Bot-Lec (Sem-1) - Chapter 3: The Evolution of Populations and Species
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
species
a group of organisms that can reproduce naturally with one another and create fertile offspring
gene pool
all the alleles of all the genes in a freely interbreeding population
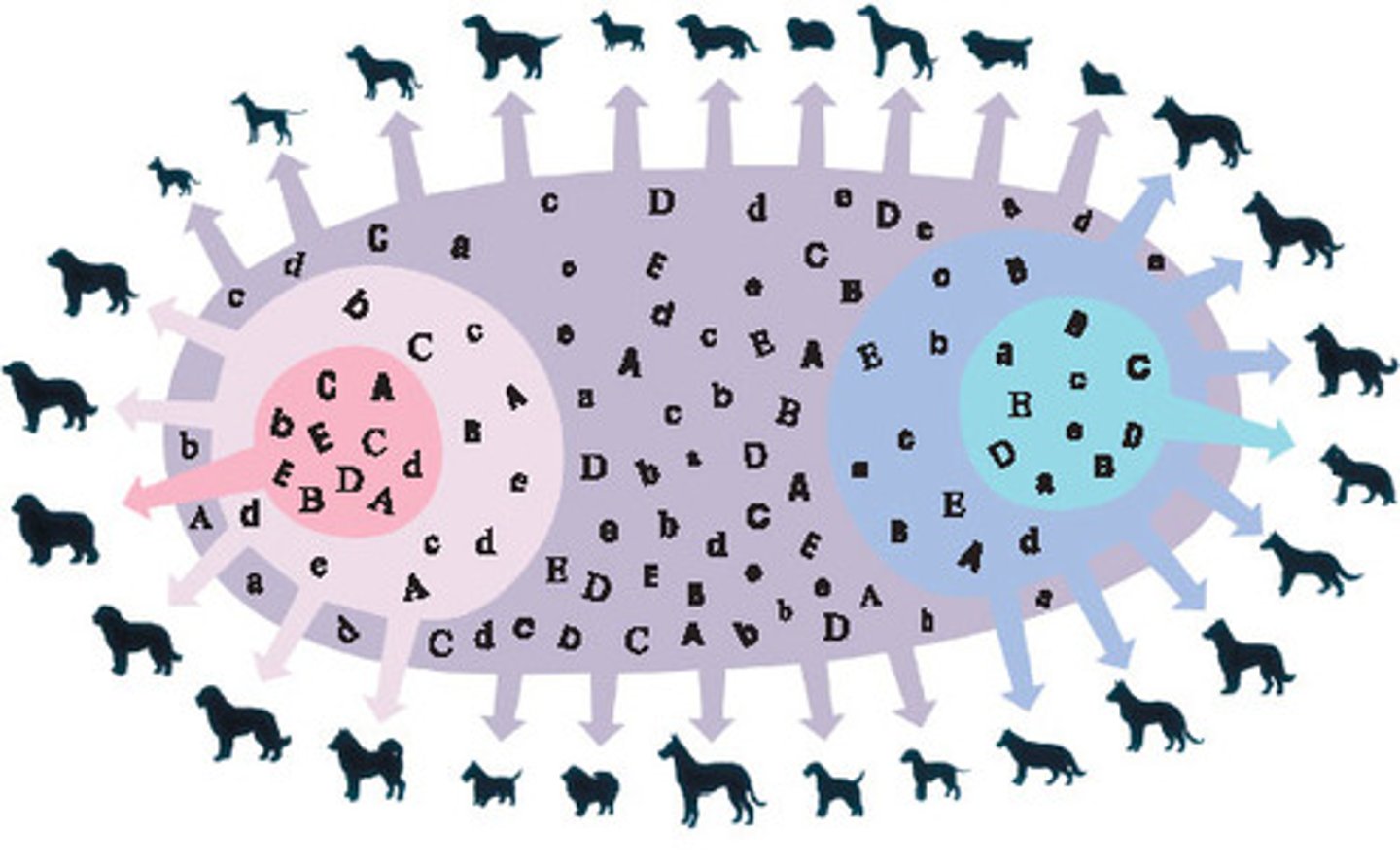
alleles
different versions of a gene
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism; an organism's complete set of genes; the alleles, or variant forms of a gene, that are carried by an organism
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
