Enzymes Theory
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are Enzymes?
They are proteins.
What are proteins also called?
Proteins are biological molecules also called polypeptides.
What are polypeptides (proteins) made up of and its purpose?
Polypepides (proteins) are made up of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds.
The amino acids present and their order are what makes each protein specific for a function.
How many types of amino acids are there?
There’s 20 different aminoacids.
They can have different polarity and charge, depending on their R-group/side chain.
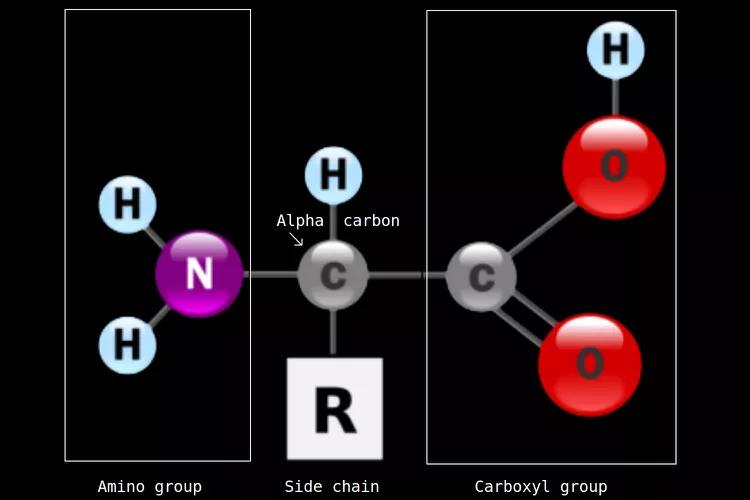
What is the basic structure that all amino acids have?
Aimno group (NH2) = Nitrogen with two Hydrogen coming from it.
Variable R-group = The Nitrogen is then connected to the Alpha Carbon which has a Hydrogen coming off it. An R is placed underneath.
Carboxyl group (COOH) = another Carbon attached to the C, doubled bonded to an Oxygen, and then an oxygen of the C with an H.
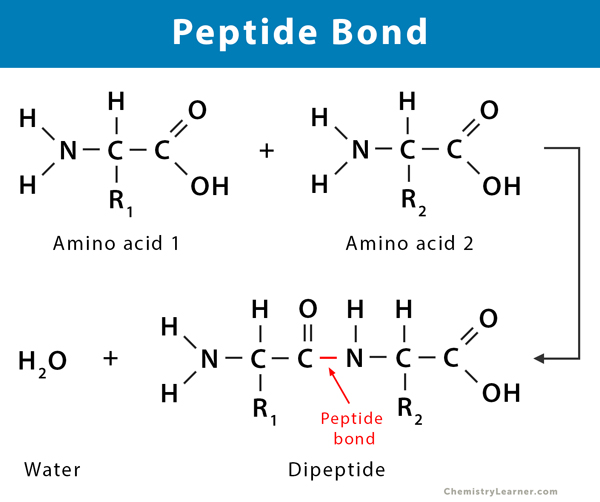
What is a dipeptide and its structure?
2 amino acids that bond together during a condensation reaction, forming a dipeptide and water molecules.
This bond is a peptide bond.
What is a polypeptide structure?
When more amino acids are added to a dipeptide, a polypeptide chain is formed.
A protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains folded into a highly specific 3D shape.
What are the four levels of structure in a protein (polypeptide)?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Each of these play an important role in the overall structure and function of protein.
Enzymes are proteins, so they also have this structure.
What is the Primary Structure?
It is the order of the amino acids,
the order is determined by the DNA sequence of the gene for the protein.
It must be correct for the protein to be able to function correctly.
