Thyroid hormones
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What does the thyroid gland produce
T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine)
These regulate metabolism, growth and development
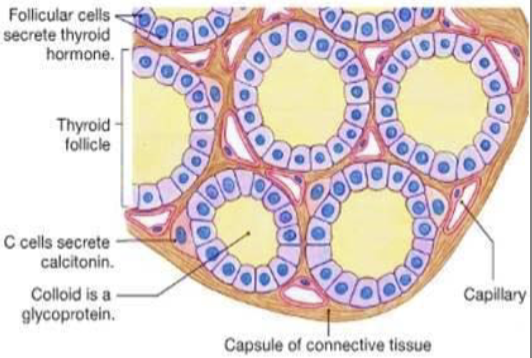
Thyroid follicles
Consists of follicular cells surrounding a lumen filled with colloid
Colloid is composed of thyroglobulin (precursor of T3 and T4)
Follicular cells - synthesize thyroglobulin + secrete it in colloid
Parafollicular cells (C-cells) - secrete calcitonin (regulate calcium homeostasis bu lowering blood calcium levels)
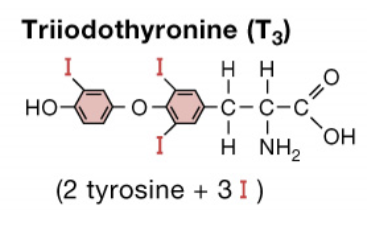
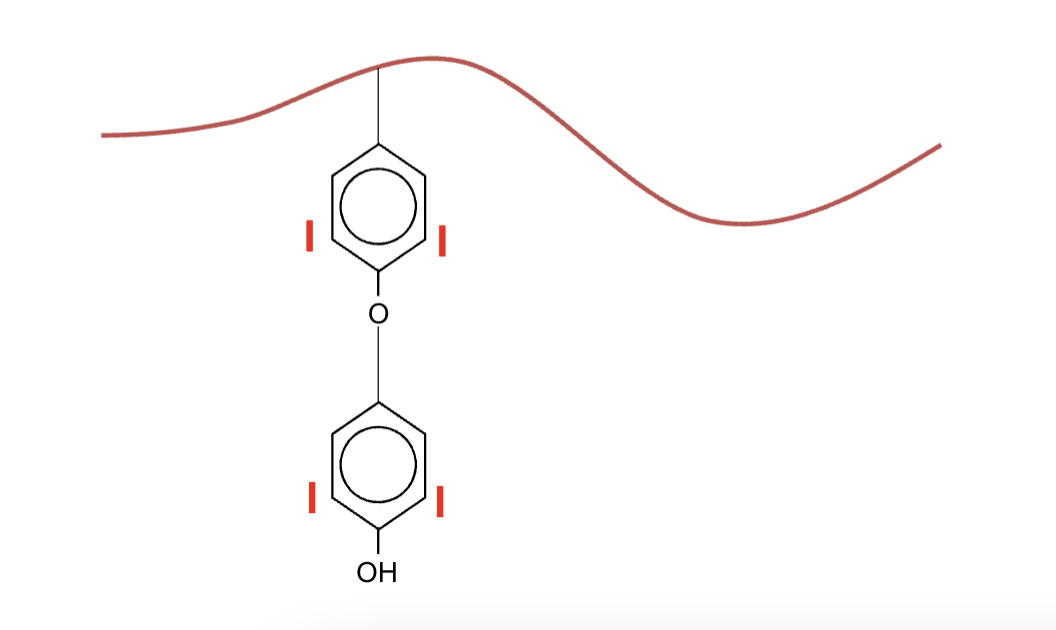
Triiodothyronine (T3)
More biologically active, has 3 iodine atoms, shorter half life
Has higher affinity for nuclear receptors
Thyroxine (T4)
Less active but more abundant, has 4 iodine atoms, T4 is converted into T3 peripheral tissues by deiodinase enzymes
Acts as prohormone → is converted to T3 in tissues
Essential molecules for thyroid hormone synthesis
Tyrosine - part of thyroglobulin, acts as backbone onto which iodine is added
