BIOL 2460 CHAPTER 3
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
spontaneous generation
Hypothesis stating that life could arise from nonliving matter by Aristotle
Francesco Redi
This scientist disproved spontaneous generation by showing that maggots do not spontaneously arise from decaying meat.
John Needham
Heated broth in sealed flasks. When the broth became cloudy with microorganisms, he mistakenly concluded that they developed spontaneously from the broth. He did not boil the broth long enough and thus believed that life must originate from "life force".
Lazzaro Spallanzani
Replicated Needham's experiment correctly and showed that a sealed flask of meat broth sterilized by boiling failed to grow microbes
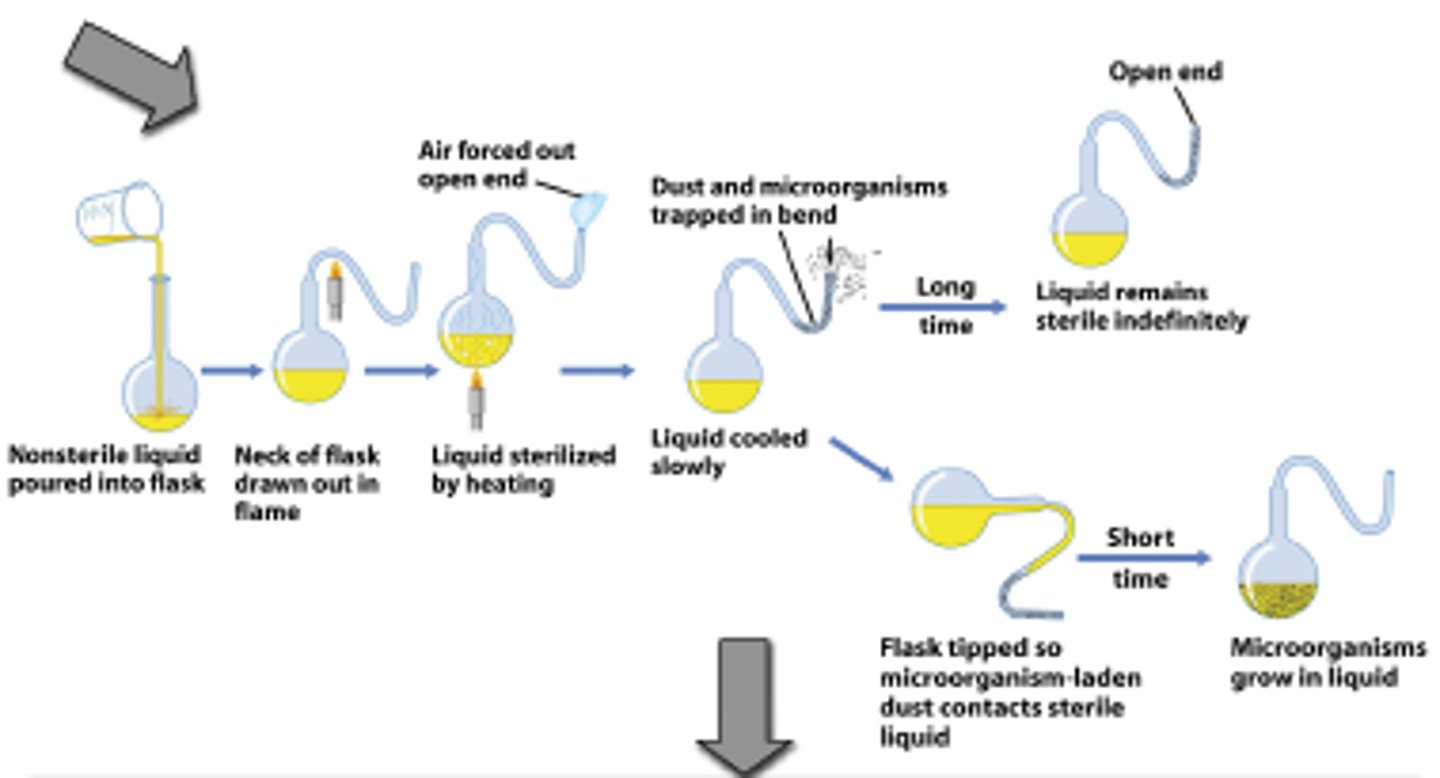
Louis Pasteur
-Disproved spontaneous generation with swan-neck flasks that blocked airborne microorganisms.
-Organisms could spoil food and, therefore, people.
Robert Hooke
First to observe "small chambers" in cork and call them cells.
Matthias Schleiden
All plants are made of cells
Theodor Schwann
all animals are made of cells
Robert Remak
All cells come from pre-existing cells (cell division). Originally came up with this idea, but later had it stolen by Virchow.
Rudolf Virchow
All cells come from other cells
endosymbiotic theory
mitochondria and chloroplasts arose as a result of prokaryotic cells establishing a symbiotic relationship within a eukaryotic host
Konstantin Mereschkowski
chloroplasts could reproduce independently and must have lived outside plant cell
Ivan Wallin
showed mitochondria outside of cell (but likely contamination)
Lynn Margulis
Developed the Endosymbiotic Theory. Mitochondria and chloroplasts of prokaryotic origin established a symbiotic relationship with a eukaryotic host.
Germ Theory of Disease
idea that infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms
Girolamo Fracastoro
"spores" can be transferred between individuals
Ignaz Semmelweis
advocated hand washing to prevent transmission of puerperal fever from one OB patient to another. Believed that contaminated physicians transferred causative agent to patients.
John Snow
Mapped the occurrence of cholera in London via water
Joseph Lister
Began using disinfectants and antiseptics during surgery. Handwashing + carbolic acid in surgery for
disinfection
Prokaryote
-unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus
-circular chromosome in nucleioid
-Domains: Bacteria, Archaea
Eukaryote
An organism whose cells contain a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane that contains several chromosomes.
