Ochem 8A Lab Final Review
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
(Exp 2) Newman Projection
-what is the main purpose?
-How does it work?
Newman Projection is a visualization of conformations of a bond.
-The main purpose is to be able to rotate structures into a staggered and eclipse formation.
-By creating a newman's projection one can see if a steric interaction occurs. The more steric strain the more in higher energy the molecule contains due to repulsion forces of electron clouds.
(Exp 2) Newman Projection
-How do you know what molecule will be lower energy or higher energy
-when comparing between an eclipse and a staggered, the staggered will always be the lowest energy and the eclipse will always be higher in energy.
-when comparing between multiple staggered molecules, anti is always lower in energy than gauche.
-When comparing to multiple eclipse molecules the same idea is in place, bulkier groups closed together will have higher energy than farther apart ones.
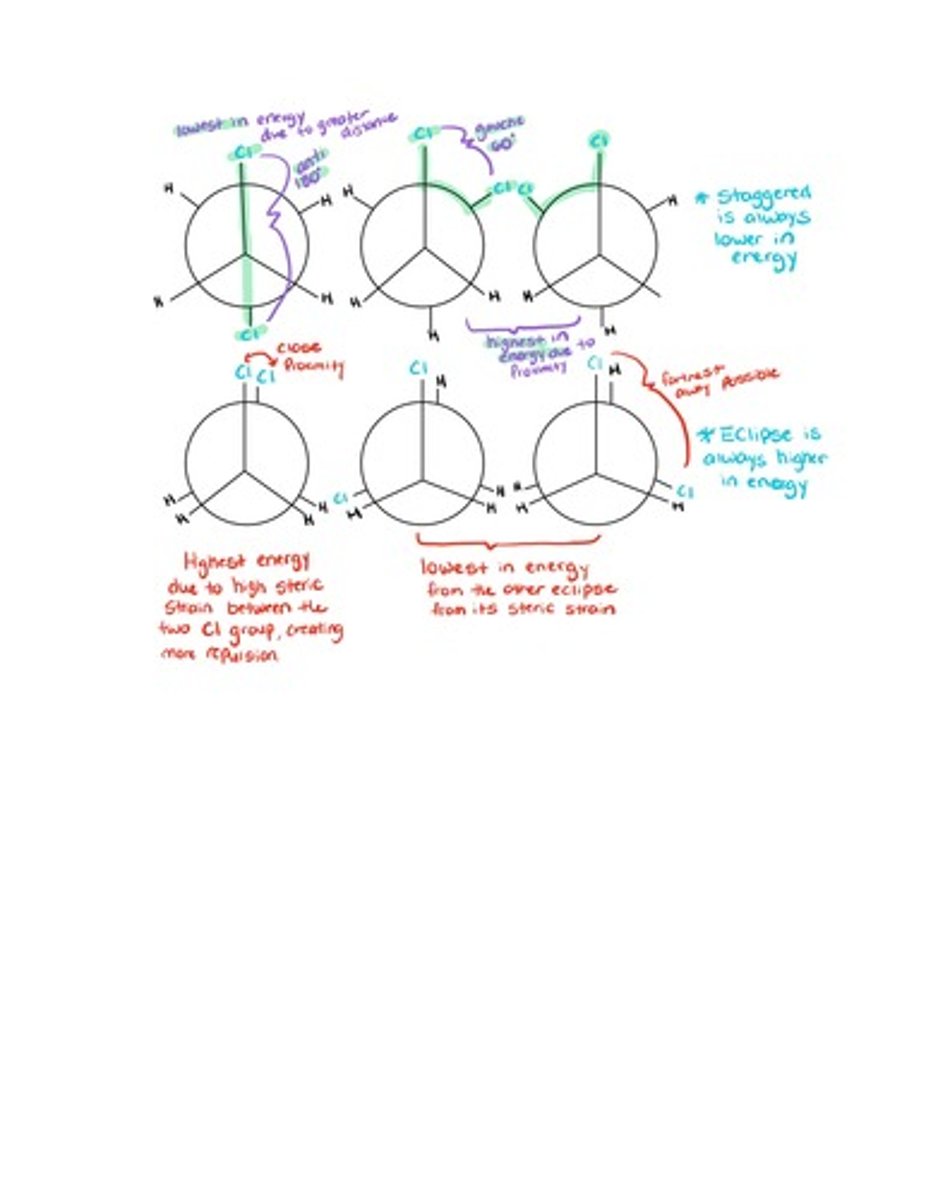
(Exp 2) Cyclohexane Conformations
-what is the main purpose?