Iodine - obtained from diet, essential for hormone formation
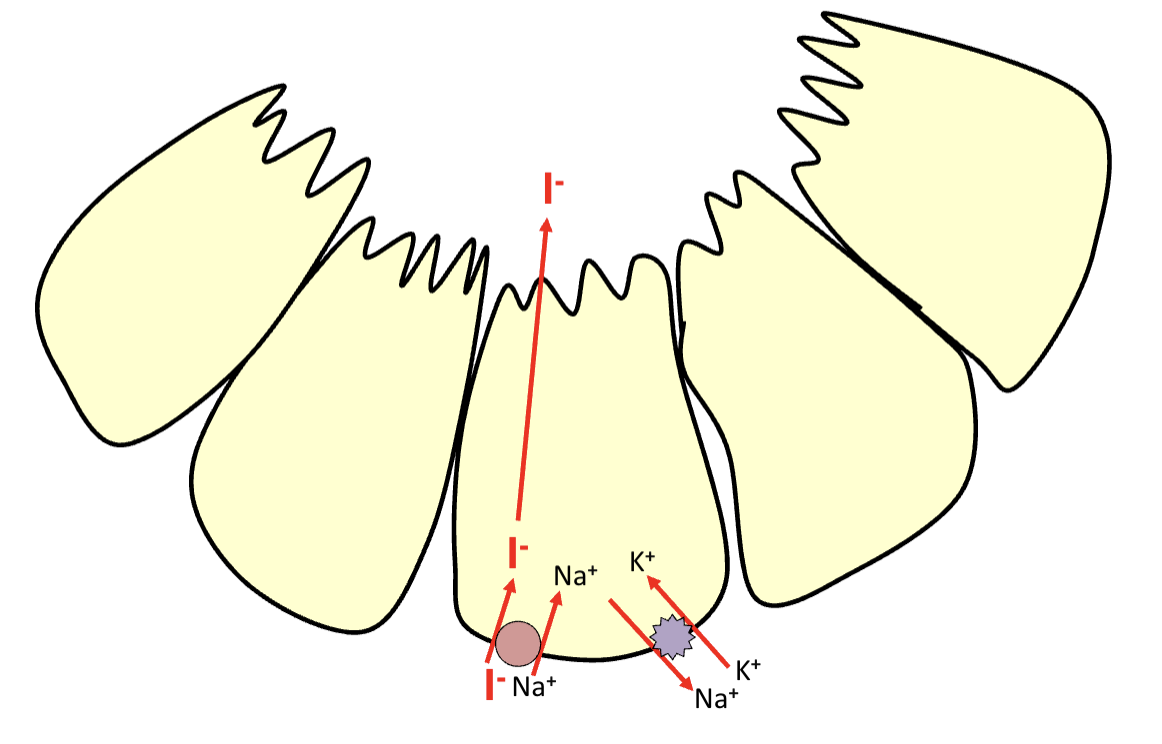
Collection and concentration of iodide
Iodide is transported from bloodstream to thyroid follicular cells via sodium-iodide symporter (NIS)
Then it is moved into the colloid by pendrin transporter
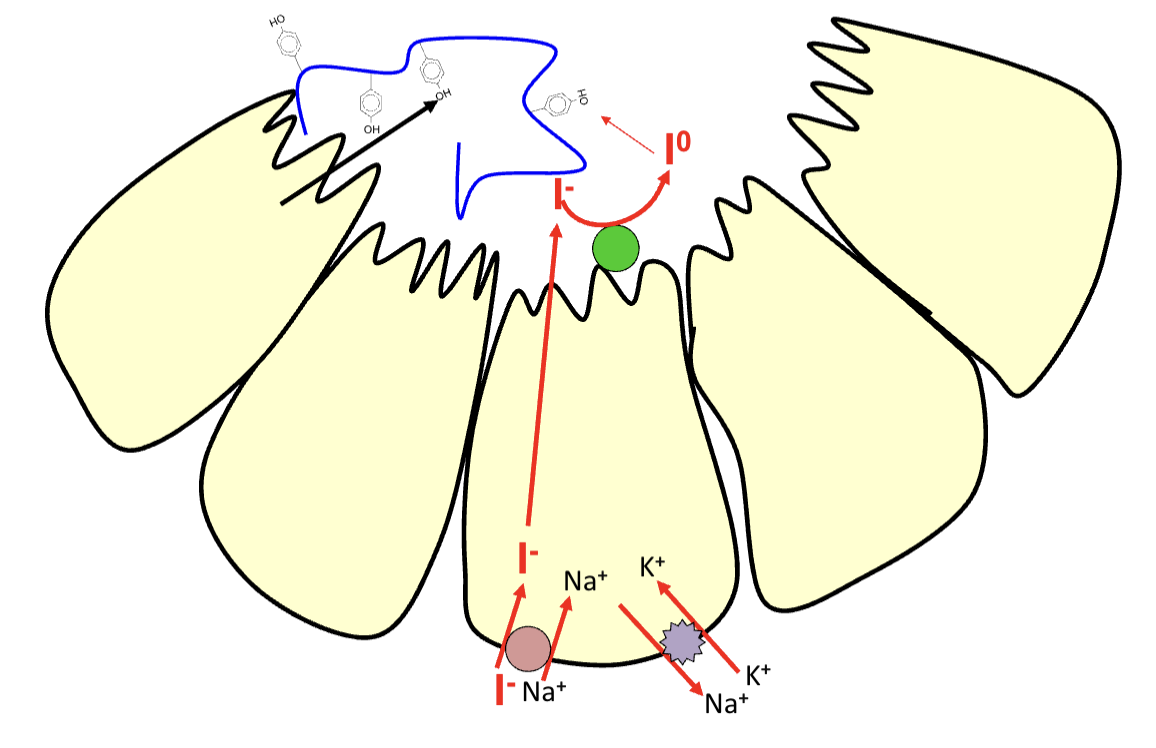
Oxidation and iodination
Inside the colloid, iodide is oxidised to iodine by enxyme thyroid peroxidase
Iodine is attached to tyrosine residues in thyroglobulin to form MIT, DIT
MIT (monoiodotyrosine) - 1 iodine, DIT (diiodotyrosine) - 2 iodines
Attachment
2 iodinated tyrosines are coupled together, and are catalysed by TPO
DIT + DIT → T4, DIT + MIT → T3
Hormones are still bound to thryoglobulin and stored in colloid
Secretion
When TSH stimulates thyroid, iodinated thyroglobulin is endocytosed back into the follicular cells
Lysosomes digest thyroglobulin and release T3 and T4 into circulation
MIT and DIT that are not coupled are deiodinated and recycled
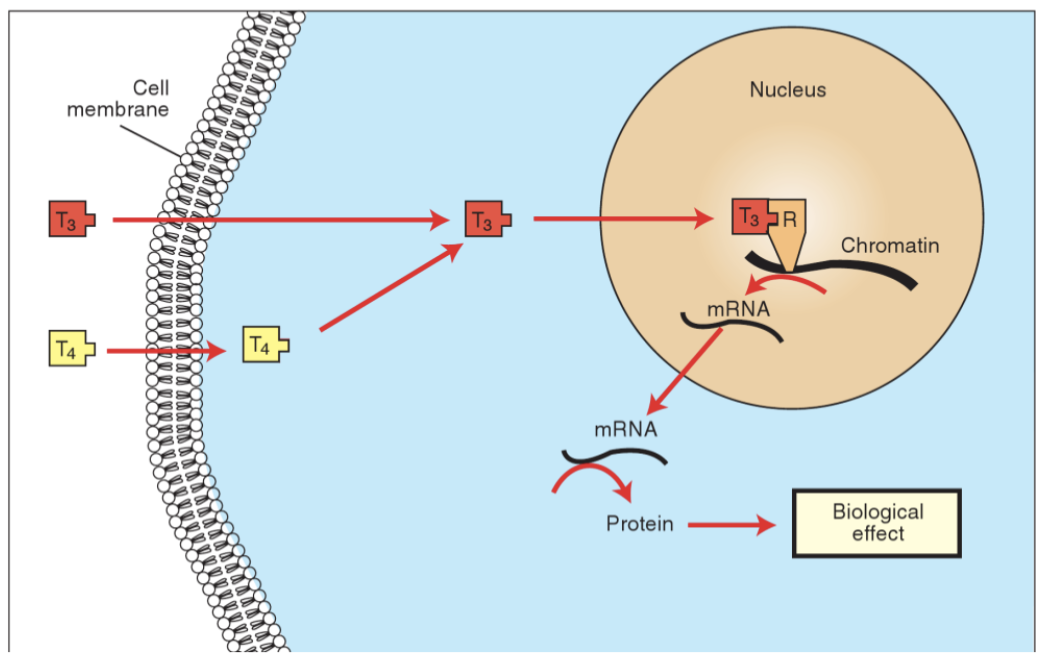
Action
T3 and T4 enter target cell
