
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
What is small bowel obstruction associated with?
Dilated bowel loops proximal to site of obstruction
What are the symptoms for a patient with a SB obstruction?
Epigastric pain
Distention
What are the ultrasound findings of a small bowel obstruction?
Tubular or round echo-free
6% fluid-filled
Compressibility of bowel
What is the differential diagnosis for a SB obstruction?
Appendicitis
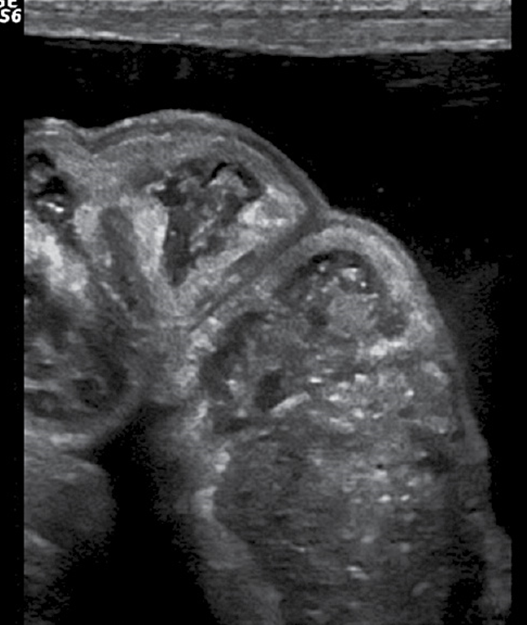
What is this image showing?
SB obstruction / dilation
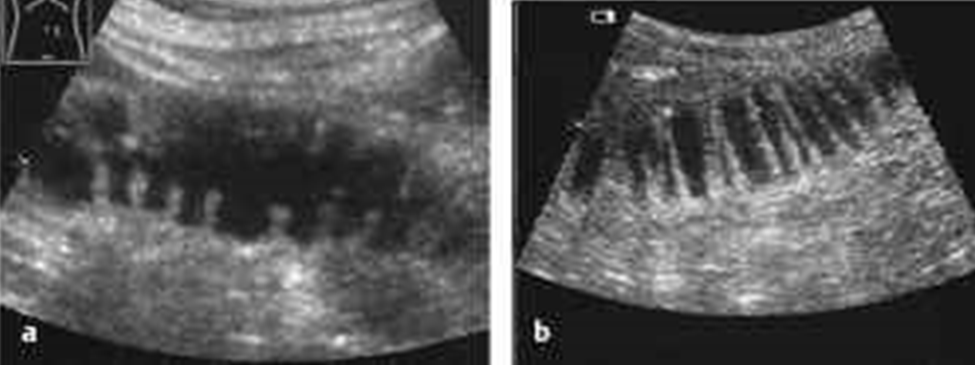
What is this image showing?
SB obstruction / dilation
Fluid filled loops are not ALWAYS associated with obstruction. Could be from:
Over hydration
Gastroenteritis
Paralytic ileus
Dilated, fluid-filled loops without peristalsis
Sonographer needs to demonstrate …. in relation to fluid-filled loops
Pliability & compressibility of the bowel wall
How is Acute Appendicitis caused?
From obstruction & inflammation leading to ischemia of vermiform appendix
Acute Appendicitis results in: (6)
Edema
Compromised vascular supply – necrosis
Increase in bacteria – infection & inflammation
Rupture (perforation)
Abscess
Peritonitis
During Acute Appendicitis, the lumen becomes obstructed from:
Fecal material – fecalith
Appendicolith
Inflammation
Mucocele
Foreign body
Carcinoma of cecum
Kinking
What are the symptoms for Acute Appendicitis?
RLQ pain
Rebound tenderness over McBurney’s point
N, V, D
Anorexia
Fever
What lab work may demonstrate Acute Appendicitis?
A high WBC = leukocytosis
Acute Appendicitis is more common at _______ _____
Younger ages
What are the differential diagnoses for Acute Appendicitis?
Acute gastroenteritis
Mesenteric lymphadenitis in children
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
Mittelschmerz
Inflammation of Meckel’s diverticulum
Regional Enteritis
Right ovarian cyst or torsion
What lab work is done to check for Acute Appendicitis?
CBC
Checking for elevated WBC = leukocytosis
Pregnancy test (if female in reproductive age)
Thorough history & examination necessary
What is the gender and age of people that are at a high risk of misdiagnosis of acute appendicitis?
Women in their 20-40s
In what group patients is Acute Appendicitis hard to diagnose?
Obese
Older
The appendix is found _______
Retrocecal
What is the normal outside diameter of the appendix?
