personnel psychology exam 3 flashcards
5.0(2)Studied by 4 people
Card Sorting
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:03 AM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
1
New cards
construct
theoretical concept on which people vary, used to explain behavior (what do we measure?). what we propose to explain aspects of behavior
ex- intelligence, motivation
ex- intelligence, motivation
2
New cards
method
specific process or technique by which domain-relevant behavioral information is __*elicited*__, __*collected*__ and subsequently __*used to make inferences*__ (how do we measure? usually measures more than one construct)
ex- interview, assessment center, tests
ex- interview, assessment center, tests
3
New cards
reliability
evaluates the consistency, stability or equivalence of a measure
4
New cards
types of reliability (4,3)
* test-retest: coefficient of stability. stability of a score over time when measuring a construct that should be relatively stable (same person takes the same test)
* equivalent forms: coefficient of equivalence. different forms of the same test should produce scored that are consistent (same person takes different forms. the more we separate them in time, the more we are likely to capture equivalent forms and test retest reliability)
* internal consistency: extent to which the test content is homogeneous. correlation is calculated within the items in the test
* split half: scores are split into 2 groups. scores of each groups are compared to see if they are correlated. usually scores are divided into even & odd numbers to account for fatigue in long tests
* coefficient alpha: correlating all possible combinations of items. the response to each item is correlated with the response to every other item
* kuder-richardson 20: reserved for dichotomously scored tests (right and wrong, true and false.)
* inter-rater: correlating scores from one rater to another. degree of agreement among assessments provided by 2 or more raters
* equivalent forms: coefficient of equivalence. different forms of the same test should produce scored that are consistent (same person takes different forms. the more we separate them in time, the more we are likely to capture equivalent forms and test retest reliability)
* internal consistency: extent to which the test content is homogeneous. correlation is calculated within the items in the test
* split half: scores are split into 2 groups. scores of each groups are compared to see if they are correlated. usually scores are divided into even & odd numbers to account for fatigue in long tests
* coefficient alpha: correlating all possible combinations of items. the response to each item is correlated with the response to every other item
* kuder-richardson 20: reserved for dichotomously scored tests (right and wrong, true and false.)
* inter-rater: correlating scores from one rater to another. degree of agreement among assessments provided by 2 or more raters
5
New cards
validity
a test’s accuracy or appropriateness for predicting or drawing inferences about criteria
6
New cards
types of validity (4, 2, 3)
* construct-related: degree to which a test is an accurate and faithful measure of the construct it’s supposed to measure. how well does our measure actually represent our theoretical construct ?
* convergent: 2 tests that attempt to measure the same thing are compared (one new test and existing measures.) tries to show that the 2 tests are correlated
* discriminant: score in a test is negatively correlated/not related at all to things that it shouldn’t be related to
* criterion-related: relationship between the score on a test and how well it is correlated to criterion (behavior in the workplace.) Most times, it is job performance
* concurrent: how well a predictor can predict criterion simultaneously (ex- predict worker’s level of productivity on the basis of a test and collect productivity data on a current group of workers. we then correlate test scores with productivity records with *no time interval between collecting the predictor and criterion data*)
* predictive: collect predictor information and use it to forecast future criterion performance. (ex- relationship between assessment and job performance)
* postdictive: scores on the criterion first and predictors later. (ex- scores on accident, then we gather risk-taken behaviors)
* content-related: degree to which subject matter experts agree that the items in a test are a representative sample of the domain of knowledge the test claims to measure
* face: how valid is the test from the perspective of test takers
* convergent: 2 tests that attempt to measure the same thing are compared (one new test and existing measures.) tries to show that the 2 tests are correlated
* discriminant: score in a test is negatively correlated/not related at all to things that it shouldn’t be related to
* criterion-related: relationship between the score on a test and how well it is correlated to criterion (behavior in the workplace.) Most times, it is job performance
* concurrent: how well a predictor can predict criterion simultaneously (ex- predict worker’s level of productivity on the basis of a test and collect productivity data on a current group of workers. we then correlate test scores with productivity records with *no time interval between collecting the predictor and criterion data*)
* predictive: collect predictor information and use it to forecast future criterion performance. (ex- relationship between assessment and job performance)
* postdictive: scores on the criterion first and predictors later. (ex- scores on accident, then we gather risk-taken behaviors)
* content-related: degree to which subject matter experts agree that the items in a test are a representative sample of the domain of knowledge the test claims to measure
* face: how valid is the test from the perspective of test takers
7
New cards
relationship between reliability and validity
a test can be reliable and not valid, but if a test is valid, then it must also be reliable. reliability sets the upper limit on validity (sqr root of a test’s reliability= upper limits of its validity)
8
New cards
ethical standards in testing (5)
* apa guidelines: what tests should be administered, how, etc.
* apa standards for educational and psychological testing: updated regularly to be representative of new science that expands on our information about psychometrics
* qualifications to administer tests: educational qualifications, certification, etc
* invasion of privacy: more information than necessary shouldn’t be revealed
* confidentiality: who should have access to the test results?
* apa standards for educational and psychological testing: updated regularly to be representative of new science that expands on our information about psychometrics
* qualifications to administer tests: educational qualifications, certification, etc
* invasion of privacy: more information than necessary shouldn’t be revealed
* confidentiality: who should have access to the test results?
