Ch. 19: Gene Mutation and DNA Repair, and Recombination
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is a mutation?
a heritable change in the genetic material
What is allelic variation?
the presence or number of different allele forms at a particular locus (locus or loci = place) on a chromosome
What are the positives and negatives of mutations?
On the positive side, mutations are the foundation for evolutionary change needed for a species to adapt to changes in the environment
On the negative side, new mutations are much more likely to be harmful than beneficial to the individual and often are the cause of diseases
What is a point mutation?
a change in a single base pair
What is transition in relation to gene mutations?
a change of a pyrimidine (C, T) to another pyrimidine or purine (A, G) to another purine
What is a transversion is relation to gene mutations?
a change of a pyrimidine to a purine or vice versa
What is a silent gene mutation, how does it alter the amino acids, and its likely effect on protein function?
base substituation mutation, no amino acids are altered, and it has no likely effect on protein function
this is due to the degeneracy of the genetic code
What is a missense gene mutation, how does it alter the amino acids, and its likely effect on protein function?
base substitution gene mutation, 1 amino acid is altered, and it has a neutral or inhibitory effect on protein function (depending on the type of amino acid replaced)
ex) sickle cell disease
What is a nonsense gene mutation, how does it alter the amino acids, and its likely effect on protein function?
base subsititution gene mutation, many amino acids are altered, and it has a negative effect on protein function
base substitutions that change a normal codon to a stop codon
What is a frameshift gene mutation, how does it alter the amino acids, and its likely effect on protein function?
addition/deletion gene mutation, many amino acids are altered, and they have a negative effect on protein function
involves the addition/deletion of a number of nucleotides that is not divisible by three
What is the missense mutation is sickle cell disease?
change in a part of a wild-type beta-blobin gene from a Glu to Val.
What is the effect of a mutation of a promoter on gene expression or phenotype?
may increase or decrease the rate of transcription
up promoter mutations will increase transcription
down promoter mutations will decrease transcription
What is the effect of a mutation of a enhancer/operator site on gene expression or phenotype?
may disrupt the ability of the gene to be properly regulated
What is the effect of a mutation of a 5’-UTR/3’-UTR on gene expression or phenotype?
may alter the ability of mRNA to be translated; may alter mRNA stability
What is the effect of a mutation of a splice recognition sequence on gene expression or phenotype?
may alter the ability of pre-mRNA to be properly spliced
What are examples of gene mutations outside of coding sequences?
mutations in promoters, enhancers/operator sites, 5'-UTR/3'-UTR, splice recognition sequence
What is a wild-type genotype?
the relatively prevalent genotype
What is a foward mutation?
changes the wild-type genotype into some new variation
A wildtype allele ⇀ A Mutant allele
What is a reverse mutation?
also called a reversion, it changes a mutant allele back to the wild-type
A Mutant allele ⇀ A wildtype allele
What are examples of mutations that are described based on their effects on the wild-type phenotype?
deleterious mutations, beneticial mutations, conditional
What are deleterious mutations?
mutations that decrease the changes of survival
the most extreme version of this mutation is called lethal mutations.
What are beneficial mutations?
mutationst that enhance the survival or reproductive success of an organism (depending on the environment)
What are conditional mutations?
mutations that affect the phenotype only under a defined set of conditions (such as temperature sensitive mutations)
What is a chromosomal breakpoint?
the site of breaking and rejoining during chromosomal rearrangement
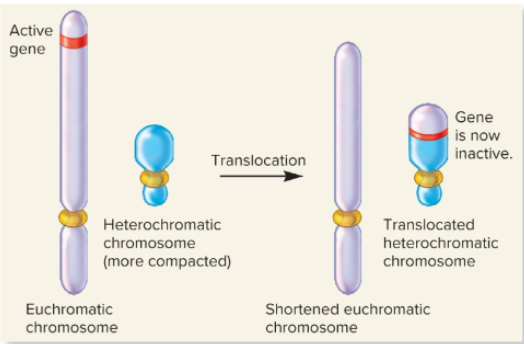
What is the position effect during changes in chromosome structure?
a gene may be left intact, but its expression may be altered because of its new location
What are the causes of position effects?
movement to a position next to regulatory sequences
movement to a heterochromatic region
What picture shows a position effect due to regulatory sequences?
