2.6 - Electromagnetic Waves
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What kind of waves are electromagnetic waves?
transverse waves
What do all electromagnetic waves do?
transfer energy as radiation from the source of the waves to an absorber
can travel through a vacuum such as in space
travel at the same speed through a vacuum or the air
How fast do all electromagnetic waves travel?
300 million metres per second (m/s) through a vacuum, the speed of light
What do electromagnetic waves form?
a continuous spectrum of waves
What are the distinctions between the continuous spectrum of waves?
waves with a very short wavelength, high frequency and high energy
waves with a very long wavelength, low frequency and low energy
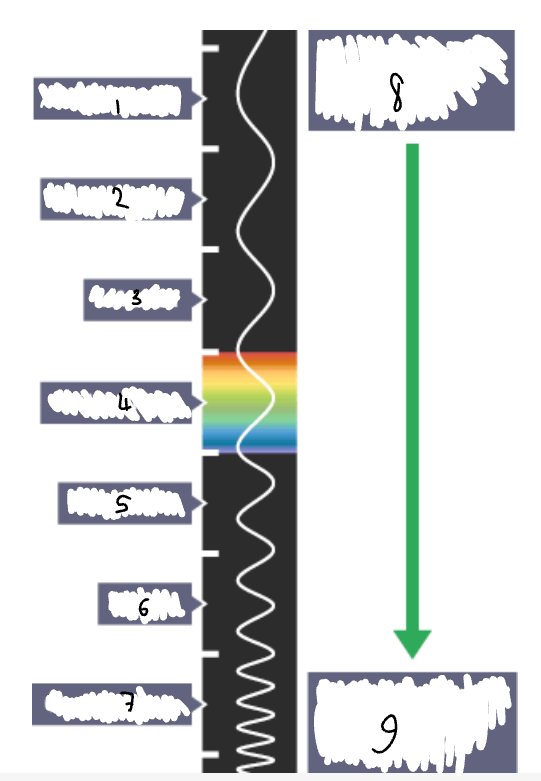
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum is 1?
radio waves
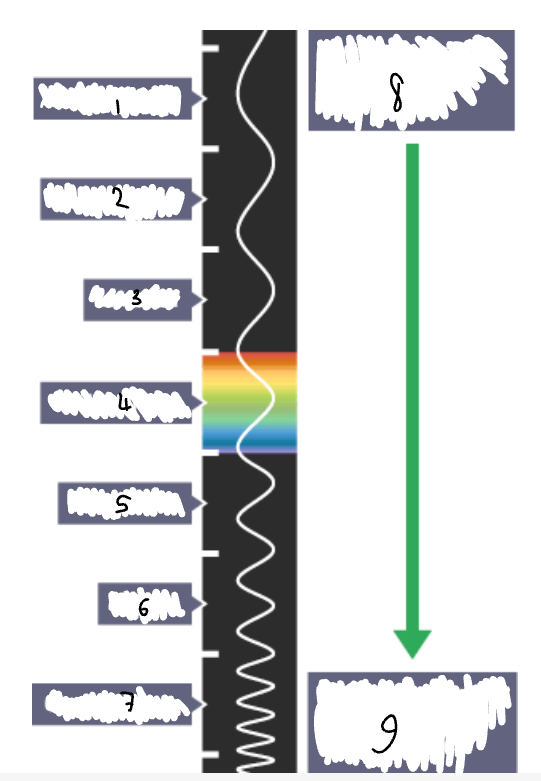
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum is 2?
microwaves
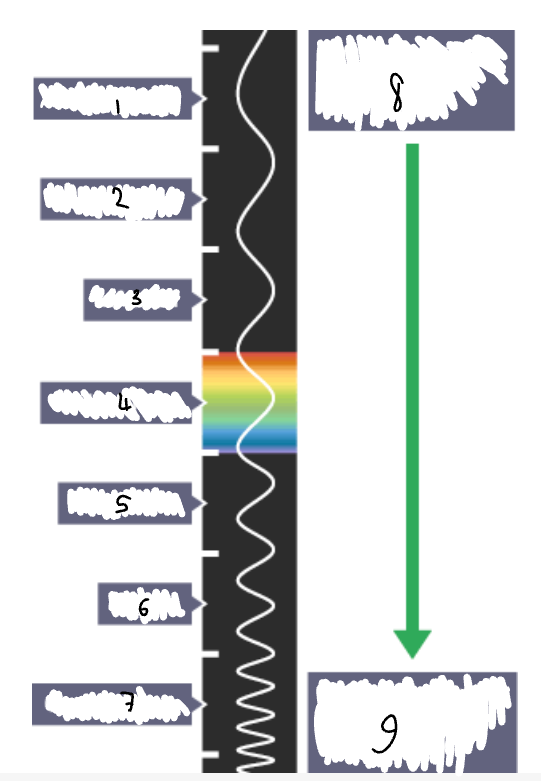
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum is 3?