9
New cards
sources of information about tests (4,2)
* mental measurement yearbook
* tests in print
* publisher catalogs
* consulting forms
* off the shelf tests: able to be used for any job
* custom tests: job/company specific
* tests in print
* publisher catalogs
* consulting forms
* off the shelf tests: able to be used for any job
* custom tests: job/company specific
10
New cards
resumes & application blanks
brief summary of an applicant’s education, work experience, and qualifications. people can be fired for willful falsification on their resumes. also serve as an indirect measures of math ability, physical ability, leadership & interpersonal skill
* 20-45% of all resumes and job applications include one major fabrication
* .35-.37 validity for personal history data (education, experience)
* 20-45% of all resumes and job applications include one major fabrication
* .35-.37 validity for personal history data (education, experience)
11
New cards
letters of recommendation (3,4)
* low validity (r = .14): self-selection bias, tend to be very favorable, conversion process (converting the letter into a score to calculate the validity is not an exact process)
* 4 key pieces of information make up a letter of recommendation
* degree of (writer) familiarity with candidate
* degree of (writer) familiarity with job in question
* specific examples of performance
* individuals to whom candidate is compared: the people you work with are compared to you. this influences how favorable/harsh the assessment of your performance will be
* tends to be more about the writer than the prospect
* 4 key pieces of information make up a letter of recommendation
* degree of (writer) familiarity with candidate
* degree of (writer) familiarity with job in question
* specific examples of performance
* individuals to whom candidate is compared: the people you work with are compared to you. this influences how favorable/harsh the assessment of your performance will be
* tends to be more about the writer than the prospect
12
New cards
reference checks (5,4)
* future employer can obtain info about
* employment and educational history: did this person work for you, in what capacity, for how long
* evaluation of applicant’s character: in general, how would you describe the person. strengths and weaknesses
* evaluation of applicant’s job performance
* willingness to rehire
* useful if information given by previous employer was observed and candid, but can cause lack of discriminability
* .26 validity
* failure to conduct a reference check can lead to an organization being accused of negligent hiring
* the data gathered is best if: questions are consistent and job relevant, responses are written
* employment and educational history: did this person work for you, in what capacity, for how long
* evaluation of applicant’s character: in general, how would you describe the person. strengths and weaknesses
* evaluation of applicant’s job performance
* willingness to rehire
* useful if information given by previous employer was observed and candid, but can cause lack of discriminability
* .26 validity
* failure to conduct a reference check can lead to an organization being accused of negligent hiring
* the data gathered is best if: questions are consistent and job relevant, responses are written
13
New cards
interviews: functions (2)
* fills in information gaps: elaborating on things you have in your resume
* assess factors only measurable in face to face interaction: charisma/enthusiasm, communication skills, professionalism, punctuality, etc.
* assess factors only measurable in face to face interaction: charisma/enthusiasm, communication skills, professionalism, punctuality, etc.
14
New cards
interviews: what contributes to their validity? (6)
* higher validity (.42) for structured interviews (ask the same questions in the same order for everyone)
* first impressions (correlated with the assessment employer makes at the end), verbal and nonverbal cues
* interviewer experience: more experience→ more valid results
* contrast effects, rating errors: educate raters about possibility of errors
* personal factors: physical appearance. doesn’t necessarily have a big impact on the results of the interviews
* note-taking: writing down a bit of the answer to justify rating
* first impressions (correlated with the assessment employer makes at the end), verbal and nonverbal cues
* interviewer experience: more experience→ more valid results
* contrast effects, rating errors: educate raters about possibility of errors
* personal factors: physical appearance. doesn’t necessarily have a big impact on the results of the interviews
* note-taking: writing down a bit of the answer to justify rating
15
New cards
interviews: degree of structure and types of questions (2, 4)
* degree of structure: questions (same/different questions? same/different order?) and answers (standardized rating scales for answers)
* unstructured interview: general intelligence, education, work experience, interests
* structured: job knowledge, interpersonal and social skills, problem solving
* types of questions: situational, hypothetical, future-oriented. experience/behaviorally based (past)→ slightly more valid
* unstructured interview: general intelligence, education, work experience, interests
* structured: job knowledge, interpersonal and social skills, problem solving
* types of questions: situational, hypothetical, future-oriented. experience/behaviorally based (past)→ slightly more valid
16
New cards
interviews: what do they measure? (7)
* mental capability
* knowledge and skills
* *basic personal tendencies*: openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism/emotional stability
* *applied social skills*
* interests and preferences
* organizational fit: are you going to work well in a certain organization with certain people?
* physical attributes
* knowledge and skills
* *basic personal tendencies*: openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism/emotional stability
* *applied social skills*
* interests and preferences
* organizational fit: are you going to work well in a certain organization with certain people?