-How does it work?
cyclohexane conformation are the different types of conformation that can be adopted by rotating bonds in the ring.
-substituents are either axial or equatorial, axial point up or down and equatorial point outward.
DRAW EXAMPLE OF WHICH IS MORE STBALE IN CYCLOHEXANE
(Exp 3) Extractions and TLC
How to differentiate an aqueous vs organic solvent.
To determine which layer is which, one can simply add distilled water to the funnel. Whichever layer increases in size must be the aqueous layer and the other is the organic layer. At this point the two layers can be separated into their respective beakers.
(exp 3) what is the difference between a polar and non polar molecule?
-polar: unequal sharing of atoms, they tend to have a charge or create a dipole moment.
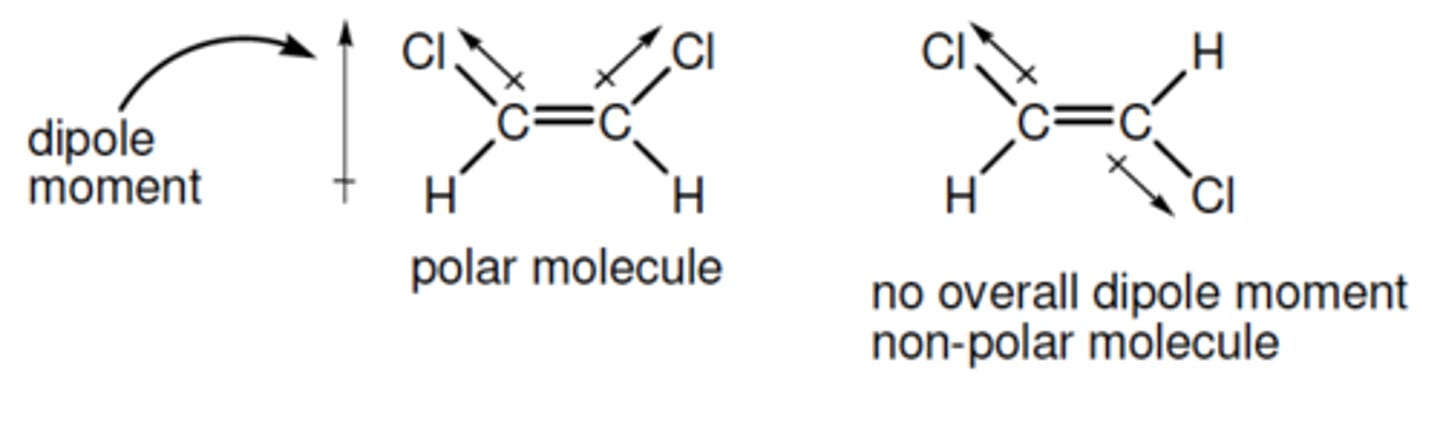
(Exp 3) Where are organic molecules more likely to dissolve in a organic solvent or aqueous solvent?
Organic molecules are more likely going to dissolve in an organic solvent especially non polar ones.
(Ex 3) If you have a mixture of naphthalene and NaCl
-which will dissolve in water?
which will dissolve in hexane?
Since salts tend to dissolve more in aqueous solution or in water it is believes that NaCl should dissolve more in water.
-Since naphthalene is a organic molecule ( Hydrogens and Carbons) it should dissolve in hexane or non polar molecule.
(Ex 3) what is miscibility?
is the ability of two compounds being able to mutually dissolve each other
(Exp 3) What is a solution-Phase extraction?
It is a liquid-liquid extraction.
- two immiscible liquids are put into a separatory funnel and it separates them due to not creating a homogenous mixture.
(Exp 3) What determines which liquid is on top and below in the separatory funnel?
it is based off of density, lower density will be resting on the top and denser liquids will be resting on the bottom. (aqueous solution is usually at the bottom while organic layers are at the top)
(Exp 3) If we add a solid mixture of naphthalene and NaCl, which layer will dissolve which compound?
Since NaCl and naphthalene are mixted together in order to seperate them we have to use a liquid liquid extraction, NaCl is a polar molecule and ionic so it will dissolve in water since it is polar, naphthalene is an organic mixture and will better dissolve in hexane solution. When placed in a separatory funnel it will for two layers and organic layer and aqueous solution, aqueous tend to be denser and are found in the bottom and organic layers tend to be on the top.
(Exp 3) Using Acid-Base Properties to separate using LLE, what is the purpose of this?
Sometimes molecules are so similar in structures that it needs to be using an acid and base to see what it dissolves better in, organic molecules can react to either acid or base and form a salt, then cause be used to determine if it soluble in aqueous or organic layer.