infrared radiation
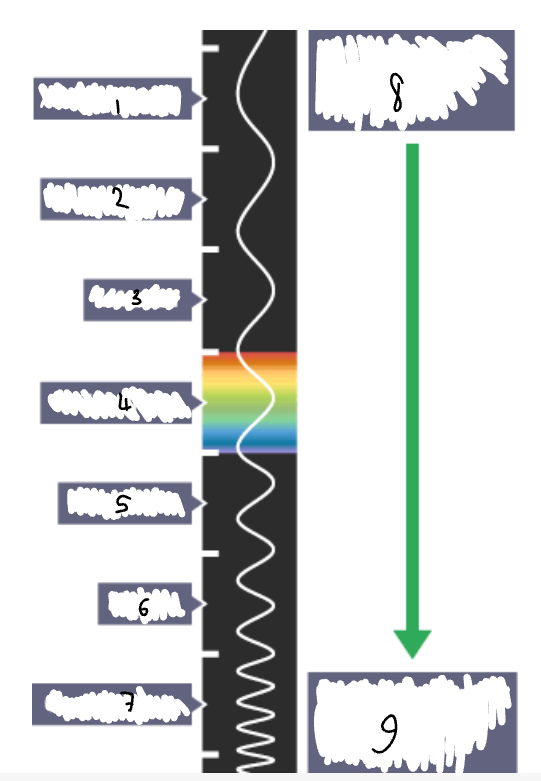
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum is 4?
visible light
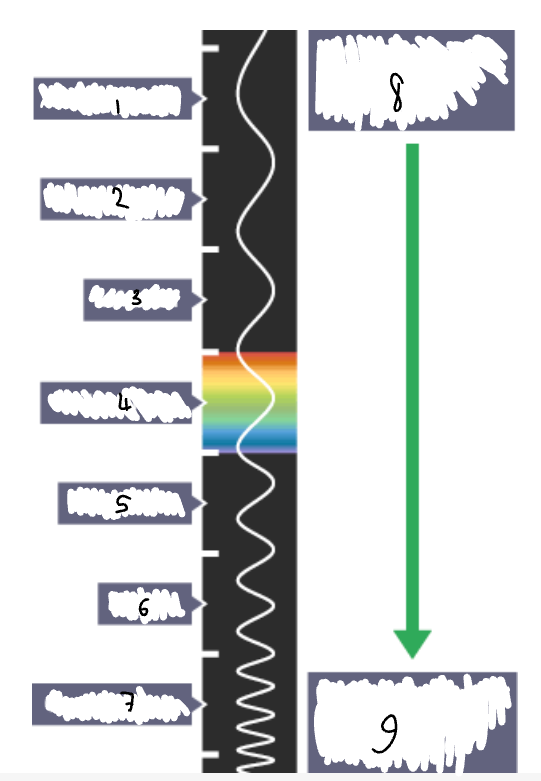
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum is 5?
ultraviolet
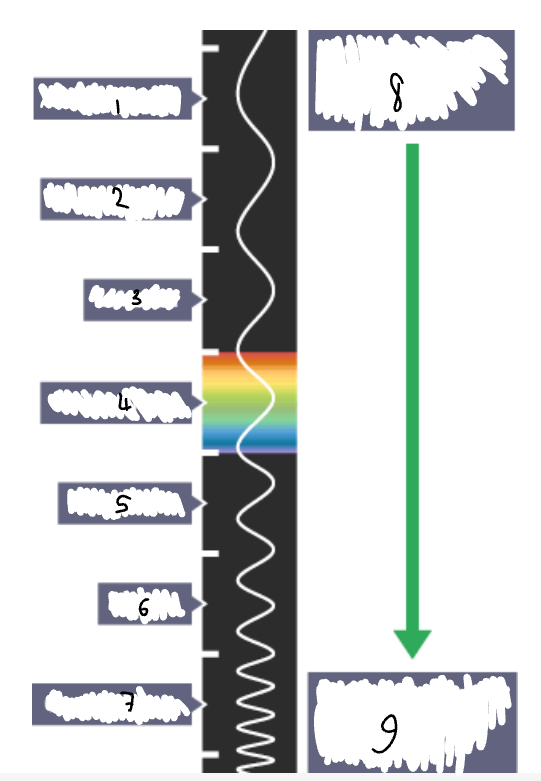
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum is 6?
