Integumentary system
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is composed of the integumentary system?
Skin
Where is skin thickest?
Heels
Where is skin thinnest?
Eyelids
What is the skin’s functions?
Protection
Temperature regulation
Excretion of urea, salt, and sweat
Production of vitamin D
Sensory reception
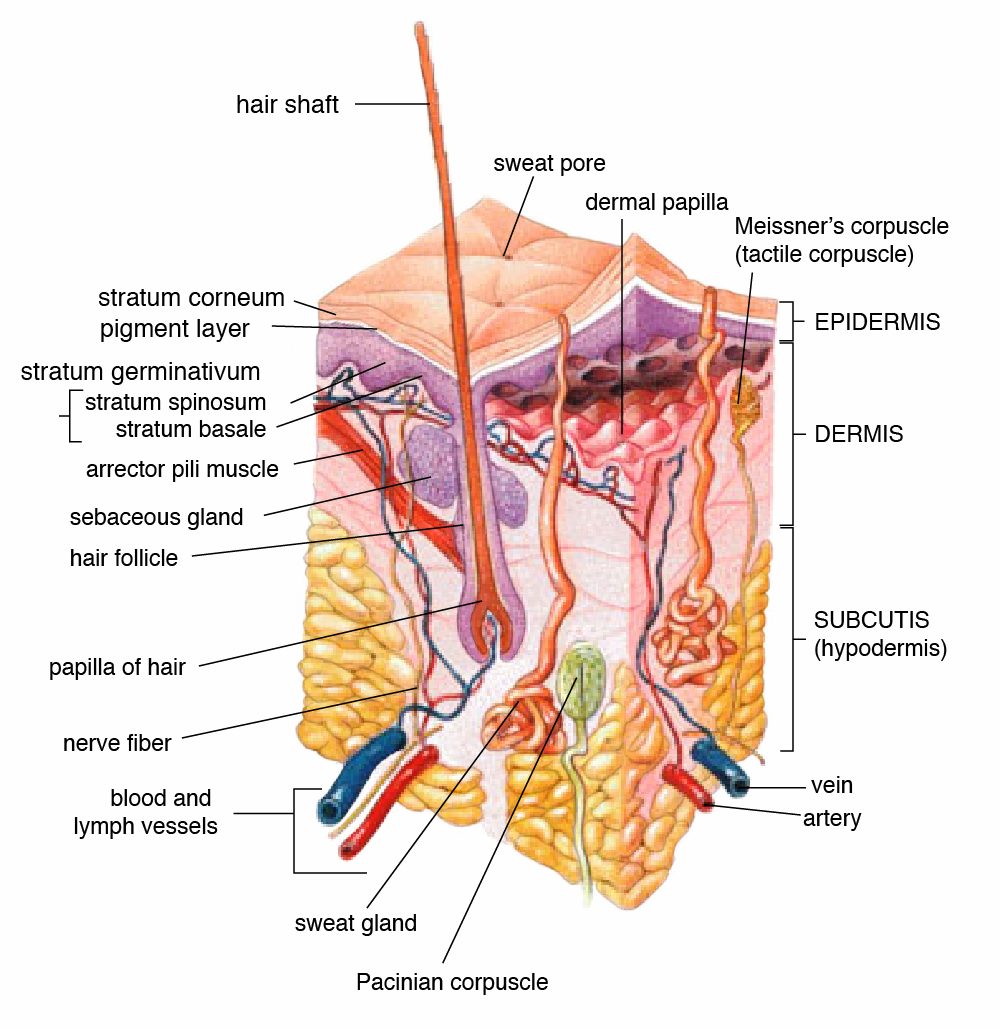
Epidermis
The most outer layer of the skin, it is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Keratinization
Accumulation of protective keratin (skin cells which produce keratin die off as they reach the upper layer, leaving only keratin behind)
Stratum basale
Deepest layer of the skin, attaching to the dermis
Cells here ACTIVELY divide
Contains merkel cells and melanocytes
What are the 3 layers of skin from deep to superficial?
Hypodermis, dermis, and epidermis
Stratum spinosum
Cells here take on a spiny appearance as they extend
Contains many intermediate filaments (tonofilaments) to resist tension and contains protein prekeratin for structure
Contains Langerhans cells
Stratum granulosum
Contains keratinocytes and tonofilaments
End of the skin cell’s life
What do tonofilaments contain?
