Muscle Neurons and such
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
An ATP-powered antiporter in the plasma membrane called?
Na+/K+ pump
First step of Na+/K+ pump?
3 Na+ and ATP bind pump
ATP breaks down to ADP & P and releases energy
Second step of Na+/K+ pump
Energy powers shape change of pump?
Third step of Na+/K+ pump
Shape changes → 3 Na+ transported into extracellular fluid out of the cell?
Fourth step of Na+/K+ pump
Fifth step of Na+/K+ pump?
2 K+ bind
Sixth step of Na+/K+ pump?
Phosphate released
Seventh step of Na+/K+ pump?
2 K+ into the cell
Na+/K+: Inside of the cell becomes more negative, maintaining an electrical gradient, what is this?
Net result
The Na+/K+ pump keeps correct ion balance for resting membrane potential and allows action potentials to occur, what is this?
Effect on cell
The stable, negative charge inside a resting neuron, is what?
Resting membrane potential
More Na+ outside and K+ inside, with leaky K+ channels letting K+ out, what is this?
Cause of resting membrane potential
Creates the electrical baseline needed for neurons and muscle cells to fire action potentials, what is this?
Why resting membrane potential matters
Na+/K+ channels are closed, what is this?
Resting phase
Na+ channels open, Na+ rushes in, making it positive inside, what is this?
Depolarization definition
Na+ channels close, K+ channels open, K+ flows out, restoring negativity, what is this?
Repolarization definition
K+ channels stay open slightly too long, causing brief overshoot of more negative inside the cell, what is this?
Hyperpolarization definition
Na+/K+ pump restores ion balance to resting potential, what is this?
Return to rest
What type of channels does the Na+/K+ pump use to control timing and flow of ions?
Voltage gated
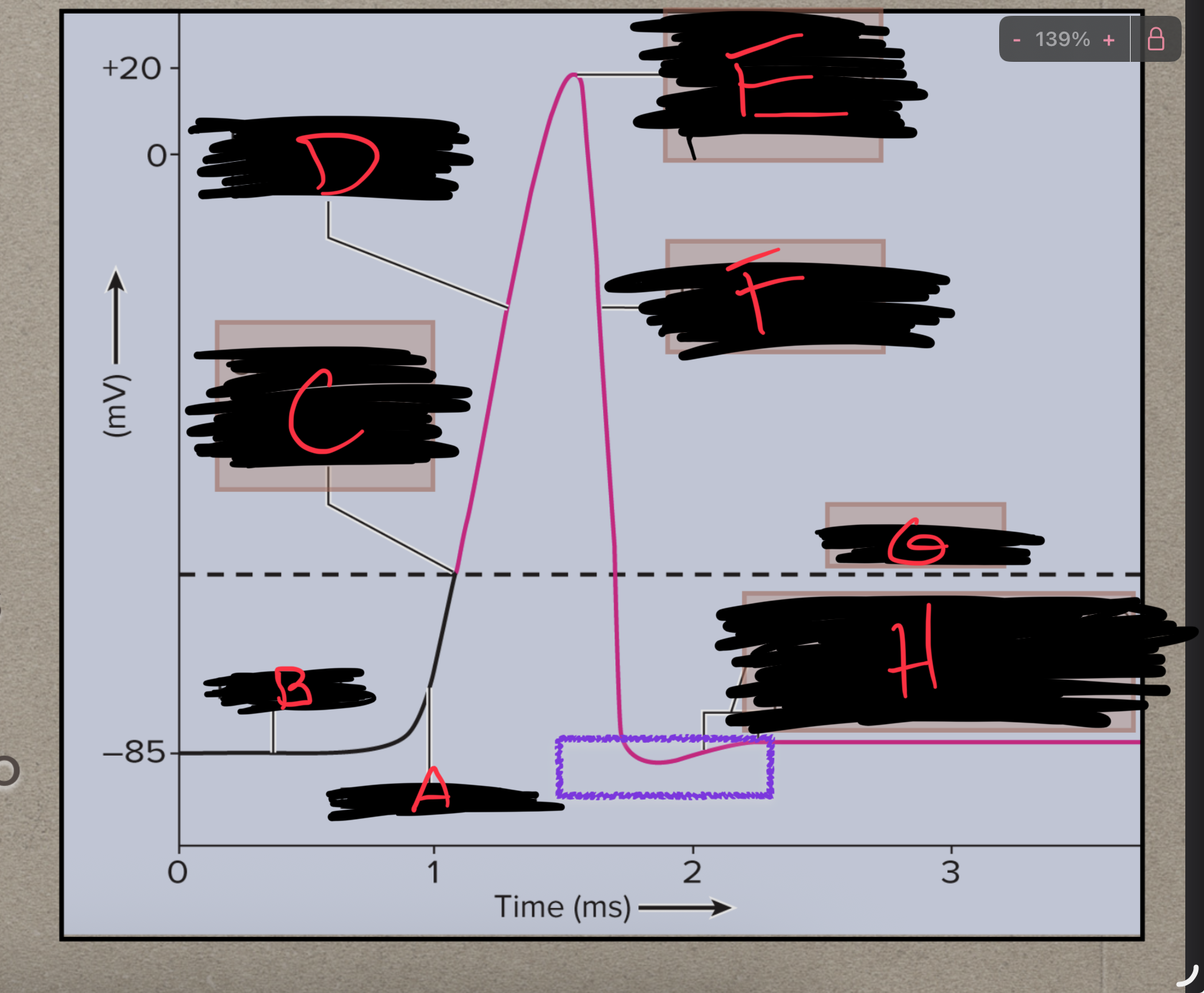
What is A?
