Pharm II: E2 - ALL
1/516
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
517 Terms
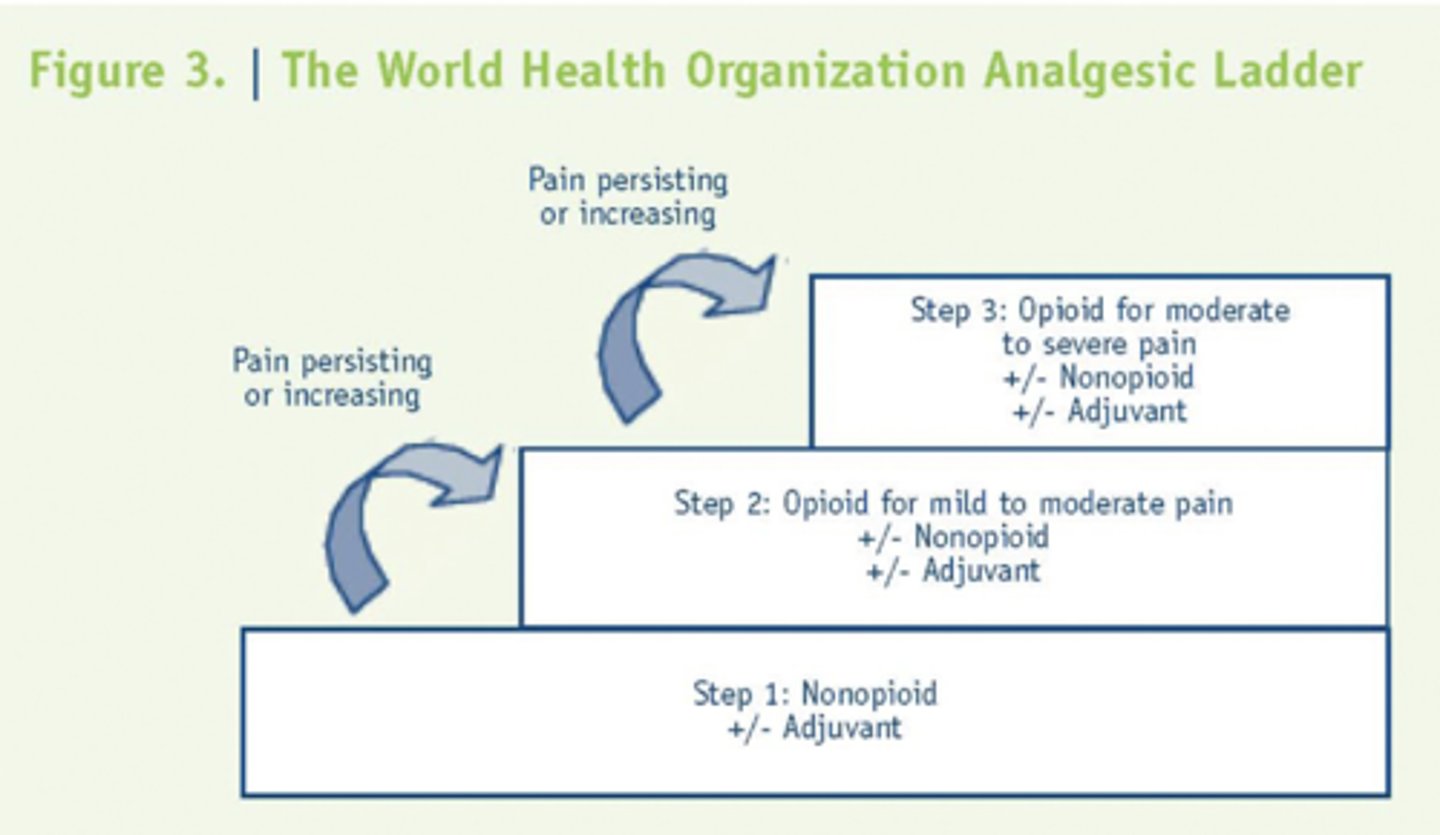
WHO analgesic ladder
- Step 1: Nonopioid analgesic
- Step 2: opioid for mild/mod pain
- Step 3: opioid for mod/severe pain
What is Analgesic activity
- prostaglandins sensitize pain fiber
- pain from inflammation and tissue damage
- for mild/mod pain
COX 1 vs. COX 2:
Constitutive action on blood vessels, stomach, and kidneys
COX 1
COX 1 vs. COX 2:
Inducible action on inflammation and blood vessels
COX 2
COX 1 vs. COX 2:
Increased incidence of heart attack, stroke
COX 2
What are some first choice therapies for somatic and visceral pain?
