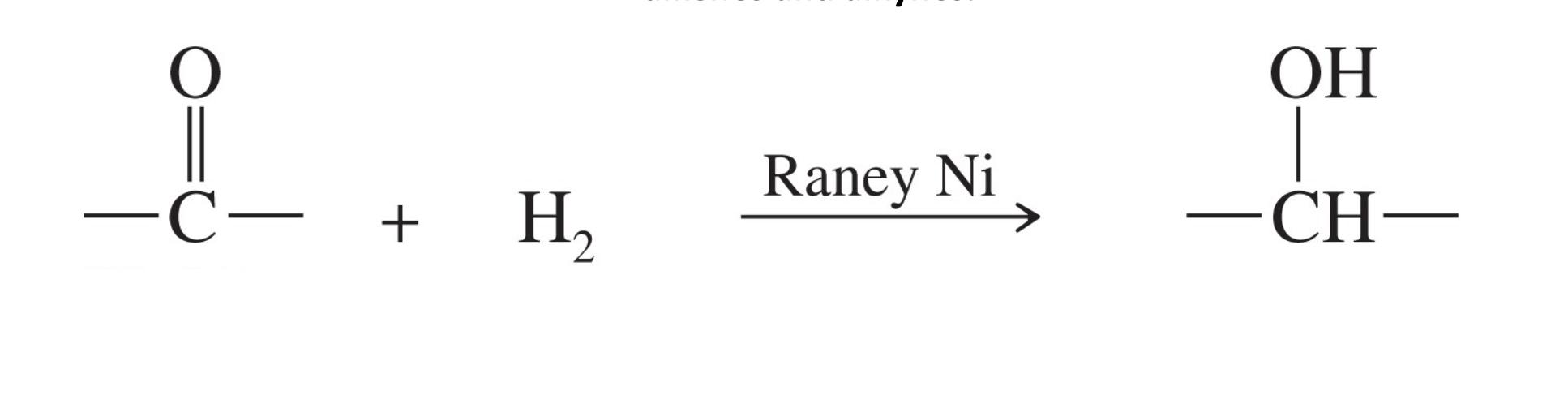Chapter 10 reactions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Making grignard reagents
Reagent Mg
Added to: R-X
ethers need to be present
Starting product R-X
End product R - MgX
Organolithium reactions
Reagent 2 Li
React the same like gringards
Starting product : R-X
End: Li - R and X- LI
Making alcohol using organometallics (MgX)
reagent: R-MgX
need and ether
R adds to the product
the double of O is released
H30 is added to make alcohol
Depending on how many R were to the original product being added you can make 1,2,3 alcohols
Ester
R - C (=O) - OR
organometallic with ester (R-Mgx)
Reagent: R-MgX
Product being attacked : Ester (R - C (= O) - OR )
End product : (3) tertiary alcohol with 2 identical alkyl group
Mechanism
the organometallic (R- MgX) attacks the carbon and double bond breaks
the intermediate: the OR group leaves and the O becomes a double bond again forming a keton
Another R - MgX comes in and add an R and the double bond with O breaks
H30 comes in and make the O into a OH
organometallic with Acid chloride (R-Mgx)
Reagent: R-MgX
Product being attacked : acid chloride → R - C ( = O) - X
x= Cl , Br, I
End product : (3) tertiary alcohol with 2 identical alkyl group
Mechanism
the R from R- Mgx attacks the acid chloride and causes the double bond with O to break
X halide leaves and causes the O to go back to a double bond and this forms a keton
Another R-MgX comes in and the R attacks the carbon again cause the double bond with O to break
H3O comes in and make O → OH
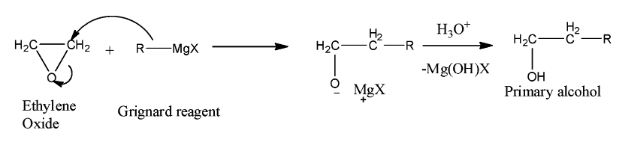
Addition to ethylene Oxide
both grignard and lithium reagent attack epoxides and opens them
REACTION IS USED: to extend the length of carbon chain by two carbon
Reagent: R -MgX
mechanism:
the R from R -MgX attacks the carbon and that cause the epoxide ring to open
so there is one carbon connected to a R group the Other Carbon connects to the O
H3O is added to make O a OH
Limitation or Organometallics
Gringards are good nucleophile but present in acid its strong base
Ex: OH,NH,SH
In the presence of multiple bond with strong electronegative element it will be a nucleophile
ex: C=O , C = N
Reduction Of Carbon
Reagents used NABH4 and LiALH4
this is used to add hydrogen instead of R goups
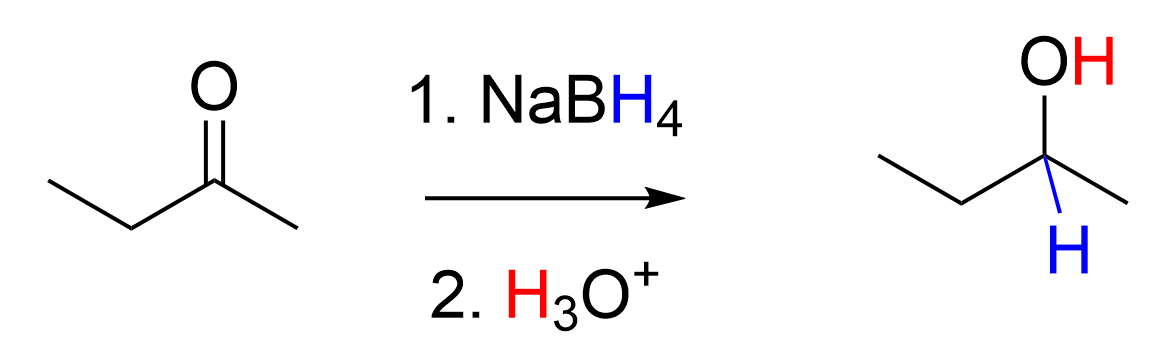
Hydride reduction with Sodium borohydride
Only reacts with Ketones and aldehydes
Reagent: NaBH4
works in the presence of a acid (H3O) or Ester (R - C (=O) - OR)
Mechanism:
the H from the BH4 acts like a hydride and adds the H to the Carbon of the aldehyde or keton
the Double bond of O breaks
H30 comes in an give a H to O to make OH
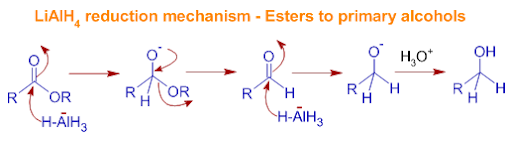
Lithium Aluminum Hydride
Reagent: LiAH4 or LAH
stronger reducing agent, dangerous to work with
WORKS WITH: all of them, Aldehyde, Ketone, Ester , Acid (anion)
But it is easier to reduce with Ester , Acid (anion)
Works the same like Sodium borhydride for aldehyde and ketone but with ester and acid it works different:
Mechanism
the H from the LiAH4 adds to the carbon
the double bond with O breaks
the OR leaves, or the strongest lG leaves
the double bond of O is formed
Another LiAH4 comes in gives a hydrogen again and the double bond with O breaks
H30 comes in and makes O into OH
Catalytic hydrogenation
Reagent : raney Ni
more reactive than Pd,PT catalyst
Hydrogen and ranny ni reduces ketons alkenes, alkyne