Carbonyls 6B
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are Carbonyls
Molecules that contain the C=O
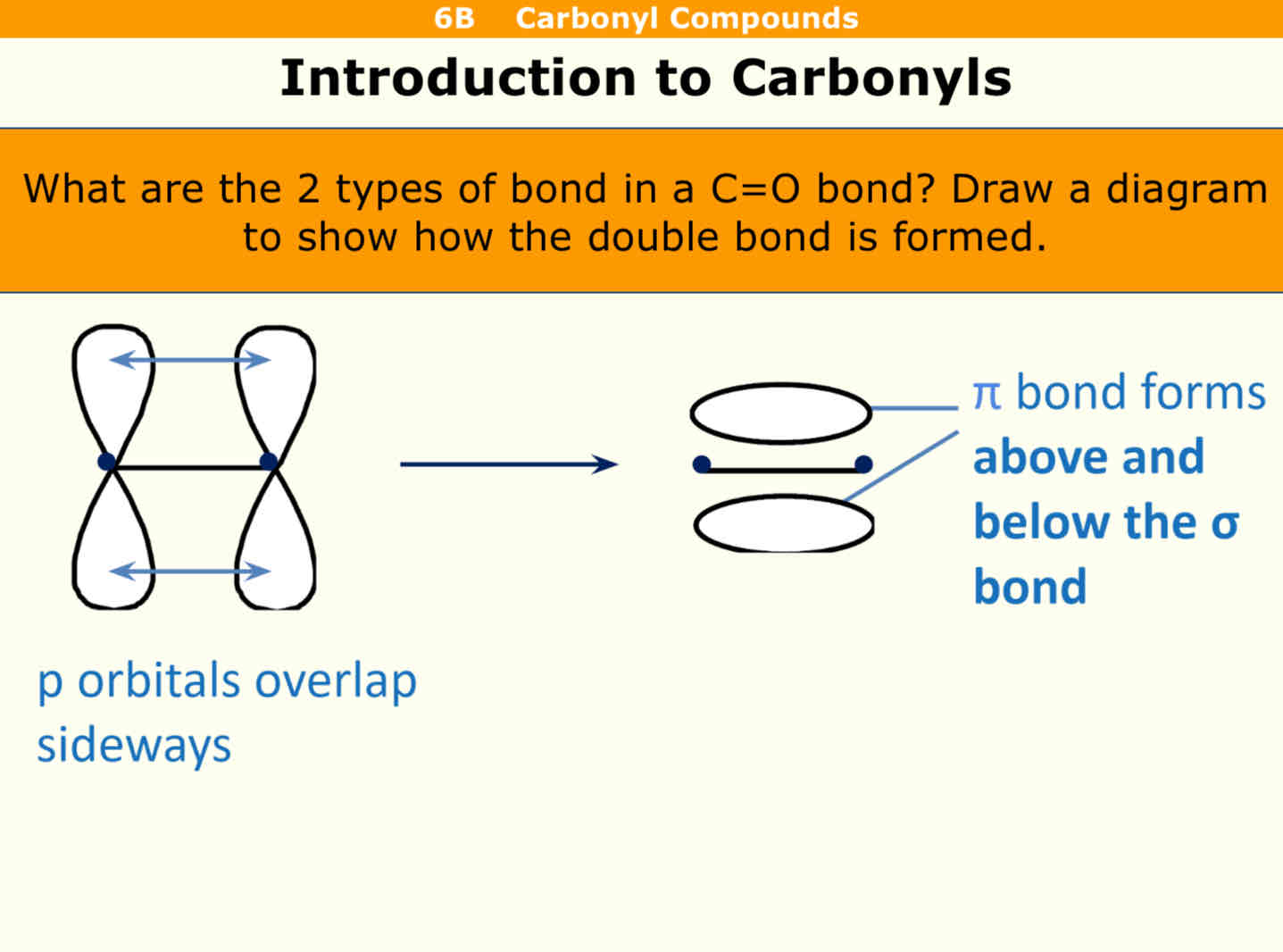
What are the two types of bond in a C=O
P orbitals overlap sideaways
Pi bonds form above and below the sigma bond
Bond angle and shape of carbonyls
120°
Trigonal planar
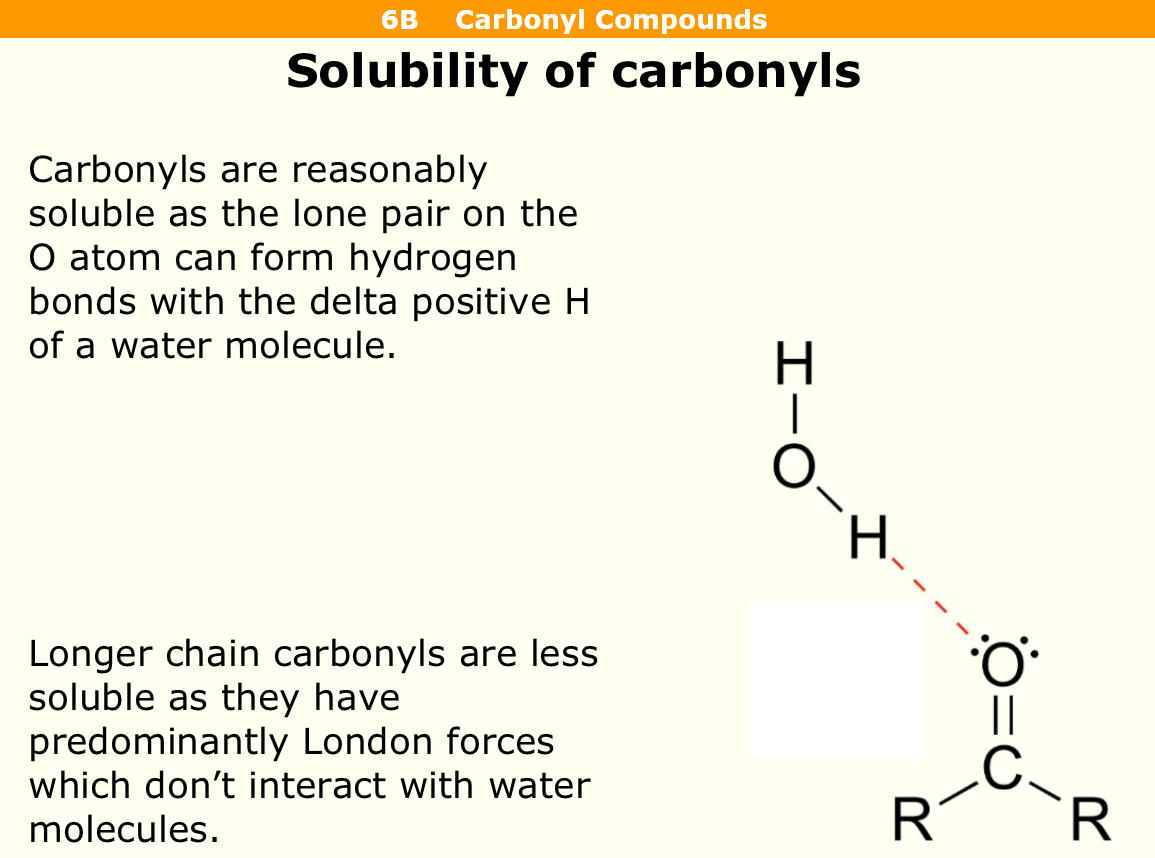
Are carbonyls soluble
They are reasonably soluble as there is a lone pair on oxygen atom that can form hydrogen bonds