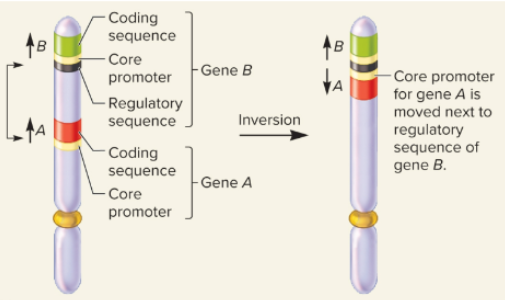
What picture shows the position effects due to translocation to a heterochromatic chromosome?
What do geneticists classify animals cells into?
germ-line cells and somatic cells
What are germ-line cells?
Cells that give rise to gametes such as eggs and sperm
What are somatic cells?
All other cells minus germ-line cells.
What are germ-line mutations?
mutations that occur directly in a sperm or egg cells, or in one of their precursor cells
What are somatic mutations?
mutations that occur directly in a body cell that is not part of the germ-line
What are spontaneous mutations?
mutations that occur spontaneously by underlying causes within the cell
What do spontaneous mutations result from?
abnormalities in cellular/biological processes (errors in DNA replication)
What are induced mutations?
mutations caused by environmental agents, also known as mutagens, that alter DNA structure. (can be chemical/physical agents)
What are the three types of chemical changes that cause spontaneous mutations?
depurination, deamination, oxidative damage
What is depurination?
the removal of a purine (G or A) which an apurinic site due to the unstable covalent bond between deoxyribous and a purine base.
Fortunately, these apurinic sites can be repaired, although if the repair system fails a mutation may arise when DNA polymerase adds a random base during DNA replication.
What is deamination?
the removal of an amino group from the cytosine base.
DNA repair enzymes can recognize uracil as an inappropriate base in DNA and remove it, however, if the repair system fails, a C-G to A-T mutation will result during subsequent rounds of DNA replication.
What is deamination of 5-mathylcytosine?
where 5-methylcytosine can be deaminated into thymine, a normal constituent of DNA
repair enzymes cannot determine which of the two bases on the two DNA strands is the incorrect base, so, methylated ccytosine bases tend to create hot spots for mutations.
What is oxidative stress?
an imbalance between the production of ROS (reactive oxygen species) and an organism’s ability to break them down using enzymes and antioxidants.
this may lead to DNA damage and mutation
Which of the following does NOT cause a frameshift mutation?
5'-ATTTCGGGTTAA-3' To 5'-ATTTGGTTAA-3’ (2 base deletion)
5'-ATTTCGGGTTAA-3' To 5'-ATTTAA-3’ (6 base deletion)
5'-ATTTCGGGTTAA-3' To 5'-ATTTCTAA-3’ (4 base deletion)
5'-ATTTCGGGTAA-3' To 5'-ATTTTTCGGGTAA-3’ (2 base addition)
5'-ATTTCGGGTTAA-3' To 5'-ATTTAA-3’ (6 base deletion)
This is because a frameshift mutation involves the addition or deletion of a number of nucleotides that is divisible by three
A point mutation occurs in the middle of the coding sequence for a gene. Which type of mutation, silent, missense, and nonsense, would be most likely to disrupt protein function?
A missense mutation most likely disrupts protein function because it would cause an amino acid change.
A silent mutation most likely disrupts protein function because it would cause the protein to be much shorter.
A nonsense mutation most likely disrupts protein function because it would cause an amino acid change.
A nonsense mutation most likely disrupts protein function because it would cause the protein to be much shorter.
A nonsense mutation most likely disrupts protein function because it would cause the protein to be much shorter.