* physical attributes
17
New cards
interviews: good practices (9)
* link questions to job analysis
* ask same questions of each candidate
* anchor rating scales: specify what each point means
* use interview panels: more than one interviewer (score inter-rater reliability)
* combine ratings mathematically: more systematic, better data
* provide training on how to conduct interviews
* document development procedures: who, what, when, where, how
* institute feedback system to interviewers
* video interview for later review
* ask same questions of each candidate
* anchor rating scales: specify what each point means
* use interview panels: more than one interviewer (score inter-rater reliability)
* combine ratings mathematically: more systematic, better data
* provide training on how to conduct interviews
* document development procedures: who, what, when, where, how
* institute feedback system to interviewers
* video interview for later review
18
New cards
cognitive ability/general mental ability tests (4)
* strong validity (.5)→ recent evidence shows that it might be less valid. maybe due to the old data being collected form manufacturing jobs in the 60s which is something we’ve move away from
* stronger for more complex jobs
* typical math and verbal sections
* subgroup mean differences are problematic
* 1sd black-white difference
* .5-1 sd asian-white difference
* stronger for more complex jobs
* typical math and verbal sections
* subgroup mean differences are problematic
* 1sd black-white difference
* .5-1 sd asian-white difference
19
New cards
integrity/honesty tests (4)
* overt tests: attitudes toward theft and dishonesty, admissions of theft and other illegal activities (it is obvious what they are measuring)
* personality-based tests: capture things such as conscientiousness and infer attitudes from that. (ex- rarely overindulge (+) resist/oppose authority (-))
* predict counter productive work behaviors
* r= .41 for job performance; r=-.13 for theft
* personality-based tests: capture things such as conscientiousness and infer attitudes from that. (ex- rarely overindulge (+) resist/oppose authority (-))
* predict counter productive work behaviors
* r= .41 for job performance; r=-.13 for theft
20
New cards
polygraph testing (4)
* instrument that measures aspects of the autonomic nervous system
* construct validity concerns: we infer from the results of the tests if the person is lying or not
* 1988 employee polygraph protection act→ illegal to use polygraph tests for pre-employment purposes if you are a private employer
* exceptions: security services and manufacturers of controlled substances
* results depend on skill of examiners and tests can be beaten
* construct validity concerns: we infer from the results of the tests if the person is lying or not
* 1988 employee polygraph protection act→ illegal to use polygraph tests for pre-employment purposes if you are a private employer
* exceptions: security services and manufacturers of controlled substances
* results depend on skill of examiners and tests can be beaten
21
New cards
drug testing (5, 3)
* technical analysis of a biological specimen (urine, hair, blood, sweat, saliva) to determine the presence/absence of specific drugs. often done for screening in pre-employment situations. can be done after the person has already been hired. usually expensive and can test the presence of drug & which drug is being used
* used in the military military, sports, and public safety jobs
* related to absenteeism (59% higher absenteeism rate/more likely) and turnover (47% higher turnover rate)
* some argue that it invades right to privacy?
* acceptance factors: informing people in writing, part of company policy (do they screen? test? how regularly?), presenting in a medical or safety context
* used in the military military, sports, and public safety jobs
* related to absenteeism (59% higher absenteeism rate/more likely) and turnover (47% higher turnover rate)
* some argue that it invades right to privacy?
* acceptance factors: informing people in writing, part of company policy (do they screen? test? how regularly?), presenting in a medical or safety context
22
New cards
physical ability tests (2, 4)
* tests physical abilities relevant for work performance
* static strength: ability to use muscle to lift, push, pull or carry objects
* explosive strength: ability to use short bursts of muscle force to propel oneself or an object
* gross body coordination: ability to coordinate the movement of the arms, legs, and torso in activities where the whole body is in motion
* stamina: ability of the lungs and circulatory (blood) systems of the body to perform efficiently over time
* generally defendable different standards for men and women
* static strength: ability to use muscle to lift, push, pull or carry objects
* explosive strength: ability to use short bursts of muscle force to propel oneself or an object
* gross body coordination: ability to coordinate the movement of the arms, legs, and torso in activities where the whole body is in motion
* stamina: ability of the lungs and circulatory (blood) systems of the body to perform efficiently over time
* generally defendable different standards for men and women
23
New cards
situational judgement tests (6)
* test of problem solving in which the test taker rates various possible solutions in terms of their feasibility or applicability
* low fidelity (not highly realistic, usually a paper and pen test)
* question asks what is the most effective option and least effective option. sme’s are asked which option is best, try to come to consensus, and that’s how we come up with a scoring key
* high face validity: people think the test they are taking is valid
* cognitively loaded: higher in cognitive ability→ higher scores
* time consuming and difficult to create, but generally well accepted
* low fidelity (not highly realistic, usually a paper and pen test)
* question asks what is the most effective option and least effective option. sme’s are asked which option is best, try to come to consensus, and that’s how we come up with a scoring key
* high face validity: people think the test they are taking is valid
* cognitively loaded: higher in cognitive ability→ higher scores
* time consuming and difficult to create, but generally well accepted
24
New cards
computerized adaptive testing (3)
* form of assessment using a computer in which the questions have been precalibrated in terms of difficulty, and the examinee’s response (right/wrong) to one question determines the selection of the next question
* advantages: could get a more refined score, could be shorter from more knowledgeable people, immediate scoring
* disadvantages: can’t skip questions or go backwards, discomfort for people who prefer taking tests on paper
* advantages: could get a more refined score, could be shorter from more knowledgeable people, immediate scoring
* disadvantages: can’t skip questions or go backwards, discomfort for people who prefer taking tests on paper
25
New cards
personality inventories (2)
* big 5 factors (ocean)→ useful for understanding people’s behavior in the workplace
* openness to experience
* ***conscientiousness*** best predictor across all jobs
* extraversion best for managerial or sales positions
* agreeableness
* neuroticism
* social desirability concern: answer in a way that is socially desirable and portray yourself in a more positive light
* openness to experience
* ***conscientiousness*** best predictor across all jobs
* extraversion best for managerial or sales positions
* agreeableness
* neuroticism
* social desirability concern: answer in a way that is socially desirable and portray yourself in a more positive light
26
New cards
dark triad of personality (4)
* cluster of three personality disorders associated with counterproductive work behavior
* machiavellianism: manipulation and exploitation of others
* narcissism: pride, egoistic, lack of empathy
* psychopathy: continuously antisocial, selfish, and remorseless
* machiavellianism: manipulation and exploitation of others
* narcissism: pride, egoistic, lack of empathy
* psychopathy: continuously antisocial, selfish, and remorseless
27
New cards
faking (5)
* behavior of job applicants to falsify or fake their responses to items on a personality inventory to create a favorable impression
* 2 types: self-deception (unconscious) and impression management (conscious effort to portray yourself in a positive light)
* people can increase their scores by .5 sd, but this can be reduced with instructions
* doesn’t seem to significantly affect the validity with job performance
* can faking be a good thing? salesperson, customer service, political figures, pr jobs… good ability to present yourself better could be beneficial
* 2 types: self-deception (unconscious) and impression management (conscious effort to portray yourself in a positive light)
* people can increase their scores by .5 sd, but this can be reduced with instructions
* doesn’t seem to significantly affect the validity with job performance
* can faking be a good thing? salesperson, customer service, political figures, pr jobs… good ability to present yourself better could be beneficial
28
New cards
assessment centers: characteristics, types of activities, what is assessed (6)
* series of group-oriented activities that provide the basis for predictions of work performance
* characteristics: management-level personnel, people are evaluated in groups, multiple assessors, multiple exercises
* types of activities: LGD (leaderless group discussion), IB (in basket→ go through the motions of processing paperwork), Role-play (managerial position)
* assessors rate dimensions of performance such as oral and written communication, leadership skills, decision making ability, etc.