mathematical prediction that allele and genotype frequencies do not change from generation to generation in the absence of microevolutionary processes; shows that if the population is large, the process of inheritance by itself does not cause changes in allele and genotype frequencies; tells us what to expect when a sexually reproducing population is not evolving
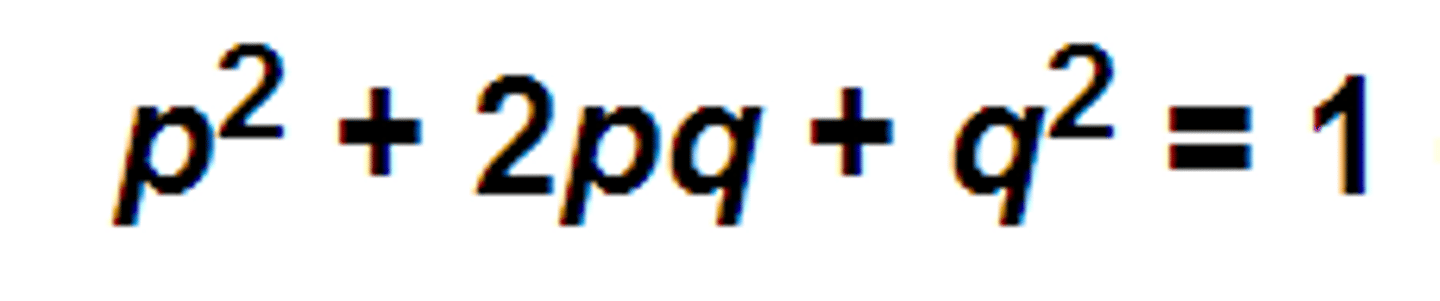
microevolution
small-scale evolutionary changes caused by changes in allele or genotype frequencies in a population over a few generations
mutation
(alteration in a cell's genetic material) is the source of new alleles in a gene pool
Pereskia sacharosa
leaf cactus
Ferocactus wislizenii
fishhook cactus

genetic drift
change in frequency of an existing gene variant in the population due to random chance
