APII lab practical II
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
EKG, Heart, Blood, Endocrine, Spirometry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Sinoatrial node
Start of electrical pathway in heart
Internodal pathway
Connection between sinoatrial node and atrioventricular node
Atrioventricular node
rebroadcasts the signal to AV bundle
Atrioventricular bundle
Path of electrical activity after leaving atrioventricular node
Bundle branches
Where atrioventricular bundle forks into two paths
Purkinjie fibers
thin fibers that deliver electrical fiber to cardiac muscle tissue
Lead
a pair of electrodes that measures electrical current in one direction
Lead I (standard)
measures from right arm to left arm
lead II (standard)
measures from right arm to left leg
lead III (standard)
measures from left arm to left leg
what direction does electricity flow?
negative to positive
Which one of the 3 standard leads measures electrical activity in the same direction as the orientation of the heart?
II
What plane do the 3 standard leads measure electrical activity in?
coronal/frontal plane
What happens when a patient needs a thorough cardiac work-up?
12 lead EKG
3 standard leads + 3 argumented leads + 6 precordial lead
What plane does the argumented lead measure electrical activity in?
Coronal/Frontal
Argumented leads
Center out: aVF, aVL, aVR
aVR lead
CT (center) to right shoulder
aVL
Center (CT) to left shoulder
aVF
Center (CT) down
6 precordial leads (chest leads) placement
V1 - under median end of right clavicle under 4th rib
V2 - under median end of left clavicle under 4th rib
V3 - directly lateral to V2 on 5th rib
V4 - on mid clavicle line in 5th intercostal space
V5 - on side of chest in line with V4
V6 - under arm on side of torso in line with V5
ECG standard grid paper measurement
1 second = 25mm
1 small ECG box =
0.04 sec
in height 1 small ECG box =
0.1 mv
one big box = 5 small boxes. How long?
0.04×5=0.2 sec
How many big ECG boxes in 1 sec?
5
What is the p wave?
atrial depolarization
How long should the p wave be?
0.12 sec or less
what is the QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
How long should the QRS complex last
0.08 sec or less
What is the T wave?
Ventricular repolarization
Where should the T wave start and why?
isometric baseline because there is no current in heart during this wave
What is the PR interval?
indictive of how long it takes for signal to travel from SA node and be rebroadcasted from AV node
How long should the PR interval be?
0.2 sec
P-P or R-R interval
goes from start of one to start of next
helps determine heart rate
ST segment
If elevated indicates MI
from start of P wave to start of QRS complex
PR interval
from end of P wave to start of QRS complex
PR segment
QRS complex
from start of Q wave to end of S wave
from start of QRS complex to end of T wave
QT interval
From end of QRS complex to start of T wave
ST segment
steps of determining heart rate from ECG graph
1) count up small boxes in P-P or R-R interval
2) multiply this number by 0.04
3) divide 60 by answer to 2
Sinus Rhythm
normal heart rate
slower than normal heart rate
Sinus Bradycardia
faster than normal heart rate
Sinus Tachycardia
Irregularly irregular ECG
atrial fibrillation
normal ECG pattern
regularly regular
Regularly irregular