Keratohyaline granules (from keratin)
Lamellated granules (waterproofing glycolipid)
Stratum lucidum
Only found in thick skin, such as the palms and soles of the feet
Around 3 rows of dead keratinocytes to increase strength
Appears clear
Stratum corneum
Thick layer of dead keratinocytes
Thickened plasma membranes
Protects skin from abrasion and penetration
Keratinocytes
90% of cells
Produces keratin (protective fibrous protein)
Produces antibodies and enzymes
Melanocytes
Produces melanin for protection, which is then transferred to keratinocytes for protection
Langerhan cells
Immune response
From red bone marrow
Markel cells
Connection to sensory nerves with Merkel discs for the sensation of touch
Dermis layer
The second layer of skin, which is the connective tissue and contains the blood vessels and nerves
Contains flexure lines
Flexure lines
Permanent creases that can be seen on the exterior of the body due to deep connective tissue
What are the names of the two layers of the dermis
Papillary layer (top layer near the epidermis)
Reticular layer (bottom layer)
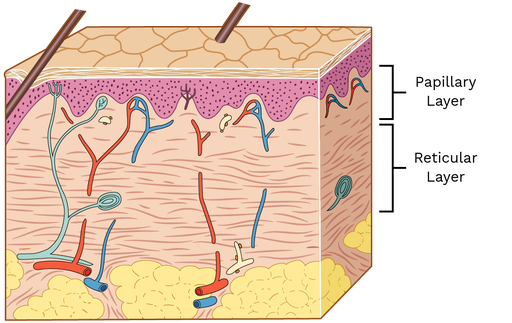
What does the outer papillary region contain
Areolar connective tissue
Dermal papillae connect to the epidermis
Meissner corpuscles for the sensation of touch
Free nerve ending (very sensitive)
Reticular region
80% of the thickness of the dermis layer
COntains dense irregular connective tissue
What does the reticular region contain, excluding the skin tissue?
Adipose cells
Hair follicles
Nerves
Sebaceous oil gland
Sudoriferous sweat glands
Collagen and elastic fibres
Lines of cleavage
Also known as tension lines
Indicates the predominant direction of underlying collagen fibres
Creaveses throughout the body (wrinkles)
Epidermal ridges
Contours of the underlying dermal papillae
Formation of fingerprints
Increase grip through friction
Raised bumps
What is the hypodermis made of?
Areolar and adipose CT
Hypodermis
Deepest layer of the skin, also known as the superficial fascia
Anchor’s skin
Helps insulate
What are the 3 pigments that contribute to skin colour?
Melanin, carotene, and hemoglobin
Melanin
Created from tyrosine, shades of skin
Ie. freckles
Carotene
Yellowish pigment
Found in all skin types in the dermis, hypodermis, and stratum corneum
Hemoglobin
Usually found in lighter skin, causing a red hue to the skin
Nevus
Benign overgrowth of melanocytes
Commonly known as a mole
Albinism
Inability to produce melainin
Vitiligo
Loss of melanocytes which leads to patches of whitened skin
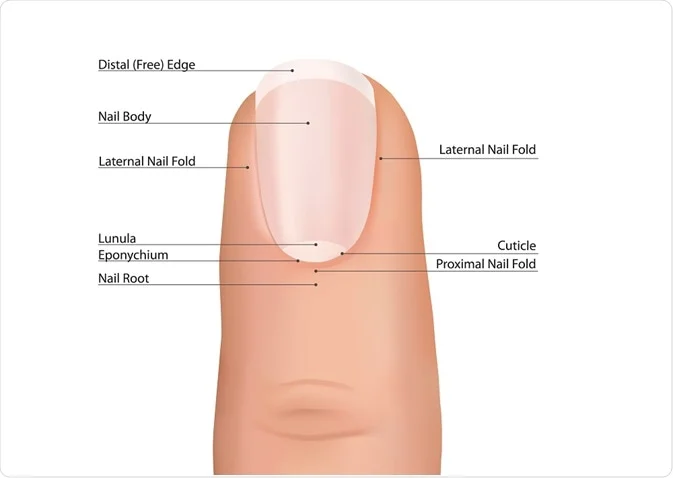
What are nails made of?
