Digestive Tract Anatomy & Function
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
digestive system
to obtain and use nutrients
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination
Ingestion
w/ teeth, tongue, lips
Digestion
process of breaking down food/feed by mechanical and chemical (enzymes) into smaller molecules to be absorbed and nutrients used for body function
Absorption
process of moving products of digestion (ie. glucose, amino acids, fatty acids) form digestive tract into bloodstream. most in SMALL INTESTINE; also rumen
Elimination
removal of undigested
Teeth
none in poultry
upper in monogastric but not in ruminants
mastication = chewing
Prehension in mouths
varies, seize and grasp to bring food into mouth
variations in lip & number/type/size of teeth
ie. canine teeth - tearing; molars - grinding
Salivary glands
lubricate for deglutition (aka swallowing)
sodium bicarbonate (very basic pH)
may have enzymes secreted (ie. lipase - breakdown lipids)
monogastric and ruminant esophagus
transport food from mouth to stomach
peristalsis - wavelike contraction of smooth muscles
Monogastric stomach
“gastric” - of the stomach - ie. gastric juices
temporary food storage
begin/continue breakdown of nutrients absorption
hydrochloric acid (HCL) secretion - low pH; very acidic
enzyme secretion - pepsin: protein; lipase: lipids
leaves as chyme
chyme
mixture of feed, saliva, and gastric secretions
Monogastric and ruminant small intestine
3 segments: duodenum, jejunum, ileum
major site of nutrient digestion and absorption
pancreas empties into duodenum
Monogastric large intestine
3 segments: cecum, colon, rectum
key role is water absorption
aka. “hindgut”
“hindgut”
much larger in horse than other monogastric
key in horses; some digestion/absorption in other monogastric
horse is hindgut fermenter
microbes present to digest fiber
Horse as “hindgut fermenter”
~38% volume foregut - mouth through small intestine
~62% volume hindgut - large intestine
Colic
abdominal pain originating from gastrointestinal tract
“gut ache”
Common causes of colic
