co-ownership
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
co-ownership
= concurrent ownership
2 or more ppl have interest in ownership of the same property at the same time
the use of trust
ss.34-36 LPA 1925 - requires the use of trust in all cases of co-owned property
trustee - has paper title - has to look over the land
beneficiary - has the benefit of land
A + B buy a house together - in law A+B are trustees, in equity they are beneficiaries
s.34(2) Trustee act 25 - max number of trustees = 4 adults - minimum age of 18 yrs
co-ownership types
joint tenancy
tenancy in common
joint tenancy
don’t have specific shares - own whole interest in property simultaneously
impact of death - right of survivorship applies - if B dies, A becomes sole owner - unless written otherwise in a will
tenancy in common
each owner has a specific undivided share + the can decide relative value of shares
doctrine of survivorship does not apply - If B dies, goes to relative/whoever in will
JT + TiC within a trust
trustees (at law) can only be joint tenants - s1(6) LPA 1925: a legal estate in land is not capable of subsisting or of being created in an undivided share in land
beneficiaries can be joint tenants or tenants in common (in equity)
beneficial JT
JT in equity + law
upon death - doctrine of survivorship applies - remaining owner gets the interest + becomes sole owner
beneficial TiC
at law JT - TiC in equity (beneficiary)
upon death - at law - doctrine of survivorship applies + remaining T becomes sole trustee
but in equity - doctrine doesn’t apply + share is passed down
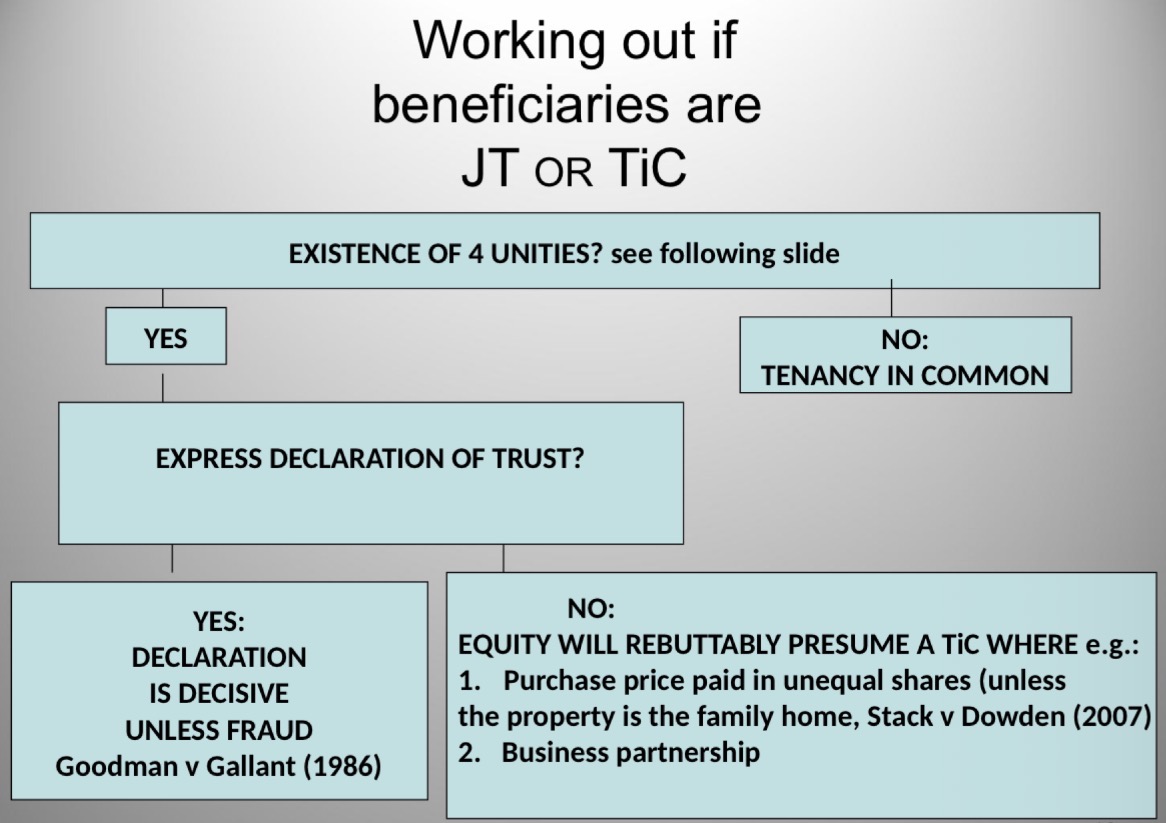
pre-conditions for existence of JT + TiC
JT: 4 unities must be present
P - possession: each equally entitles to possession of whole property
I - interest: identical interest in property - type of proprietary right they have in property
T - title: acquire title by same doc
T - time: interest in property vests at same time
TiC: only need P - possession
must be unity of possession - undivided in possession of physical property
working out if beneficiaries are JT or TiC
co-ownership + severance
the conversion of JT into a TiC
legal JT - no - s.36(2) LPA 25 - no severance of JT of legal estate so as to create a tenancy in common in land shall be permissible - cannot sever legal estate
beneficial JT - yes - beneficiaries become entitled to equal portions of property value - Goodman c Gallant (1986) - other T can remain in joint tenancy at the same time + T w severance gets only their share
methods of severance
statutory severance - notice in writing under s.36(2) LPA 1925