A gene mutation changes a base pair from A:T to G:C. This change causes a gene to encode a truncated protein that is nonfunctional. A bacterial cell carries this mutation cannot survive at high temperatures. Pick a correct list of the genetic terms that best describes this type of mutation.
A→G
T→C
At the DNA level: A transversion/Its effect on the amino acid sequence: A missense mutation/Its effect on phenotype: A beneficial mutation
At the DNA level: A deletion/Its effect on the amino acid sequence: A frameshift mutation/Its effect on phenotype: A lethal mutation
At the DNA level: A transition/Its effect on the amino acid sequence: A silent mutation/Its effect on phenotype: A conditional mutation
At the DNA level: A transition/Its effect on the amino acid sequence: A nonsense mutation/Its effect on phenotype: A conditional mutation
At the DNA level: A transition/Its effect on the amino acid sequence: A nonsense mutation/Its effect on phenotype: A conditional mutation
Methylated cytosine bases tend to produce hotspots for spontaneous mutations. Which of the following mutations is typically observed at a C:G base pair in which the cytosine is methylated?
C:G ➔A:T
C:G ➔G:C
C:G ➔T:A
C:G ➔CC (one base insertion)
C:G ➔A:T
What are mutagens?
agents that later the structure of DNA and thereby cause mutations
Why is the pubic concerned about mutagens?
they are often involve in cancer and can cause gene mutations that may have harmful effects in future generation
What can mutagens be classified into?
chemical and physical mutagens
What ways can mutagens alter DNA structure?
base modifiers, intercalating agents, base analogues
How do base modifiers alter DNA structure?
some covalently modify base structure and other disrupt pairing by alkylaing bases
ex) nitrous acid (HNO2), which replaces amino groups with keto groups, changing sytosine to uracil and adenine to hypoxanthine
ex) some chemical mutagens disrupt the appropriate pairing between nucleotides by alkylating bases within the DNA
How do intercalating agents alter DNA structure?
directly interferes with replication process
they have a flat planar structure which distorts the helical structure of DNA. When DNA replication occurs, the daughter strand may contain single-nucleotide additions and/or deletion resulting in frameshifts
ex) acridine dyes, proflacin, ethidium bromide
How do base analogues alter DNA structure?
incorporate into DNA and disrupt structure
ex) 5-bromouracil) is a thymine analogue that can be incorporated into DNA instead of thymine. it can pair w/ guanine/adenine.
What physical mutagens alter DNA structure?
ionizing radiation (x-rays, gamma rays)
has a short wavelength, high energy and can penetrate deeply into molecules creating free redicals; which causes, base deletions, oxidized bases, single nicks in DNA strands, cross-linking, chromosomal breaks.
nonionizing radiation (UV light)
uses less energy, can penetrate as deeply, and causes the formation of cross-linked thymine dimers
What are mutation rates?
the likelihood that a gene will be altered by a new mutation
What is mutation frequency?
the number of mutant genes divided by the total number of genes in a population.
What test is used to evaluate mutagenicity?
Ames Test
uses strains of salmonella typhimurium that cannot synthesize the amino acid histidine (due to mutations).
a second mutation may occur, thereby restoring the ability to synthesize histidine
The ames test monitors the rate at which this second mutation occurs
What is the multi-step process for DNA repair?
An irregularity in DNA structure is detected
The abnormal DNA is removed
Normal DNA is synthesized
What is direct repair?
the reversal of covalent modifications of nucleotides by specific enyzmes
What does photolyase do during DNA repair?
it repairs thymine dimers by spliting the dimers and restoring the DNA to its original condition. It uses energy of vidible light for photoreactivation
What does alkytransferase do during DNA repair?
it repairs alkylated bases by transfering the mathyl or ethyl group from the base to a cysteine side chain within the alkyltransferase protein, which inactivates the alkyltransferase.
What does base excision repair (BER) do?
it removes a damaged/abnormal bases, such as uracil; 3-methyladenine; 7-methylyguanine, through enzymes called DNA N-glycosylases.