Hard keratin (think of modified epidermis)
What are the main parts of the nail
Free edge
Body or plate
Lunula
Root - cell division occurs here with the matrix
Eponychium - cuticle
What is hair made of?
Flexible, dead, keratinized cell
What are parts of the hair?
Shaft- above the surface
Root - Into the dermis, site of division
Hair follicle - Surrounds the root for protection
Papilla - Blood supply
Sebaceous oil glands, arrector pili muscles, and hair root plexi
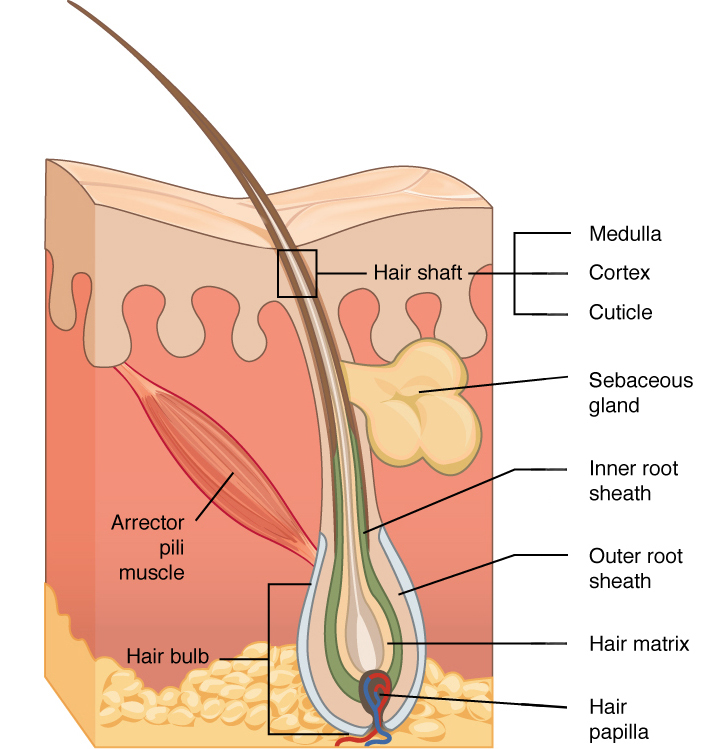
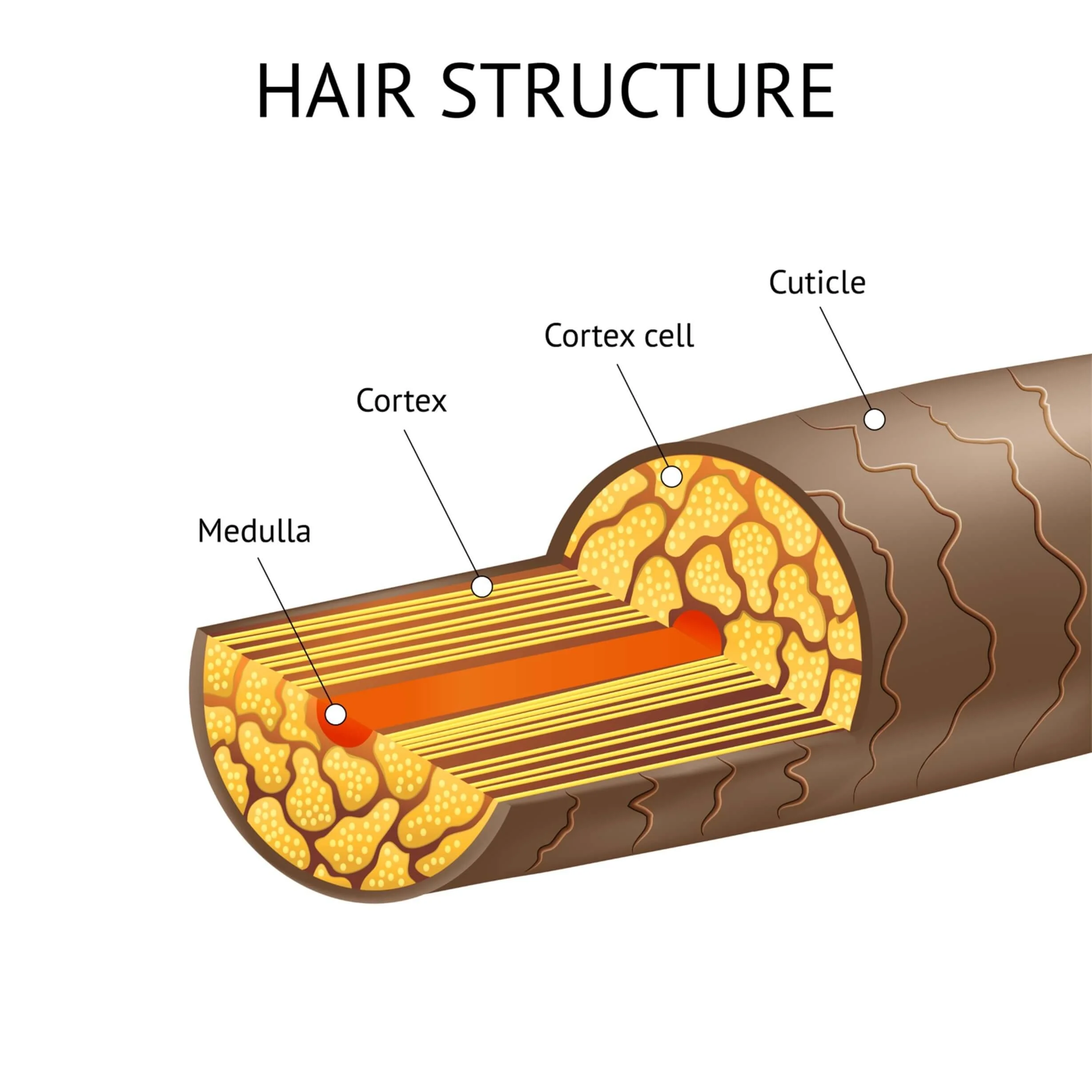
What are the 3 concentric layers of keratinized cells?
Medulla - Central core
Cortex - Surrounds medulla
Cuticle - Outermost layer
Vellus hairs
Softer body hairs, usually on women and children
Terminal hairs
Coarser body hairs, usually in the pubic, armpit, scalp, and chest hair
What are some main factors in hair thinning?
Aging
Male pattern baldness
Weight loss
Post-partum
Disease
Stress
Merocrine secretion
These types of cells secrete the product
Eccrine sweat glands
Aprocine secretion
These types of cells pinch off vesicles to release the product
Mammary glands
Holocrine secretion
These types of cells break down entirely to release the product
Sebaceous glands
What type of glands are sebaceous glands?
Simple alveolar glands that use holocrine secretion
Sebum
Oily substance that collects dirt, softens hair and skin up, and plays an anti-bacterial role
Sweat
Filters blood
99% of water and some salts