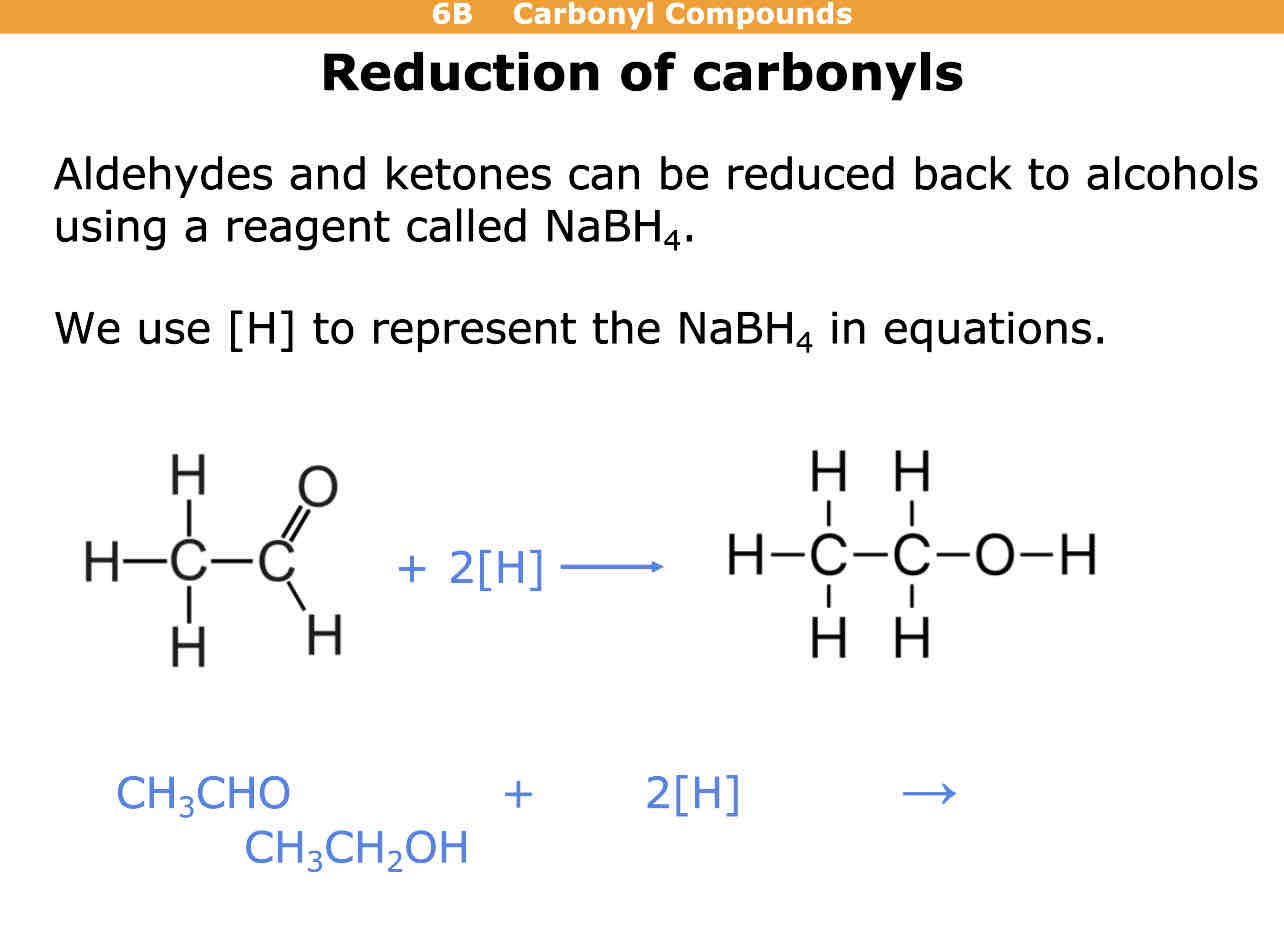
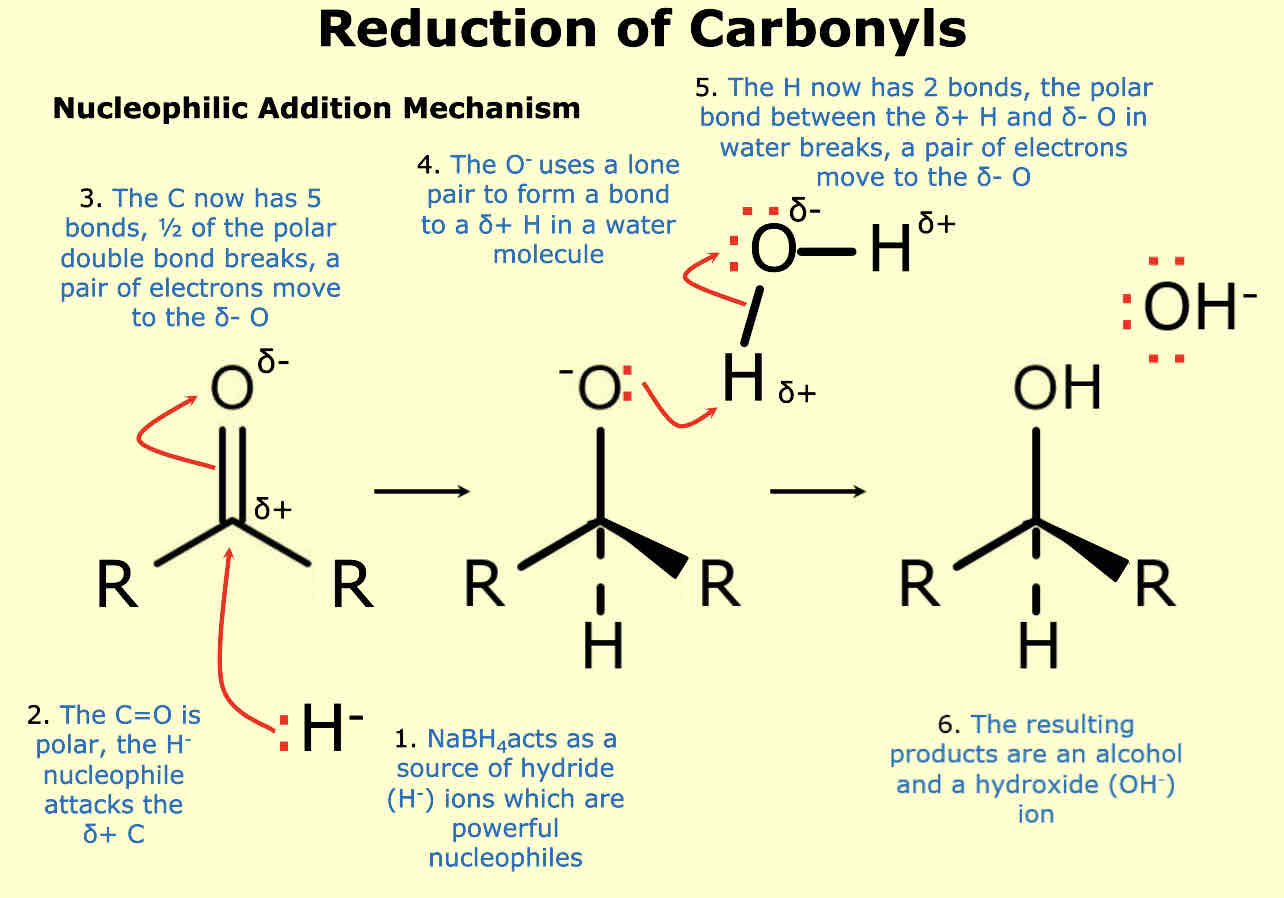
How are aldehydes and keystones reduced back into alcohols
Using NaBH4
Sodium tetrahydrioborate (III)
How is sodium borohydride represented in these reactions
[H]
Example of reduction of carbonyls
What is the mechanism for reduction of carbonyls
Nucleophillic addition
Two reagents used to test for carbonyls
what do both of them test for