gene flow
movement of alleles between local populations due to migration and subsequent interbreeding
natural selection
the principle that, among the range of inherited trait variations, those contributing to reproduction and survival will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
no selection
all equal in survival and reproduction, phenotype does not affect survival; normal distribution
stabilizing selection
trims off extreme phenotypes, variation about the mean is reduced
directional selection
shifts the curve in one direction, changing the average value of the character
disruptive selection
trims off intermediate phenotypes, results in two or more peaks
biological species concept
concept that a species consists of one or more populations whose members can interbreed to produce fertile offspring and cannot interbreed with individuals of other species
liger
lion + tigress; stronger bite force than tigon due to larger head
tigon
tiger + lioness
reproductive isolation
situation in which reproductive barriers prevent members of a species from successfully interbreeding with members of another species; timing or structure
temporal isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations reproduce at different times
nocturnal
active at night
diurnal
active during the day
plasticity
ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to different environments
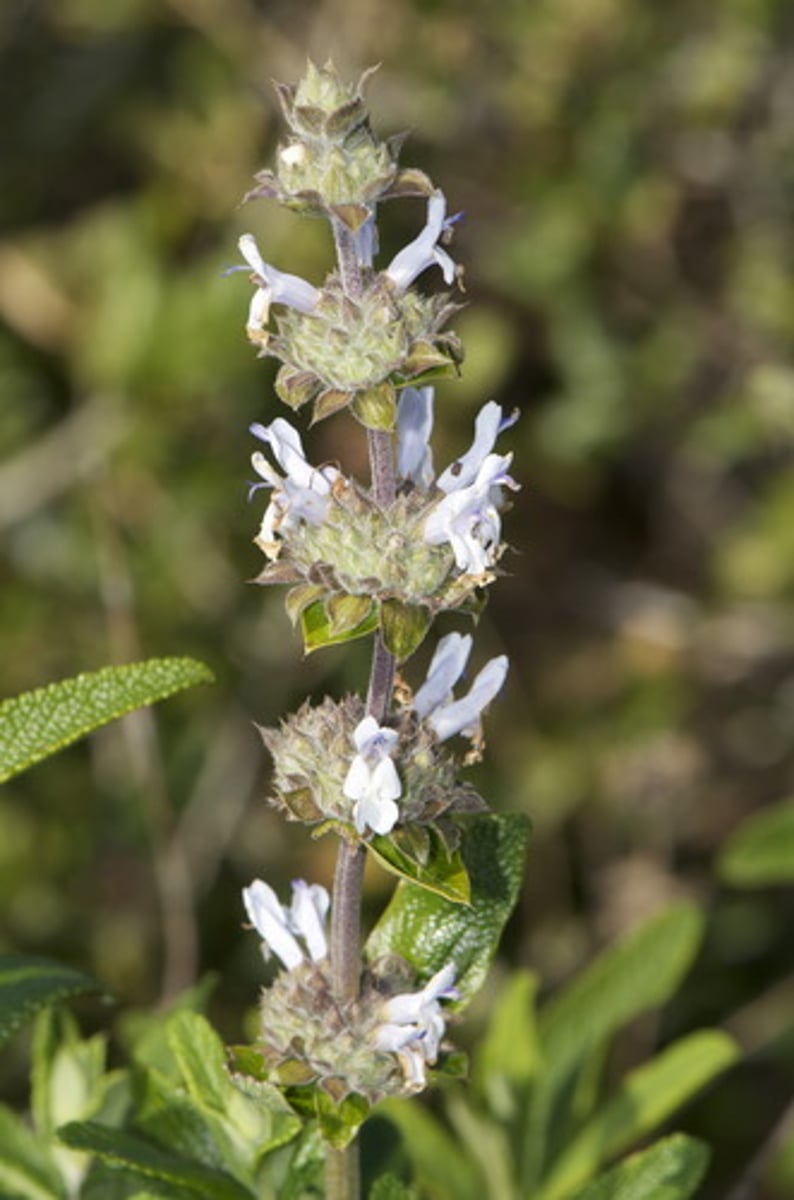
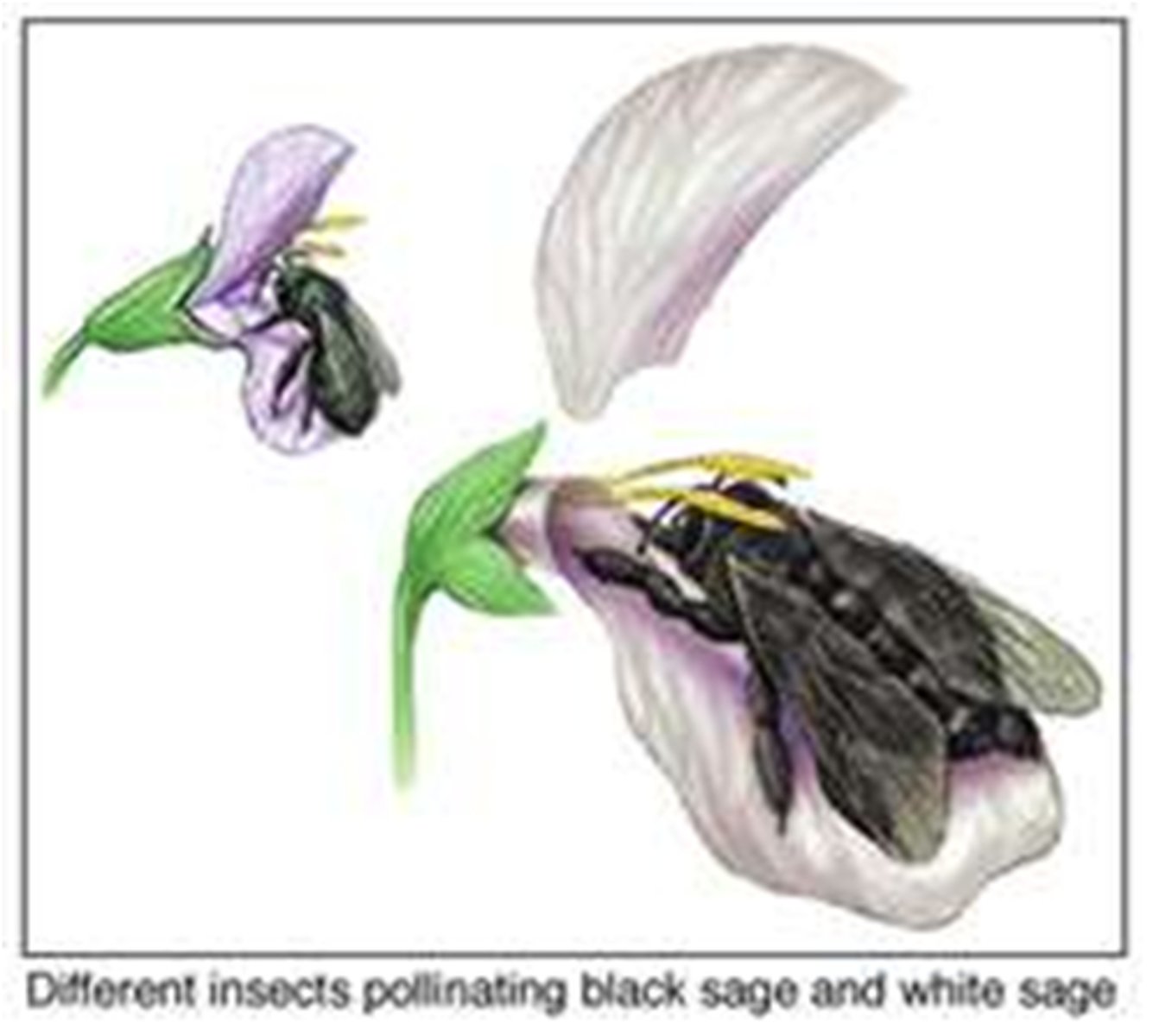
Salvia mellifera
black sage flowers; early spring

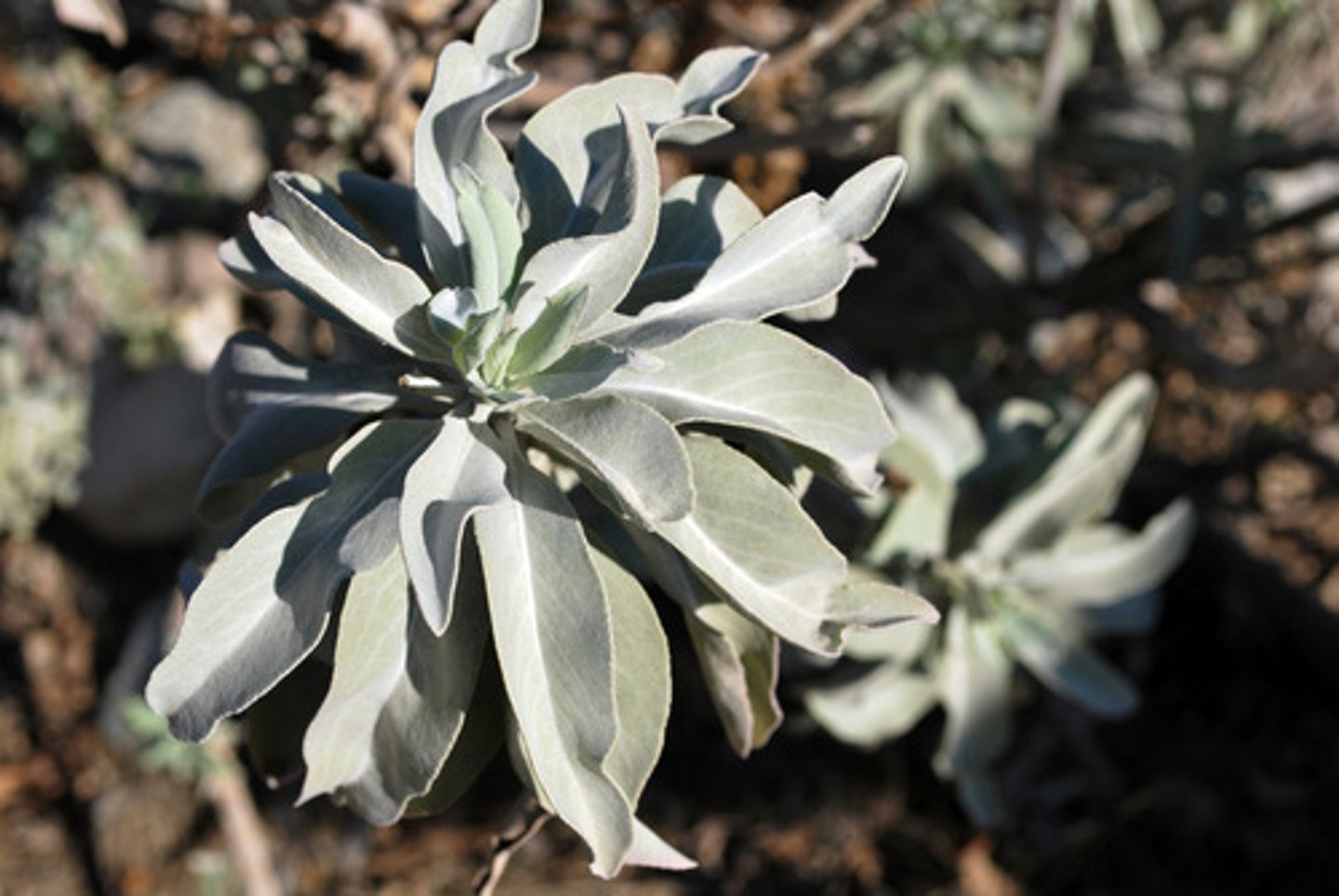
Salvia apiana
white sage flowers; unopened in early spring

structural isolation
organisms are unable to reproduce due to differences in their genital organs
allopatric speciation
evolution of a new species that occurs when one population becomes geographically separated from the rest of the species and subsequently evolves
geographic isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations are separated physically by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains, or stretches of water