* predicts promotability (r=.39) better than performance
* poor construct validity
* characteristics: management-level personnel, people are evaluated in groups, multiple assessors, multiple exercises
* types of activities: LGD (leaderless group discussion), IB (in basket→ go through the motions of processing paperwork), Role-play (managerial position)
* assessors rate dimensions of performance such as oral and written communication, leadership skills, decision making ability, etc.
* predicts promotability (r=.39) better than performance
* poor construct validity
29
New cards
work samples (4)
* examples of work-related problems or tasks that require the applicant to solve the problem as if they were on the job
* high fidelity simulations with high face validity
* good validities (.42-.66) correlation between job sample and job performance
* time consuming and expensive
* high fidelity simulations with high face validity
* good validities (.42-.66) correlation between job sample and job performance
* time consuming and expensive
30
New cards
biodata (4)
* biographical information or information on the history of a person’s life is considered in accordance to the principle that “past behavior is an excellent predictor of future behavior”
* r = .35-37 for job performance
* r =.77-.79 for turnover
* criticized for being atheoretical, invasive, and susceptible to faking
* r = .35-37 for job performance
* r =.77-.79 for turnover
* criticized for being atheoretical, invasive, and susceptible to faking
31
New cards
evaluation of predictors (5,2)
* validity
* fairness
* applicability/relevance
* cost
* applicant reactions: better reactions lead to stronger intentions to accept offer, recommend employer to others, etc
* perceived favorability: interviews, work samples, resumes
* perceived less favorably: personality tests, personal contacts (references), honesty tests
* face validity is important
* fairness
* applicability/relevance
* cost
* applicant reactions: better reactions lead to stronger intentions to accept offer, recommend employer to others, etc
* perceived favorability: interviews, work samples, resumes
* perceived less favorably: personality tests, personal contacts (references), honesty tests
* face validity is important
32
New cards
unproctored internet testing (3)
* administering exam online without a live proctor
* cheating/faking concerns are dealt with by giving instructions not to cheat, a retest possibility, and the use of webcams
* device differences may lead to different scores for equally qualified people
* cheating/faking concerns are dealt with by giving instructions not to cheat, a retest possibility, and the use of webcams
* device differences may lead to different scores for equally qualified people
33
New cards
social media and employment screening (3)
* pictures and personal information can be used in the screening process. controversial because some see it as unfair or an invasion of privacy
* facebook: SHRM has been keeping track of the use of the internet for screening candidates since at least 2006
* linkedin: more professional (work-related), endorsements questionable
* facebook: SHRM has been keeping track of the use of the internet for screening candidates since at least 2006
* linkedin: more professional (work-related), endorsements questionable
34
New cards
what are the best predictors? (6)
* Structured Interviews .42
* Job knowledge tests .40
* Empirically-keyed biodata .38
* Work sample tests .33
* Cognitive ability tests .31
* Integrity tests .31
* Job knowledge tests .40
* Empirically-keyed biodata .38
* Work sample tests .33
* Cognitive ability tests .31
* Integrity tests .31
35
New cards
validity generalization
* extent to which a predictor’s validity generalizes to other similar jobs or contexts
* opposite of validity generalization: validity is situationally-specific (a given predictor predicts for one job but not necessarily for other jobs)
* meta-analysis→ aggregation of multiple studies to address sampling error
* opposite of validity generalization: validity is situationally-specific (a given predictor predicts for one job but not necessarily for other jobs)
* meta-analysis→ aggregation of multiple studies to address sampling error
36
New cards
organizational strategies (4)
* speed strategy: some orgs make themselves stand out based on the way they provide products and services faster than their competitors (ex- amazon, mcdonald’s, ups)
* selection: people who are quick on their feet, quick problem solvers
* innovation strategy: latest and greatest. innovative and creative ideas (ex- tech companies)
* selection: people who embrace new things and are open to new ideas