Deiodinase converts T4 into T3, in cytoplasm, as it is more active
T3 enters the nucleus, binds to thyroid receptors already attached to DNA
When bound, it activates or represses the transcription of specific genes
mRNA is produced, leading to synthesis of proteins that change cell function
Main binding proteins in plasma
Thyroxine-binding globulin - major carrier of T$ and T3, high affinity
Transthyretin - binds T4 more than T3
Albumin - binds large amounts but with weak affinity
Actions of thyroid hormones
Stimulate transcription of GH and PRL genes in pituitary
T3 enhances GH receptor expression in target tissues like bone and muscles
Increases absorption of glucose from digested food (glucose transporters)
Increases number of mitochondria → boosts ATP production
T3 increases beta-adrenergic receptors which makes them more sensitive to epinephrine
Thyroid hormone effect on protein synthesis
Normal levels - T3 and T4 stimulate ribosomes and activate genes that tell the cell to make proteins, supports growth, tissue repair and muscle building
High levels - body metabolism speeds up → needs more energy, it starts breaking down muscle proteins to use amino acids for glucose production
Thyroid hormone effect on carbohydrates
Low levels - favour the storage of glucose as glycogen, promotes energy storage
High levels - rapid breakdown of glycogen, make glucose from amino acids…
T3 major target - Na+/K+ ATPase pump
When more pumps are made, more ATP is consumed to keep them working
higher ATP demand → higher metabolic rate (because pumps need energy, cells consume more glucose and oxygen to produce more ATP)
Thyroid hormones actions → increase oxygen consumption

Thyroid hormone actions on the cardiovascular system

Thyroid hormone action on the respiratory system

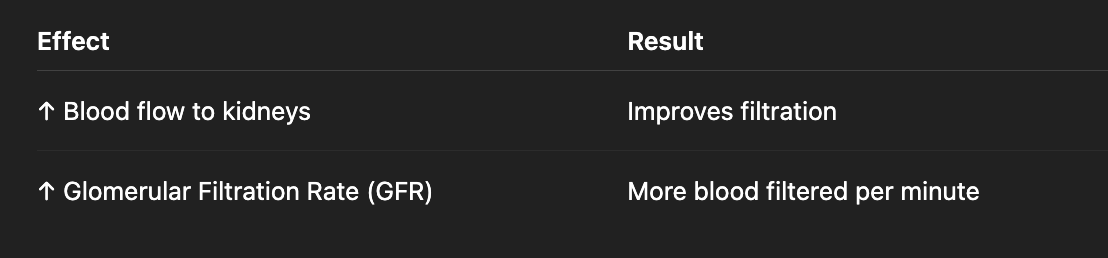
Thyroid hormone action on renal system
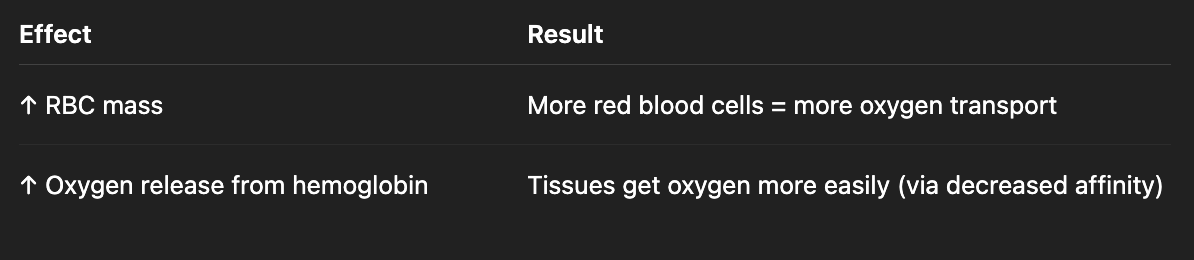
Thyroid hormone action on oxygen carrying capacity
Thyroid hormone action on growth and tissue development

Thyroid hormone action on nervous system

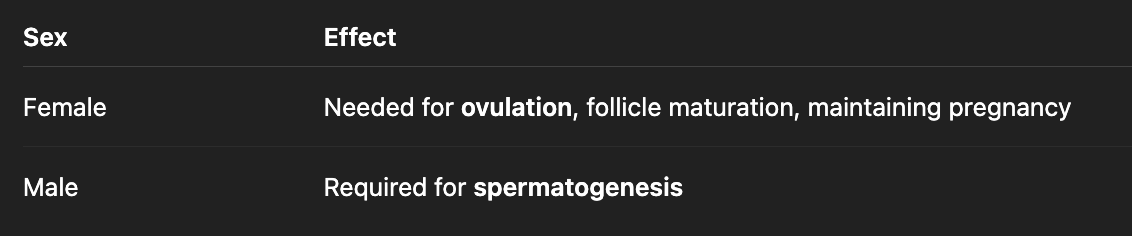
Thyroid hormone action on reproductive system
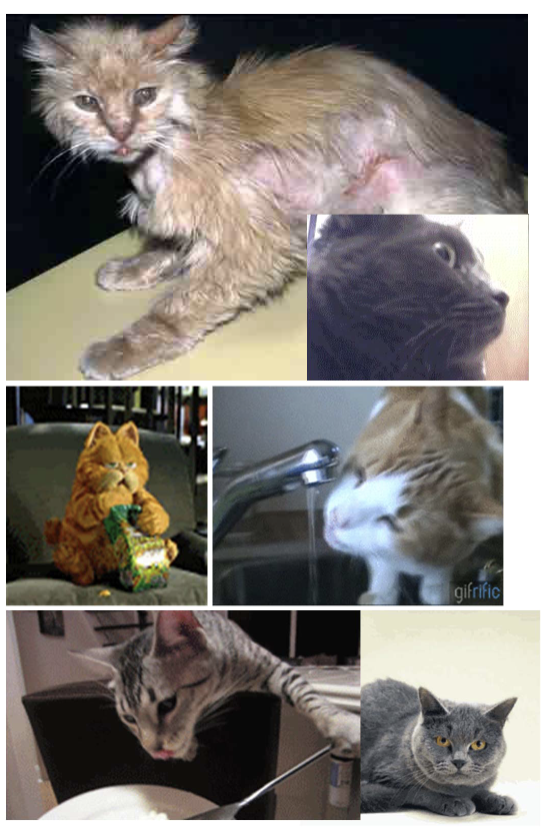