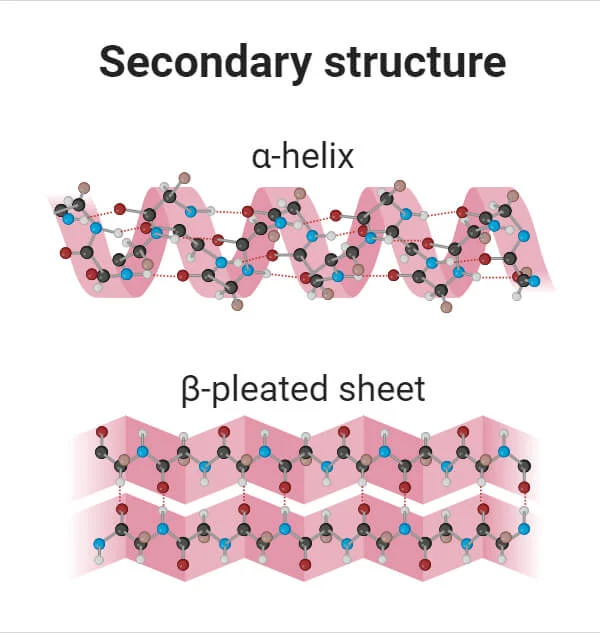
What is the Secondary Structure?
When regions of the polypeptide chain coil or fold.
A coiled region is called an alpha-helix
A folded region is called a beta-pleated sheet
What is the Tertiary Structure?
Happens when the polypeptide folds up into an overall 3D structure.
Bonds and interactions hold together the 3D shapes between the R groups of adjacent amino acids.
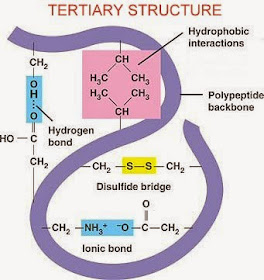
What are the different types of bonds?
Disulphide bridge, Ionic bonds, Hydrogen bond, Hydrophobic interactions
What do Disulphide bridges form between?
They form between amino acids which have sulphur in their R groups.
This is a strong covalent bond. (nonmetals)
What do Ionic bonds form between?
They form between amino acids with oppositely charged R groups.
Weaker than a covalent bond but stronger than the others.
(m & nm)
What do Hydrogen bond form between?
Forms between amino acids with slightly oppositely charged R groups (R groups with differences in electronegativity).
Weakest type of bond in the tertiary structure.
First to break when a protein denatures.
What do Hydrophobic interactions form between?
R groups which are hydrophobic, position themselves on the inside of the 3D shape.
Hydrophilic R groups position themselves on the outside of the 3D shape.
What are Globular proteins?
Enzymes are globular proteins - resemble a ball or globe shape.
The teritary structure is important to determine how enzyme works.
What do enzymes do?
They are biological catalyst used in chemical reactions to speed them up.
What is the structure of the enzyme and its uses of an active site/substrate?
Enzymes are proteins with an active site
The active site is an area where a substrate binds to
A substrate is a molecule affected by the action of an enzyme.
The active site is a specific shape that is complementary to the shape of the substrate.
If the active site is altered in any way, it will not bind with a substrate and can not carry out its function. - It has denatured.
What is the collision theory?
For chemical reactions to occur, the reactants must collide with energy greater than or equal to the activation energy.
What are the 4 ways to increase that rate of reaction with catalyst?
1) Increase the concentration of the reactants
2) Increase the surface area of a solid reactant.
Means there is more/larger reactants to collide
3) An increase in temperature means the particles will have more kinetic energy and will move faster so there will be more collisions.
4) Add a catalyst (enzyme) = lowers the activation energy required so more of the collisions will have enough energy to cause a chemical reaction.
What is an Enzyme-Substrate complex?
- Each enzyme will only catalyse one particular chemical reaction with one particular substrate. - This property is called specificity.
The substrate binds with the active site of the enzyme and forms an enzyme-substrate complex. (lock & key method)
The chemical reaction takes place in the enzyme-substrate complex, and the substrate is converted into a product.
What factors affect enzyme activity?
Temperature,
pH,
Concentration of substrate
Concentartion of enzyme.
If we change these, we change the rate of reaction.