Depolarization
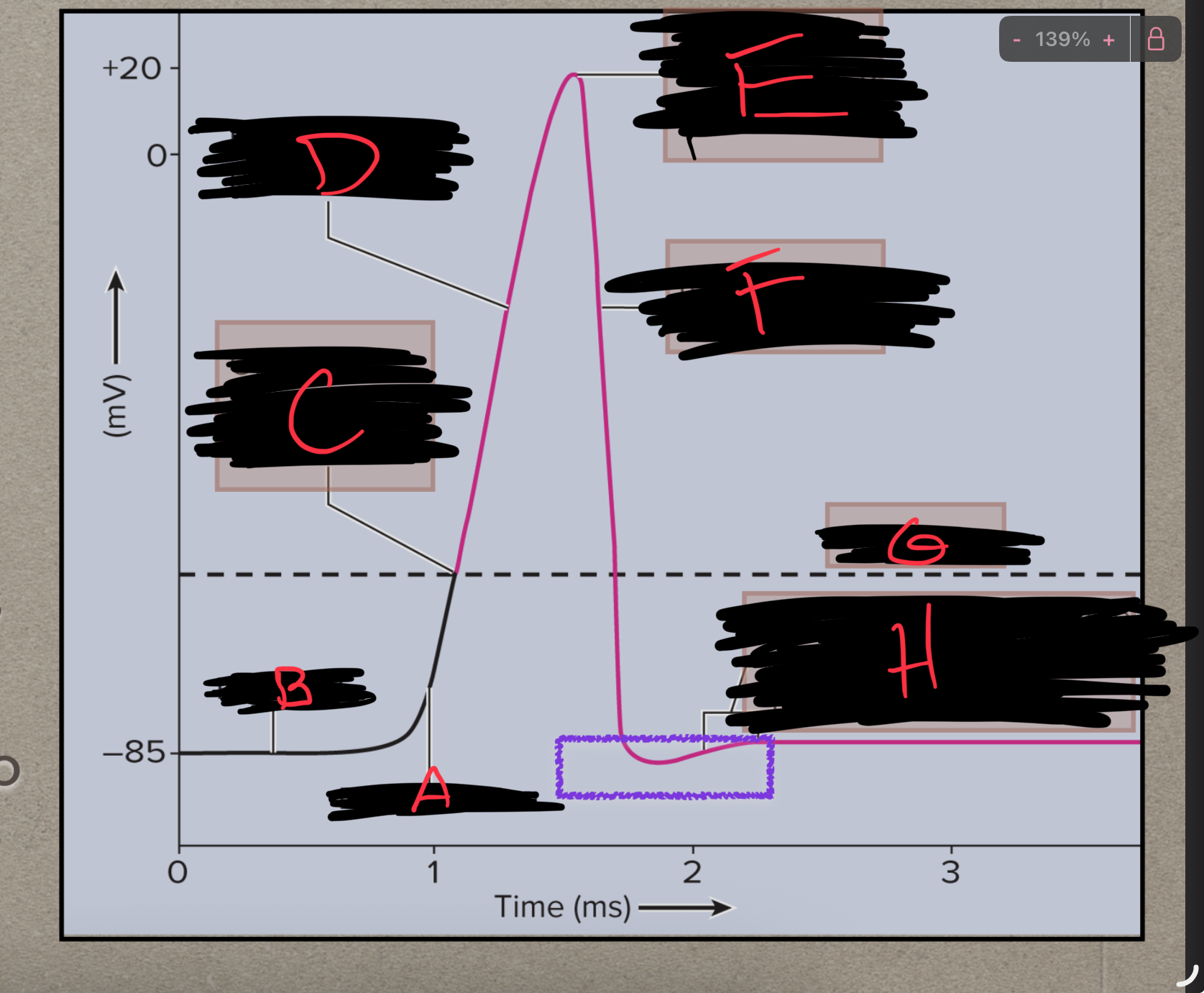
What is B?
Polarized
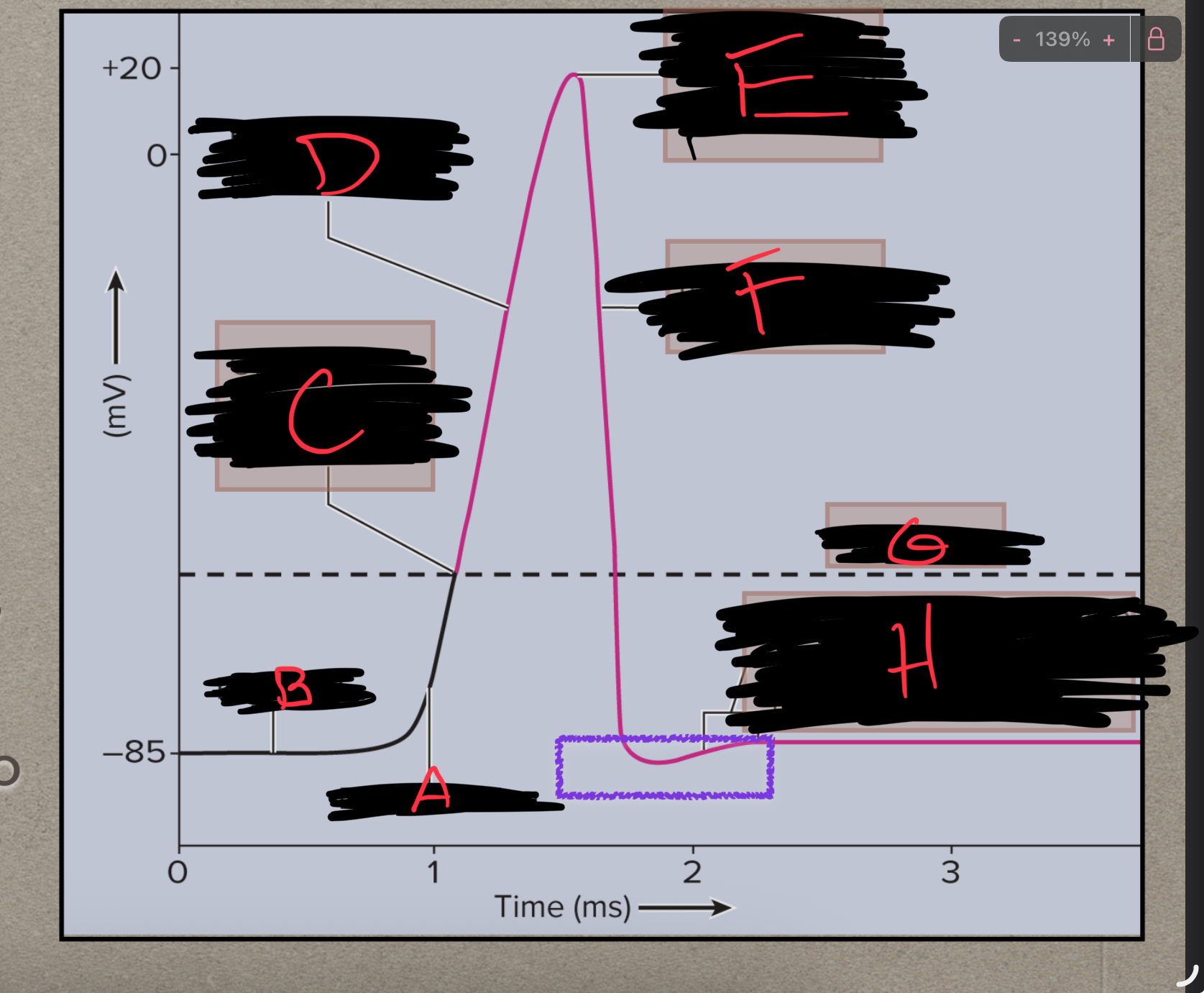
What is C?