2% urea with metabolic waste
Where are sebaceous glands found?
Everywhere except the palms and soles of our feet
Eccrine gland
A type of sweat gland that produces sweat through merocrine secretion
True sweat
Temperature control
Ceruminous glands and mammary glands
A type of gland that is a modified version of the apocrine glands
Simple coiled tubular
Ear wax production
Collects debris and pathogens
First-degree burn
Epidermis is damaged
Second-degree burn
The upper part of the dermis is damaged
Blisters
Scars
Third-degree burn
Dermis is fully damaged
appears white, red, or black
Basal cell carcinoma
Least malignant and the most common
Squamous cell carcinoma
Keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum (may appear more black)
Melanoma
Cancer of the melanocytes (deep within)
most dangerous because of the rate of duplication
Where does the epidermis develop from?
Ectoderm
Where does the dermis/hypodermis develop from?
Mesoderm
Where do the melanocytes develop from?
Neural crest cells in the endoderm
Describe the timeline of skin development in the fetus
The 4th month is well-formed
The 5th to 6th month has lanugo (hairs)
7th month, sebaceous glands form to produce vernix caseosa (waxy substance)
Epidermal wound healing
Superficial wounds that only affect the epidermis
Deep wound healing
The dermis and/or subcutaneous layer is damaged
( Macrophages - inflammation - clot - protein fills - scar tissue from fibroblast replaces it )