Hyperthyroidism
Low thermogenesis - fewer Na+/K+ pumps → less mitochondrial activity→ less ATP use and heat production
Skin/hair - dry skin, rat tail, hyperpigmentation, symmetric alopecia
Behaviour - lethargy, drowsiness, mental dullness
Weight - weight gain, metabolism slows down → energy stored as fat
Cardiovas - lower heart rate due to reduced stim of b-adrenergic receptors
Blood - bone marrow doesnt produce enough RBC (low metabolism)
Cretinism - in puppies, stunt in physical and mental development
Goitre - by iodine deficiency of TSH overstim → enlarged thyroid gland
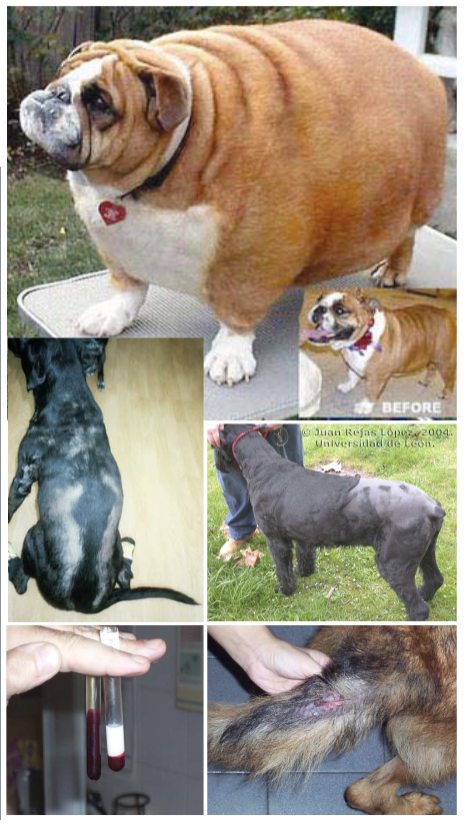

Hyperthyroidism
Weight - weight loss, increased appetite, excessive metabolism
Muscles - protein catabolism increases, muscles shrink and weaken
Cholesterol - enhanced lipid metabolism → low cholesterol
Heat - heat production by increased ATP and mitochondrial activity
Cardiopulm - increased heartrate and breathing rate (panting, hypertension and murmurs)
Erythrocytosis - increased RBC
Neuromuscular - tremors, agitation, twitches, stimulation of NS
Goitre - enlarged thyroid