< or = 6mm
What is the normal wall measurement of the appendix?
< or = 2-3mm
What is the normal length of the appendix?
1-9 inch (average 3 in.)
What should you identify in a normal appendix?
Blind end of the appendix
If it is compressible
Graded compression over McBurney’s point
When looking at the appendix you should image with what transducer(s)?
Curvilinear
High frequency linear
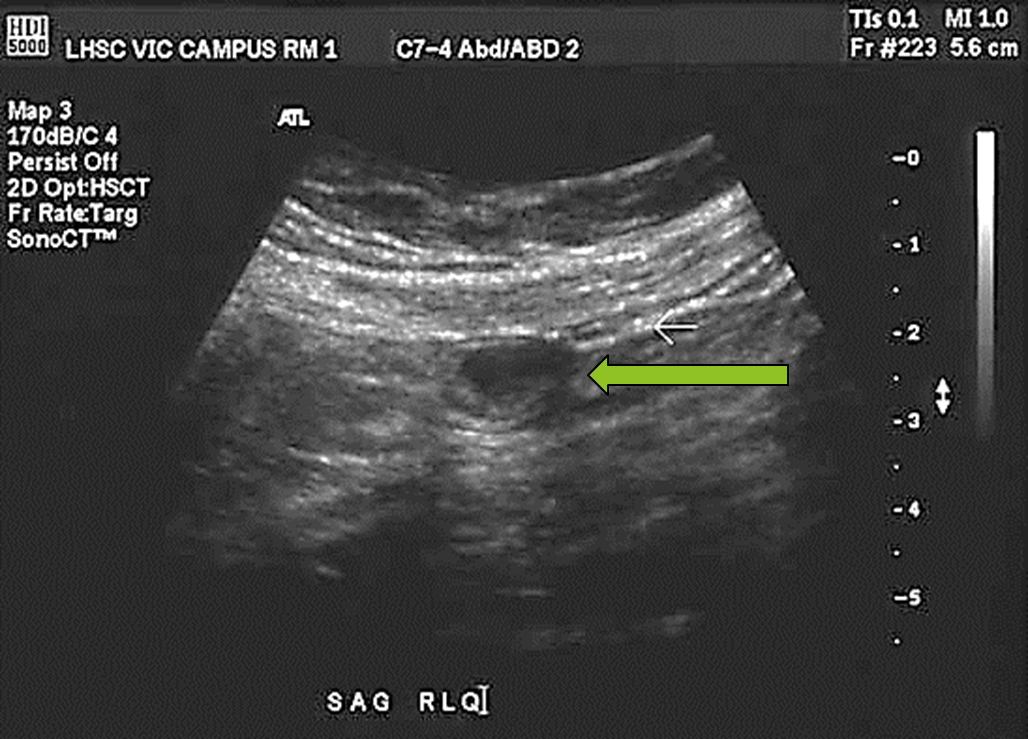
This is a transverse view of the appendix, but the location of the transducer is…
Longitudinal to the body
How might you identify an Inflamed Appendix/Appendicitis?
Target lesion in RLQ
Thickening of bowel wall
From edema
Noncompressible mass
Lack of peristalsis
Appendicolith (calcifications)
Hyperemic
May be fluid or abscess collection
Evaluate quadrants looking for free fluid
What is the abnormal diameter for a appendix?
> 6mm
What is the abnormal wall thickness?
>2mm
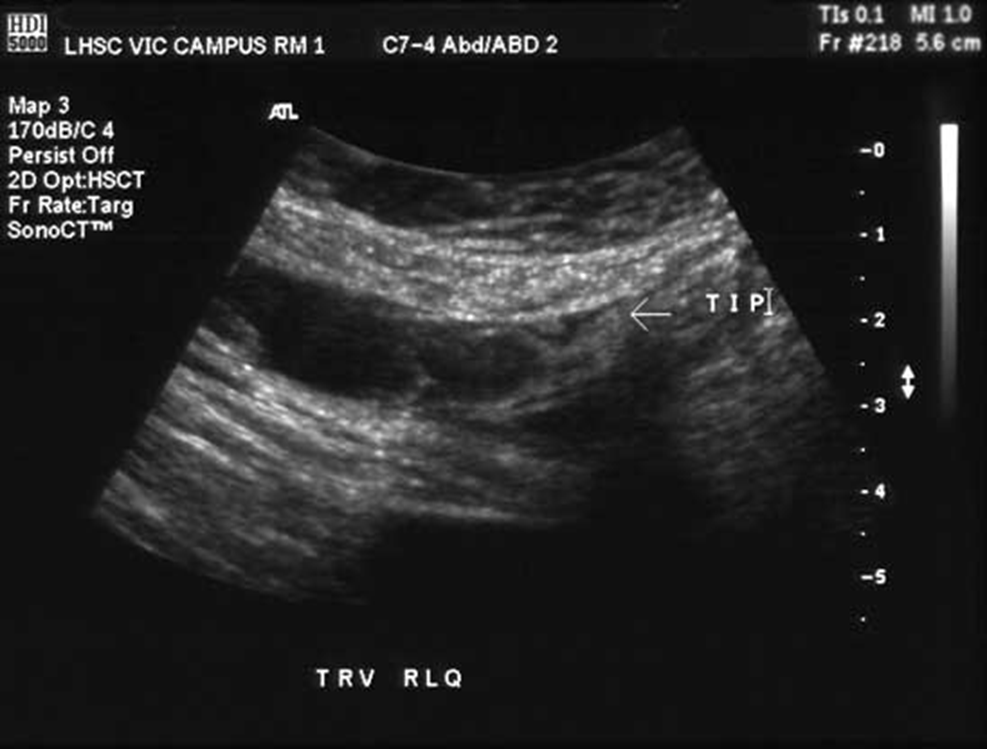
What is this image showing?