Na+ channels open
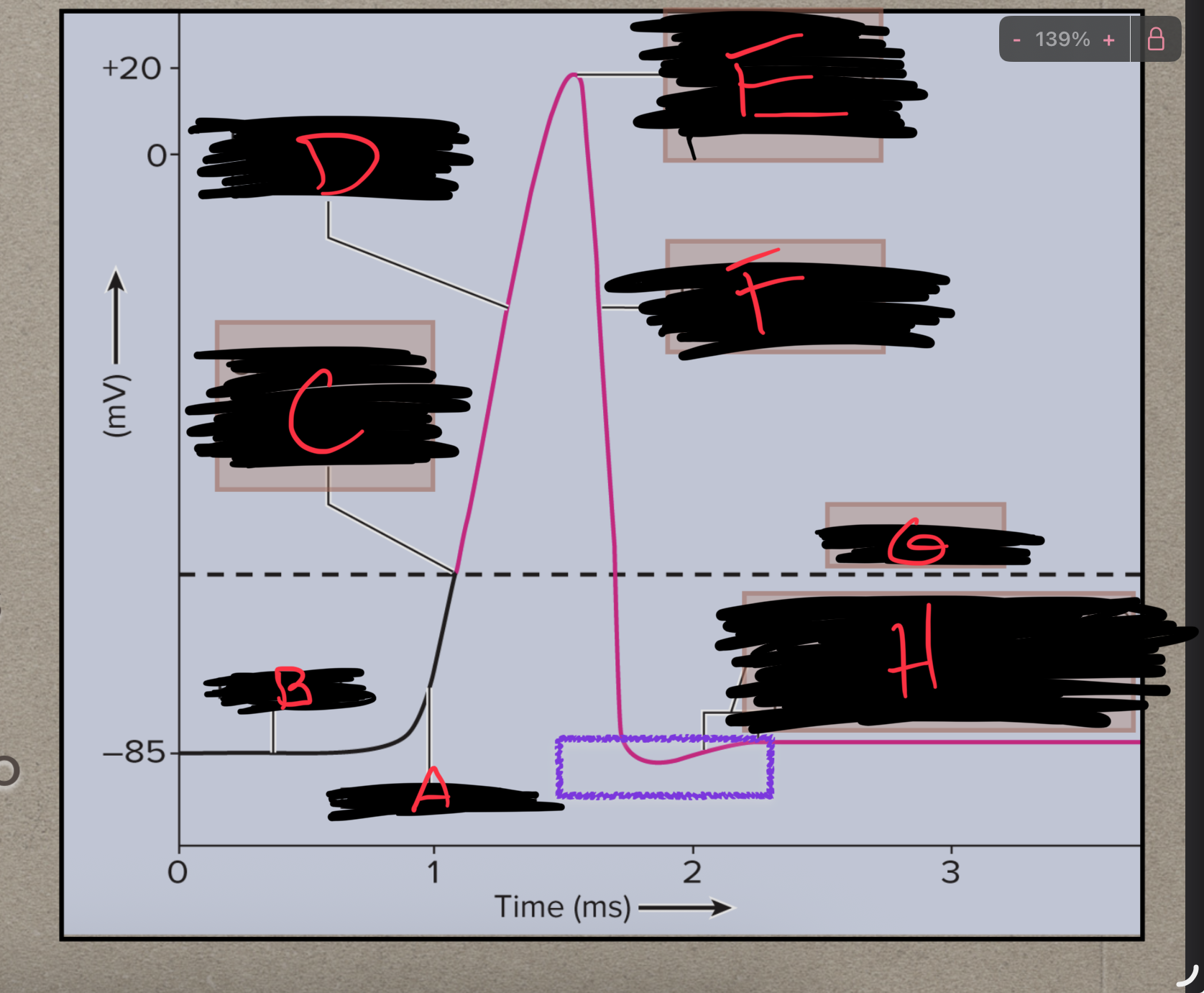
What is D?