-Domain: Eukarya
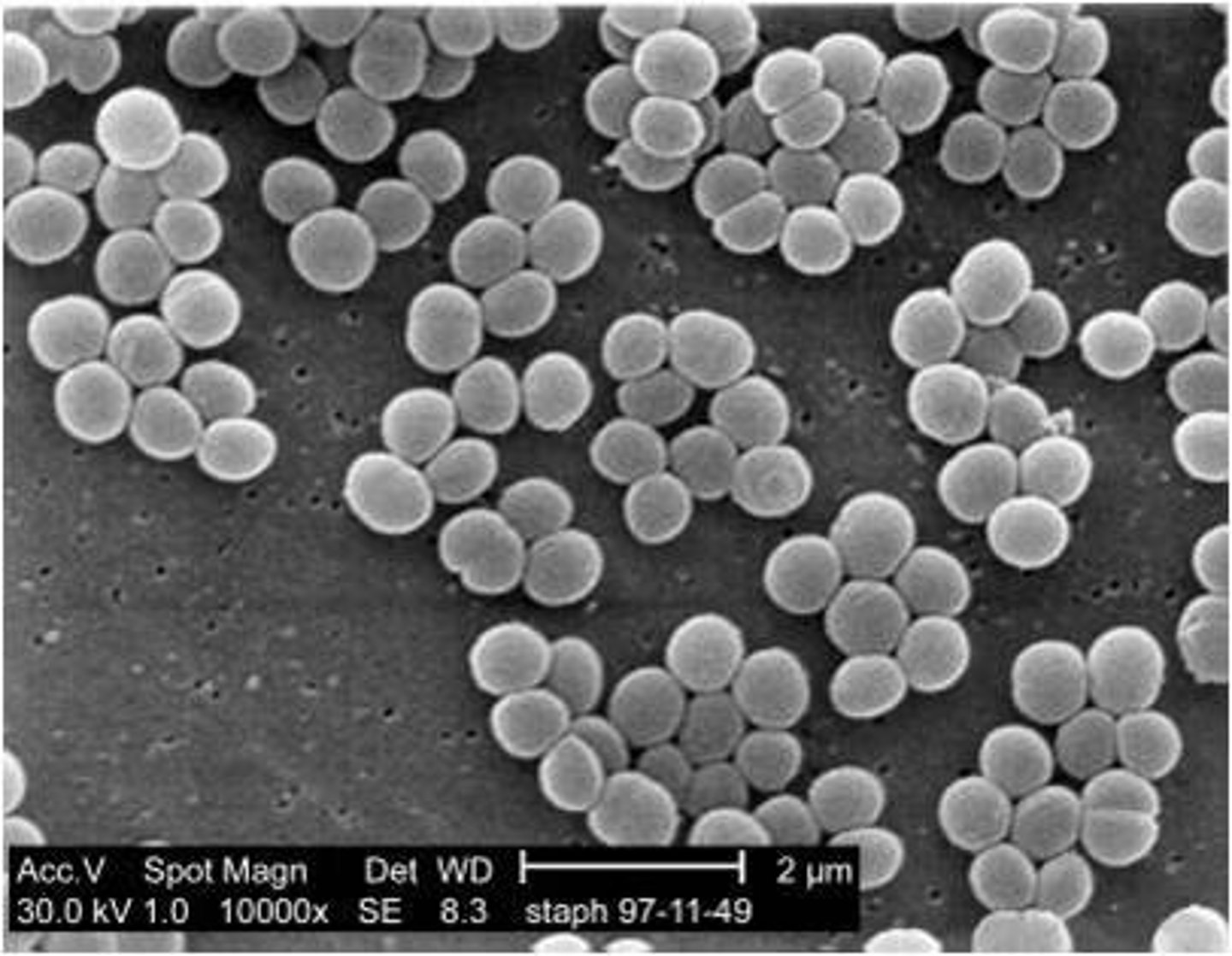
-coccus (pl. -cocci)
berry-shaped
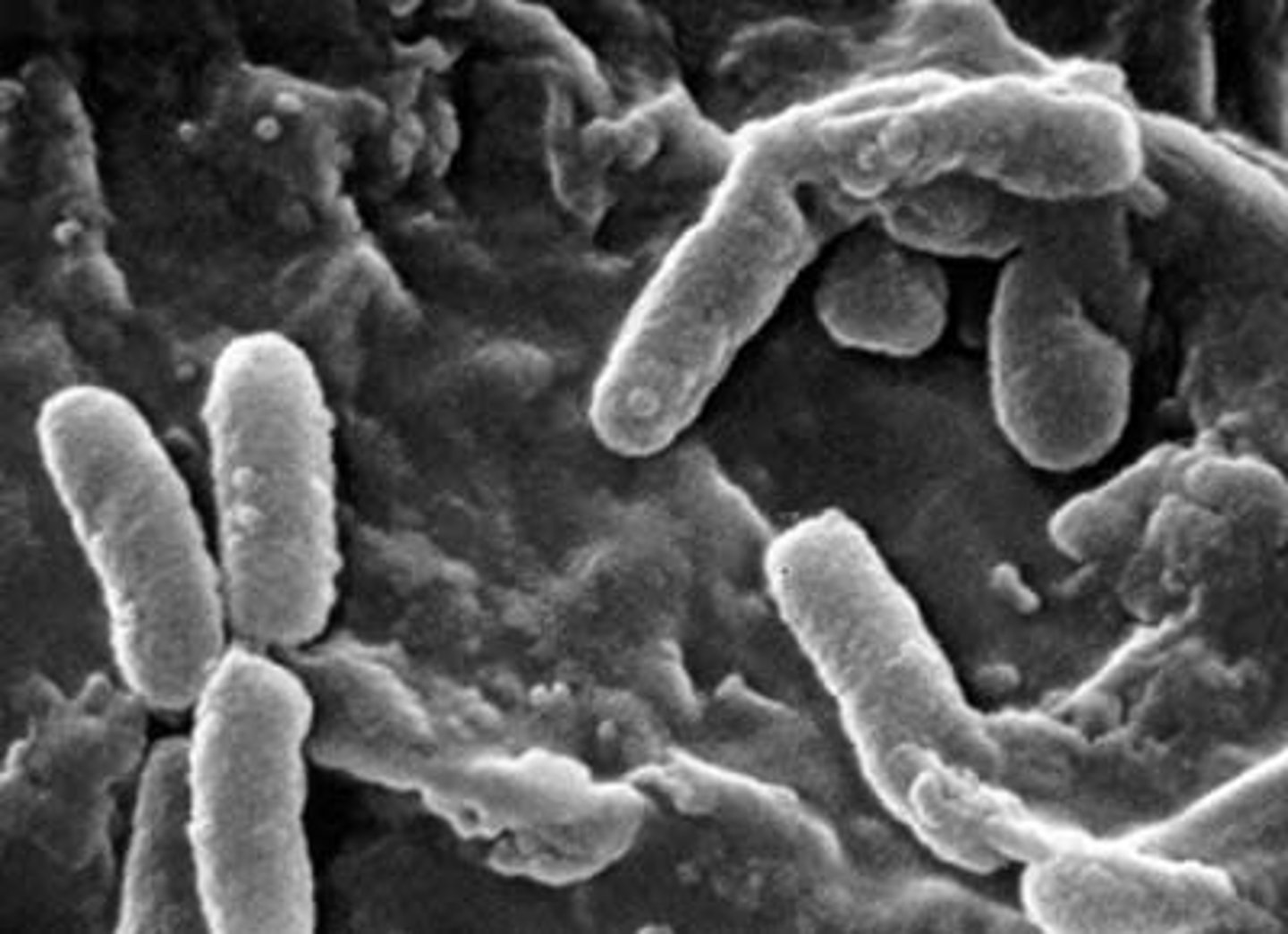
Bacillus
Rod shaped bacteria
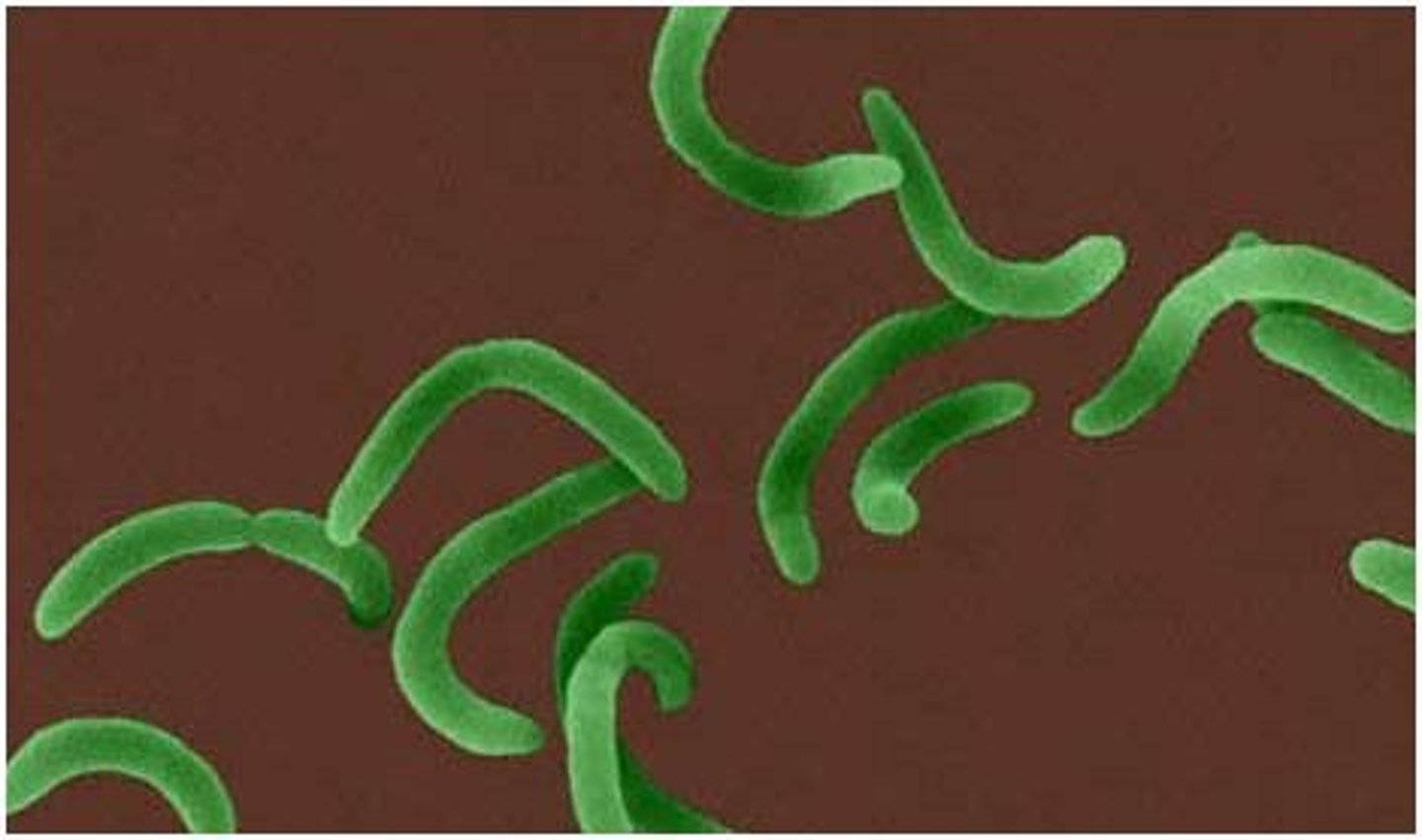
Vibrio
curved rod
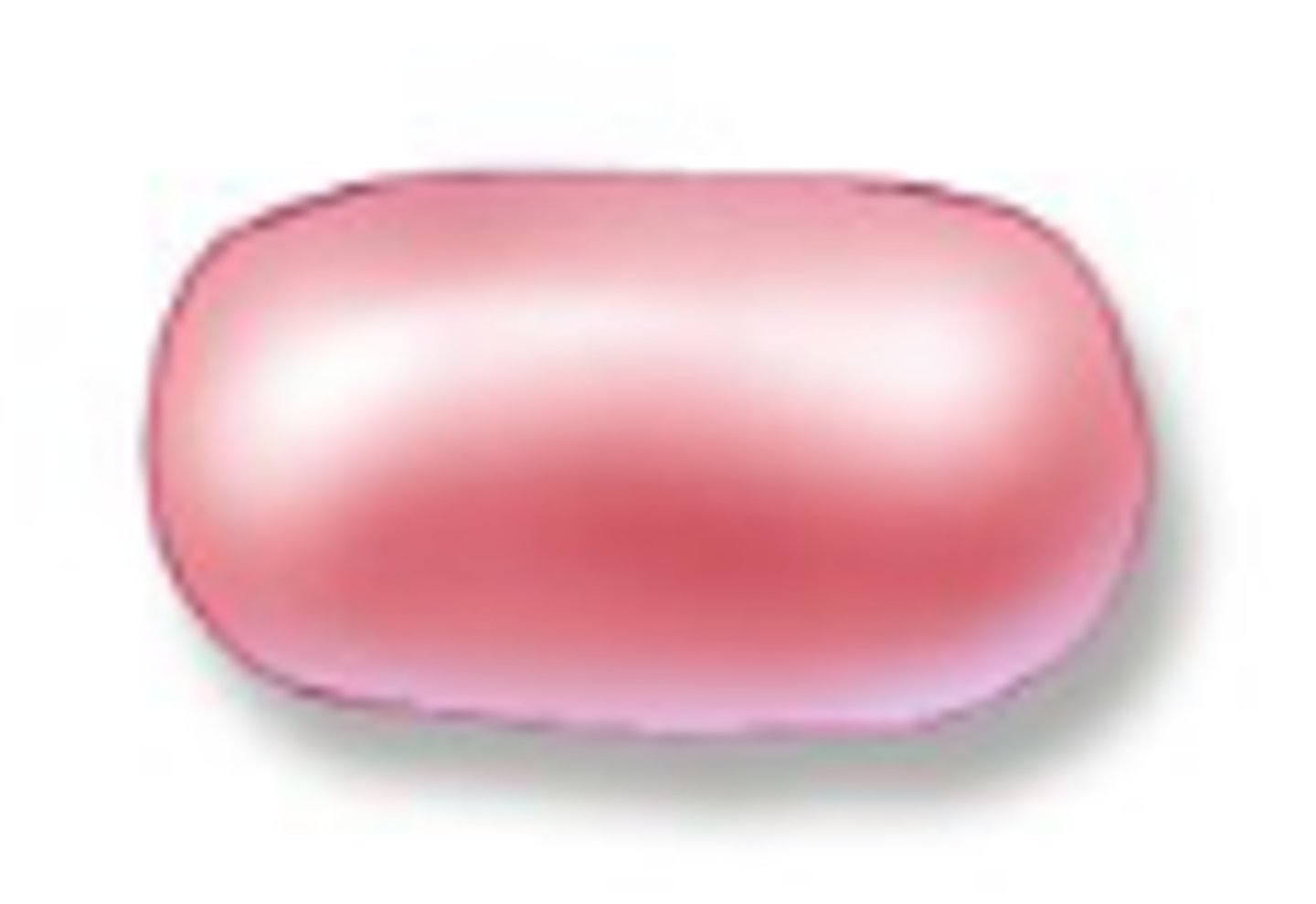
Coccobaccilus
short rod

Spirillum
spiral shaped bacteria
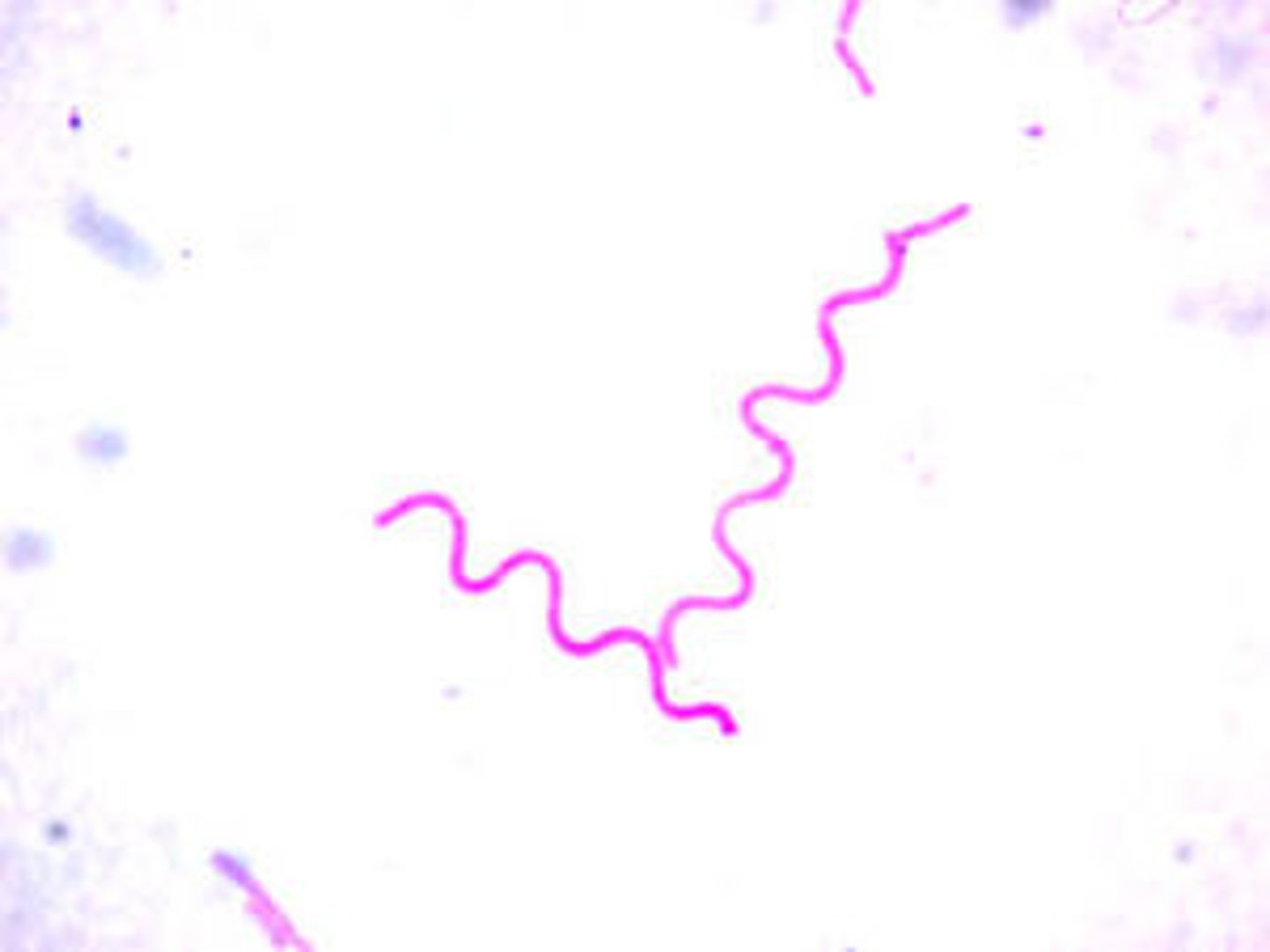
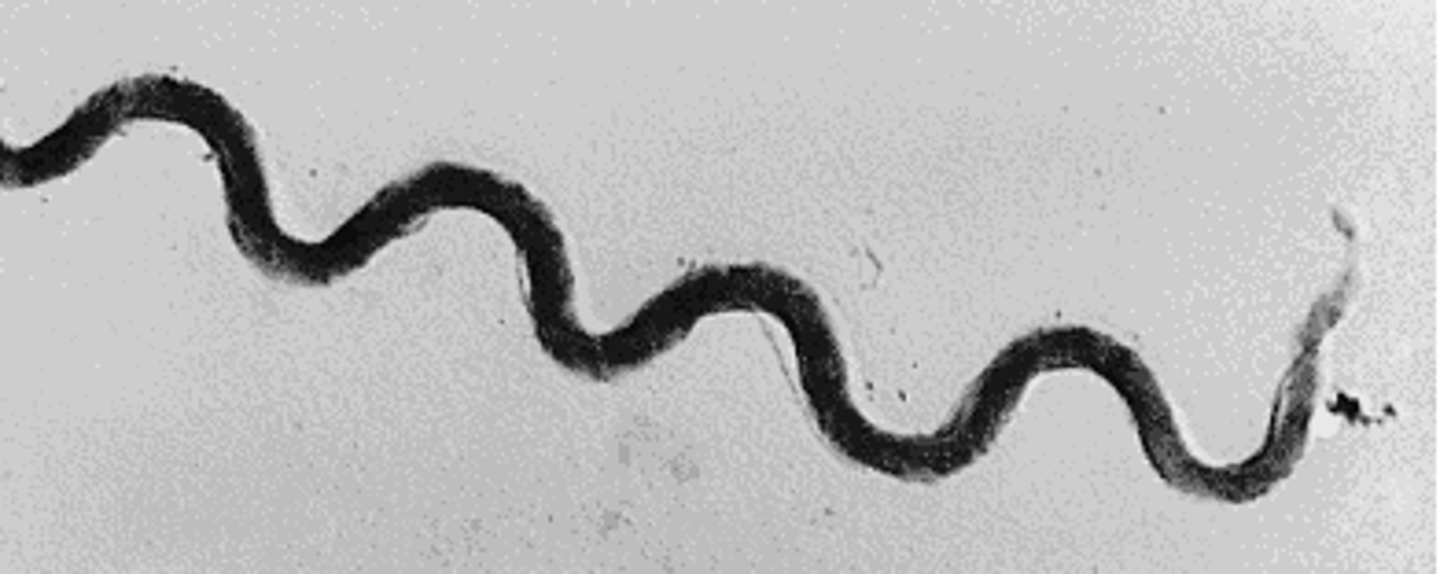
Spirochetes
long, loose, helical spiral
Crenation
shrinking of red blood cells. Occurs in a hypertonic solution of a cell without a cell wall
