heart failure (pharmacology)
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
heart failure
complex clinical syndrome that can result from any structural or functional cardiovascular disorder causing systemic perforation inadequate to meet the body's metabolic demand without excessively increasing left ventricular filling pressures
left ventricular ejection fraction
the volume of blood % pumped with each ventricular contraction
SV = (LV end-diastolic volume) - (LV end-systolic volume)
formula for stroke volume in relation to left ventricular volume
LVEF = SV/(LV end-diastolic volume) x 100
formula for LVEF
50-70%
normal LVEF in an adult
systolic dysfunction (HFrEF)
reduced LVEF = _________
decreased ejection fraction due to enlarged ventricles
systolic dysfunction results in....
lower amount of blood being ejected due to stiff ventricles (hypertrophy); ejection fraction stays the same, but the amount is lower
diastolic dysfunction results in...
hyper/hypotension, SOB
common symptoms of acute heart failure
airway management (keep patient upright, oxygen therapy, intubation/full ventilatory support)
main mode of treatment for acute heart failure
Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV)
BIPAP and CPAP apply pressure to the lungs to open up the alveoli and improve ventilation and oxygenation
BiPAP (bilevel positive airway pressure)
Mask that ventilates either by facial or nasal mask with inspiratory pressure is higher and expiratory pressure is lower; tries to keep alveoli open, forces air and fluid to cross alveolar membrane and back into the cardiovascular system --> gets fluid out!
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure)
a device that is commonly used to regulate breathing during sleep as a treatment for sleep apnea
Diuretics
medications administered to increase urine secretion in order to rid the body of excess water and salt
aortic stenosis
use caution in using diuretics in patients with...
IV
preferred mode of administration for diuretics
loop diuretics
drugs that act in the ascending limb of loop of henle by clocking the reabsorption of Na+/K+/Cl-
block reabsorption of Na+/Cl-/K+ into the bloodstream from the ascending loop of henle
loop diuretic MOA
increased Na+, K+, Cl- excretion; profound diuretic action (water follows solutes)
effects of loop diuretics
Furosemide (Lasix), Bumetanide (Bumex), Torsemide (Demadex)
loop diuretic medications
volume depletion, hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypochloremia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, hyperuricemia, hyperglycemia, hypotension, ototoxicity
adverse effects of loop diuretics
vasodilator therapy
medications that correct elevated filling pressures and/or left ventricular afterload
nitroglycerine, nitroprusside, nicardipine
vasodilator therapy agents
2-3
when managing acute heart failure, one must not have more than _______ grams of sodium daily.
1.5-2
when managing acute heart failure, one must not have more than _______ L of fluid daily.
manage associated/contributing conditions (hypertension), lifestyle modifications, pharmacologic therapy, device therapy, cardiac rehabilitation, serial assessments
key ways to manage chronic heart failure
increased after load/ventricular remodeling
hypertension can caused what issues that can exacerbate heart failure?
beta blockers, ace inhibitors, ARBs, hydralazine, calcium channel blockers (dihydropyridine), loop diuretics
preferred agents to treat hypertension in someone with chronic heart failure
smoking cessation, weight management, sodium/fluid restriction, restrict ETOH/illicit drugs, daily weight monitoring
lifestyle modifications that help manage chronic heart failure
so that they can make sure they are not retaining fluid/exacerbating their heart failure
why should one with chronic heart failure check their weight every day?
volume status, kidney function
in patients with chronic heart failure, dosing of diuretics will depend on _________ and _________.
asymptomatic/symptomatic left ventricular dysfunction
ACE inhibitors are imperative in patients with what condition(s)?
low
ACE inhibitors are began at _____ doses
cough
ARBs are given to patients that are ACE inhibitor intolerant due to...
beta blockers can actually make heart failure symptoms worse, since they won't let the pump work harder/squeeze faster; can be bad b/c they can decrease CO (Too relaxed)
why should one be careful in their use of beta blockers for heart failure?
inotropic therapy (do not give BB to those who required this recently)
dopamine/epinephrine
cariogenic shock
results when an inefficient heart cannot sustain adequate circulation
very low
when starting a pt on a beta blocker, start doses...
Cavedilol, Metoprolol, Bisoprolol
go to beta blockers for one with CHF
Carvedilol
beta-blocker with alpha-blocking activity
Metoprolol
beta blocker that is cardiac specific
resistant edema, reduction/cessation
_______ or more severe decompensation may require dose ______ or ______ of beta blockers
ACEI
in pts with CHF, are ACEI or beta blockers given first?
ACE inhibitors, as they provide rapid hemodynamic benefit and will not exacerbate HF in the short term
in CHF patients, _______ are given first because...