Depolarization
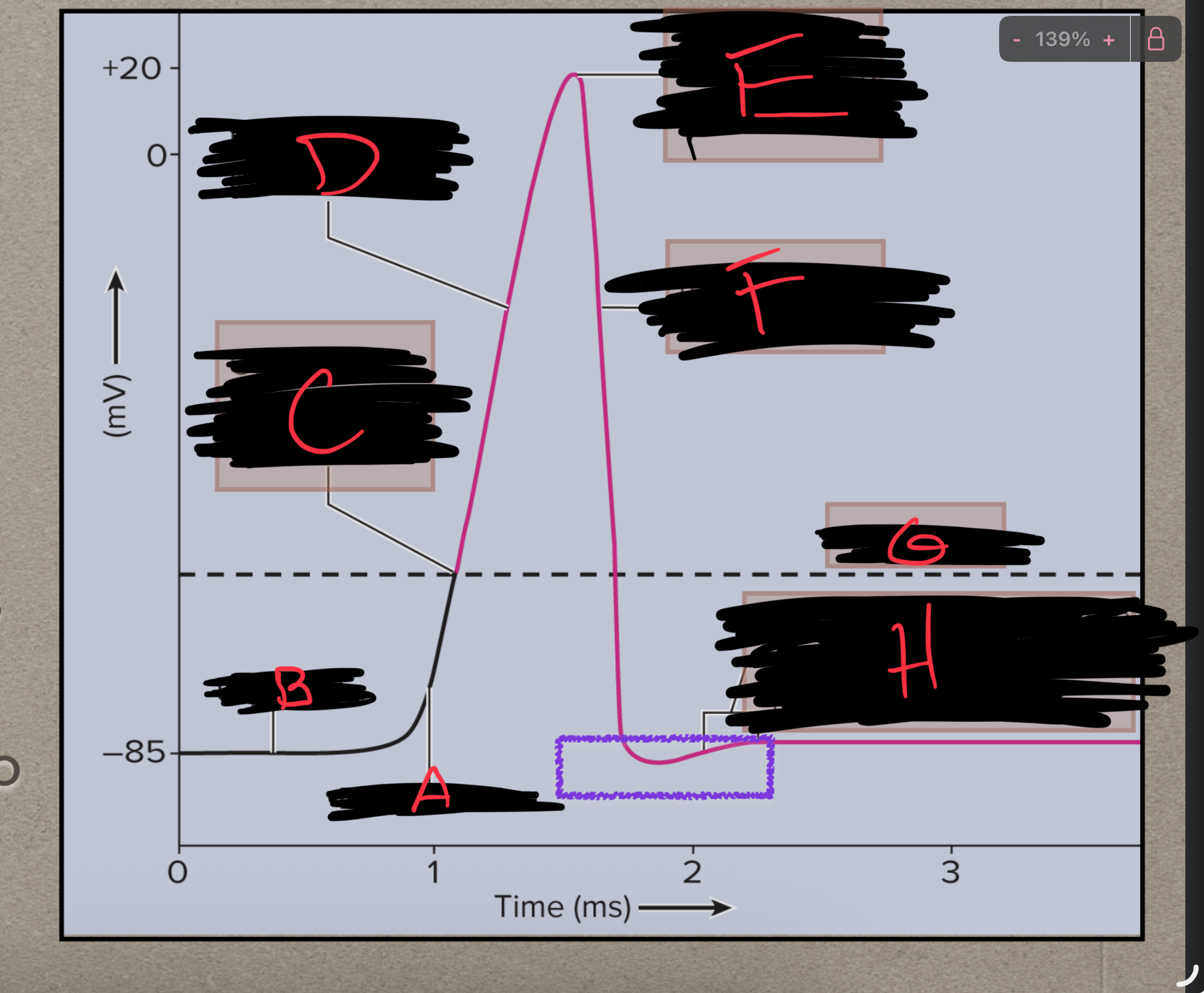
What is E?
Ka+ channels open
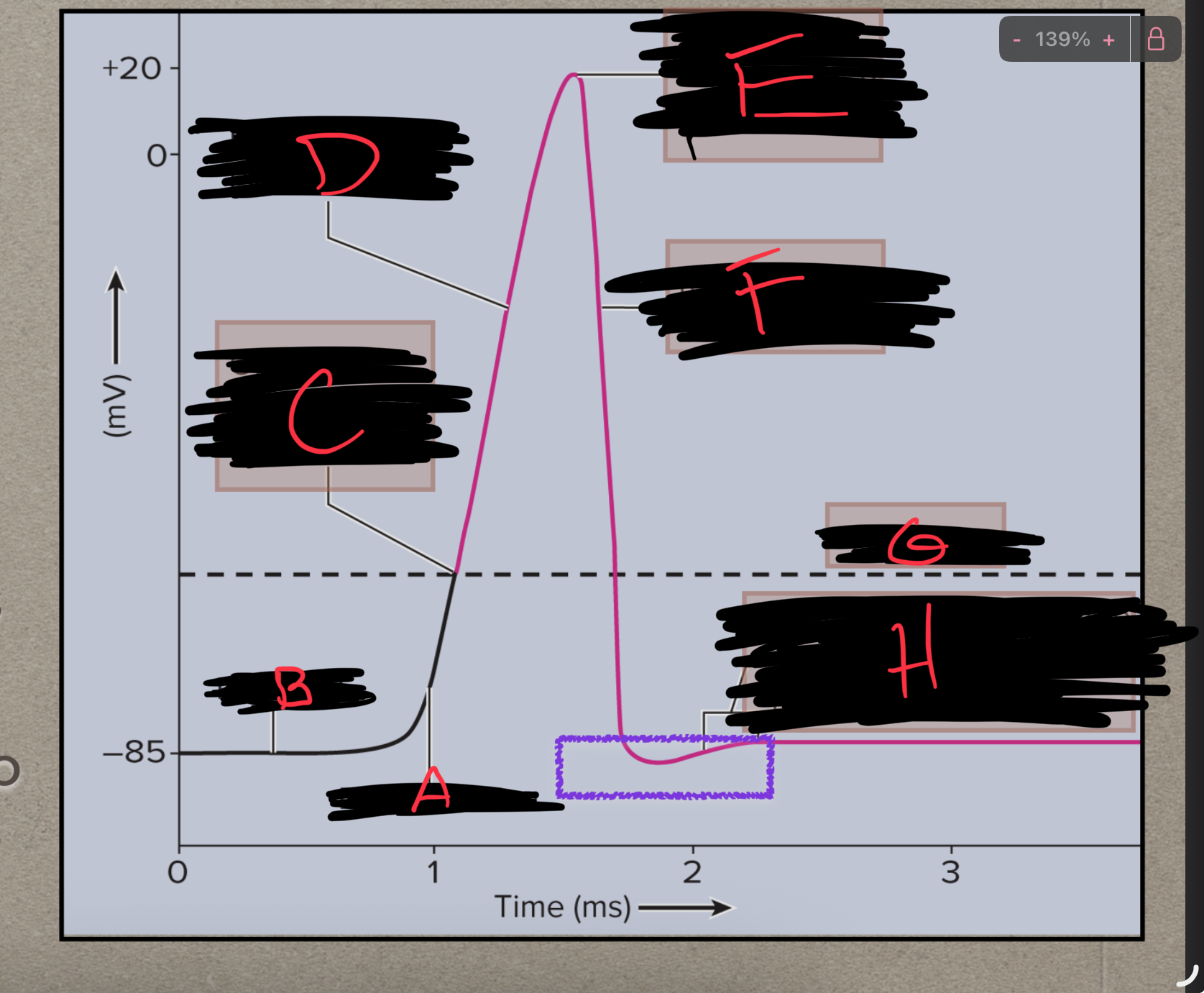
What is F?