Plasmolysis
Happens in a hypertonic solution of a cell with a cell wall. Plasma membrane pulls away from cell wall, allowing cell to maintain some shape and integrity
Prokaryotic Chromosomes are
haploid
nucleoid-associated proteins (NAPs)
-a set of DNA-binding proteins found in bacteria that facilitate chromosome compaction and organization
-similar to histones
Plasmids
-Extrachromosomal ring of accessory DNA in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes.
-confer advantageous traits like antibiotic resistance
70s ribosomes
smaller ribosomes found in prokaryotes
50s and 30s
Inclusions
-stores excess nutrients
-reduce the buildup of osmotic pressure when gaining
Volutin (metachromatic granules)
inclusions that store polymerized inorganic phosphate that can be used in metabolism and assist in the formation of biofilms.
sulfur granules
Inclusion that stores elemental sulfur for metabolism in bacteria
Polyhydroxy butyrate (PHB)
Inclusion that is surrounded by a phospholipid monolayer embedded with protein
gas vacuoles (inclusions)
alters buoyancy so prokaryotic cells can adjust location in water column
Magnetosomes (Inclusion)
-inclusions of magnetic iron oxide or iron sulfide surrounded by a lipid layer
-allow cells to align along a magnetic field, aiding their movement
carboxysomes (inclusion)
-composed of outer shells of thousands of protein subunits
-RuBisCO and carbonic anhydrase for carbon
metabolism
Endospore
allow some bacterial cells to survive long periods without food or water and in extreme environments. Structure formed in a dormant state to protect the genome.
