MGMT 3000 Guhde Exam 1
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
management
Attainment of organizational goals in an effective and efficient manner through planning, organizing, leadings, and controlling organizational resources
plan
charting a course for operation
organize
putting all policies and procedures together before the flight
lead
support and encourage your employees throughout the flight
control
make sure nothing falls through the cracks
Peter Drucker
management is about human beings. Its task is to make people capable of joint performance, to make their strengths effective and their weaknesses irrelevant. (founder of modern management)
four functions of a manager
planning, organizing, leading, controlling
organization
social entity that is goal-directed and deliberately structured
organizational effectiveness
degree to which the organization archives a stated goal
organizational efficiency
refers to the amount of resources used to archive an organizational goal
high performance
attainment of organizational goals by using resources in an efficient and effective manner
effective
completing the task to its fulfillment
efficiency
getting the task done with as little resources as possible
technical management skills
skills such as engineering, manufacturing, or finance. important at lower organizational levels, but they become less important as managers move up the hierarchy
human management skills
skills such as leading, communicating, and relating to other people. increasingly important for managers at all levels and in all types of organizations
conceptual management skills
skills such as knowing where one's team fits into the total organization and how the organization fits into the industry. needed by all managers, but especially those at the top
supervisory/first level managers
responsible for production of goods and services
middle managers
responsible for business units and major departments (only needed when your organization is big)
top mangers
responsible for the entire organization
humanity of production
looking at the employee as more than just a worker, as a human being
things of production
management focus is on production
classical perspective
large complex organizations developed in the 19th and 20th centuries completely focusing on the THINGS OF PRODUCTION. four subfields (scientific management, bureaucratic organizations, administrative principles, management science)
scientific management
improve efficiency and labor productivity through scientific methods
bureaucratic organization
organization depends on rules and records
administrative principles
considers the productivity of the entire organization
management science
application of mathematics, statistics, and other quantitative techniques to management decision making and problem solving
Henry Fayol
identified the Five Functions of Management and the 14 Principles of Management
humanistic perspective
satisfied workers produce more which allows workers to reach their full potential
theory X
the average human has a dislike for work and will avoid it if possible so humans need to be controlled by strict rules or punishment in order to work
theory Y
the average human DOES NOT inherently dislike work and they will learn and seek responsibility under proper conditions
behavioral sciences approach
Scientific Methods + sociology, anthropology, economics, psychology, etc. to develop theories about human behavior and interaction in an organizational setting
organizational development
Set of management techniques that uses behavioral sciences to improve organizations heal and effectiveness
systems thinking
the ability to see the distinct elements of a situation as will as the complexities
systems
set of interrelated parts that function as a whole to achieve a common purpose
subsystems
parts of a system that depend on one another
synergy
the whole is greater than the sum of its parts
contingency view
managers must determine what method will work with every new situation
big data analytics
technologies, skills, and processes for searching and examining massive sets of data to uncover hidden patterns and correlation
internet of things
smart devices that communicate with other devices
AI
does the work that humans find unsatisfying
radical decentralization
employees have authority to make key decision about their work, eliminating much of hierarchical reporting (theory y)
employee engagement
the emotional commitment the employee has to the organization and its goals
nudge management
Being able to influence people and still allowing them the freedom of choice
external environment
factors OUTSIDE the organization that effect inside the organization. two levels: task environment and general environment
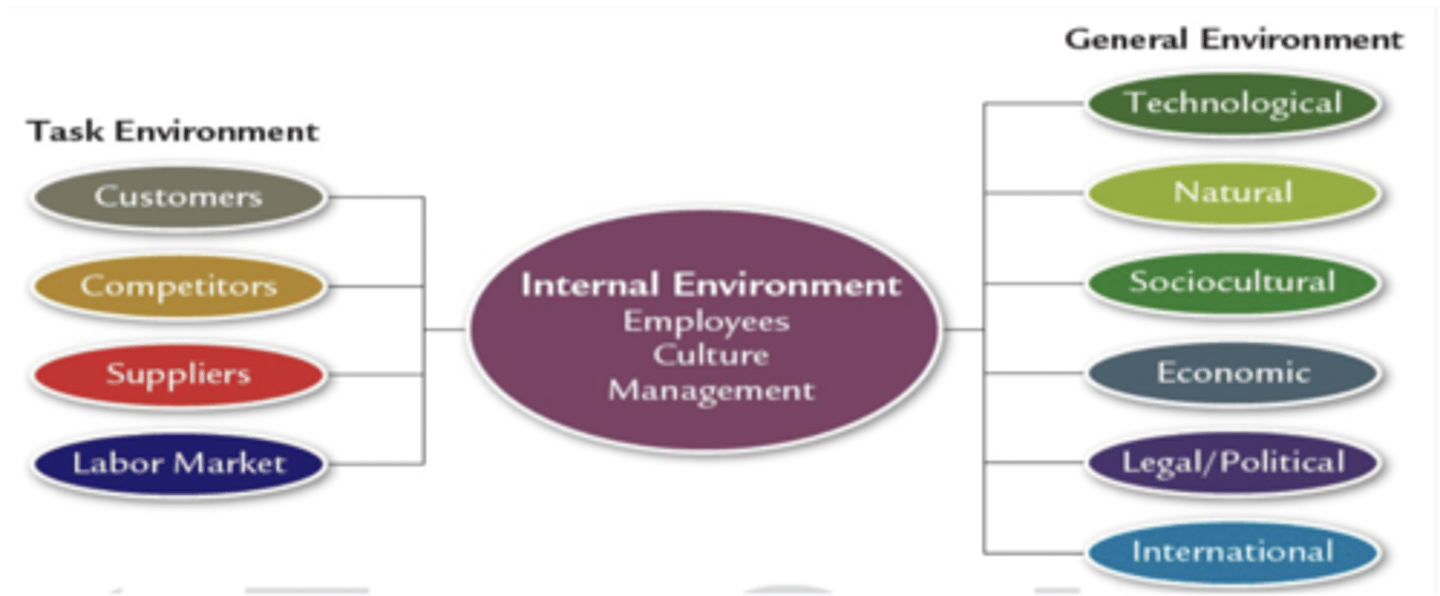
task environment
Factors that affect organization DIRECTLY (customers, competitors, suppliers, labor market)
general environment
Factors that affect organizations INDIRECTLY. international, technological, sociocultural, economic, legal–political, and natural factors
international factor
includes events originating in foreign countries, as well as new opportunities for U.S. companies in other countries
technological factor
includes scientific and technological advancements in a specific industry
sociocultural factor
represents the demographic characteristics, norms, customs, and values of the general population
economic factor
the general economic health of the country or region in which the organization operates (Consumer purchasing power, the unemployment rate, and interest rates)
legal-political factor
includes government regulations at the local, state, and federal levels, as well as political activities designed to influence company behavior
natural factor