* quality-enhancement strategy: best quality of products (ex- luxury brands)
* cost-reduction strategy: who offers it cheaper (ex- walmart, costco)
* selection: people who are quick on their feet, quick problem solvers
* innovation strategy: latest and greatest. innovative and creative ideas (ex- tech companies)
* selection: people who embrace new things and are open to new ideas
* quality-enhancement strategy: best quality of products (ex- luxury brands)
* cost-reduction strategy: who offers it cheaper (ex- walmart, costco)
37
New cards
recruitment
the process of attracting people to apply for a job for the purpose of expanding or replenishing the workforce
38
New cards
organizational perspective in recruitment (3)
* large applicant pool: larger pool= more options
* most qualified applicants
* diversity: more representation in the organization and the extent to which applicants satisfy such needs
* most qualified applicants
* diversity: more representation in the organization and the extent to which applicants satisfy such needs
39
New cards
applicant perspective in recruitment (3)
* attractiveness/ desirability of the organization: what is important to people in an org
* face valid assessments
* fair treatment (social validity)
* face valid assessments
* fair treatment (social validity)
40
New cards
recruitment sources (6)
* internal: employee referral (tends to work for the organization because people are likely to recommend good people that reflect well on themselves), transfer, promotion
* advertisements
* newspapers, magazines, radio, tv
* websites (organizational or third party)
* social media: existing employee connections or organization account
* employment agencies/ out-processing center
* school recruiters/career fairs
* walk-ins
* networking
* advertisements
* newspapers, magazines, radio, tv
* websites (organizational or third party)
* social media: existing employee connections or organization account
* employment agencies/ out-processing center
* school recruiters/career fairs
* walk-ins
* networking
41
New cards
recruitment pyramid (5)
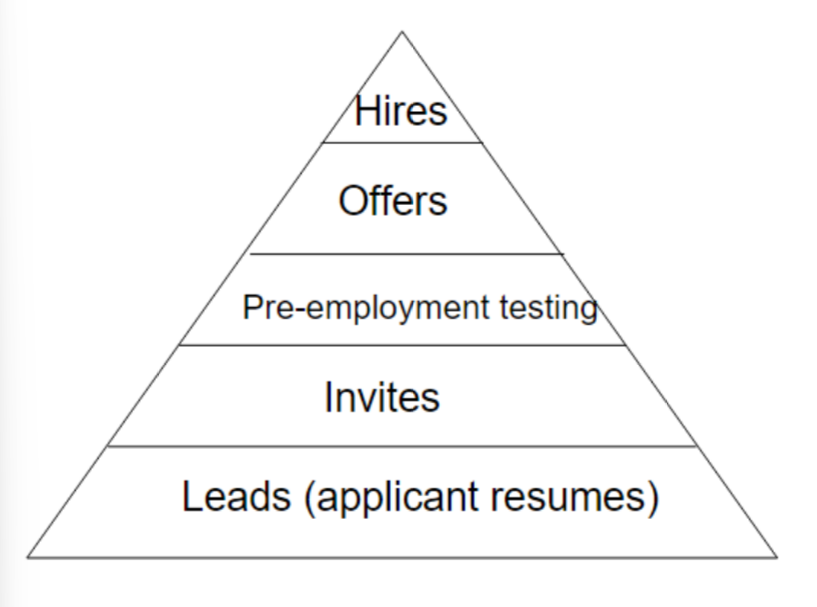
42
New cards
time lapse data (7)
* Permission to hire/post position \~7 days
* Position posted \~14 days (time for people to see it and respond)
* Review resumes \~7 days
* Invite to interview and schedule \~5 days (contact possible employee)
* Conduct interview, rank order, extend offer \~3 days
* Offer to acceptance \~7-14 day (negotiation period, higher pay, additional benefits…)
* acceptance to work \~14 days
* Position posted \~14 days (time for people to see it and respond)
* Review resumes \~7 days
* Invite to interview and schedule \~5 days (contact possible employee)
* Conduct interview, rank order, extend offer \~3 days
* Offer to acceptance \~7-14 day (negotiation period, higher pay, additional benefits…)
* acceptance to work \~14 days
43
New cards
job offer timing (2)
* quicker offers are more likely to be accepted
* there is no difference on performance ratings or turnover for employees hired after quick offers and those who accepted later offers
* there is no difference on performance ratings or turnover for employees hired after quick offers and those who accepted later offers
44
New cards
social media for recruitment
* social networks use targeting tools to advertise based on sex and gender
* eeoc found that 2018 facebook employment opportunity advertisements violated civil rights acts by targeting certain genders and age groups
* eeoc found that 2018 facebook employment opportunity advertisements violated civil rights acts by targeting certain genders and age groups
45
New cards
applicant reactions/ candidate experience
refers to how job candidates perceive and respond to selection tools (e.g., personality tests, work samples, situational judgment tests) on the basis of their application experience. includes perceptions of fairness and justice, feelings of anxiety, and levels of motivation
46
New cards
selection factors (4)
process of identifying who should be offered the job from a pool of applicants. key factors:
* validity of the predictor
* selection ratio/Predictor cut-off: number of people who apply relative to the number of people hired
* criterion cut-off: criterion is job performance in most cases. minimum level of job performance
* base rate: number of current employees that are successful if the individuals were randomly hired (50/50 chance that a random person is a good employee or not)
* validity of the predictor
* selection ratio/Predictor cut-off: number of people who apply relative to the number of people hired
* criterion cut-off: criterion is job performance in most cases. minimum level of job performance