incorrect wave pattern but predictable timing (consistent P-P/R-R)
Irregularly regular
Normal Wave pattern, not consistent P-P or R-R
Irregularly irregular
completely unpredictable
Graph of squiggles
Ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular tachycardia
hill like ECG
Heart block
long pauses in ECG
Premature ventricular contraction (PVC)
sharp downward spike in ECG
Spirometry
A voluntary test regarding the strength of the inspiratory and expiratory muscles of the patient as well as the lungs ability to stretch and recoil
what does SVC stand for
Slow vital capacity test
What does FVC stand for
Forced vital capacity test
Tidal volume
Volume inhaled or exhaled in a quiet breath (~500ml)
Inspiratory reserve volume
Volume inhaled beyond a normal tidal inhalation (max)
Expiratory reserve volume
Volume Exhaled beyond a normal tidal inhalation (max)
Residual volume
volume of air left after maximal exhalation
Functional residual capacity
amount of air remaining after quiet exhalation
Inspiratory capacity
Air we can inhale after quiet exhalation
Vital capacity
Maximum amount of voluntarily movable air
Total lung capacity
Maximum air lungs can hold
What is the equation for Functional residual capacity
FRC = ERV + RV
What is the equation for vital capacity
VC = TV + IRV + ERV
What is the equation for total lung capacity
TLC = TV + IRV + ERV + RV
What is the equation for inspiratory capacity
IC = TV + IRV
FEV1
Air exhaled after 1 sec
PIF
peak inspiratory flow. fastest moving air in (neg side)
PEV
peak expiratory flow. fastest moving air out (pos side)
Restrictive lung pathology
FVC would be small
FEV1 would be low
FEV1/FVC would be 75%+
SVC would be small
Obstructive lung pathology
FVC would be normal
FEV1 would be low
FEV1/FVC would be <75%
SVC would be normal
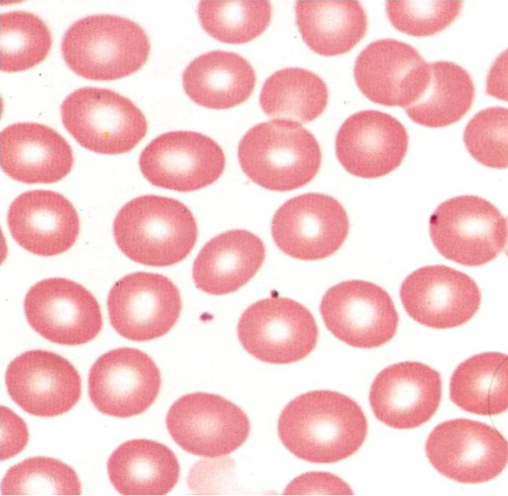
What are these?
Erythrocyte
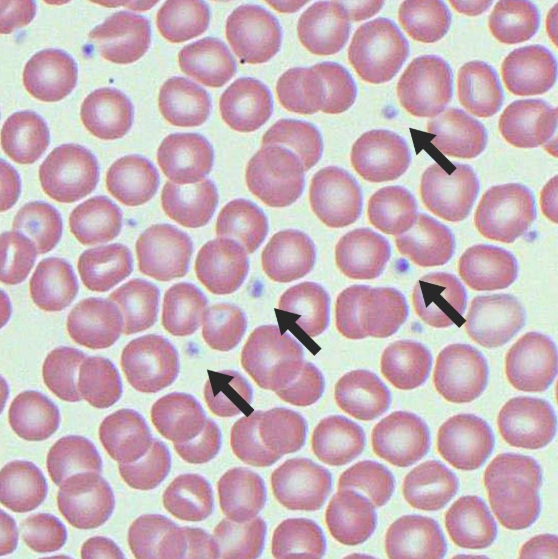
What are these?
Thrombocyte
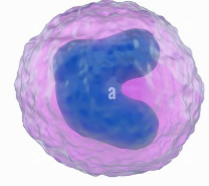
What is this?
Monocyte
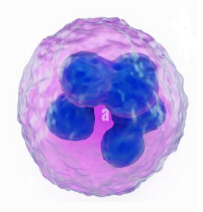
What is this?
Neutrophil

What is this?
Basophil
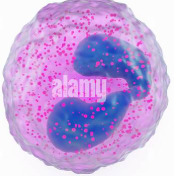
What is this?
Eosinophil

What is this?
Lymphocyte
What is sound one when using a stethoscope?
Closing of atrioventricular valves
What is sound Two when using a stethoscope?
Closing of semilunar valves
What is the average pulse rate?
70-74 bpm
What is the normal range for resting pulse?
60-100 bpm
What are the blood pressure units?
mm/Hg (millimeters of mercury)
what is a typical blood pressure?
<120/80
What is the blood pressure cuff called?
Sphygmomanometer
What is the top blood pressure number?
Systolic pressure (action)
What is the bottom blood pressure number?
Diastolic pressure (relax)
What is the first sound heard when taking blood pressure?
Korotkoff sound (systolic pressure)
What is the last sound heard when taking blood pressure?
Diastolic pressure (still a Korotkoff sound)
Pulse pressure equation
PP = SP - DP (30-50 normal)
What is equation for mean arterial pressure?
MAP = DP + 1/3 PP (> or equal to 60 mmHg good)
Normal female hematocrit range
35-45%
Normal male hematocrit range
43-55%
what antibody does type A blood have
Anti B
what antibody does type B blood have
Anti A
what antibody does type AB blood have
none
what antibody does type O blood have
Anti A and anti B
type A + can donate to?
A+ or AB+