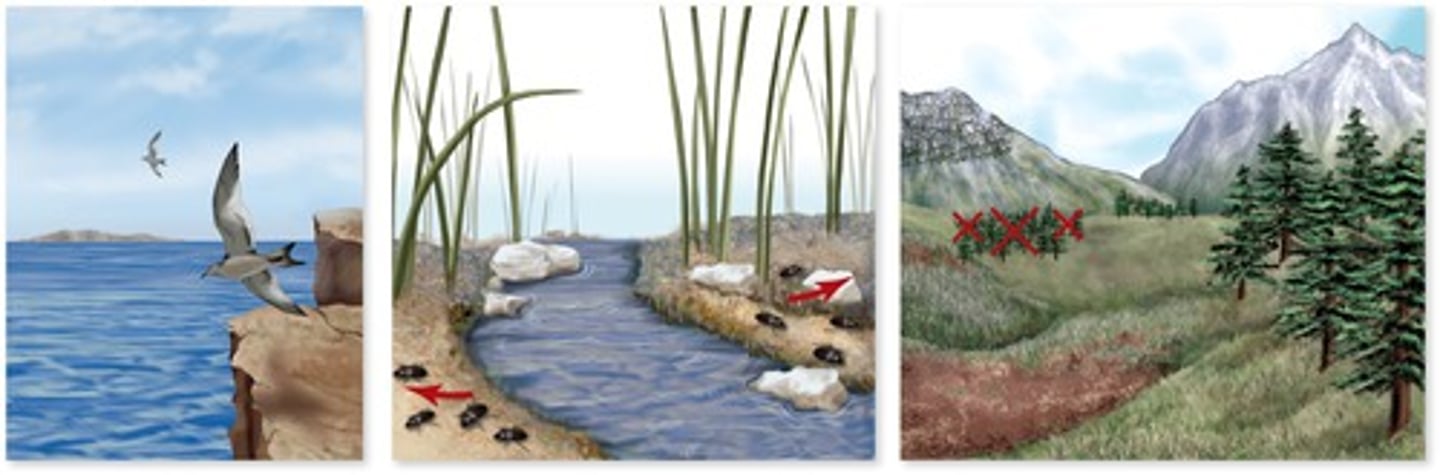

clinal variation
gradual change in the phenotype of a species over a geographic gradient
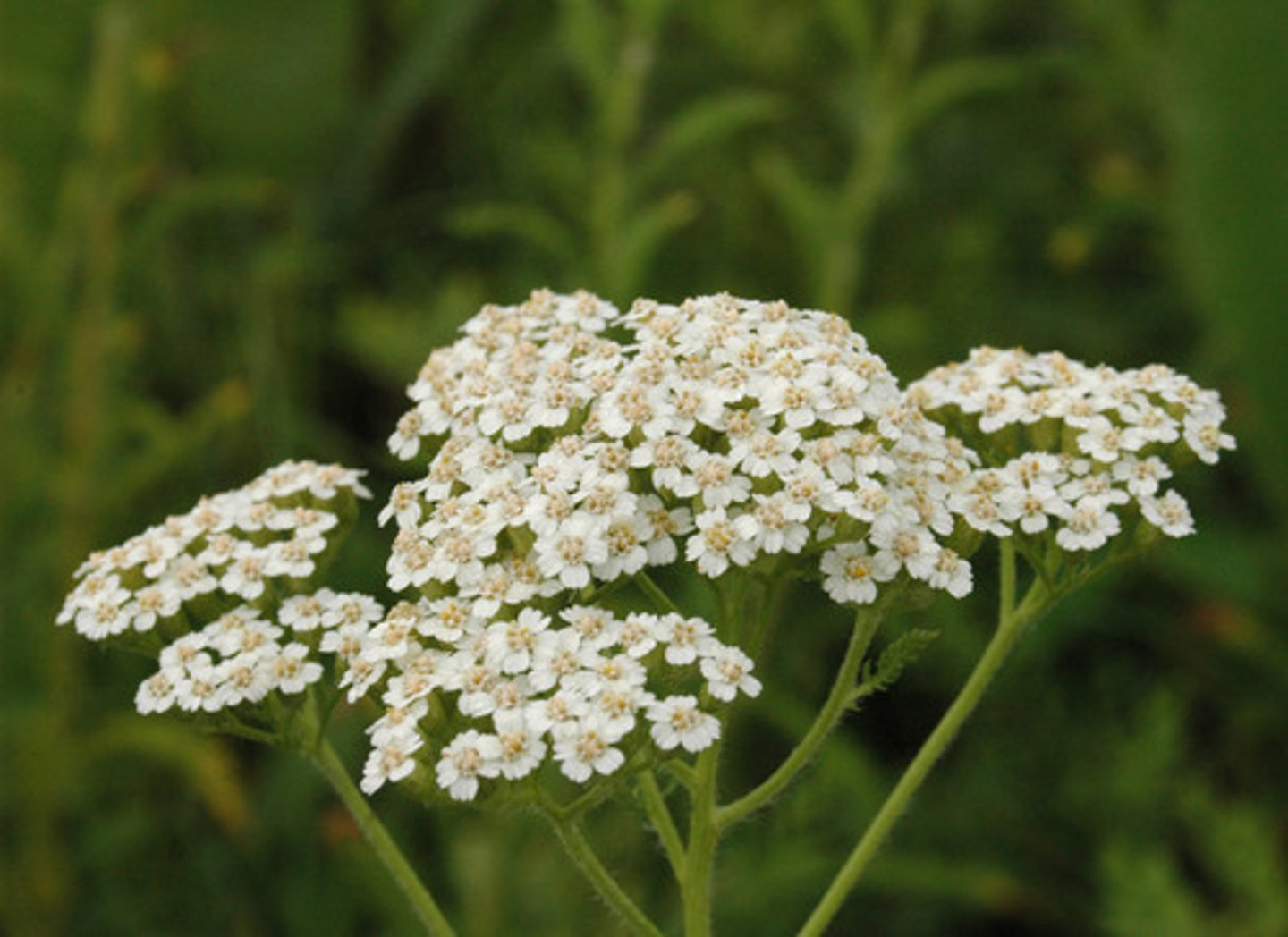
Achillea millefolium
yarrow

sympatric speciation
evolution of a new species that occurs within the parent species' geographic region; may occur as a result of allopolyploidy in an interspecific hybrid
Primula floribunda
orange flower
Primula kewensis
yellow-orange flower
Primula verticillata
yellow flower
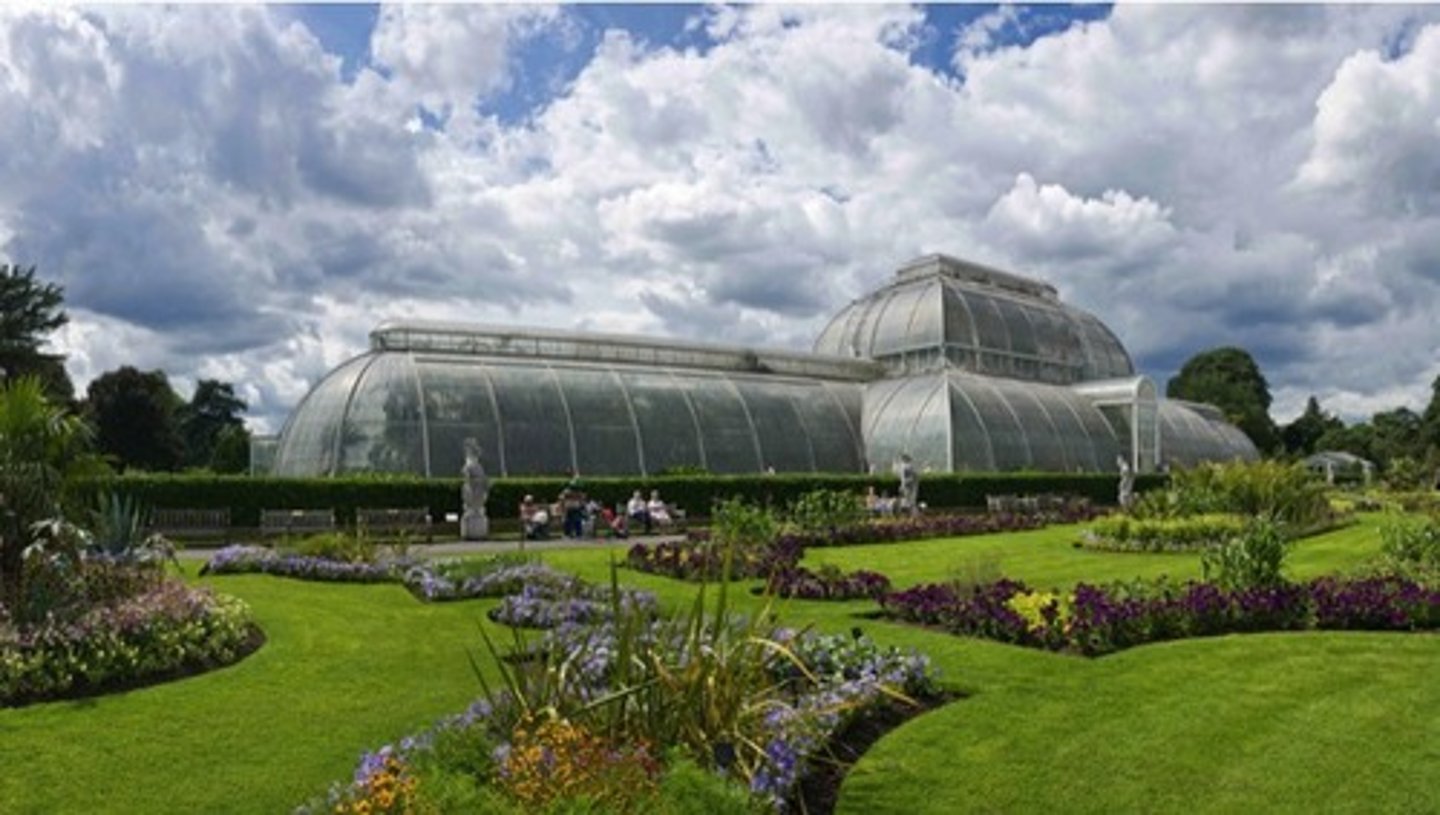
Kew Gardens
a botanic garden in southwest London that houses the "largest and most diverse botanical and mycological collections in the world"

interspecific hybrid