Fluid within the appendix
What is Mucocele?
(Rare pathology) Gross enlargement of appendix due to accumulation of mucoid substance within lumen
What are the 3 classifications of Mucocele?
Mucosal Hyperplasia
Mucinous Cystadenoma
Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma
What is Mucosal Hyperplasia?
Over growth
What is Mucinous Cystadenoma?
Cystic benign legion or neoplasm causing an enlargement
What is Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma?
Malignant tumor in appendix
What are the symptoms for Mucocele?
RLQ pain
25% are asymptomatic
What lab work can be done to check for Mucocele?
CBC
Increased WBC
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
CEA (may be elevated) – cancer marker
What are the ultrasound findings for Mucocele?
Cystic mass, Well-defined hypoechoic mass with fine internal echoes
Complex mass with high-level echoes
Calcification possible
What is the differential diagnosis for mucocele?
Appendicitis
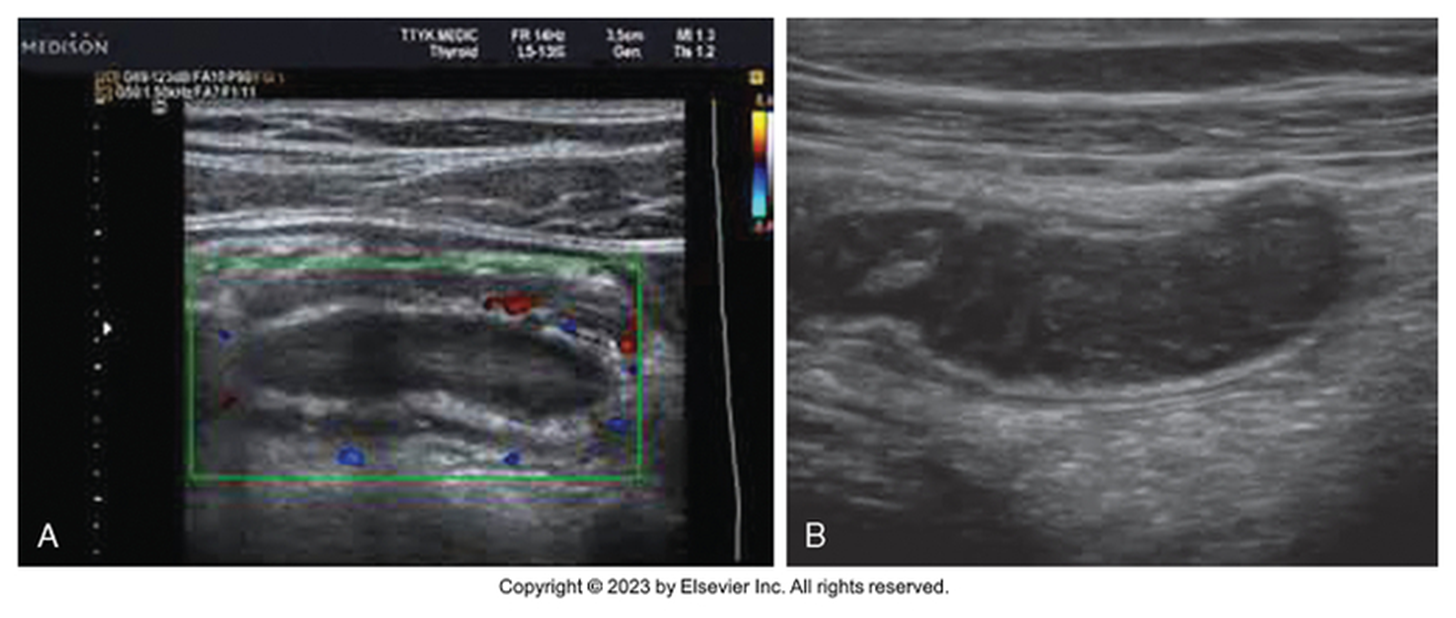
What is this image showing?