x-rays
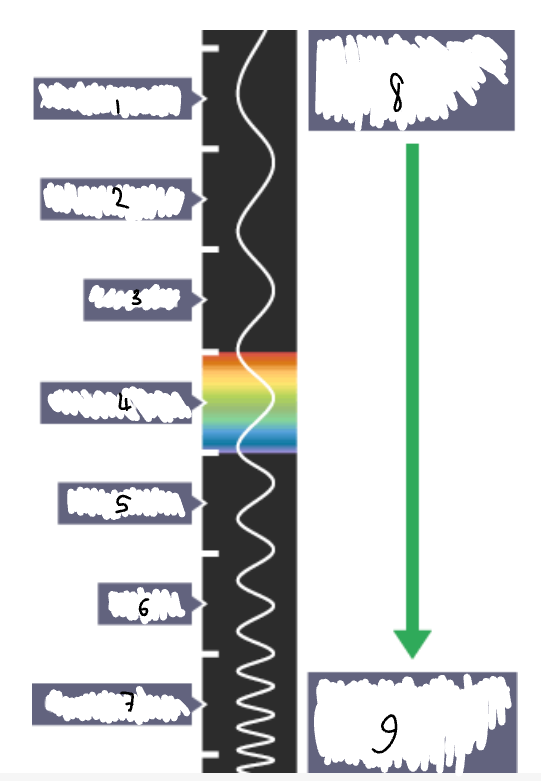
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum is 7?
gamma rays
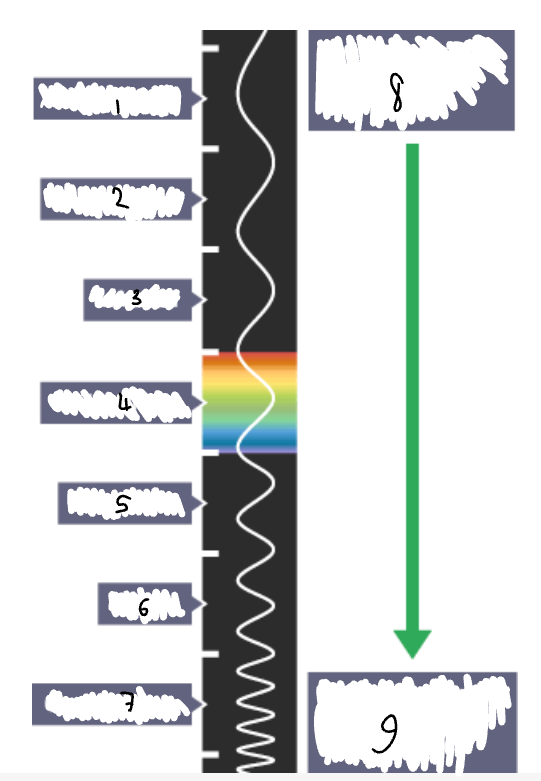
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum is 8?
long wavelength
low frequency
low energy
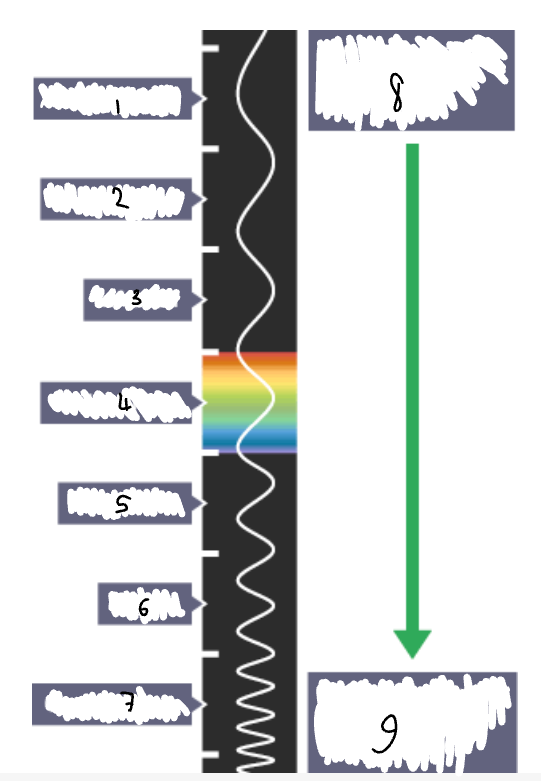
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum is 9?