the offspring of individuals belonging to different species; usually dies at an early stage of embryonic development; if it survives to adulthood, it usually cannot reproduce successfully
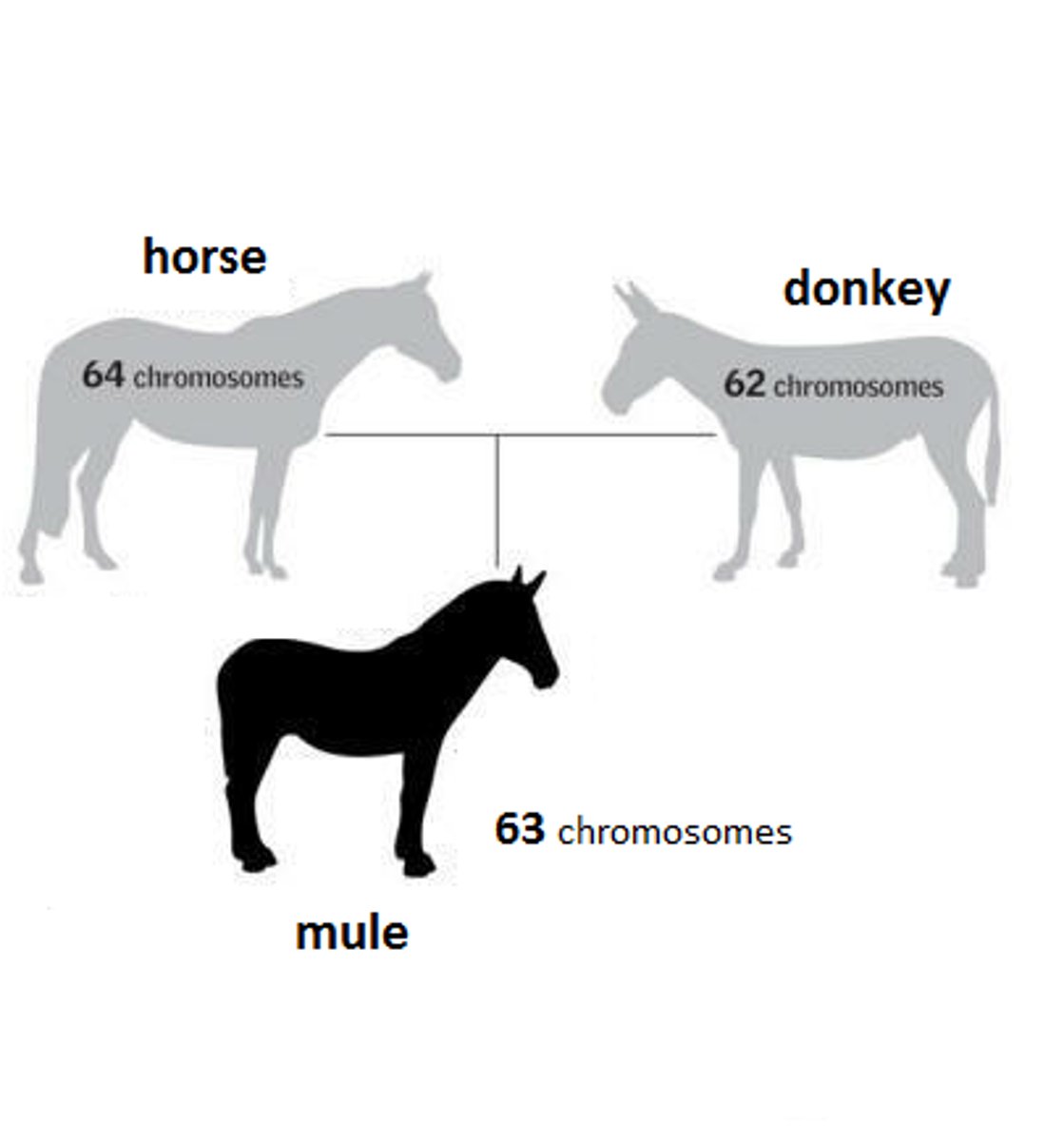
allopolyploidy
situation in which an interspecific hybrid contains two or more sets of chromosomes from each of the parent species; may enable the interspecific hybrid to reproduce successfully as a new species
adaptive radiation
evolution of many related species from an ancestral species
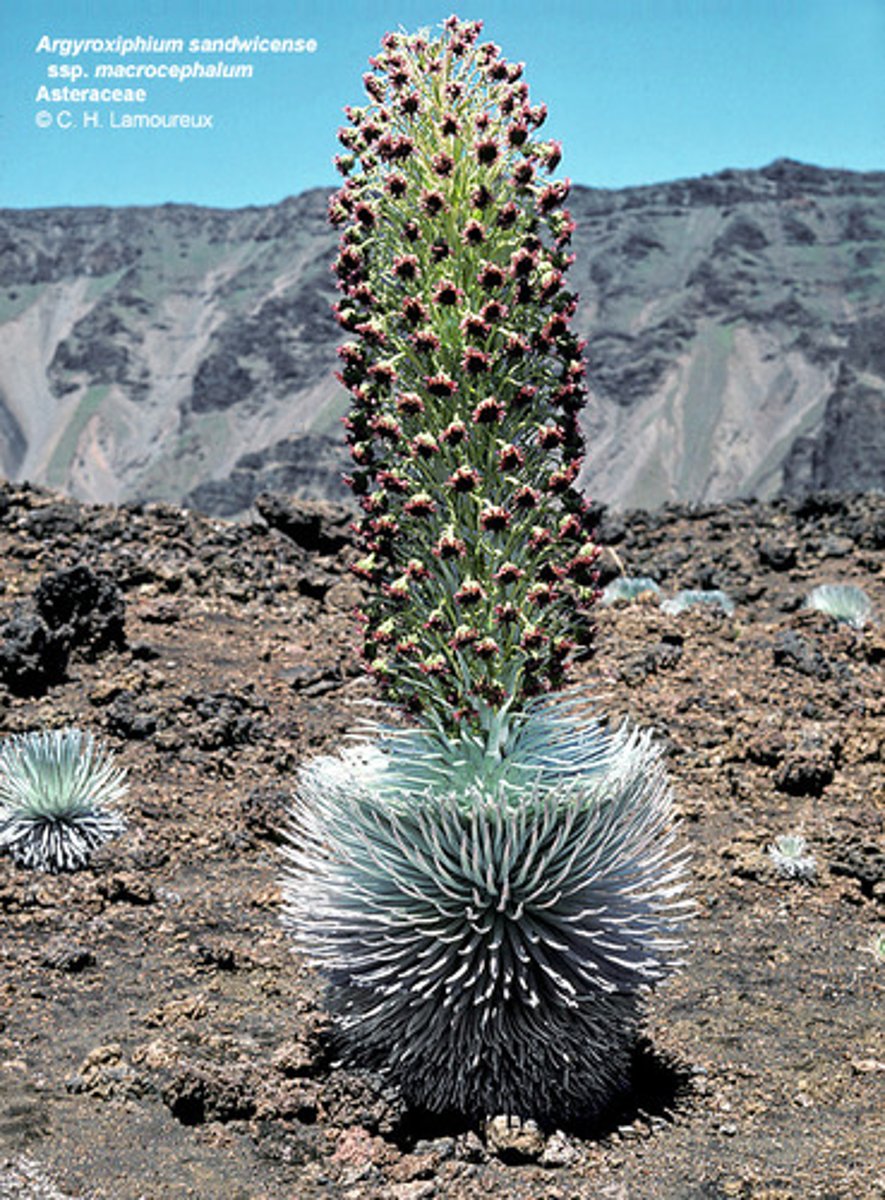
Argyroxiphium sandwicense
Haleakala silversword; only found in the upper slope of the Haleakala Crater in Maui

Wilkesia gymnoxiphium