- NSAIDs
- Acetaminophen (APAP)
- Corticosteroids
What is the second line treatment option for somatic and visceral pain if the first line options are ineffective?
Opioids
What are the first choice therapy options for neurpathic pain?
- Antidepressants
- Anticonvulsants
- Baclofen
What is the second line treatment option for neurpathic pain if the first line options are ineffective?
Opioids
What is the FIRST LINE therapy for lower back pain and osteoarthritis?
Acetaminophen

What is used in post-operative pain management to reduce the need to use opioids?
IV Tylenol (Ofirmev)
How might Acetaminophen be useful in surgical patients who need opioids?
It can allow you to RX less opioids bc it is opioid sparing
Where is Acetaminophen more potent?
Centrally → inactivated by peroxidases found in inflamed tissue
When should Tylenol dose be limited?
in patients with hepatic impairment
What is the daily limit of Acetaminophen (Tylenol)?
*There will probs be some question on this... in the Kahoot he combined it with Hydrocodone/325 and asked max allowable tabs in a day --> answer was 12... (4000/325))
4 g/day
What is the key that differentiates Aspirin from other NSAIDs?
It is a permeant bonding irreversible, noncompetitive anti-platelet medication
A patient presents with Tinnitus and fever. They are hyperventilating and are dehydrated. They mentioned that they decided to take a bunch of an over the counter pill for fun, but can't remember the name. What might be the culprit based on the patients symptoms?
*Hint: the patient is presenting with overdose sx
Aspirin
How is Aspirin excreted?
Renally
A 7 yo patient with a URI presents to the ER vomiting, confused, and with a fine, macular (flat) rash that can cover the entire body. On PE you find an enlarged liver. You draw labs and find increased aminotransferase, serum ammonia, prothrombin time, hypoglycemia, and metabolic acidosis. The patients mom gave the patient a medication for the fever, but nothing else.
What drug might be the culprit?
Aspirin → Reyes Syndrome
What are the contraindications of Salicylates (Aspirin)?
- bleeding disorders
- pregnancy
- children with fever associated w/ viral disease → Reye's syndrome
What is the treatment for Reye's syndrome?
Glucose and Mannitol
What drugs are orally absorbed have high protein binding, are more potent and are used for Arthritis, Muscle Pain, and Dysmenorrhea?
Propionic Acid Derivatives → “Profen, Proxen, Prozin”
What are some of the Propionic Acid Derivatives?
- Ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, Ibuprin)
- Naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve)
- Naproxen Na (Anaprox)
- Ketoprofen (Orudis)
- Fenoprofen (Nalfon)
- Flurbiprofen (Anaid)
- Oxaprozin (Daypro)
Which Propionic Acid Derivative has the LONGEST half life (40-60 hrs)?
Oxaprozin (daypro)
How are Propionic Acid Derivatives excreted?
Hepatic conjugation and renal excretion
What drugs are nonselective for COX1 and COX2?
NSAIDs
What actions do NSAIDs have?
- analgesic
- antipyretic
- anti-inflammatory actions
What are the NSAIDs we should know?
- Aspirin (ASA)
- Ibuprofen
- Naproxen
- Indomethacin (Indocin)
- Ketorolac (Toradol)◾
- Tolmetin (Tolectin)
- Piroxicam (Feldene)
- Meloxicam (Mobic)
- Nabumetone (Relafen)
- Diclofenac (Voltaren)
What are some common side effects of NSAIDs?
- Gastric/intestinal ulceration → decreased mucous d/t lack of PGs
- Decreased platelet aggregation → bleeding
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Prolong gestation → Delay spontaneous labor, adverse fetal effects (ductus arteriosus)
- Asthma bronchospasm
- Impaired hepatic fxn
- Dec renal fxn in susceptible pts
Which medication is best to close off the ductus arteriosus in kids back in the day, but works best as an anti-inflammatory?
Indomethacin (Indocin)
NOTE: he said that IV ibuprofen is used nowadays
A patient taking HCTZ (diuretic) inquires about taking Indomethacin (Indocin) in combination, why might this be a problem?
it decreases the effects of diuretics
What is the go-to IV NSAID for acute pain?
*note: NOT an effective anti-inflammatory
Ketorolac (Toradol)
How many days is Ketorolac (Toradol) use limited to? (MAX limit)
"Great test question to ask!!!!"