* base rate: number of current employees that are successful if the individuals were randomly hired (50/50 chance that a random person is a good employee or not)
47
New cards
selection decisions
* false negative: people who failed the selection test and were thus predicted not to succeed on the job but who would have succeeded
* true negative: people we predict will not be succeed because they did not passed the selection test and end up actually being unsuccessful
* false positive: people who passed the selection test and were thus predicted to succeed on the job but perform unsatisfactorily after being hired
* true positive: people we predict will succeed because they passed the selection test and end up actually being successful
* true negative: people we predict will not be succeed because they did not passed the selection test and end up actually being unsuccessful
* false positive: people who passed the selection test and were thus predicted to succeed on the job but perform unsatisfactorily after being hired
* true positive: people we predict will succeed because they passed the selection test and end up actually being successful
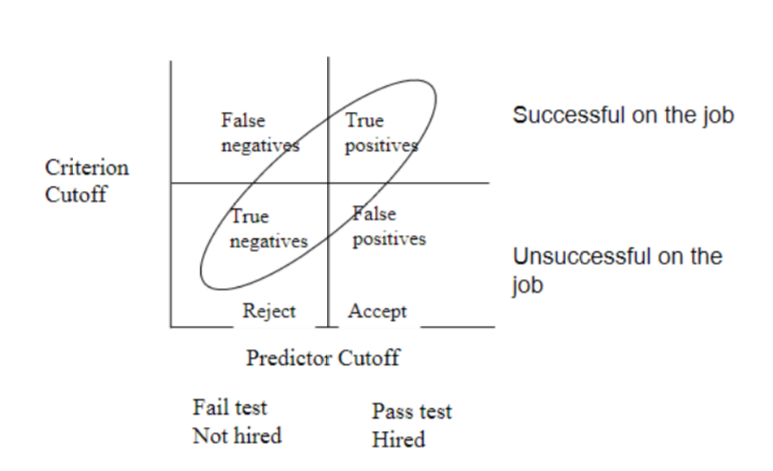
48
New cards
banding
* a group of scores are considered equivalent and not differentiated between when making a selection decision. used when interpreting standardized test scores and grades.
* based on the idea that no test is perfect (allow for wiggle room in order to accommodate for potential errors), and calculated from the standard error of measurement.
* fixed (only looking at one range) or sliding (usually when many people are being hired)
* based on the idea that no test is perfect (allow for wiggle room in order to accommodate for potential errors), and calculated from the standard error of measurement.
* fixed (only looking at one range) or sliding (usually when many people are being hired)
49
New cards
utility analysis (6)
means of determining the value of a tool used (e.g. predictor) for making personnel decisions to the organization. expressed in $$ terms→ what you get in return financially for implementing something. determined by:
* validity of the predictor: how well does it relate to outcome of interest?
* cost to administer the predictor & the predictor itself
* number of people who do this job: if more people use the predictor, the more you will get out of it
* number of people hired each year to do this job: might not have to use predictor regularly if you have lower turnover
* typical tenure in this job: how long people stay affects how often you hire
* Variance (SD) of performance: capture variability in performance in general. if people don’t vary a lot, there’s not much to predict about how they will perform as employees
* validity of the predictor: how well does it relate to outcome of interest?
* cost to administer the predictor & the predictor itself
* number of people who do this job: if more people use the predictor, the more you will get out of it
* number of people hired each year to do this job: might not have to use predictor regularly if you have lower turnover
* typical tenure in this job: how long people stay affects how often you hire
* Variance (SD) of performance: capture variability in performance in general. if people don’t vary a lot, there’s not much to predict about how they will perform as employees
50
New cards
benchmarking (8)
process of comparing a company’s products or procedures with those of the leading companies in an industry
* recruitment sources: where do we distribute information about a position?
* selection tools: predictors used (interviews, etc)
* compensation, benefits, and incentives: what do we offer?
* training programs
* evaluation metrics
* turnover data
* survey results: employee engagement
* organizational records: safety metrics (e.g., injuries), sales, services provided, number of customers
* recruitment sources: where do we distribute information about a position?
* selection tools: predictors used (interviews, etc)
* compensation, benefits, and incentives: what do we offer?
* training programs
* evaluation metrics
* turnover data
* survey results: employee engagement
* organizational records: safety metrics (e.g., injuries), sales, services provided, number of customers
51
New cards
placement and classification
* placement: process of assigning individuals to jobs based on one test score
* classification: process of assigning individuals to jobs based on two or more test score. more complex but results in a better assignment of people to jobs than placement.
* classification: process of assigning individuals to jobs based on two or more test score. more complex but results in a better assignment of people to jobs than placement.