Sporylation
process of forming an endospore
-DNA replicates
-membrane forms around dna
-forespore forms more membranes
-protective cortex forms around spore
-protein coat forms around cortex
-spore is released
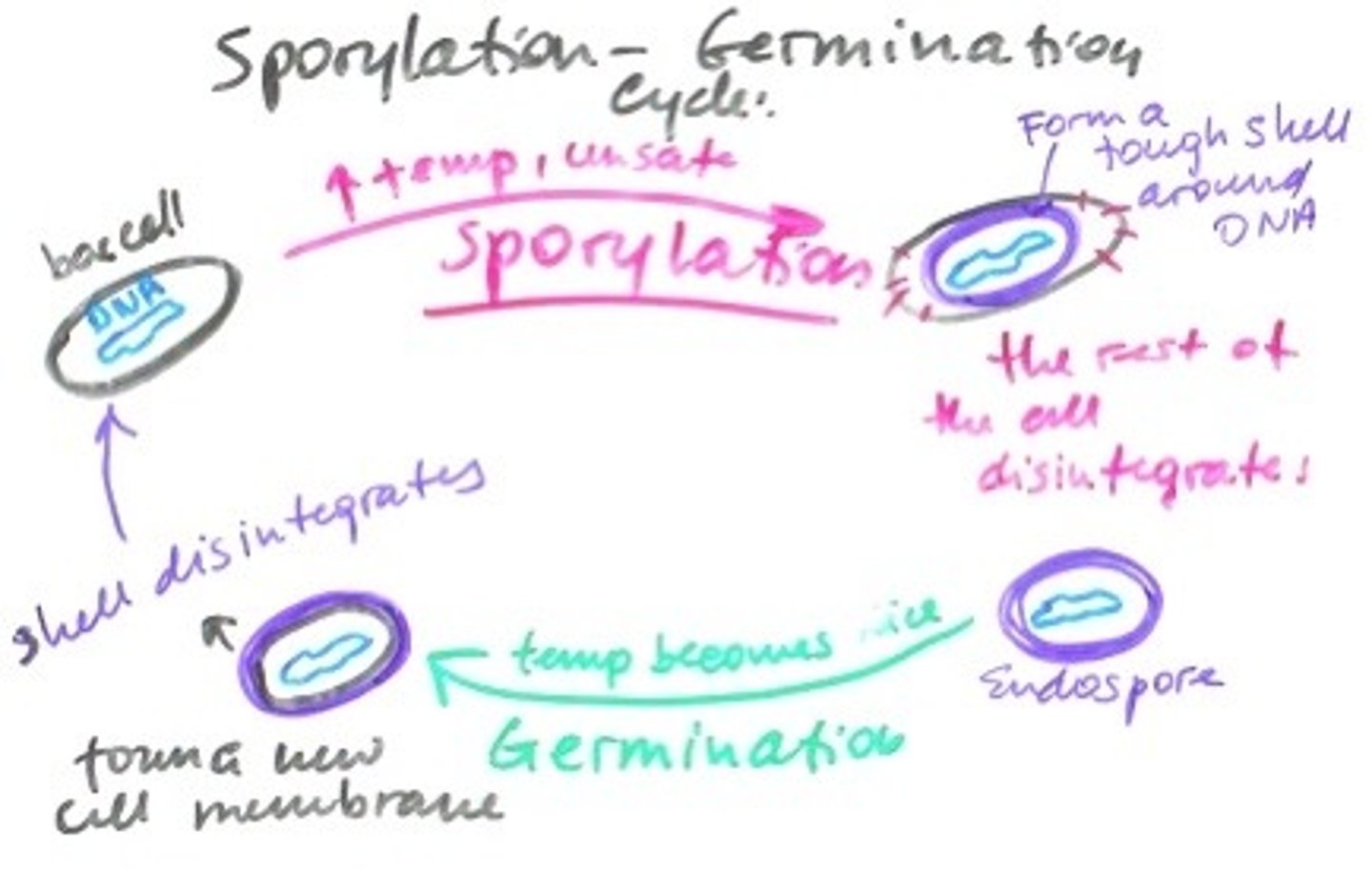
germination
endospore returns to vegetative state
Archael Membranes
-formed with ether linkages
-branched chains
-sometimes lipid monolayered
peptidoglycan
Cell wall of bacteria
Glycocalyx
A sugar coat that allows cells to adhere to surfaces, protects against desiccation, antibiotics, and or disinfectants
-capsules and slime layer
capsule
organized layer located outside of the cell wall and usually composed of polysaccharides or proteins
slime layer
-a less tightly organized layer that is only loosely attached to the cell wall and can be more easily washed off
-made of polysaccharides, glycoproteins or glycolipids
Glycocalyces
-Function in the formation of biofilms
-Adhere cells to one another and inanimate objects
Biofilm
A surface-coating colony of one or more species of prokaryotes that engage in metabolic cooperation.
S-layer
An outermost cell surface layer composed of protein or glycoprotein present on some Bacteria and Archaea. Thought to help with ridgetness and against osmotic pressure
Fimbriae
-short bristle-like proteins projecting from the cell surface by the hundreds
-enable a cell to attach to surfaces and to other cells
pilli
-less numerous protein appendages that aid in attachment to surfaces or transfer of DNA
F pilus (sex pilus)
important in the transfer of DNA between bacterial cells
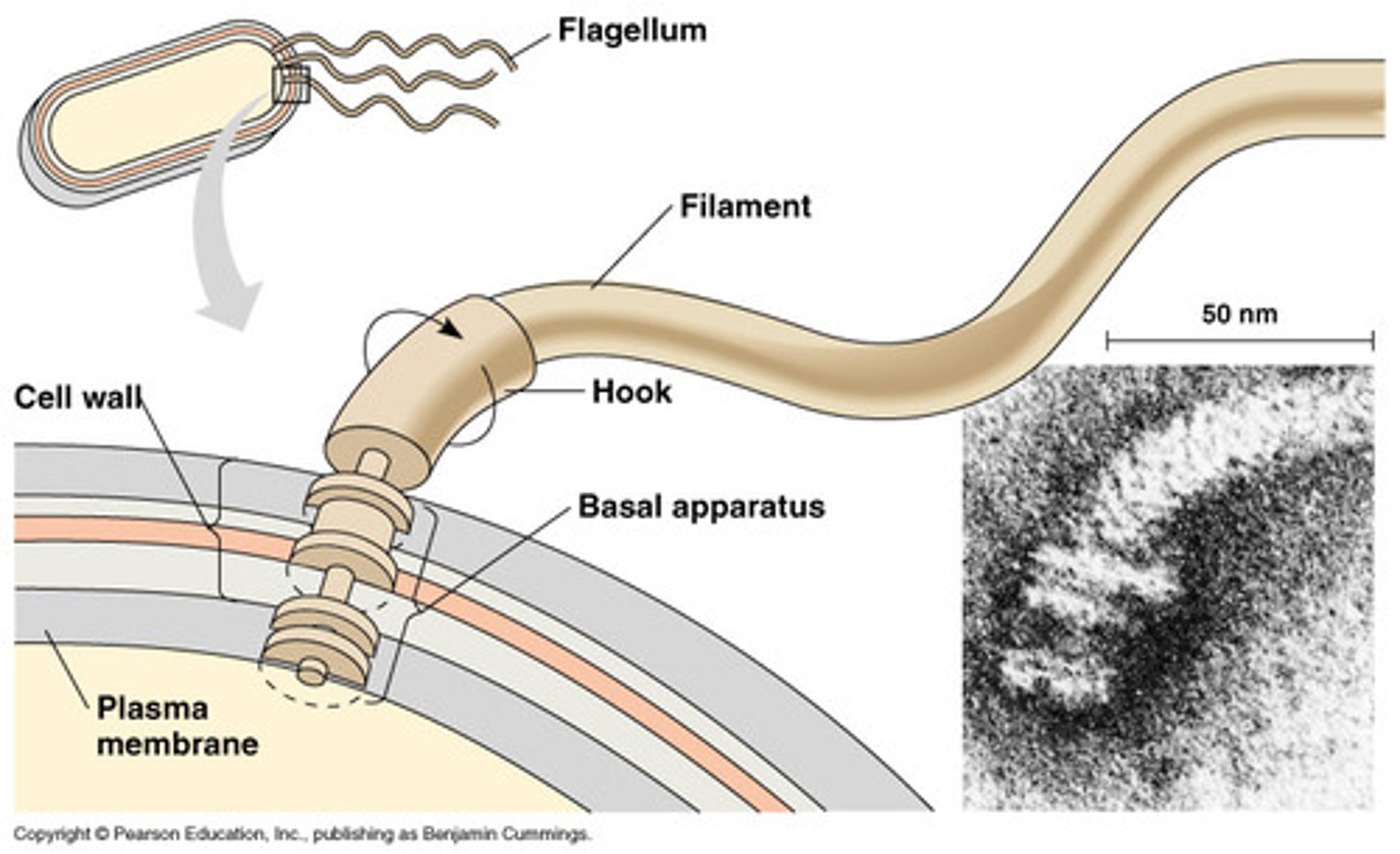
basal body
motor for the flagellum and is embedded in the plasma membrane
monotrichous flagella
one flagella
Amphitrichous
flagella at both poles of the cell
Lophotrichous
cluster of flagella at one or both ends
Peritrichous
flagella all over