common law severance - 3 methods in Williams v Hensman (1861)
severance by operation of law - forfeiture - one Jt murders another JT causing a severance
statutory severance
s.36(2) LPA 1925: where any T desires to sever the JT in equity, shall give to other JTs a notice in writing of such desire
its form - unilateral act, one JT can serve notice to others w/out consulting them - no specified form just in writing - Quigley v Masterson (2011)
its content - Harris v Goddard (1983)
evidence of intention to sever - wording
need for immediacy - not in future
its service
the addressee - all the JTs
method of service - s.196 LPA 25
method of service
s.196(4) LPA 25: notice can be sent by registered or recorded delivery to last known place of abode or business of person to be served
s.196(3) LPA 25: notice can be left at, or affixed to, last known place of abode or business of person to be served
first class post - Kinch v Bullard (1999) - valid service + comes under ss.3 - postman acts as agent + leaves notice at property
lack of receipt/change of mind
lack of receipt by addressee:
Kinch v Bullard: beneficial JT, wife wants to serve notice + become TiC, Fri solicitor sends notice by post, Sat husband has heart attack, wife doesn’t want severance anymore, court ruled severance took place as soon as notice arrived at property
don’t need to see it
change of mind by sender: K v B
obiter dicta - can change mind if you tell person of this before notice arrives
common law severance
William v Hensman (1861):
an act operating on one’s own share - unilateral conduct
mutual agreement - Burgess v Rawnsley (1975)
mutual conduct - Greenfield v Greenfield (1979) + B v R
unilateral conduct
an act of one JT operating upon his own beneficial share by a legally enforceable act - sale, mortgage, bankruptcy - in equity - may still own trust in law
mutual agreement
an agreement between all the JT indicating a common intention to sever - not legal but more than inconclusive negotiations
Burgess v Rawnsley: 2 friends buy a house - JT in equity, only orally agreed he would buy out share in house + price, dies + daughter claimed severance
court held that severance took place upon when they reached a oral agreement - daughter got half share of house
course of dealing
which shows that the interest of all the JT were mutually treated as constituting a TiC - course of dealing which shows they wanted severance
can get inconclusive negotations
Greenfield v Greenfield: 2 brother buy house, turned into 2 flats when both married, 1 brother dies + wife entitled to property under will - wife argued making it into 2 flats = course of dealing to sever