Repolarization
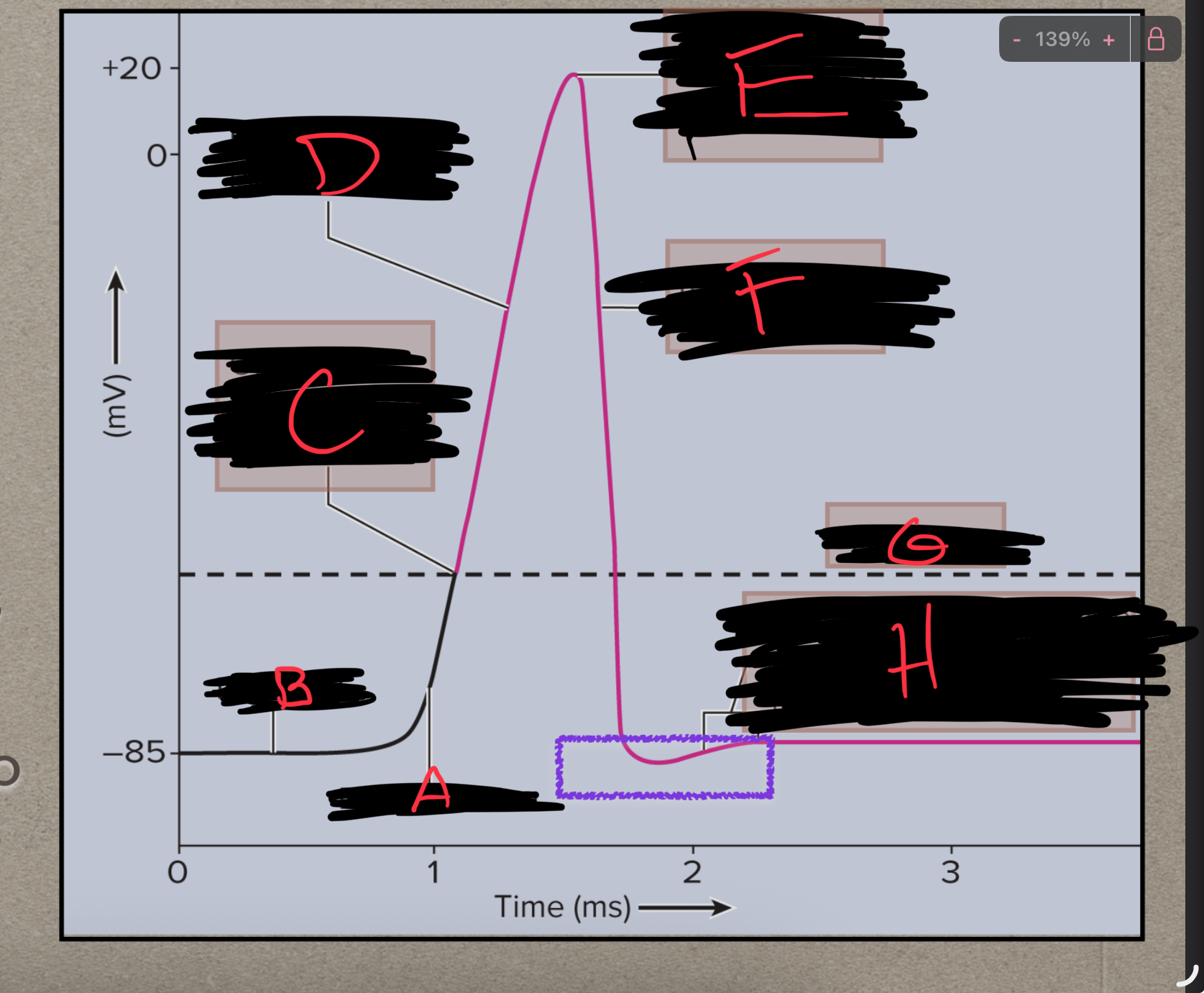
What is G?