2,4 DNPH (Brady’s reagent) and Tollens Reagent
Brady’s reagent is used to test for Aldehydes or Ketones
Tollens is used to identify an aldehyde
Positive and negative observation of Brady’s reagent
Positive = orange solution goes to orange precipitate
Negative = solution remains an orange solution
Reagent and conditions for Tollens reagent
Ammoniacal silver nitrate
Positive and negative test observation for Tollens reagent
Positive = silver mirror forms
Negative = no reaction/ solution remains colourless
What Type of reaction is Tollens
What type of reaction is Brady’s
Oxidation
Condensation (produces water)
How do you test for a carboxylic acid and what is positive result
How do you test for primary and secondary alcohols and what is positive result
How do you test for an alkene and what is positive result
How do you test for a phenol and what is the positive result
Sodium carbonate and effervescence
Acidified potassium dichromate and orange solution turns green
Add bromine water and it will decolourise it
Add bromine water and it forms a white precipitate
how to test for all alcohols
what is the observation
how to test for an acyl chloride and what is the observation
PCl5
misty fumes are observed
water
misty fumes are observed
3 ways to test an aldehyde
Acidified potassium dichromate, Tollens, Brady’s
How can else can you test for aldehydes and ketones
Fehlings solution
Warm with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution
What is the result for aldehyde and ketones for fehlings solution
What is the result for warm iodine and sodium hydroxide solution
Aldehyde =blue solution to red/orange ppt
Ketone = no change and stays blue
Aldehyde = no change
ketone = Yellow precipitate with antiseptic smell
what is the test for haloalkanes
test with silver nitrate
silver chloride = white
silver bromide = cream