gas buildup (abrupt diet change)
impaction of feed/other obstructions
abnormal contractions
inflammation of GI tract (ENTERITIS)
“twisted gut” - intestines twisted
Colic prevention
avoid dehydration
ample forage/limited grains
smaller meals at regular intervals
gradual vs abrupt ration changes
“Rumination” in ruminants
process of regurgitation of undigested feed and chewing it a second time and swallowing again
aka. “chewing their cud”
further breakdown of feedstuffs
regurgitation, remastication, resalivation, redeglutition
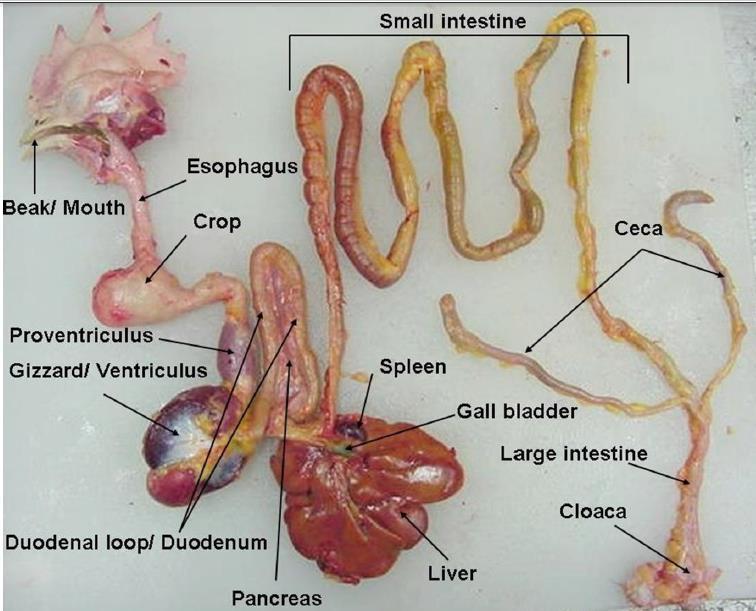
Ruminant digestive tract
reticulum, rumen, omasum, abomasum
Reticulum
aka. honeycomb; “hardware stomach”
assist in regurgitation
fermentation of feed
trap indigestible foreign materials
no glands
less absorptive then rumen
Rumen
aka. paunch
w/ reticulum 85%+ of volume in mature ruminant
left side of anima
“fermentation vat”
microbial fermentation
bacteria, protozoa, fungi
normal pH 5.8 to 6.8
Omasum
aka. many piles; like pages of book
Abomasum
“true stomach”
fermentation
an enzymatically controlled anaerobic breakdown of an energy-rich compound
papillae
increase surface area for absorption
volatile fatty acids (VFAs)
key product of carbohydrate fermentation absorbed here
are waste product for rumen microbes
key source of energy
includes: acetate (C2), propionate (C3), butyrate (C4)
acidosis
challenge in feedlot cattle/lambs/goats
pH becomes too low (>5.5)
abrupt diet changes; too much grain (highly fermentable) in short period of time
beneficial rumen microbes killed
Ruminant digestive issues
acidosis and bloat
bloat
trapped excess gas in rumen - distended left side of animal
inability to eructate
types: frothy (bubbles) - lush pastures; dry (free gas) - feedlot
adequate hay in diet to lessen incidence
Abomasum
functions exactly like monogastric stomach
glands - secrete HCl, enzymes
animal begin to digest microbes here too
horse gets limited use of microbes as protein sources
cow digestive tract image
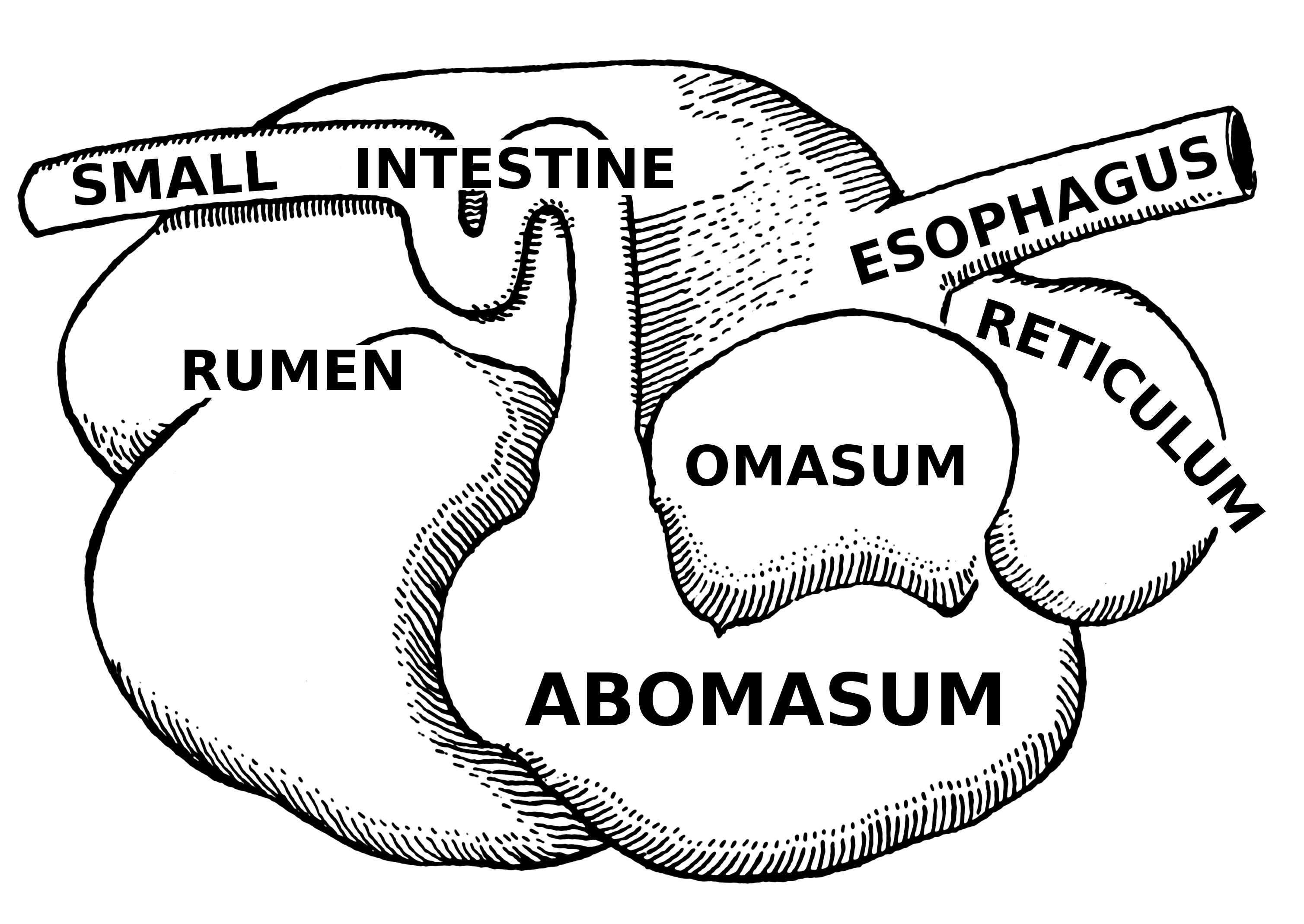
chicken digestive tract image