5 day → HIGH RISK for stomach ulcers
What NSAID has a BLACKBOX warning for GI effects?
Ketorolac (Toradol)
What NSAID is more potent than Aspirin and has analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory actions?
Tolmetin (Tolectin)
Which NSAID is rapidly reversible, competitive, with slow onset and used for arthritis?
*Note: Has fewer GI side effects
Piroxicam (feldene)
Which NSAID is more selective for COX2 and good for patients at risk or have previously had GI Ulcers?
Meloxicam (mobic)
Which NSAID is a prodrug, active metabolite, with some COX 2 selectivity and used for RA and OA?
Nabumetone (relafen)
Which NSAID can be used topically as a gel?
"interesting"
*Note: Good for arthritis and patients with kidney disease
Diclofenac (Voltaren)
An elderly patient with RA and kidney disease is looking for something to help reduce her pain. What might be a good option?
(gave an example like this in class)
Diclofenac (Voltaren)
What are the main concerns with COX2 selective inhibitors?
CV safety → inc. stroke and MI
What was the problem with drugs that are purely COX-2 inhibitors like Rofecoxib (Vioxx) -- Note this drug has been removed from the market?
By inhibiting COX-2 only you get rid of prostaglandins, but you increase pro-platelet aggregation substances like prostacyclins which caused an imbalance leading to increased incidence of MI and Stroke in patients
What is our main COX 2 selective agent that is used?
Celecoxib (Celebrex)
What kind of patient might we consider Celecoxib (Celebrex) for?
Those patients experiencing major GI issues → selective for COX 2
What are the COX-2 selective agents?
*Note: benefit is limited GI side effects
- Celecoxib (celebrex) (go to)
- Etodolac (lodine)
List the COX2 selective agents in order from most to least COX2 inhibition
Etoricoxib > Valdecoxib = Rofecoxib >>> Celecoxib
What agents have toxicity that can inhibit PGI2 production more than TXA2 production in epithelial cells of blood vessels.
Note: Can increase MI and stroke
increase BP and renal fxn
COX 2 selective agents
Where do Mu opioids affect the spinal cord?
The dorsal root
Which opioid receptors affect afferent neurons in dorsal spinal cord and are responsible for analgesia, respiratory depression, and euphoria?
Mu receptors
Do opioids work at the site of injury?
No, redirects pain signal
Is physical dependence associated with addition?
no
What occurs when someone with a physical dependence on opioids discontinues them?
Withdrawal → N/V, sweating, dysphoria, not fatal
What is described as "use despite known harm"?
Addiction
What are characteristic of addiction?
psychological dependence → impaired control of drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm, craving
What is a state of adaptation in which effects of the drug diminish over time?
Tolerance
Is addiction associated with physical dependence?
yes
What is pseudotolerance?
Increased activity or disease progression → change in pain state (but the opioids were never changed in order to deal with the change in pain then it can appear as though the meds aren't working as well when the pt is just taking the incorrect dose)
What is pseudoaddiction?
When a patient craves med, but cravings stop when pain is controlled → due to under-treatment
Why can patients die from relapsed drug use after attending rehab?
Their tolerance decreased and they took their previously tolerant dose → overdose
What is expected in patients on long-term opioid therapy
physical dependence
What program can be used to aid in determining if a patient is a drug-seeker?
E-Forcse
How should opioids for acute pain be prescribed?
3 day limit
"acute pain exemption" must be written on Rx for 7 days
You want to Rx a patient Loratab. What is the max number of pills you can prescribe to the patient for acute pain? (without an acute pain exemption)
(Example given in class)
12 pills
3 day limit → patient will take one pill every 6 hours → 4 x 3 = 12
What is an example of C-1 substance?
heroin
marijuana
no acceptable medical use and high abuse potential
What is an example of a C-2 substance?
cocaine
some medical use with high degree of abuse
What are the Opioids we should know?
- Codeine (Tylenol #3) ◾
- Morphine (MS Contin, Duramorph)
- Hydrocodone (Norco, Lortab)
- Oxycodone (Roxicodone, OxyContin)
- Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
- Fentanyl (Sublimaze)
- Methadone
- Meperidine (Demerol)
- Buprenorphine (Suboxone, Subutex)
How is Codeine (tylenol #3) converted to morphine?
In the liver via CYP2D6
How are individuals who under-express CYP2D6 going to handle Codeine (tylenol #3)?