Mucocele
Primary adenocarcinomas are ______, but may present as ________ _______ with perforation
RARE, acute appendicitis
Mucocele is a malignant or benign mass?
Benign
What is Meckel’s Diverticulum?
Pouchlike herniation in the distal ileum
What are the symptoms for Meckel’s Diverticulum?
Obstruction
Rectal bleeding
Tenderness
Diverticular inflammation
Elevated WBC
What is the differential diagnosis for Meckel’s Diverticulum?
Appendicitis
What is Crohn’s Disease?
Regional Enteritis – regional inflammation
Where does Crohn’s Disease normally affect?
The terminal from the ileum to the cecum
What are the symptoms for Crohn’s Disease?
Diarrhea
Fever
RLQ pain
What are the ultrasound findings for Crohn’s Disease?
Symmetrically swollen bowel
Uniformly increased wall thickening
Rigidity to pressure from transducer
Absent or sluggish peristalsis
What are the differential diagnoses for Crohn’s disease?
Appendicitis
Meckel’s Diverticulum
Diverticulitis
Is Crohn’s disease a malignant or benign disease?
Benign
Is a Lymphoma tumor benign or malignant?
Malignant
What is Lymphoma?
Multiple nodules/masses, will most likely involve mesenteric vessels
What age does Lymphoma normally occur at?
65 years of age
What is the most common tumor of the GI tract in children? And in what ages?
Lymphoma
< 10 years of age
What are the symptoms for Lymphoma?
Intestinal blood loss
Weight loss
Anorexia
Abdominal pain
Intestinal obstruction
Palpable mass
What are the ultrasound findings of Lymphoma?
Large discrete intraperitoneal mass
Target pattern
Lumen may be dilated with fluid
Frequently involves:
Mesenteric vessels & nodes
Pseudokidney or hydronephrotic pseudokidney
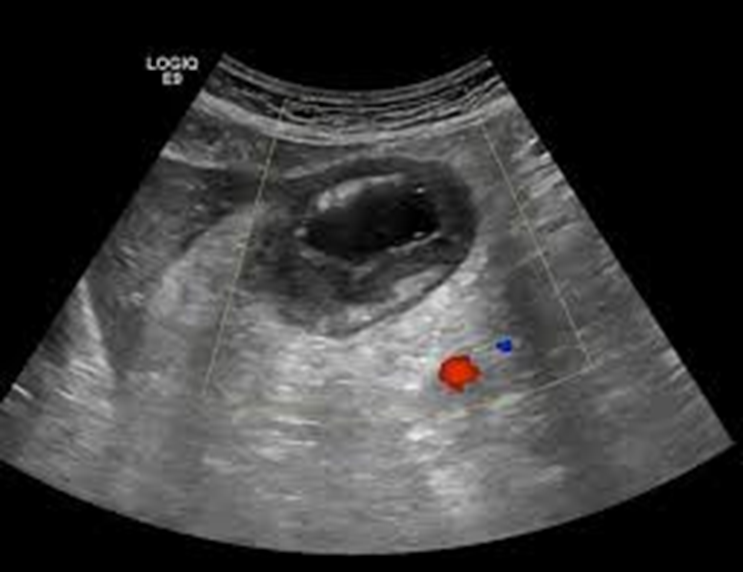
What is this image showing?
A lymphoma
What are the differential diagnoses for a Lyphoma?
Pseudokidney
Leiomyosarcoma
What is a Leiomyosarcoma?
Rare, malignant smooth muscle tumor
______ of primary small bowel tumors are _____________
10%, Leiomyosarcoma
Leiomyosarcoma tumors affect what age of people?
50-60s
Leiomyosarcoma are found more commonly in ______ children who are _____ years of age
Male, 8
What are the symptoms for Leiomyosarcoma?
Abdominal pain
Palpable mass
What are the ultrasound findings of Leiomyosarcoma?
Large, solid mass
Containing necrotic areas anterior to solid viscus
Color Doppler – demonstrate low-velocity flow in mass
What is the differential diagnosis for Leiomyosarcoma?
Lymphoma