Chapter 3, Lesson 2: The Cell Surface
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 3, Lesson 2 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
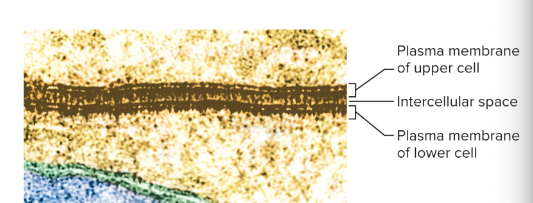
Plasma membrane
The border of the cell; has intracellular and extracellular faces to define cell boundaries and interact with other cells and materials
Phospholipids
Makes up 75% of the membrane lipids; arranged in a bilayer of hydrophilic phosphates and hydrophobic tails
Cholesterol
Makes up 20% of the membrane lipids, holds phospholipids and can stiffen membrane
Glycolipids
Makes up 5% of the membrane lipids, are phospholipids with short carbohydrate chains on the extracellular face
Integral proteins
Proteins that penetrate the membrane; hydrophilic regions contact the cytoplasm, while hydrophilic regions contact the lipids
Peripheral proteins
Proteins that adhere to one face of the membrane and are tethered to the cytoskeleton
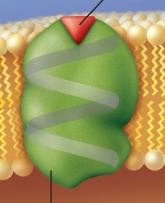
Receptors
Protein that binds to chemical messengers such as hormones sent by other cells
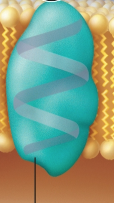
Enzyme
Protein that breaks down a chemical messenger and terminates its effect
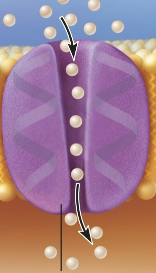
Channel
Protein that is constantly open and allows solutes to pass in and out of the cell
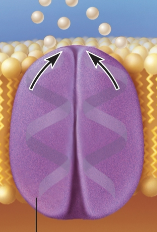
Gated channel
Protein that opens and closes to allow solutes to pass through at certain times
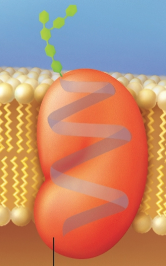
Cell-identity marker
A glycoprotein distinguishing the body’s own cells from foreign cells
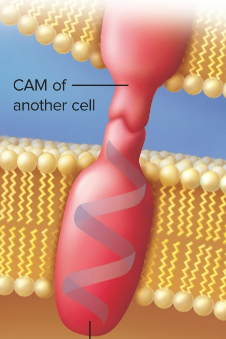
Cell-adhesion molecule
A molecule that binds one cell to another
Second messenger systems
Systems within a cell that communicate with receptors to send messages internally
Glycocalyx
A fuzzy coat external to the membrane made up of glycoproteins and glycolipids
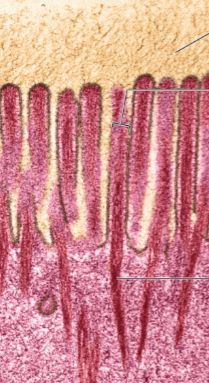
Microvilli
Extensions of the membrane developed in cells specialized in absorption (stomach cells)
Cilia
Hair-like processes 7 to 10 um long, found on nearly every cell for monitoring nearby conditions
Nonmotile cilia
Found on sensory cells of the nose
Motile cilia
Found in the respiratory tract and ventricles of the brain, beats in waves sweeping materials in one direction
Chloride pumps
Pumps Cl- into extracellular fluid alongside Na+ and H2O so mucus can flow; these being broken result in cystic fibrosis (mucus buildups)
Flagella
Whip-like structure identical to cilium’s with undulating movement; sperm is the only functional one in humans
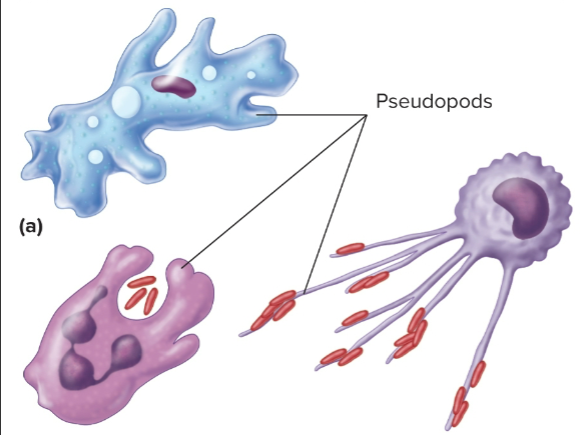
Pseudopods
Continually changing extensions of the cell that vary in shape and size; used for locomotion and foreign particle capture