The medication will not work great (decreased analgesic effects) bc they will not get the morphine due to under-expressing CYP2D6 which is what converts Codeine to Morphine. They will also be resistant to the dangerous effects.
How are individuals who over-express CYP2D6 going to handle Codeine (tylenol #3)?
The analgesia effects are going to be working VERY well bc they are able to convert Codeine to Morphine, but they are are at a much greater risk for respiratory depression
Why do opioids cause respiratory depression?
(Question Wood asked in class)
It turns off the CO2 detector → no response from brain even though CO2 levels are rising
When is codeine more/less effective?
- less → CYP2D6 enzyme deficient pts
- more → CYP2D6 enzyme hyperactive pts → more conversion to morphine
Which drug has a BLACKBOX warning for ultra-rapid CYP2D6 metabolizing children with T&A (tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy)?
Codeine (tylenol #3)
People of which descent should avoid Codeine (tylenol #3)?
- Middle Eastern descent
- North African descent
How is Morphine (MS Contin, Duramorph) metabolized?
Hepatic metabolism via glucuronidation
Morphine-3-glucuronide vs. Morphine-6-glucuronide:
Hyperalgesia, Allodynia, Hyperactivity
Morphine-3-glucuronide
Morphine-3-glucuronide vs. Morphine-6-glucuronide:
Greater analgesic properties
Morphine-6-glucuronide
Which opioid has significant release of histamine causing pruritis?
*Note: not allergic rxn
Morphine (MS Contin, Duramorph)
How are metabolites of Morphine (MS Contin, Duramorph) cleared?
Renally → may accumulate in elderly, renal failure pts
Which type of patient would we stay away from using Morphine (MS Contin, Duramorph) for pain?
Elderly folks with renal issues → causes greater risk for adverse effects like respiratory depression
A patient presents to the ER in a panic bc they can't stop itching. The patient recently had surgery and was given a pain medication, but cannot recall what it was. NKDA. What is the most likely culprit of the patients pruritius?
Morphine (MS Contin, Duramorph)
Which type of antihistamines would we give to a patient suffering from itching due to morphine use?
Second generation! (Zyrtec, Claritin, Allegra, etc.)
First generation can cause more sedation along with the morphine
What is the active form of Hydrocodone (Norco, Lortab), converted via CYP2D6?
Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
What drug was frequently the #1 prescribed medication in the US, but was recently made a Class II (formally Class III) making it more regulated and difficult for providers to hand out like candy?
Hydrocodone (Norco, Lortab)
What is commonly used in conjunction with Hydrocodone (Norco, Lortab)? Why might this be an issue?
Acetaminophen → we must make sure to account for all sources of acetaminophen (4 grams a day max)
Why is Oxycodone (Roxicodone, OxyContin) twice as potent as oral morphine?
improved bioavailability
How is Oxycodone (Roxicodone, OxyContin) metabolized?
P450 2D6 to oxymorphone (active analgesia)
What is the effect of Oxycodone (Roxicodone, OxyContin) in patients with a CYP2D6 deficit?
Decreased effects
What is the long-acting form of Oxycodone?
OxyContin

How is Hydromorphone (Dilaudid) metabolized?
Glucuronidation
Hydromorphone-3-glucuronide vs. Hydromorphone-6-glucuronide:
Myoclonus activity
Hydromorphone-3-glucuronide
Which has a higher half life: Hydromorphone (Dilaudid) or Morphine (MS Contin, Duramorph)?
Morphine (MS Contin, Duramorph)
What is a benefit of Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)?
Less histamine release → less pruritis
If a patient has severe pruritis on Morphine (MS Contin, Duramorph), what is a better option?
Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
When and why might Hydromorphone (Dilaudid) be a better opioid to use?
For procedure recovery due to its short half life and less histamine release
Fentanyl (Sublimaze) is ____x more potent than morphine
100x
If our patient has a true allergy to phenanthrene opioids such as Morphine and Oxycodone, which drug might be useful?
Fentanyl (Sublimaze) → synthetic
What expedites the release of Fentanyl (Sublimaze) patches?
"Interesting" - also asked this again during review
Heat
What form of Fentanyl (Sublimaze) is used for acute pain?
IV
What form of Fentanyl (Sublimaze) is used for Chronic Pain?
Long acting forms
What drugs have a similar profile to Fentanyl (Sublimaze) and can be used in the surgical setting in patients that have full opioid allergy?
- Alfentanil (Alfenta)
- Sufentanil (Sufenta)
- Remifentanil (Ultiva)