court held physically dividing house was for convenience, no intention to sever
trusts of land
trusts of land and appointment of trustees act 1996 (TOLATA)
power of trustees
s.6: for the purpose of exercising their functions as trustees, the trustee of land have all powers of absolute owner
power of sale, leasing, mortgaging
s.6(5): the trustees must have regard to the rights of beneficiaries and
s.6(6): must not act contrary to any rule of law or equity
restrictions on powers of trustees
s.10: consent - an expressly created trust can impose a requirement for consent from named parties to dealings w land
cant sell w/out consent from X
s.11: consultation - duty on trustee to consult w adult beneficiaries entitles to interest in possession
so far as practicable
giving effect to wishes of majority by value - so far as those wishes are consistent w the general interest of trust - beneficiary who has majority by value (share)
beneficiary’s right to occupy (s.12)
a beneficiary w an interest in possession has right to occupy the trust property
s.12: the right arises if -
the purposes of trust include making trust land available for occupation
OR
the T’s hold land so as to be available, and
land is suitable for occupation
beneficiary’s right to occupy (s.13)
s.13(1): where +1 beneficiary’s entitled to occupy, Ts can exclude 1 or more but not all of the beneficiaries
they:
must act reasonably 13(2)
and take into account the matters set out in 13(4)
and can exclude a beneficiary already in occupation 13(1)
s.13(3): T can impose reasonable conditions on occupying beneficiaries
s.13(6): occupying beneficiary may be required to pay compensation to excluded beneficiary
application to court to resolve disputes
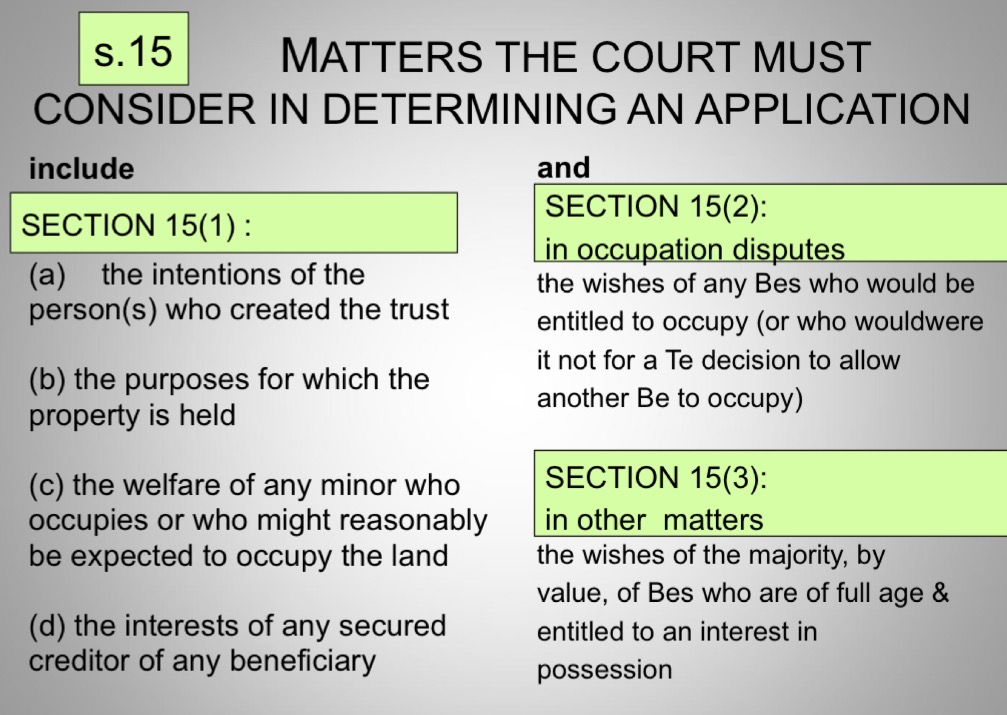
s.14(1) who can apply:
any trustee of land
any beneficiary under a trust of land
s.14(2) orders the court can make:
any order it thinks fit in relation to -
the exercise by the trustees of any of their functions
for the purpose of declaring nature or extent of any persons interest
matters court must consider in determining an application for disputes
Fred Perry v Ivan Genis (2014):
husband selling counterfeits, FP charged order over house to sell in order to be paid, 2 children living in property
court gave priority to creditors over family but delayed sale of house so family can find place to live
application for sale by trustee in bankruptcy
bankruptcy automatically severs any beneficial JT
the trustee in bankruptcy must
apply to court order under s.14 TOLATA
then court will apply criteria in s.335A Insolvency Act 1986