Threshold
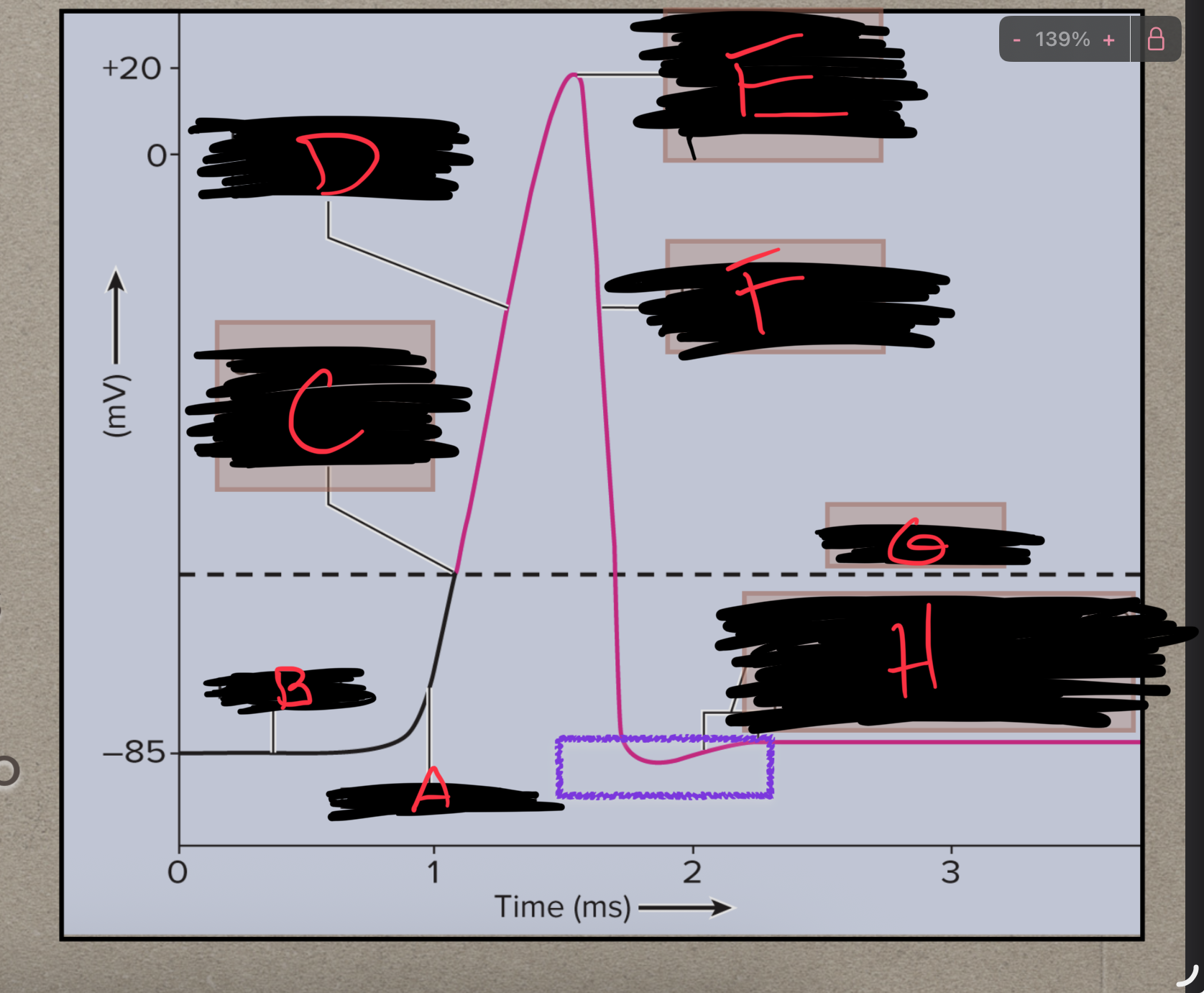
What is H?
Back to resting membrane potential
The location where a motor neuron meets a muscle fiber is called what?
Neuromuscular junction
Presynaptic terminal, synaptic cleft, postsynaptic membrane, what are these?
Structures involved in neuromusclar junction
What is the key neurotransmitter in neuromuscular junction?
Acetylcholine
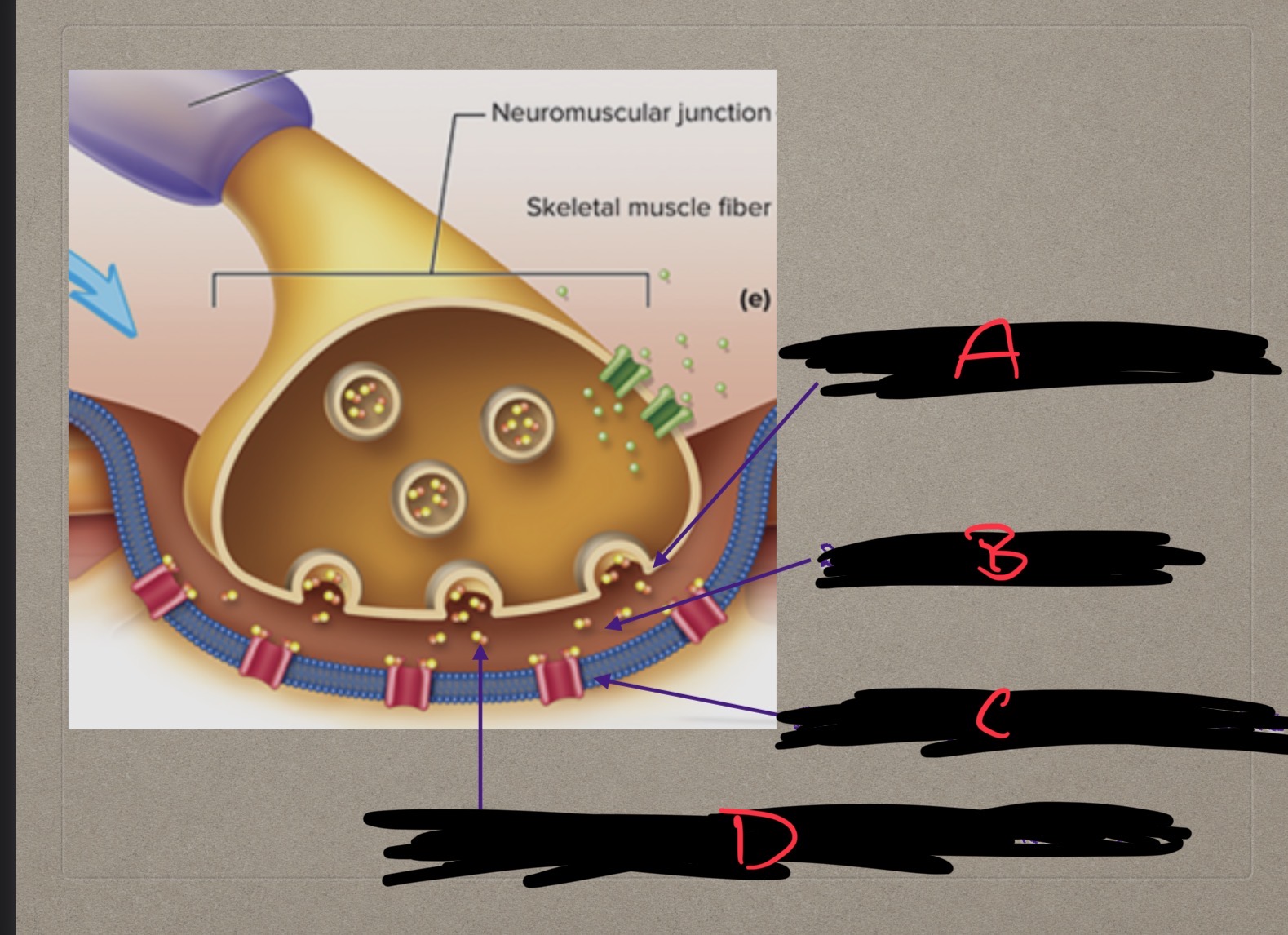
What is A?