short wavelength
high frequency
high energy
What does the behavior of an electromagnetic wave in a substance depend on?
frequency
What are long wavelength electromagnetic waves?
radio waves
microwaves
infrared
visible light
What are short wavelength electromagnetic waves?
ultraviolet
x-ray
gamma ray
What is the frequency range of radio waves?
105 - 1010 Hz
What is the wavelength range of radio waves?
103 - 10-2 m
What is the frequency range of microwaves?
1010 - 1011Hz
What is the wavelength range of microwaves?
10-2 - 10-3m
What is the frequency range of infrared radiation?
1011 – 1014Hz
What is the wavelength range of infrared radiation?
10-3 - 10-6 m
What is the frequency range of visible light?
1014 - 1015Hz
What is the wavelength range of visible light?
106 - 10-7m
What is the frequency range of ultraviolet?
1015 - 1016Hz
What is the wavelength range of ultraviolet?
10-7 - 10-8
What is the frequency range of x-rays?
1016 - 1018Hz
What is the wavelength range of x-rays?
10-8 - 10-10m
What is the frequency range of gamma rays?
1018 - 1021Hz
What is the wavelength range of gamma rays?
10-10 - 10-14m
How are radio waves produced?
oscillations in an electrical circuit
What are radio waves absorbed by?
by a receiver aerial
What happens when radio waves are absorbed?
they may create an alternating current with the same frequency as the radio waves
What can EM waves of a wide range of frequencies do?
be absorbed or produced by changes inside an atom or nucleus
How are gamma rays produced?
changes in the nucleus of an atom
What happens when electrons in an atom move down energy levels?
they emit EM waves
What are the uses of radio waves?
television and radio signals
Why are radio waves suitable for their use?
can travel long distances through air
longer wavelengths can bend around obstructions to allow detection of signals when not in line of sight
What are the hazards of radio waves?
can penetrate the body and cause internal heating
What are the uses of microwaves?
satellite communicates
cooking food
Why are microwaves suitable for their use?
can pass through Earth’s atmosphere to reach satellites
can penetrate into food and are absorbed by water molecules in food heating it
What are the hazards of microwaves?
can penetrate the body and cause intern at heating
What are the uses of infrared?
electrical heaters
cooking food
infrared cameras
Why is infrared suitable for their use?
all hot objects emit infrared waves sensors can defect these to turn them into an image
can transfer energy quickly to heat rooms and food
What are the hazards of infrared?
can damage or kill skin cells due to heating
What are the uses of visible light?
fibre optic vommunications
Why is visible light suitable for their use?
short wavelength means visible light carries more information
What are the hazards of visible light?
can damage the retina
What are the uses of ultraviolet?
energy efficient lights and artificial sun tanning
Why is ultraviolet suitable for its use?
carries more energy than visible light
some chemicals used inside light bulbs can absorb UV and emit visible light
What are the hazards of ultraviolet?
can damage skin cells causing skin to age prematurely and increasing the risk of skin cancer and can cause blindness
What are the uses of x-rays?
medical imaging and treatments
Why is x-rays suitable for their use?
pass easily through flesh but not denser materials like bone
high doses kill living cells, so can be used to kill cancer cells
What are the hazards of x-rays?
form of ionising radiation which can kill or damage cells, cause mutation of genes and lead to cancers
What are the uses of gamma rays?
medical imaging and treatments
Why is gamma rays suitable for its use?
pass easily through flesh but not denser materials like bone
high doses kill living cells, so can be used to kill cancer cells - gamma rays can also be used to kill harmful bacteria
What are the hazards of gamma rays?
form of ionising radiation which can kill or damage cells, cause mutation of genes and lead to cancers