What are DNA N-glycosylases?
these enzymes can recognize an abnormal base and cleave the bond between it and the sugar in the DNA
What is nucleotide excision repair (NER)?
a repair sysmte that repairs DNA damage of thymine dimers, chemically modified bases, missing bases, some types of crosslinks
Where is nucleotide excision repair (NER) found?
is found in all eukaryotes and prokaryotes, although the system has been better understood in prokaryotes
What key proteins are foud in the NER system?
UvrA, UvrB, UvrC and UvrD
Named as such because they are involved in Ultraviolet light repair of pyrimidine dimers
They are also important in repairing chemically damaged DNA
What human genetic diases are due to defects in NER?
xeroderma pigmentosum and cockayne syndrome
all involve an increased sensitivity to sunlight
What is the mismatch repair system?
the system that kicks in when an incoorect base is added to the growing strand by mistake during DNA replication and DNA polymerases 3’ to 5’ proofreading ability fails to detect base mismatches and fix them
What proteins are involves in the mismatch repair system in E. coil?
MutL, MutH, and MutS detect the mismatch and direct its removal from the newly made strand (nonmethylated)
the proteins are named Mut because their absence leads to a much higher mutation rate then normal.
What repairs double-strand breaks in DNA?
homologous recombination repair (HRR) and nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ)
What is the process of repair of a DNA double-strand break via HRR?
the unbroken strands (sister chromatids) are used as templates to synthesize DNA
since sister chromatids are genetically identica, homologous recombination can be an error-free repair mechanism
HRR occurs during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle in eukaryotes
What is the repair process of a double-strand break via NHEJ?
broken ends are recognized by end-binding proteins (formation of crossbridge)
processing may result in deletion of a small region (not error free)
does NOT occur in E. coil, occurs during G1 phase of cell cycle.
What happens when a a replicative DNA polymerase encounters a damaged region?
it is swapped for a translesion synthesis (TLS) polymerase, which replicates through DNA lesions.
A negative consequence of translesion-replicating polymerases is their low fidelity (causes mutations at a higher rate during replication)
For an Ames test, two different His- strains are available; one detects base substitutions (His-A) and the other frameshift mutations (His-B). After culturing these strains with ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) separately, we plated cells on media lacking histidine. Which of the following correctly predicts the results from this experiment?
Compared to untreated control groups, the number of revertant colonies should be increased for His-B strain (frameshift mutations) but not for His-A strain (base substitutions).
Compared to untreated control groups, the numbers of revertant colonies should be increased for both His- strains.
The number of revertant colonies should not be increased for either of His- strains even after treatment with this chemical.
Compared to untreated control groups, the number of revertant colonies should be increased for His-A strain (base substitutions) but not for His-B strain (frameshift mutations).
Compared to untreated control groups, the number of revertant colonies should be increased for His-A strain (base substitutions) but not for His-B strain (frameshift mutations).
In E. coli, a methyltransferase enzyme encoded by the dam gene recognizes the sequence of 5'-GATC-3' and attaches a methyl group to the nitrogen at position 6 of adenine. E. coli strains that are missing the dam gene are known to have higher rates of spontaneous mutations than wild-type strains. Why?
This is because MutS is unable to recognize the parental strand.
This is because MutS is unable to recognize the daughter strand.
This is because these strains are unable to recognize the daughter strand as a repair template to remove incorrect bases in the parental strand during mismatch repair.
This is because these strains are unable to recognize the parental strand as a repair template to remove incorrect bases in the daughter strand during mismatch repair
This is because these strains are unable to recognize the parental strand as a repair template to remove incorrect bases in the daughter strand during mismatch repair
Depurination creates an apurinic (AP) site. If not repaired, it can cause a base substitution during DNA replication (see Fig. 19.7). Which of the following may repair AP sites prior to DNA replication?
Photolyase
Base excision repair
Mismatch repair
Non-homologous end joining
Base excision repair