quantum numbers
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what is n
the principal quantum number
what is l (lowercase L) what does it determine
orbital angular momentum quantum number (or azimuthal quantum number)
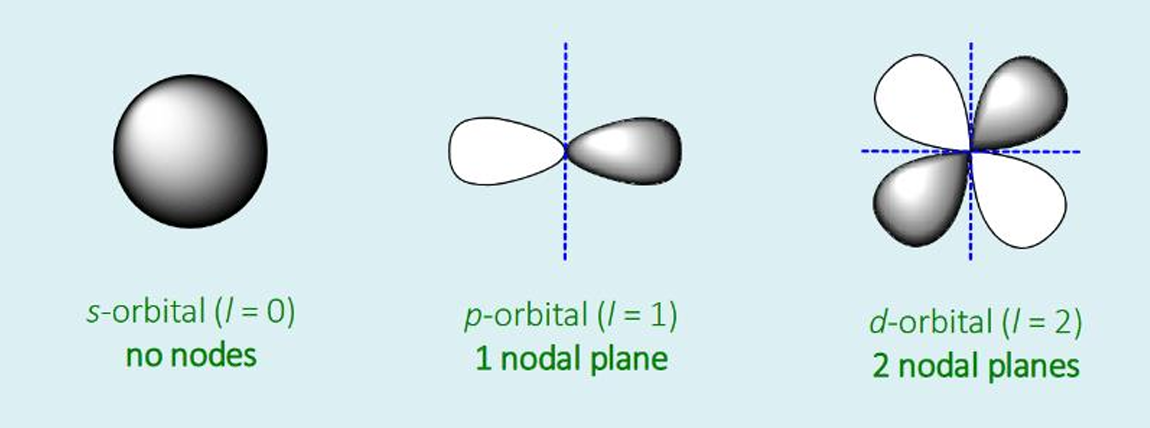
determines the shape of an atomic orbital by giving the number of nodal planes in each orbital type (as orbitals change phase at their nodal planes)
value of l (L) for s, p and d orbitals
s: l = 0
p: l = 1
d: l = 2
what is ml and what does it determine
magnetic quantum number
determines the direction of an atomic orbital
value of ml for s, p, d and what values can it take
can take the values: -l, (-l+1), …, (l-1), l
s (l = 0): ml = 0 only (spherical so no preferred direction)
p (l = 1): ml = -1, 0 or 1
d (l = 2): ml = -2, -1, 0, 1 or 2
s, p, d orbitals for each shell n
1 s orbital, 3 p orbitals when n ≥ 2, 5 d orbitals when n ≥ 3
what is ms and what does it determine
spin magnetic quantum number
each orbital can hold up to 2 electrons, which are distinguished by their spin. ms describes their spin.
what values can ms take and what do they mean
electrons can spin in one of two directions, termed up (ms = +0.5) and down (ms = -0.5)