silver iodide = yellow
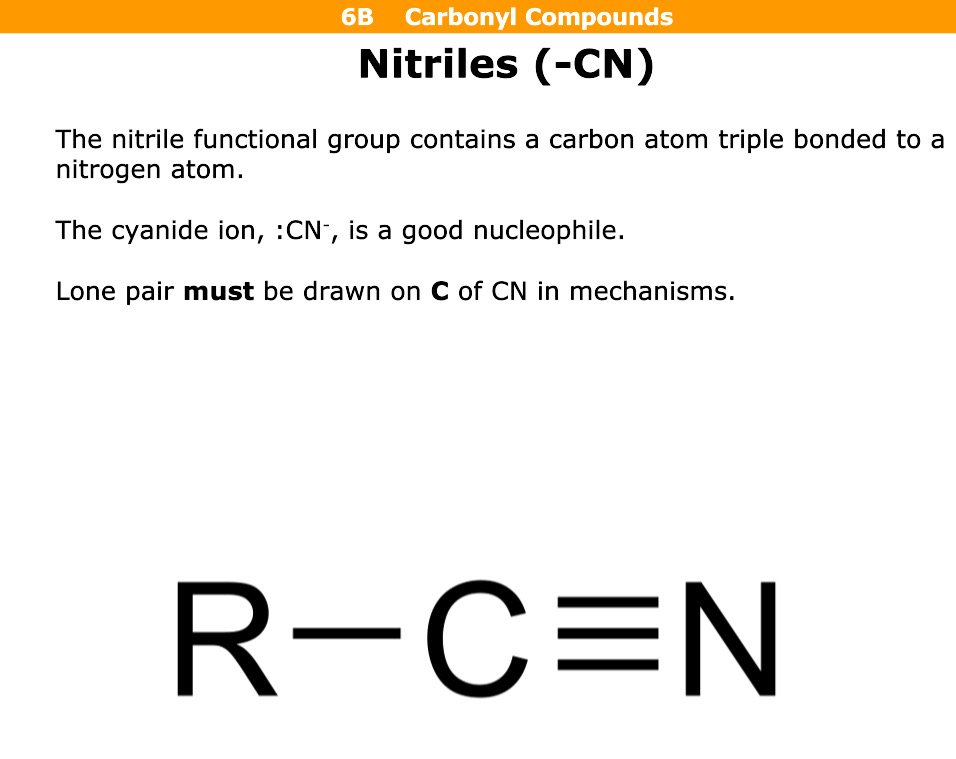
What are nitriles
Functional group with a carbon atom triple bonded to nitrogen atom
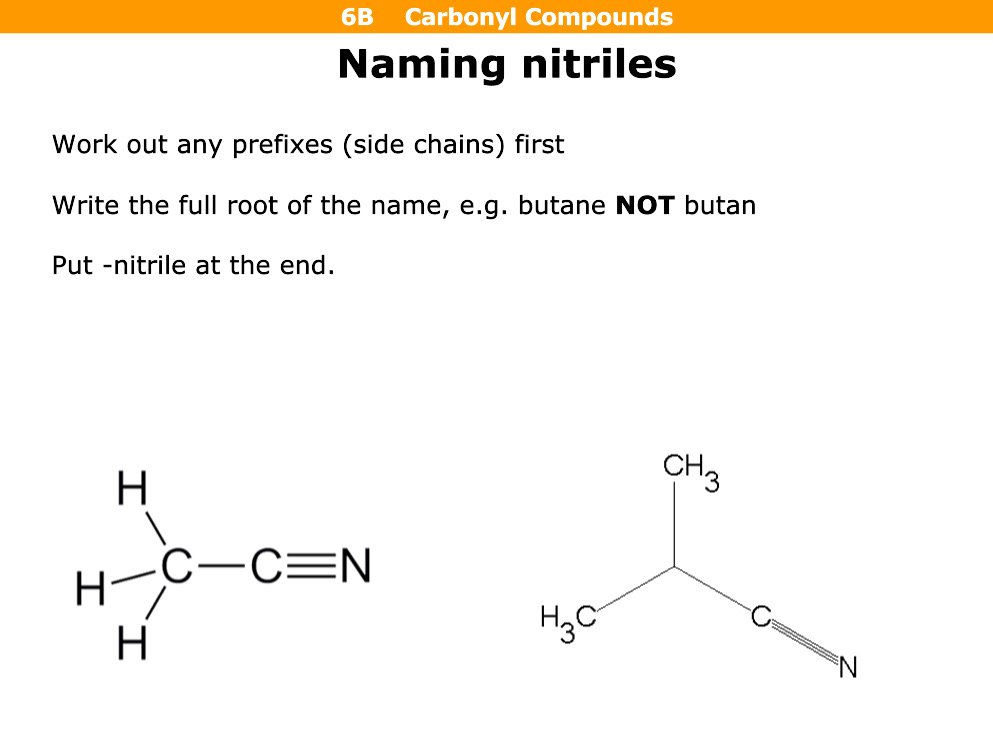
How do you name nitriles
Full name and nitrile eg: butanenitrile
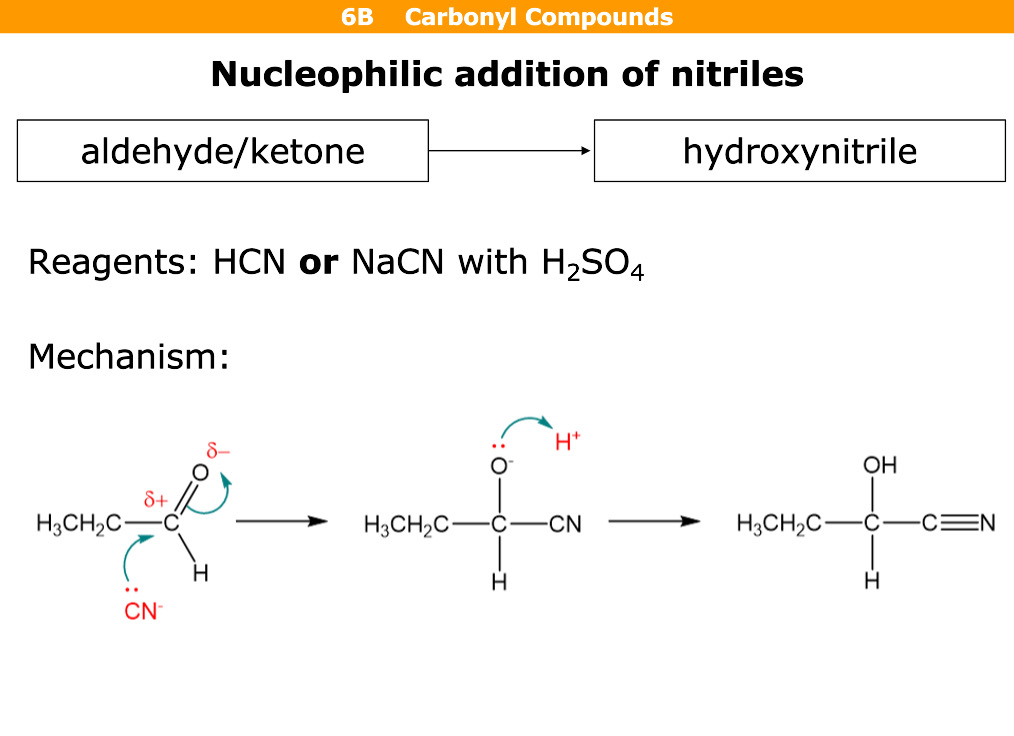
What happens in nucleophillic addition of nitriles
Reagents
Aldehyde / ketone turns back to (hydroxynitrile) - OH group on nitrile = hydroxynitrile
Reagents are HCN or NaCN with H2SO4