tumbling
clockwise rotation of flagella to reorient cells
running
counter clowise rotation of flagella to move forward
coenocyte
cells who nuclei divide but whose cytoplasm does not.
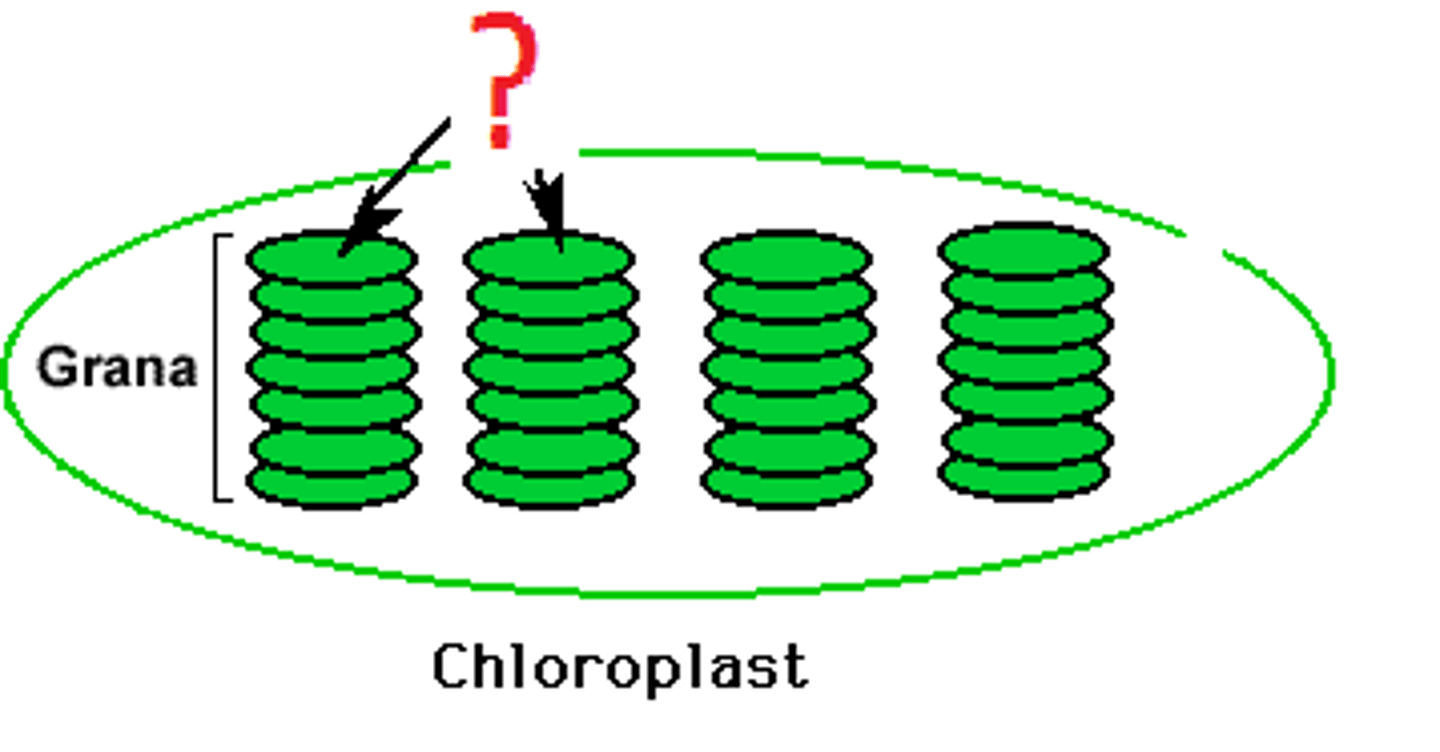
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
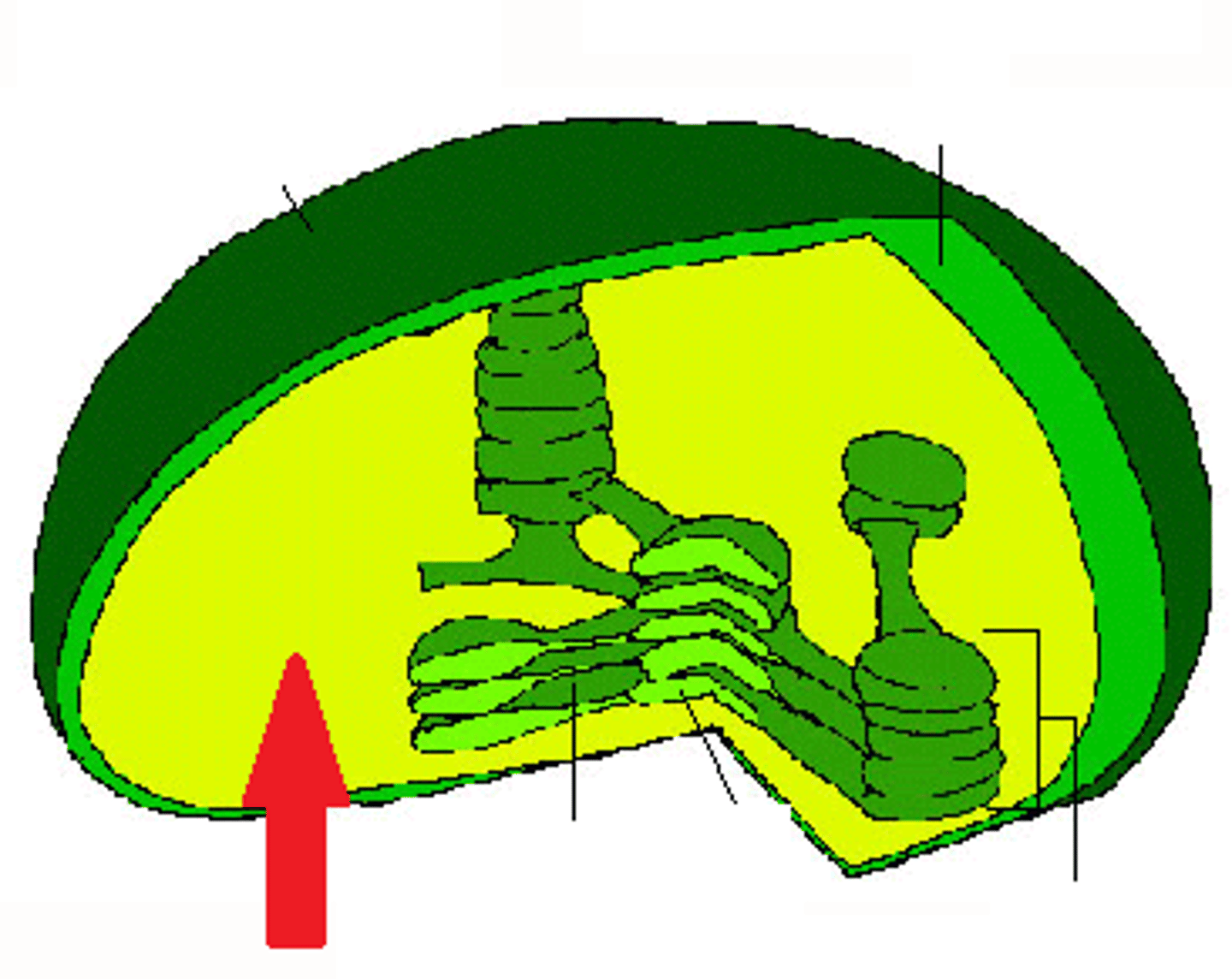
Thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
Plasma Membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Cell wall
strong, supporting layer around the cell membrane in some cells
osmosis
-gram positive = thicker cell wall
-Gram-negative = thinner cell wall
Passive transport
The movement of materials through a cell membrane without using energy
facilitated diffusion
Carrier proteins that ferry larger molecules across w/o ATP
Active Transport
membrane proteins that move molecules with ATP
group translocation
a special form of active transport that occurs exclusively in prokaryotes, the substance is chemically altered during transport across the membrane.
Cyanobacteria
Bacteria that can carry out photosynthesis with thyalcoids
Photosynthetic bacteria
chromatophores, lamellae, or chlorosomes
Ribosomes (in eukaryotes)
80S (40S small subunit + 60S large subunit) in chloroplast and mitochondria
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Makes and transports proteins (ribosomes)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
no ribosomes and synthesizes lipids, metabolizes carbs, and detoxifies compounds
Robert Koch
Koch's postulates - a specific microbe can cause a specific disease
Cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
-Archaea: Ether linkages
-Bacteria and Eukaryotes: Ester linkages
Gram negative
-Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) structure
-Contributes to fever, shock, &hemorrhaging
-E. coli O157:H7 strain has a different O-antigen (jack in the box)