(Exp 3) what are some Acid reactant functional group?(protonate)
-Amines
-Nitrogen in general
(Exp 3) Base-reactive functional group (deprotinate)
-carboxylic acid
-sulfuric acid
-phenols
(Exp 3) What is TLC and what is the main purpose of it?
What are the two phases of TLC?
-TLC is a thin layer of chromatography
-the main purpose of this is it separates compounds based on polarity
-There are two phases a stationary phase and a mobile phase.
-Stationary phase: a thin layer of silica gel and it is polar
-the mobile phase is a mixture with variable polarity
How does TLC work?
the stationary phase is polar and the compounds that are polar will interact
-the mobile phase will move the compound up the TLC plate, the more polar something is the less they move up the TLC, the non-polar compounds move up higher in the TLC plate.
-The distance produced from the baseline to the solvent front is called retention factor (Rf)
(Exp 3) What are hazards posed by aqueous hydrochloric acid?
-burning the skin
-irritate the respiratory system
(Exp 3) What are the hazards for using hexanes?
is flammable and irritates skin and eyes.
(Exp 3) WHat was the point of the experiment?
-to separate dye molecules because of different acid-base reactivity
-The solution phase extraction was used to separate molecules of different acid-base reactivity
(Exp 4) (DQ )If you eluted a TLC of a compound using 80% hexanes / 20% ethyl acetate as the solvent and obtained an Rf value of 0.5. If you changed the solvent system to 50% hexanes / 50% ethyl acetate, how would the Rf value change? Explain why.
By changing the percentage of the mixture we are maving the mixture more polar and ethyl acetate is more polar than hexane. SInce changing the polarity of the mixture, the Rf should be higher
(Ex 4) (DQ) You attempted to separate two dyes by solution-phase extraction and used a TLC to determine if the separation was successful. You ran a TLC using 80% hexanes / 20% ethyl acetate and the fraction from the organic phase remained at the baseline. Can you say that your separation was successful? What might you change to have greater certainty in the success of your separation?
No, the separation was not successful. Probably the most important conclusion of all the theory developed for thin layer chromatography is that the highest degree of resolution in a thin layer occurs in the area around the RF values between 0.3 and 0.4
Testing with other solvents or with another mixing ratio is important to know how the analyses interact with the solvents, in this case using a more polar mixture could work.
(EXP 4 DQ) A mixture of A, B, C and D are dissolved in hexanes. If you extract with aqueous HCl, which compound(s) will be transferred to the aqueous layer? If you extract with aqueous NaOH instead, which compound(s) will be transferred to the aqueous layer?
(Ex 4) Isolation by extraction
You can isolate compounds by extraction
-the way you can do it is by discarding the aqueous layer and drying the organic layer with sodium sulfate and magnesium sulfate to absorb the residual water, and then place it into a rotary evaporation.
(Exp 4) What is the purpose of a rotary evaporation?
it reduces pressure, lowers boiling point and allows the distillation of solvents at room/lower temperature.
(Exp 4) What is a silica gel and what type of interactions may be possible between a silica gel and your compounds?
-Silica gel is made up of small particles of silicon dioxide making the surface polar due to (Si-OH) group, O being the electronegative group.
-
(Exp 4) what are the two most likely ways you will be exposed to organic solvents?
by skin and eye contact and inhaling vapor
(Exp 4) What are the ways you can protect yourself from the solvents?
using PPE such as gloves, googles, and using a fume hood.
(Exp 4)Dichloromethane is a chlorinated solvent what is a hazard associated with it?
it can cause cancer, and it is harmful to inhale, and cause irritation to the skin and eyes.
(Exp 4) What is the purpose of this lab?
isolate by extraction using neutral molecules
-use acid to protonate to form an anionic species in neutral compounds to extract in organic layer.
(Exp 4) (DQ) How would compound(s) in the mixture shown be separated by: ● Dichloromethane and aqueous NaOH
● Dichloromethane and aqueous HCl
(Exp 4) Which molecule would you predict is more reactive with NaOH, acetaminophen, Acetysalicylic acid (Asprin)
(Exp 4) (DQ) Which nitrogen atom in caffeine is most basic? and why?
(Exp 5) What is a boiling point?
Boiling point refers to a liquid gas transition in temperature
(Exp 5) What are intermolecular forces can you think of?
-dipole dipole interaction: polar covalent bond it has to do with electronegativity as well it has a lesser boiling point than hydrogen bonding
-hydrogen bonding: only occuers when hydrogen is bonded to F, O, N, OH and NH have higher boiling points, but a lesser boiling point compared to ionic forces.