Spironolactone
potassium sparing diuretic that is used in addition to ACEI/ARB and BB
a beta blocker, an ACEI, and a diuretic
almost all CHF patients will be on...
increase any of the 3 or add something in to help
what is the next step in CHF treatment if pharmacologic therapy is not getting patient to their goal
ACEI/ARB and BB
Spironolactone is used in addition to...
adjuvant
Spironolactone is an ______ drug
potassium (remove potassium supplementation) and renal function
one should carefully monitor what in a patient on Spironolactone?
potassium
Spironolactone is a ________-sparing diuretic
competes with aldosterone for receptor sites in the distal renal tubules, increasing NaCl and water excretion while conserving potassium and hydrogen ions
Spironolactone MOA
treatment post MI
off label use for Spironolactone
gynecomastia, renal failure, dizziness, hepatotoxicity, hyperkalemia
side effects of Spironolactone
hyperkalemia, renal failure/anuria, Addison disease, hypersensitivity/anaphylaxisis
contraindications for Spironolactone
Digoxin
Antiarrhythmic/cardiac misc drug that is used in addition to ACEI/ARB, BB, and diuretic; adjutant drug
works on rhythm system of the hear, and helps heart SQUEEZE MORE EFFECTIVELY
function(s) of Digoxin
fatigue, dyspnea, and exercise intolerance
Digoxin is used to control symptoms such as...
to control the ventricular rate
how is digoxin used in patients with A-fib
Anti-arrhythmic/cardiac misc
Digoxin classification
inhibition of sodium/potassium ATPase pump in myocardial cells results in a transient increase of intracellular sodium, which in turn promotes calcium influx via the sodium-calcium exchange pump leading to increased contractility (SQUEEZE MORE EFFECTIVELY)
Digoxin MOA in heart failure
direct suppression of the AV node condition to increase effective refractory period and decrease conduction velocity - positive inotropic effect, enhanced vagal tone, and decreased ventricular rate to fast atrial arrhythmias
Digoxin MOA in supraventricular arrhythmias
bradycardia/heart block; ventricular arrhythmias; N/V; dizziness (esp. with toxicity); rash, laryngeal edema
Digoxin side effects
ventricular arrhythmias, hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis
contraindications for Digoxin
implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
an implanted, battery-operated device with rate-sensing leads; the device monitors cardiac impulses and initiates an electrical stimulus as needed to stop ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia; used for primary or secondary prevention of sudden cardiac death
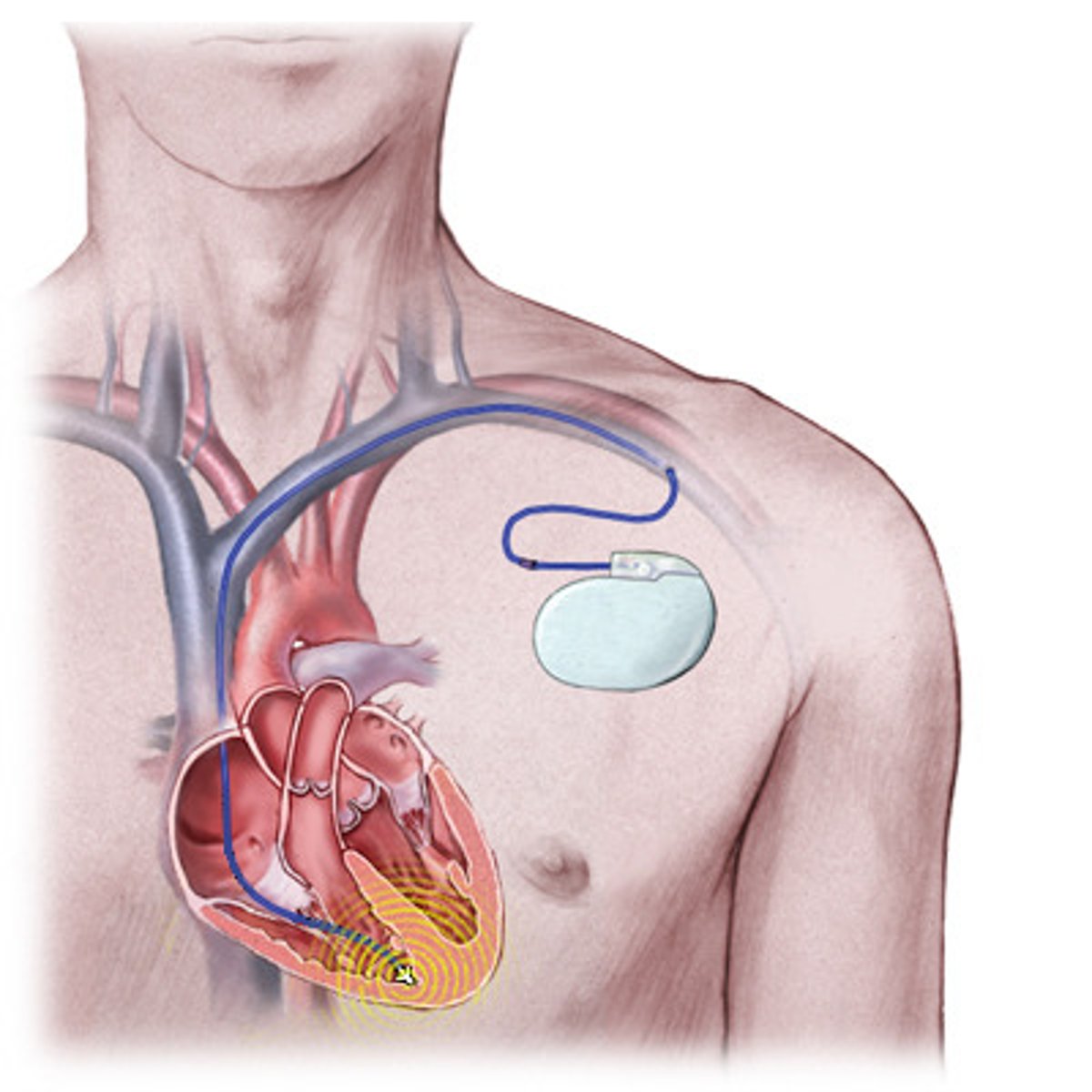
internal-defibrillators
all ______ are pacemakers, but not all pacemakers are ________
sudden cardiac death
ICD is used for primary or secondary prevention of...
cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT)
biventricular pacing used to correct desynchronization in the ventricles which would therefore increase cardiac output
sinus rhythm, reduced LVEF, prolonged QRS duration
CRT improves symptoms and survival in what kinds of patients?
Cardiac Rehabilitation
An intervention program designed to help heart patients achieve their optimal physical, medical, psychological, social, emotional, vocational, and economic status after the diagnosis of heart disease or a heart attack; beneficial effects of exercise are seen with high or low levels of training, and are apparent as early as three weeks after training.
advanced arrhythmias, other limitations to exercise, advanced HF
what are some contraindications to cardiac rehabilitation
Serial Assessment
continuing evaluation to meet changing needs; assesses status, response to therapy, and potential need for changes in management
ability to perform activities of daily living, volume status and weight, current use of alcohol, tobacco, illicit drugs, alternative therapies, and chemotherapy drugs, diet and sodium intake
what is assessed during a serial assessment
get an updated ECHO
if there are changes in a pt with CHF's treatment/status, what should you do?
annual influenza vaccine, pneumococcal vaccination
important preventative care in patients with CHF
these illnesses can exacerbate HF
why is it important for CHF pts to get their annual influenza vaccine and pneumococcal vaccination?
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
HFrEF; heart failure associated with systolic dysfunction and reduced myocardial contractility; ejection fraction is ≤ 40%.
Heart failure with improved ejection fraction
HFimpEF, previous LVEF ≤ 40%. and now with LVEF >40%
Heart failure with Mildly reduced ejection fraction
HFmrEF; LVEF 41-49% and/or evidence of increased LV filling pressures
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
HFpEF; LVEF >50% and evidence of increased LV filling pressures; "diastolic dysfunction"
volume overload (peripheral/pulmonary edema)
we use the term "congestive heart failure" when the patient shows signs of...
CAD/ischemic cardiomyopathy, diabetes, LVH, hypertension, valvular heart disease, family history, cardiotoxic agents, obesity, smoking
major risks for HF
left heart failure
the left side of the heart is weakened and results in reduced ability for the heart to pump blood into the body.
Right heart failure
the right side of the heart is weakened and results in fluid in your veins, causing swelling in the legs, ankles, and liver.
pulmonary edema (fluid backs up to lungs and causes crackles; no gas exchange)
LHF leads to....
swelling in other parts of the body --> ankles, sacrum; congestion of liver; jugular dissension
RHF leads to...
LHF
the most common cause of RHF is...
dyspnea (orthopnea, DOE, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea), edema/volume overload (pulmonary edema (crackles/spiutum), peripheral edema, jugular vein distention), abdominal distention, weakness/fatigue
presentation of a pt in heart failure
tachycardia, narrow pulse pressure, hyper/hypotension, diaphoresis, pale skin, precordial palpitation, displacement of the apex, parasternal lifting, S3 heart sound, P2 heart sound
physical exam findings on a pt with HF
S3 heart sound
Increased ventricular filling pressure (e.g., mitral regurgitation, HF), common in dilated ventricles
P2 heart sound
Pulmonic closure that occurs slightly before pulmonic closure; pulmonary insufficiency
see changes in those with systolic dysfunction; can see cause of HF (previous MI, ischemic changes, arrhythmia, signs of LVH)
purpose of an EKG on an HF pt
anemia can exacerbate HF
why do you get a CBC for a person with suspected HF?
hyponatremia is seen in HF (Na+ low --> too much water)
why do you get a serum electrolytes count for a person with suspected HF?
renal insufficiency can contribute/be caused by HF
why do you get a BUN/Creatinine for a person with suspected HF?
their LFTs would be elevated due to liver congestion
why do you get liver function tests for a person with suspected HF?
hyper/hypothyroidism can precipitate HF
why do you test TSH levels in a person with suspected HF?
Troponin
heart muscle protein released into circulation after myocardial injury
it may be elevated in acute HF, AMI can precipitate HF
why do you test for troponin levels in the blood in a pt with HF?
BNP (brain natriuretic peptide)
natriuretic hormone released primarily from the heart, particularly the ventricles (they pump it out when they're strained); measurement for this is suggested in the evaluation of pts with suspected HF when the diagnosis is uncertain