52
New cards
selection vs. training (2)
* ways to ensure the most qualified people are selected for the job: select people w/ necessary ksas or seek trainable personnel, give them training, and adopting a continuous learning environment
* inverse relationship between resources allocated to selection vs training
* inverse relationship between resources allocated to selection vs training
53
New cards
training (2)
the systematic acquisition of skills, rules, concepts, or attitudes that result in improved performance in another environment (assumption to a certain extent that you are learning info in the training context and you are then applying it to the job. what do you need to do to do your job today)
* formal: formal classes, classroom environments and simulations, workshops with consultants, online training, etc, organization sanctioned and paid for with some sort of accountability attached (a test at the end)
* informal (majority): coaching. more senior employee giving you guidance (70%)
* formal: formal classes, classroom environments and simulations, workshops with consultants, online training, etc, organization sanctioned and paid for with some sort of accountability attached (a test at the end)
* informal (majority): coaching. more senior employee giving you guidance (70%)
54
New cards
development
preparation for future job opportunities (aspire to work in the next level, giving you have the knowledge to take on more responsibilities, supervising others, etc)
* dual responsibility for both the organization and the individual
* dual responsibility for both the organization and the individual
55
New cards
when is training needed? (5,5)
* federal/state regulated: certain training is needed (if you work in a state funded organization, for example)
* remediation/deficiency: if an employee is falling short or needs a refresher. addresses current deficiencies. sometimes mandated (anticipate that skill level might decrease over time. new laws, new software, new procedures)
* new KSAttitudes needed
* new to job: learn how your new org works
* change positions: new responsibilities
* new tech/equipment: new software, new machines, etc
* new products/services: how products are different from previous ones, how they compare to competitors
* continuing education requirement/recertification: certification renewals, nurses, educators, etc
* soft skills needed: leadership, customer service, etc…
* social issues: sexual harassment, diversity, etc…
* remediation/deficiency: if an employee is falling short or needs a refresher. addresses current deficiencies. sometimes mandated (anticipate that skill level might decrease over time. new laws, new software, new procedures)
* new KSAttitudes needed
* new to job: learn how your new org works
* change positions: new responsibilities
* new tech/equipment: new software, new machines, etc
* new products/services: how products are different from previous ones, how they compare to competitors
* continuing education requirement/recertification: certification renewals, nurses, educators, etc
* soft skills needed: leadership, customer service, etc…
* social issues: sexual harassment, diversity, etc…
56
New cards
learning (3,3)
* the process of encoding, retaining, and using information. change in knowledge/skills is acquired through education or experience
* 3 phases of skill acquisition
* declarative knowledge (gma): knowledge about facts and things. general mental abilities
* knowledge compilation phase (perceptual speed): knowledge acquired as a result of learning
* procedural knowledge (psychomotor abilities): knowledge about how to use information to address issues and solve problems
* learning curve: the rate of a person's progress in gaining experience or new skills
* 3 phases of skill acquisition
* declarative knowledge (gma): knowledge about facts and things. general mental abilities
* knowledge compilation phase (perceptual speed): knowledge acquired as a result of learning
* procedural knowledge (psychomotor abilities): knowledge about how to use information to address issues and solve problems
* learning curve: the rate of a person's progress in gaining experience or new skills
57
New cards
principles of learning (6, 2, 3)
* goal-setting: having goals facilitates performance. more specific goals and challenging goals are better and lead to better performance.
* identical elements: when training, mimic the physical contexts and psychological aspects of the job
* physical fidelity: simulating the same environment (ex- simulators for driving cockpits for pilots)
* psychological fidelity: replicating cognitions and feelings people would have in this environment (ex- mimic a customer interaction)
* practice
* active vs passive: active practice is better than passive practice (hear about doing a behavior, watching others perform that behavior)
* overlearning for certain tasks: certain tasks we expect people to perform under great stress and infrequently
* distributed vs massed: over time vs. cramming.
* maintenance through self-management: idea that we have a role in our own learning and manage information we learn. combining with goal setting can be effective
* feedback (knowledge of results): without anybody else being involved, you have knowledge of something (people get feedback through visibly seeing that their actions have certain outcomes)
* reinforcement: rewards and acknowledgements
* identical elements: when training, mimic the physical contexts and psychological aspects of the job
* physical fidelity: simulating the same environment (ex- simulators for driving cockpits for pilots)
* psychological fidelity: replicating cognitions and feelings people would have in this environment (ex- mimic a customer interaction)
* practice
* active vs passive: active practice is better than passive practice (hear about doing a behavior, watching others perform that behavior)
* overlearning for certain tasks: certain tasks we expect people to perform under great stress and infrequently
* distributed vs massed: over time vs. cramming.
* maintenance through self-management: idea that we have a role in our own learning and manage information we learn. combining with goal setting can be effective
* feedback (knowledge of results): without anybody else being involved, you have knowledge of something (people get feedback through visibly seeing that their actions have certain outcomes)
* reinforcement: rewards and acknowledgements
58
New cards
training and development phases (5)
* pretraining
* needs analysis
* training methods- design
* implementation
* posttraining-evaluation
* needs analysis
* training methods- design
* implementation
* posttraining-evaluation
59
New cards
pretraining (6)
* supervisor’s support/attitude: impacts your understanding and learning
* coworker’s experiences: colleagues that have embraced or required to participate in the same training. they tell you pros/cons which influence your attitudes going in
* personal experiences: similar training before impacts you attitude in the training now (positive past experiences lead to positive attitudes)
* accountability: to what extent are you going to be held accountable for this training (do you have to take a quiz, train people in the future…)
* discretion: do you have a choice on whether or not to participate? if you choose you embrace the opportunity more
* marketing: testimonials, advertising… influences perspective about training and expectations
* coworker’s experiences: colleagues that have embraced or required to participate in the same training. they tell you pros/cons which influence your attitudes going in
* personal experiences: similar training before impacts you attitude in the training now (positive past experiences lead to positive attitudes)
* accountability: to what extent are you going to be held accountable for this training (do you have to take a quiz, train people in the future…)
* discretion: do you have a choice on whether or not to participate? if you choose you embrace the opportunity more
* marketing: testimonials, advertising… influences perspective about training and expectations
60
New cards
pretraining: motivation to learn (5,2)
* favorable work environments facilitate your motivation. culture of continuous learning
* sufficient resources: hours of professional development
* good working relations: supervisor and coworker support (help w work when you’re gone)
* belief that other’s assessments are accurate: when sent to training for remediation. if you don’t believe you are inefficient, then you will not be motivated to learn
* self-efficacy: belief in one’s own ability to master training content
* belief that training will lead to valued outcomes: if this association is not seen, then you will not be motivated to learn
* realistic preview/expectations of training activity: more understanding = more motivation
* sufficient resources: hours of professional development
* good working relations: supervisor and coworker support (help w work when you’re gone)
* belief that other’s assessments are accurate: when sent to training for remediation. if you don’t believe you are inefficient, then you will not be motivated to learn
* self-efficacy: belief in one’s own ability to master training content
* belief that training will lead to valued outcomes: if this association is not seen, then you will not be motivated to learn
* realistic preview/expectations of training activity: more understanding = more motivation
61
New cards
needs assessment (3,3)
* assessing training needs: how training aligns with organizational goals
* determining the training objective: identifying and clearly articulating training objectives
* 3 levels
* organization analysis: where does it need to happen within organization. must be targeted to specific people, do we promote bringing knowledge back to org? do we have a good environment?