Pseudopeptidoglycan
A component of (a few) archaea cell walls that is similar to peptidoglycan in morphology but contains different sugars
Basic flagella structures
basal body, hook, filament
Nucleus in eukaryotes
DNA material is surrounded by a membrane. Chromosomes are linear
Nucleolus
Dense region in the nucleus where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is synthesised
Golgi apparatus (eukaryotes)
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
-membranous disks(dictyosomes) stacked together
-Vesicles carry modified molecules to other parts of
the cell
Lysosomes
An organelle containing digestive enzymes. Breaks down food, damaged organelles, or cellular debris
Peroxisomes
Not part of the endomembrane system. Membrane-bound organelles that produce hydrogen peroxide. Contribute to lipid synthesis as well as the degradation of molecules.
Cytoskeleton in eukaryotes
Filaments inside the cell that provide structure and network for transport
-Microfilaments
-Intermediate filaments
-Microtubules
Microfilaments
intertwining actin fibers that have contraction-like movement
-Allows organisms such as amoebaslocomotion
Pseudopodia
temporary extensions ofmembrane that fill with microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
monomers that are thinner than microtubules but thicker than actin. Anchor nucleus and other organelles, and form
nuclear lamina
Microtubules
A hollow rod composed of tubulin proteins that moves vesicles around the cell, supports the cytoskeleton, functions in flagella & cilia, and cell division (centrosomes)
Mitochondria
sites for aerobic respiration, "power house" of the cell
Flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility. Made of microtubules in 9+2 fashion
Cilia
The hairlike projections on the outside of cells that move in a wavelike manner. Also, move particles away from the cell