tarweed species; resembles a yucca; found along the slopes of Waimea Canyon on the island of Kauai
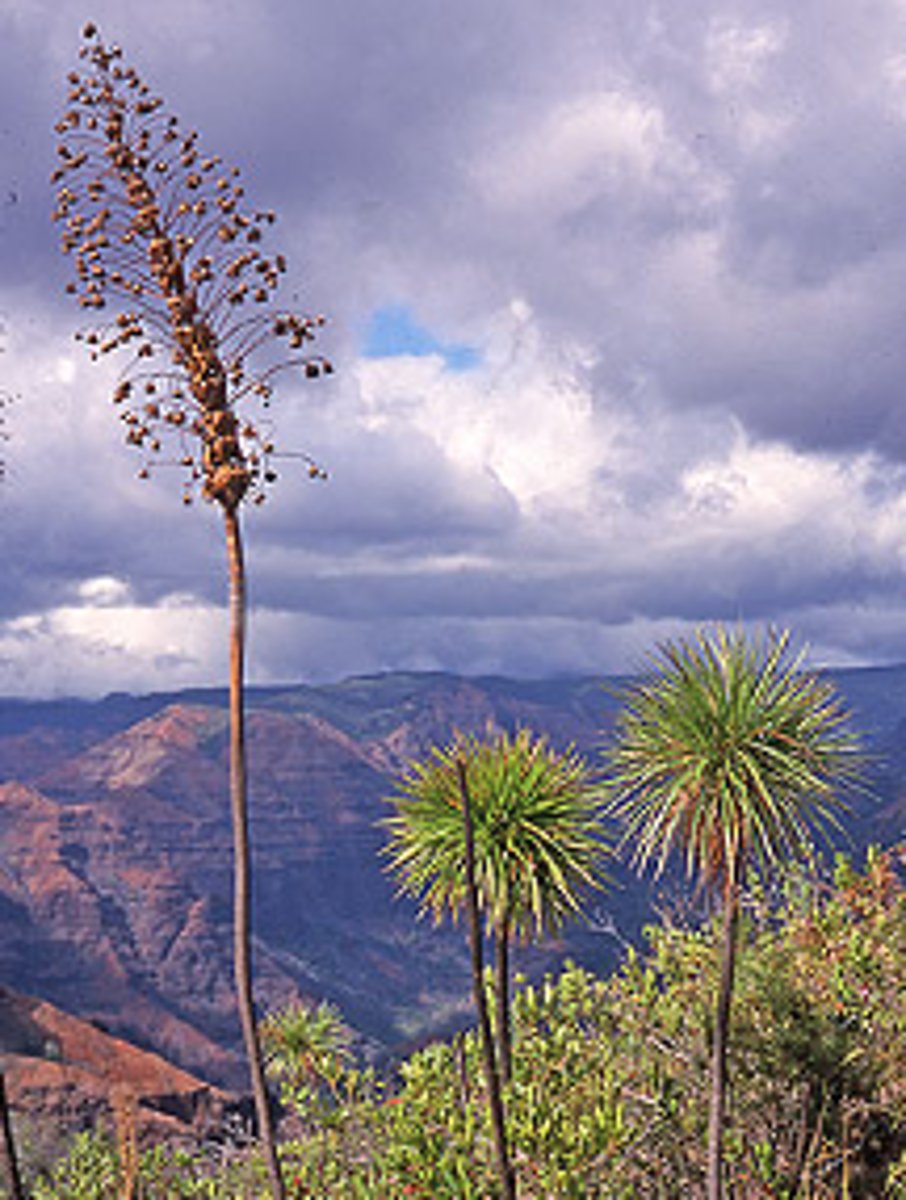

Dubautia platyphylla
a large shrub found in the moist ravines on the island of Maui
extinction
death of every member of a species
mass extinction
death of many species during a relatively short period of geologic time
endemism
a state in which species are restricted to a single region
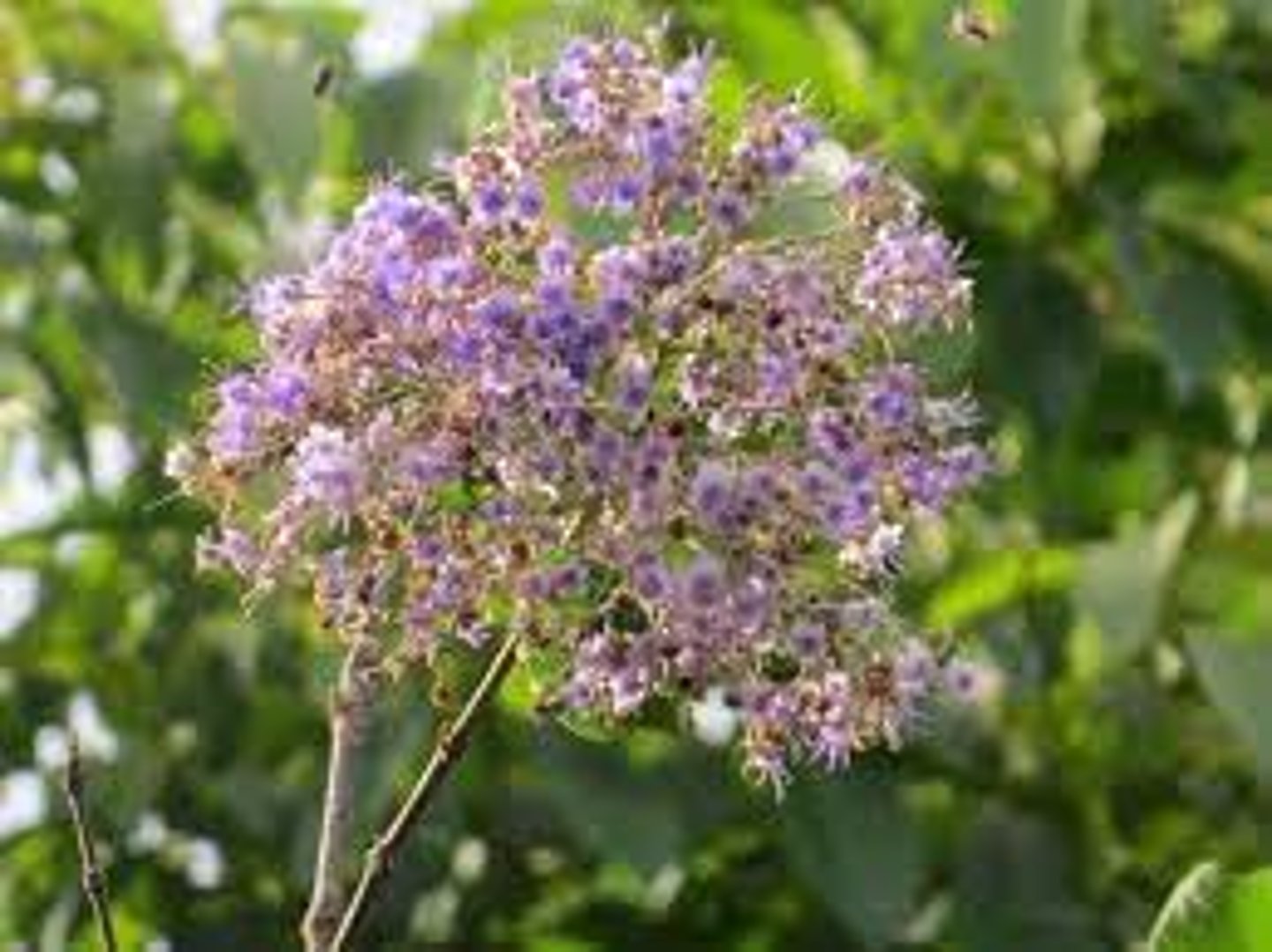
Tectona philippinensis
Philippine Teak

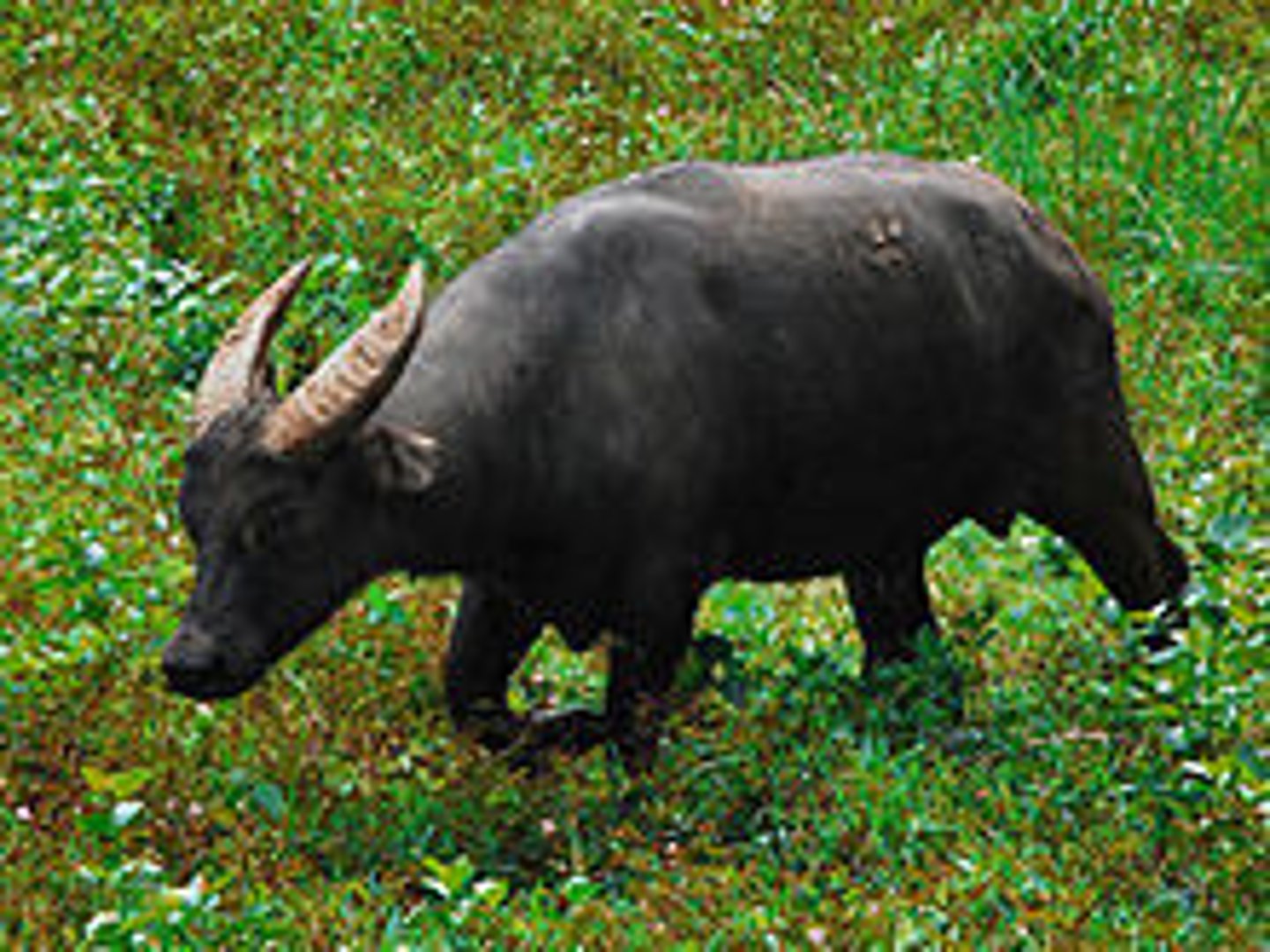
Bubalus mindorensis
Tamaraw

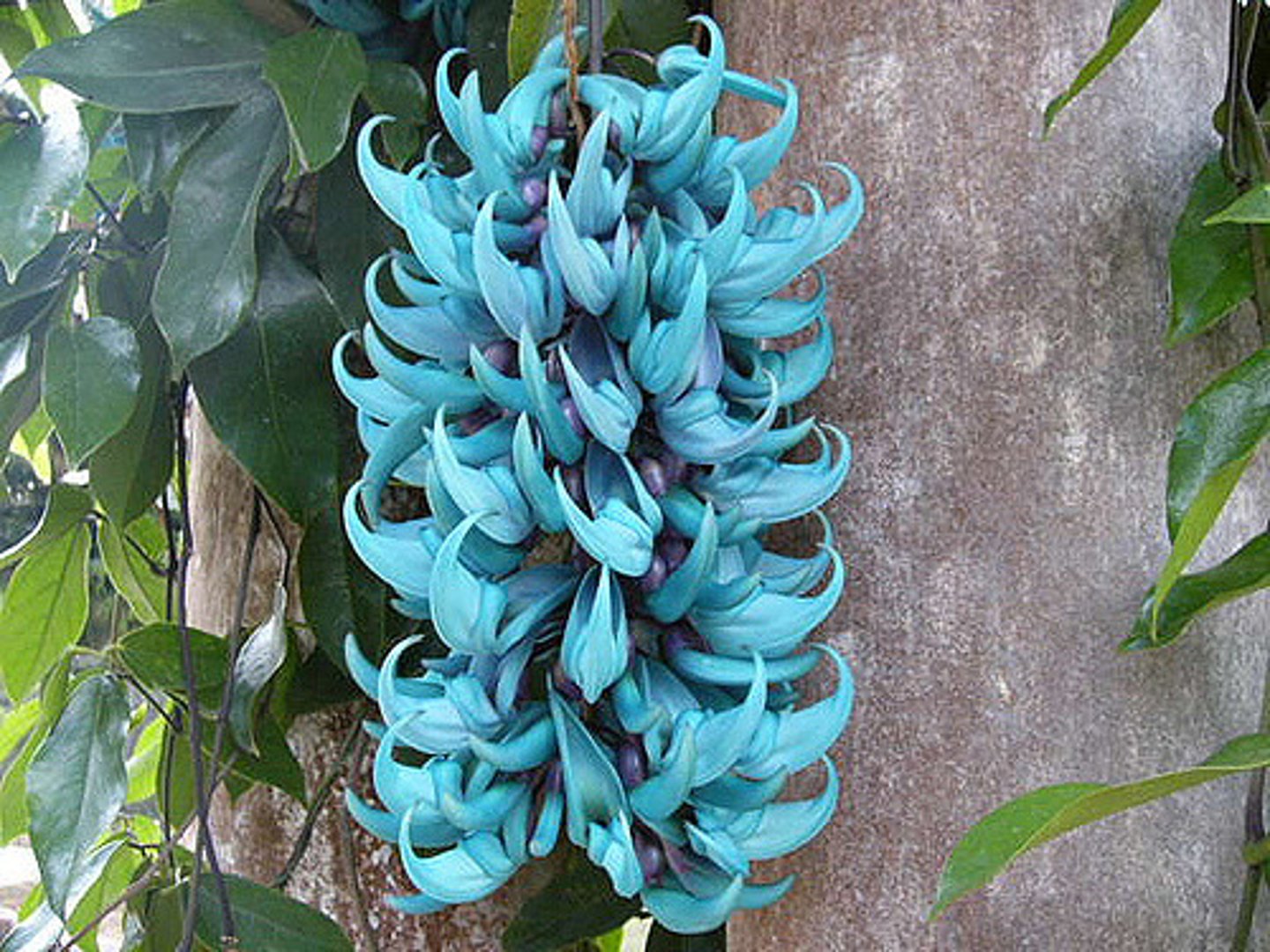
Strongylodon macrobotrys
Jade Vine

Cinnamomum cebuense
Cebu Cinnamon Tree