-van der waals dispersion (london dispersion: the weakest intermolecular force and the lowest boiling point it is mostly just carbons and hydrogens and noble gases that are bonded through this force.
-ionic forces: charges between atoms and molecules, usually have a higher boiling point.
(Exp 5) What are two hazards posed by MTBE?
-it is flammable especially when heat is present, it can also cause irritation to skin, eyes, and respiratory track
(Exp 5) what are ways you can come into contact with n-butanol?
skin and eye contact also inhaling the vapors.
(Exp 5) What is the greatest hazard posed by distilling flammable solvents? How did you avoid this hazard in
this experiment?
since the solvents and vapors are flammable avoid using flame to avoid ignition.
(Exp 5) what is the purpose of distillation?
-why did you perform distillation to separate the two molecules?
-to separate the compounds based on their boiling point and having a large difference in boiling point allows for the distillation to be simpler
-to be able to seperate them by its boiling point and use the IR spec
(Exp 5) Boiling point is directly related to the strength of the intermolecular forces between each molecule. Describe the three different intermolecular forces that are present in n-butanol, and which intermolecular force is the strongest?
hydrogen bonding id the strongest
-dipole-dipole and disperson forces are the weakest.
(Exp 5) why does n-butanol have a higher boiling point than methyl tert-butyl ether?
n-butanol has the strongest intermolecular force which is hydrogen bonding due to the presence of OH
(Exp 6) Isolation of limonene, How is it possible to isolate limonene from an orange peel?
Steam distillation is used since it can form azeotrope (constant boiling mixture) at a lower temperature. Isolation at a lower temperature prevents decomposition.
How to measure optical rotation?
1,2 = light source, unpolarized
3= polarizing filter
4=polarized light
5=sample
6,7,8= observed rotation
(Exp 6) what is the purpose of isolation of Limonene?
to isolate organic molecule by steam distillation, understanding chiral molecules and optical rotation.
(Exp 6)
What is the greatest hazard posed by using a steam distillation apparatus?
2) If you splash diethyl ether in your eyes, what should you do?
3) We are isolated limonene from a natural source. What hazards are associated with limonene, if any?
1) steam distillation is a burning hazard due to high temperatures
2) use eye wash station and rinse the eyes, notify the TA and seek medical attention
3) it is a flammable liquid, cause skin, eye irritation, can be fatal if swallowed or inhaled.
(exp 7) What is the purpose of the experiment?
to observe reactivity trends between sn1 and sn2, substiturion reaction occurs wirh nucleophile (electron rich) and electrophile (electron deficient)
(Exp 7) What are the characteristic of an sn2 reaction?
-it happens simultaneously (one step)
-nucleophile approaches from backside
(Exp 7) what are the characteristics of an sn1 reaction?
-involves two steps
-leaving group is lost first and then the nucleophile attacks
it creates a crobocation intermediate
z9exp 7) what are some safety hazard of alkyl halides and how to protect yourself?
Alkyl halides are typically considered carcinogens. These act by performing substitution reactions on your DNA. Avoid contract with them by using proper PPE (gloves, lab coat and safety glasses) and conducting the experiment in the fume hood. Gloves are not perfect barriers; if you spill a hazardous chemical on your gloves, remove them, wash your handles and obtain a clean pair. Some alkyl halides are lachrymators - meaning they cause tear production/eye irritation. Keep these in the fume hood at all times to avoid tearing up!
Hexanes and ethyl acetate are miscible solvents?
true
A rotary evaporator (rotovap) removes solvent by using reduced pressure to lower the boiling point of the solvent and remove it by distillation.
true
hexanes are a more polar solvent than ethyl acetate
true
If you add ethyl acetate to hexanes used as an elution solvent, the Rf value measured by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) will decrease.
false
How far should be the bulb of a thermometer go down the distillation head?
just below the branch arm to catch vapor
Which thermometer, the one in the distillation apparatus or the one in the sand bath, should be used to determine the boiling point of your compound(s)?
in the distillation apparatus
Why should you wrap the distillation head with glass wool, cotton or aluminum foil?
to insulate the glass and allow condensation in the condenser to collect sample
If your solvents have close boiling points, what would be the best way to separate them by distillation?
use fractional distillation instead of simple distillation.
An azeotrope is a mixture of compounds that co-distill at the same temperature.
true
A chiral molecule is not superimposable (i.e. identical) on its mirror image
true
If the R enantiomer of a molecule has a +7^o+7o optical rotation, then the S enantiomer will have an optical rotation of -7^o−7o.
true
If you have a mixture of equal parts R and S enantiomers and measure the optical rotation of this mixture, the optical rotation will be zero.
true