is celebrating and is holding a cup
Guy behind him is holding a drinking vessel → gives him more drink when he needs it
Approached by his son
Entire thing is covered in scriptures (to identify rulers and deities)
All done in standard Early Dynastic style
Profile bodies and frontly eyes
Hands are clasped (prayer position)
Flounced skirt
Broad shoulders
Mix of writing and art
Jewellery of Queen Puabi
Incredible headdress
Hold headdress
Rosettes of Eanna
Chest was covered with beads that draped down
On fingers = 10 gold rings
Lavish amount of jewellery = very wealthy
Jewellery is characterized by trades – trade network (lapis comes from Afghanistan)
Blue, red, and gold
Buried with 3 cylinder seals
Just under 5 feet tall, about 40 when she died
3 attendants in chamber with her
Massive amounts of funerary goods around her
Helmet of Meskalamdug
In adjacent tomb from the Jewellery
Tomb has lots of war gear
Material is interesting – gold and some gold and silver
Metalworking skills
Little lines of gold throughout the entire helmet
Repoussé – technique where you push designs in metalwork from the inside
Working from the inside of the helmet
Little balls of gold
Iconography: band that goes around the head (priest king), bun at the back of the head (priest king), headdresses that are depicted in stone reliefs and other statues
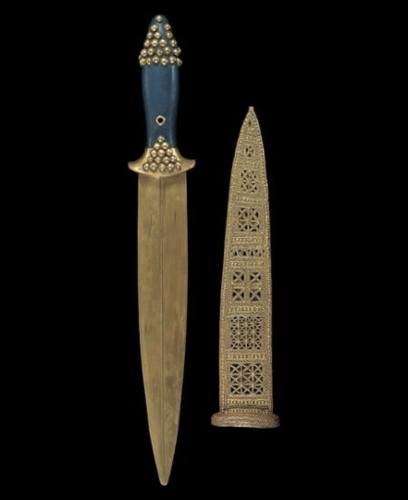
Dagger and sheath of Meskalamdug
Ceremonial weapon meant to be buried with king
Offering Stand
Would of had a table on its back
Offering stand
Other wooden objects that are covered in gold, lapis lazuli, etc
Offering for the dead
Two of these were found
One in UPenn and other at British Museum
Perched
Rosettes of Eanna
Posture in which goats could actually be in → seen in nature
Trying to eat the rosettes
Or could be a sexual stance
Fertility
Inlaid with use of bitumen and covered in precious stones
Harp from Ur
Harp found in tomb 1237 (reconstructed)
Development of critical technologies for excavation organic material
Woolley realized that they were coming across finds with organic material that disintegrated
Dirt would hold the organic material and the shape of the object
Wooden cords inlaid with gold, silver, and lapis lazuli
Woolley developed a technique of putting plaster into dirt and let it dry
Able to recover
Soundbox of harp
Harp comes from Queen Puabi’s tomb
Ancient instruments and cuneiform tablets that talks about music (what it was and what is sounded like)
Scales, tuning and playing instruments
Two basic parts to the instrument
Bull head and art scenes
Inlay (bitumen [tar like substance]) → lapis lazuli, gold, etc and stick it into the bitumen
Show wealth of royal family
Total of 11 string instruments were found at Ur
Harp on the harp
Animals are playing a harp
Object is being depicted on the object
Series of reliefs:
Donkey is playing harp
2nd: offering stand – food and bowl
Ritual scene
Preparing for a banquet or a ritual – see this on limestone plaques all the time
Animals are taking over human tasks
1st: middle → belt, but naked, and in combat scene
Flanked on both sides with mythological creatures
Early on protoliterate kings
Belt and beard make him some type of hero
4th: scorpion and human
Mythological
Drink behind him
Rattles in his hand – connects to Egypt
Bull:
Cast out of gold and bear is lapis lazuli
Bulls are associated with royal court
Royal “Standard” from Ur
Two sides
Don’t understand the function
Could be placed on top of a stick and be carried around
Not entirely sure how this was actually made
One side shows war
Other side is a banqueting scene showing victory and peace
War
Period of tension between various city-states
Read bottom to top
Bottom: chariots moving to the right
Trampling dead enemies
Horses are walking – knees start to get bent, start running, and then leaps
Get more vigorous
Middle: men walking
Top: in the middle there is the King himself
Leading men which marched up
King is larger than anyone else
Hieratic scale (taller than anyone else)
Celebration of Victory:
Bottom: animals and figures carrying
Lead by a guy in a pyrus gesture (?)
Middle: more figures being lead and walking to the celebration
Top: king is bigger
Music in celebration
There is a harp
Stele of Eannatum
“Stele of the Vultures”
Holding Anzu (Anzu clasp)
Recording of history
Victory of neighboring people
People of Uma destroyed a burial stone of Girsu and settled on the land that belonged to a city-state (Girsu)
Battle began
Result of battle
Sets this Stele up → “let’s look at what happened last time”
On the bottom, the King is holding a stake (charging at enemy), trying to get King of Uma
In top register, lots of men behind him → walking on top of dead people of Uma
Vultures carrying away heads of enemies
Plenty of writing included to spell out the victory
We know the king:
king/warrior iconography
helmet/hairstyle → hair in bun and a band circling around head
Cylinder Seal of Queen Puabi
Lapis lazuli
Worn on a necklace
Iconographic:
Bottom register – offering stand
Animal leg on the top
‘X’ in the middle
In profile, but eyes are frontal (Early Dynastic style)
Flounced skirts
Most have bare chests
Headdress on Queen Puabi
Shawl with one shoulder covered and another shoulder uncovered
Broad shoulders
Banqueting scene
People are in attendance for the Queen
Cuneiform writing (inscription to say whose seal it is) – signature
Seal states “Queen Puabi,” not queen of a husband or queen of a king
Banqueting scenes are not related to gender, but rather for royalty