all elements that occur naturally on Earth, including plants, animals, rocks, and resources such as air, water, and climate
internal organizational environment
everything INSIDE an organization that must fit the needs of the external environment and company strategy (employees, management, and corporate culture)
corporate culture
the shared values and beliefs of people from the same organization
toxic culture
exists when persistent negative sentiments and infighting cause stress, unhappiness, and lowered productivity among subgroups of employees
visible corporate culture
culture that can be seen at the surface level (Ex. artifacts such as dress, office layout, symbols, slogans, and ceremonies)
invisible corporate culture
deeper values and shared understanding held by organization members (Ex. deep beliefs and expressed values)
globalization
the extent which trade and investments, information, social and cultural ideas and political cooperation flow between two companies
global mind-set
ability of managers to to influence people, businesses, or groups that process different social, cultural, racial, political and intellectual characteristic (3 dimensions: cognitive, psychological, and social)
cognitive dimension
knowing about the foreign market
social dimension
concerns the ability to behave in ways that build trusting relationships with people who are different from yourself
psychological dimension
embracing the challenges of the foreign market
china
largest or second-largest market for a variety of products and services however, regulations and government policies make doing business in China a challenge
india
industry leader in customer service outsourcing because of large english speaking population. India is probably going to overtake China within the next 20 years
multinational corporation
controlled by a single management authority. 25% of revenue must come from outside the country's borders
ethnocentric companies
place emphasis on their home countries
polycentric companies
oriented toward the markets of individual foreign host countries
geocentric companies
world oriented and favor no specific country
serving the bottom
corporations can alleviate poverty and other social ills, as well as make significant profits, by selling their products and services to the world's poorest people
global outsourcing (offshoring)
engaging in the international division of labor so that work activities can be done in countries with the cheapest sources of labor and supplies. (Offshoring)
exporting
strategy in which the corporation maintains its production facilities within their home nation and ships its products for sale in foreign countries
partnerships
partners with a local company in a foreign market
political risk
the risk of loss of assets, earning power, or managerial control due to political changes or instability in a host country
political instability
includes riots, revolutions, civl disorders, and frequent changes in government
ethnocentrism
natural tendency of people to regard their own culture as superior and to downgrade or dismiss other cultural values
Hofstede's Value Dimensions
power distance, uncertainty avoidance, individualism/collectivism, masculinity/femininity,
power distance dimension
level of acceptance in power among people and institutions
uncertainty avoidance dimension
uncomfortable with unstructured, ambiguous and unpredictable situations
individualism/collectivism dimension
people can take care of themselves/people should look after one another
masculine/feminine dimension
achievement, heroism, assertiveness, and material success/relationships, cooperations, and group decision making
GLOBE project value dimensions
Assertiveness, Future Orientation, Gender differentiation, Performance orientation, and Human orientation
implicit communication
people send and receive unspoken cues, such as tone of voice or body language
high-context culture
people are sensitive to circumstances surrounding social exchanges, derive the meaning directly from context
low-context culture
people use communication primarily to exchange facts and information and take the meaning of words rather than context
European Union
An international organization of European countries formed after World War II to reduce trade barriers and increase cooperation among its members
BREXIT
The British Exit from the European Union
US-Mexico-Canada trade agreement
replaced NAFTA, Establishes tougher rules on labor and environmental standards and new provisions for e-commerce and information technology
ethics
code of moral principles and values that governs the behaviors of a person or group with respect to what is right or wrong
confided law
values and standards written into the legal system and enforceable in the courts
free choice
behavior not covered by law and for which an individual has complete freedom
moral agent
a person who knows right from wrong and can be held accountable for their own actions
utilitarian approach
moral behavior produces the greatest good for the greatest number of people
individualism approach
acts are considered moral if they promote the individual's best long-term interests
moral rights approach
humans have fundamental rights and liberties that cannot be taken away by an individual's decision
justice approach
moral decisions must be based on standards of equity, fairness, and impartiality (three types: distributive, procedural, and compensatory)
distributive justice
different treatment of people cannot be based on arbitrary characteristics
procedural justice
rules must be administered fairly
compensatory justice
individuals should be compensated for the cost of their injuries by the party responsible
practical approach
bases decisions on prevailing standards, society, and all stakeholders
preconventional
I follow the rules only because I'm afraid of being punished (common with children)