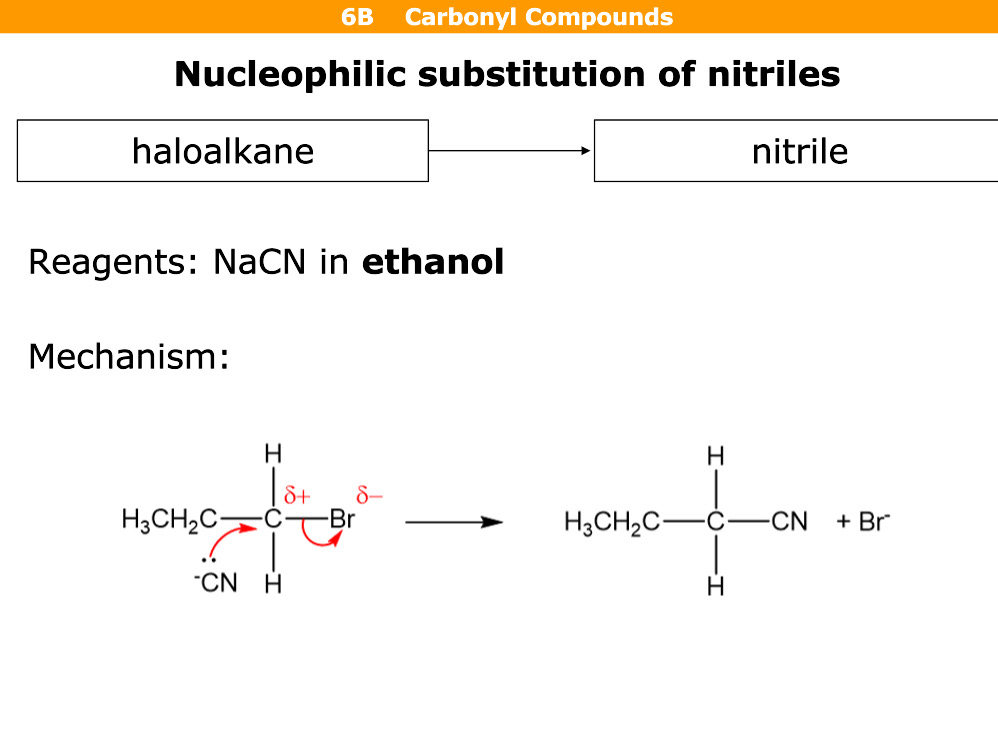
What happens in nucleophillic substitution
Reagents
Haloalkane turns into nitrile
Reagent = NaCN in ethanol
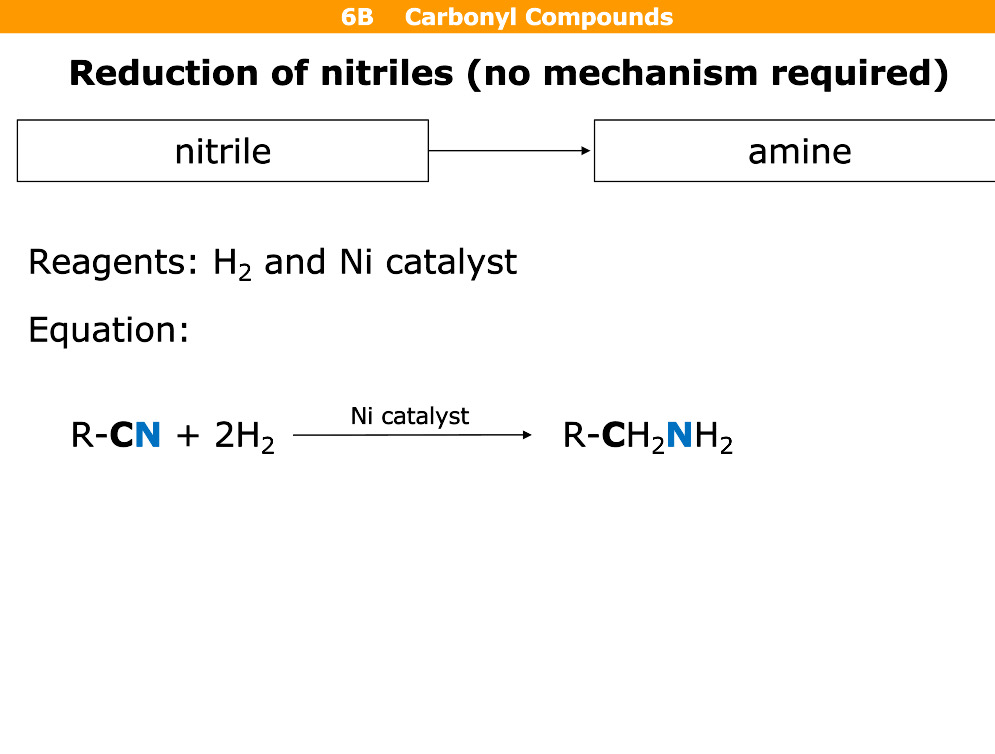
What happens in reduction of nitriles
Reagents
Nitrile goes to amine
Reagents= H2 and Nickel catalyst and 150°
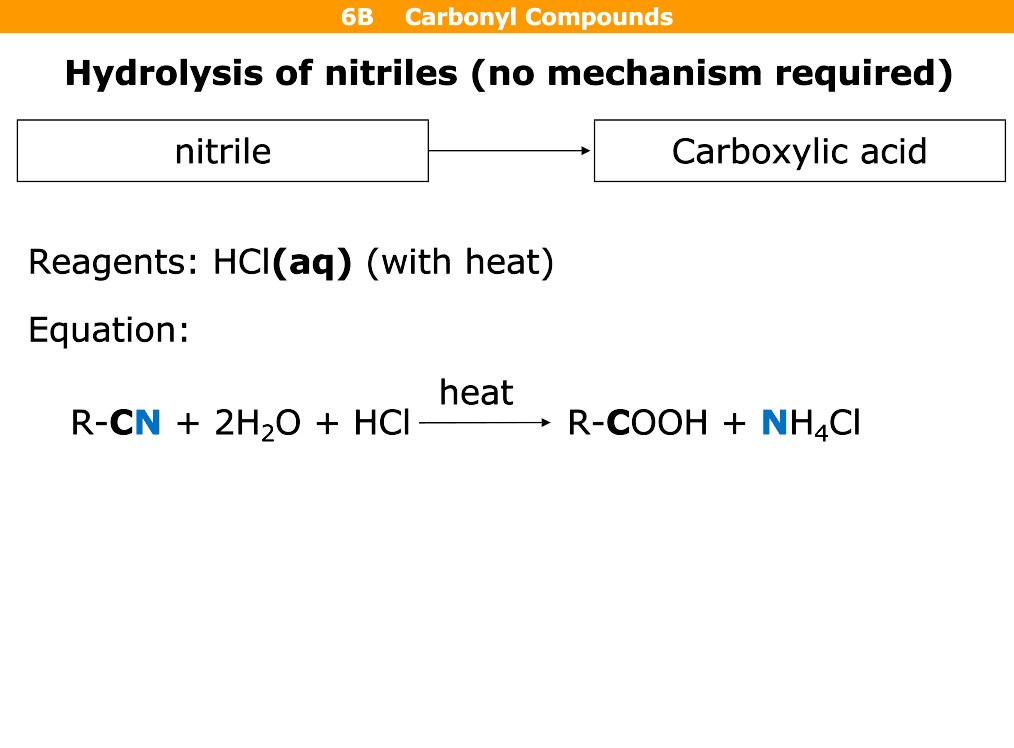
What happens in hydrolysis of nitriles
Reagents
Nitrile is turned into a carboxylic acid
Hcl(aq) with heat