Presynaptic terminal
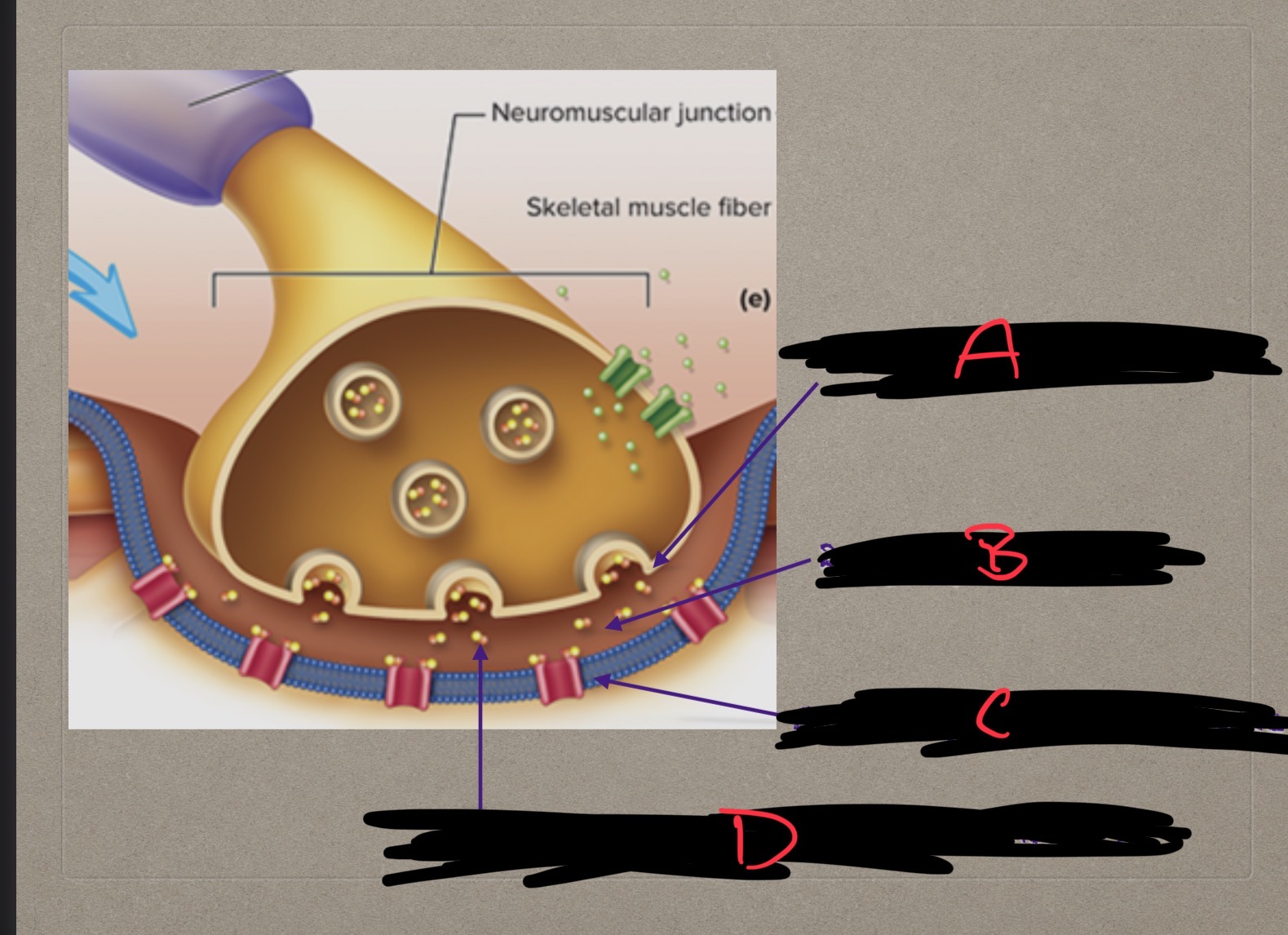
What is B?
Synaptic cleft
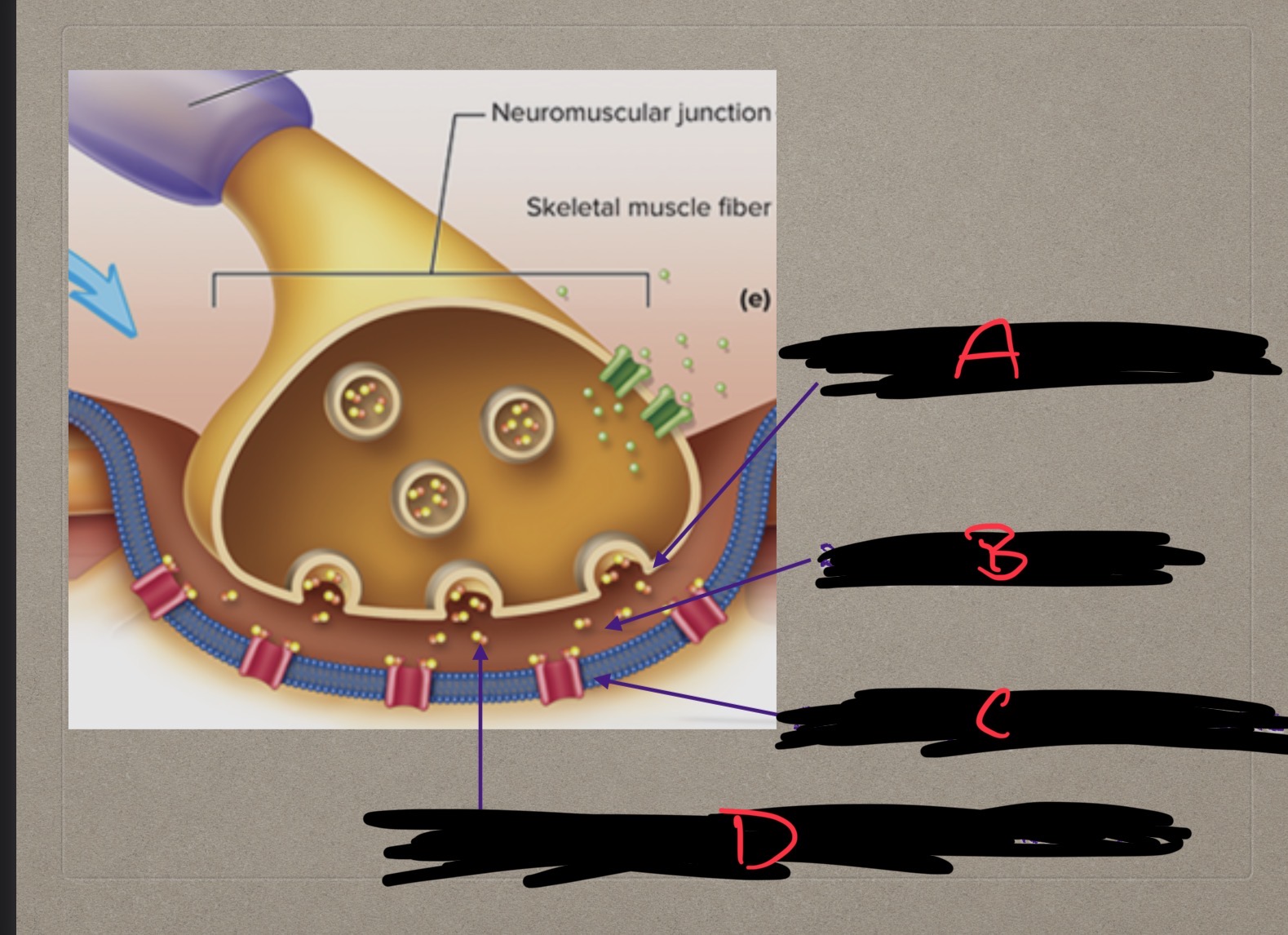
What is C?
Postsynaptic membrane
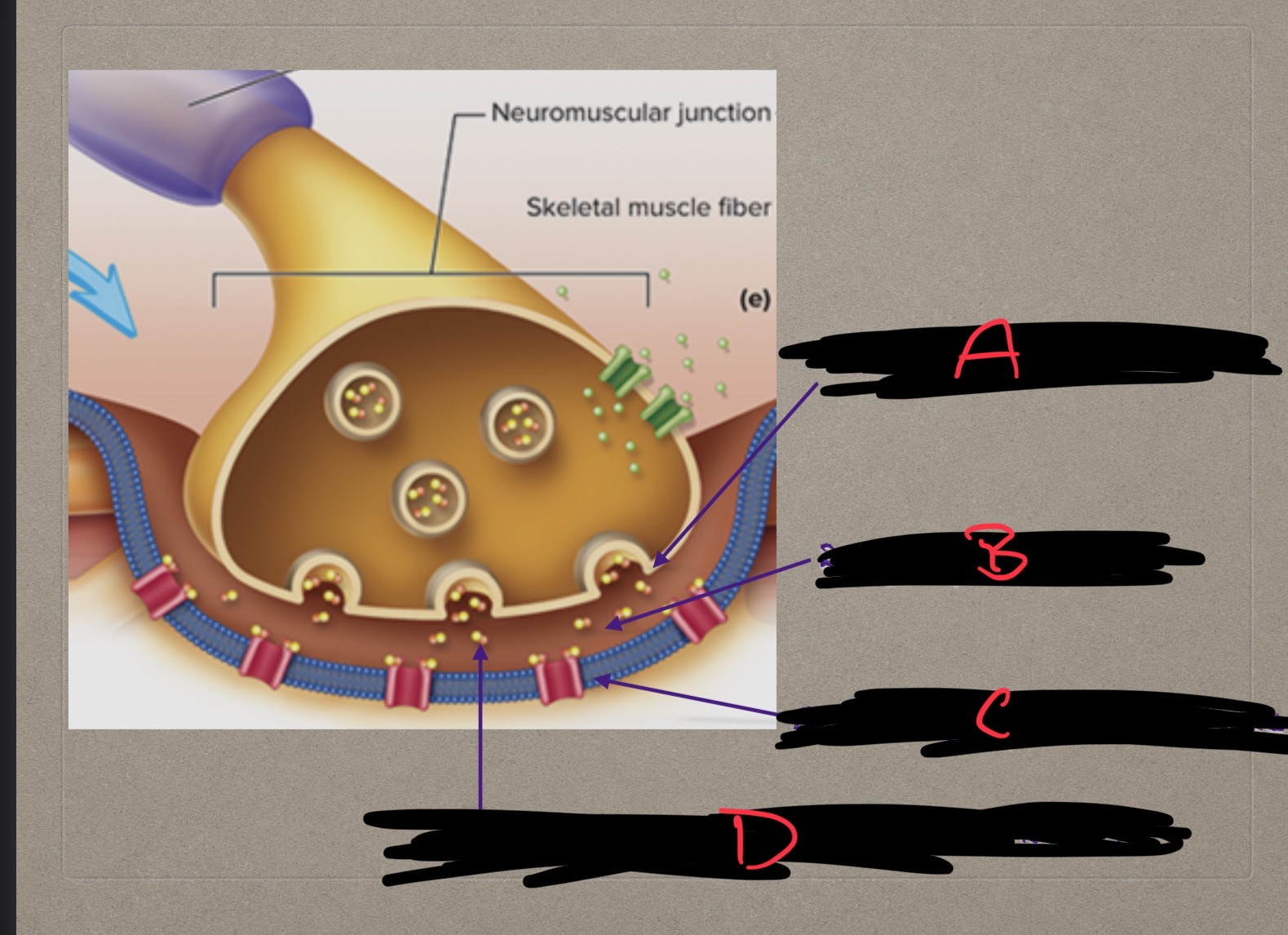
What is D?
Acetylcholine
Action potential → Ca2+ enters neuron → ACh released → ACh binds to muscle receptors → Na+ channels open → muscle contracts, what is this?
Signaling of neuromuscular junction
ACh is broken down by acetylcholinesterase → signal stops → muscle relaxes, what is this?
Stop of neuromuscular junction