Carbohydrates
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
General formula of monosaccharides
Cn(H2O)n
Three common monosaccharides
Trioses n=3
Pentoses n= 5
Hexoses n= 6
What is a isomer
Molecules having the same molecular but different structural formula due to a different arrangement of atoms (e.g glucose and fructose )
What are the 2 isomers of glucose
Alpha and beta
Hexose monosaccharides
Different Hexoses all have the same molecular formula (C6H12O6) but different arrangements of atoms.
We use different formulae to represent the different molecules.
How to number carbon atoms
Start clockwise from the oxygen atom
How are disaccharides form
Disaccharides are formed when 2 monosaccharides bond together through a condensation reaction releasing a water molecule.
draw the formation of a disaccharide
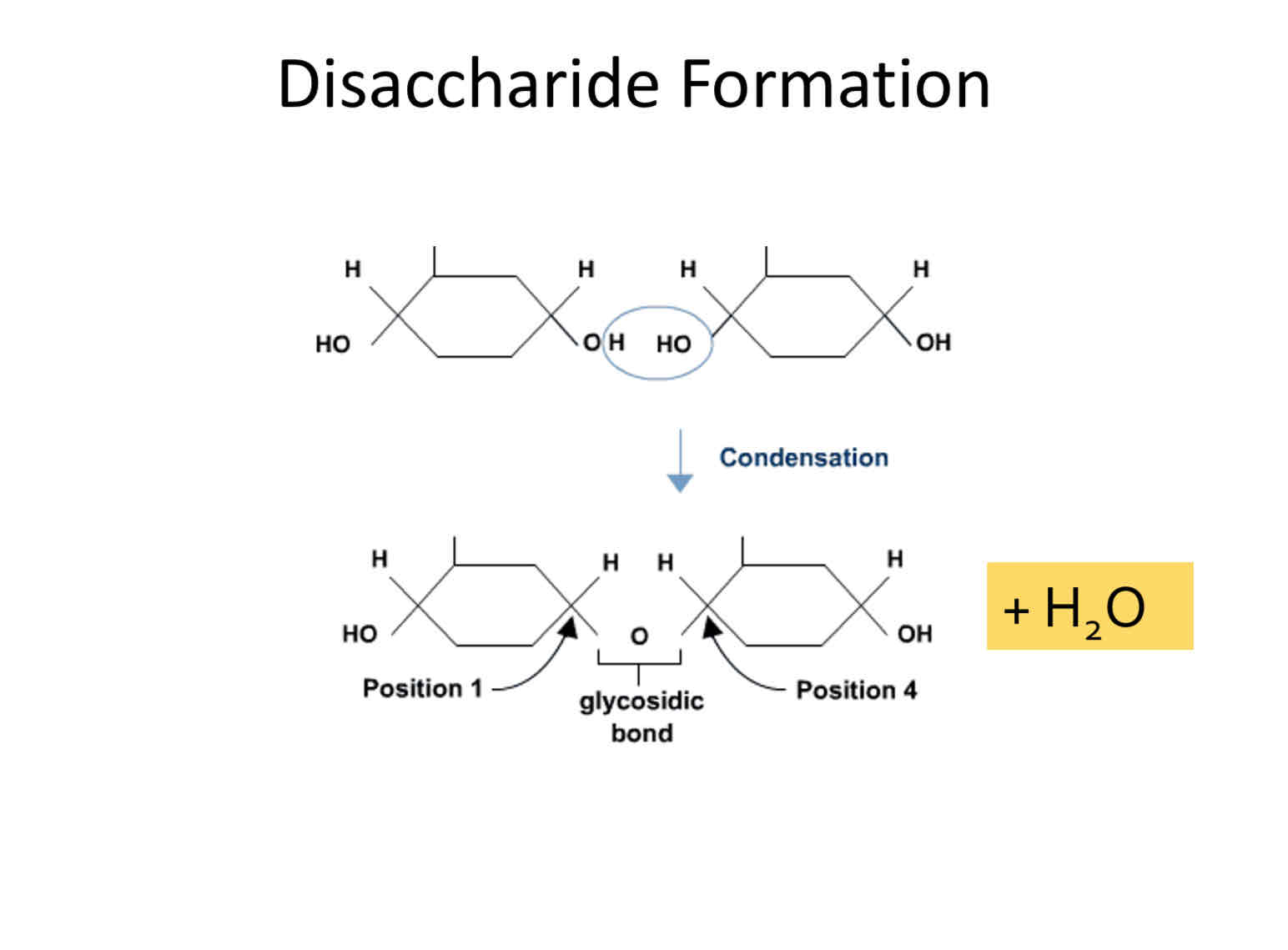
Describe the formation of maltose
A condensation reaction results in the formation of h2o
a OH group from the c1 of one glucose molecule is removed and the H atom from the C4 of another molecule bonds to make H2O
The resulting bond is glycosidic and is often referred to as a 1-4 glycosidic bond as these are the carbon atoms that form the bond
This results in the disaccharide called maltose
What are 3 examples of disaccharides
sucrose
Lactose
Maltose
What monosaccharides make sucrose
Fructose and glucose
What monosacchides make lactose
Galactose and glucose
What 2 monosaccharides make maltose
Glucose and glucose
How do you break a glycosidic bond
Hydrolysis
How does a polysaccharides form
When many monomers join through a condensation reaction
What’s the difference between alpha and beta glucose
Alpha below beta above (ABBA)