* task analysis: what needs to be trained (evaluates physical and psychological fidelity)
* person analysis: who needs to be trained? consider current levels of knowledge and skills
* determining the training objective: identifying and clearly articulating training objectives
* 3 levels
* organization analysis: where does it need to happen within organization. must be targeted to specific people, do we promote bringing knowledge back to org? do we have a good environment?
* task analysis: what needs to be trained (evaluates physical and psychological fidelity)
* person analysis: who needs to be trained? consider current levels of knowledge and skills
62
New cards
training methods (10)
* classroom-based training (lecture, audiovisual, exercises): particularly when a lot of people need to be trained
* on-the-job training: can have a negative impact on the customer (it can slow things down, etc) quality of training varies depending on who you are paired with (some people might be less patient or knowledgeable, etc)
* cross-training/ job rotation: useful for when people must be able to substitute for each other within a given department
* apprenticeship training: people are paired up with a senior person for a long period of time
* universities: some organizations have specific facilities dedicated to providing training for employees
* conferences/workshops
* gamification: more positive attitudes
* computer-based training: programmed instruction (most basic), intelligent tutoring systems, interactive multimedia systems (responsive to learner), vr training
* business games: hypothetical company with policies and procedures. people go through the motions of solving problems such as internal conflicts, financial problems, etc
* role playing: trainers and trainees are given roles and are asked to go through the motions of accomplishing certain tasks. mostly soft skills
* behavioral modeling: observing someone who has a lot of good skills. learning from observing
* simulation: replicate characteristics of the job and training environment
* on-the-job training: can have a negative impact on the customer (it can slow things down, etc) quality of training varies depending on who you are paired with (some people might be less patient or knowledgeable, etc)
* cross-training/ job rotation: useful for when people must be able to substitute for each other within a given department
* apprenticeship training: people are paired up with a senior person for a long period of time
* universities: some organizations have specific facilities dedicated to providing training for employees
* conferences/workshops
* gamification: more positive attitudes
* computer-based training: programmed instruction (most basic), intelligent tutoring systems, interactive multimedia systems (responsive to learner), vr training
* business games: hypothetical company with policies and procedures. people go through the motions of solving problems such as internal conflicts, financial problems, etc
* role playing: trainers and trainees are given roles and are asked to go through the motions of accomplishing certain tasks. mostly soft skills
* behavioral modeling: observing someone who has a lot of good skills. learning from observing
* simulation: replicate characteristics of the job and training environment
63
New cards
newer training methods (2)
* text-based “courses”: text messages convey small bits of information
* micro-training: 3-5 min videos disseminated in small chunks. refresher training, more digestible
* micro-training: 3-5 min videos disseminated in small chunks. refresher training, more digestible
64
New cards
error management training (6)
* a system of training in which employees are encouraged to make errors and learn from their mistakes
* promote making mistakes when it is safe to do so (simulated environment, computer environment…)
* early detection and recovery from errors: as you are learning to do things, any mistakes you make are pointed out earlier on so you can learn how to do things the right way
* open communication about errors: reassuring people that mistakes are common
* more useful for learning generalizable skills: not something specific to one task, but rather something more general such as the process of detecting or diagnosing
* people w higher levels of cognitive ability and openness are more likely to be successful with this kind of training
* promote making mistakes when it is safe to do so (simulated environment, computer environment…)
* early detection and recovery from errors: as you are learning to do things, any mistakes you make are pointed out earlier on so you can learn how to do things the right way
* open communication about errors: reassuring people that mistakes are common
* more useful for learning generalizable skills: not something specific to one task, but rather something more general such as the process of detecting or diagnosing
* people w higher levels of cognitive ability and openness are more likely to be successful with this kind of training
65
New cards
leadership training (management development) (4,2)
* individuals learning to perform managerial roles
* 90% of orgs offer this training
* personal skills: self awareness, knowing how to manage stress and solve problems
* interpersonal skills: managing conflict, communicating successfully
* derailment: managerial failure
* glass ceiling: barrier created by organizations that inhibits your ability to move up in an organization. women and minorities (aren’t always given the same developmental opportunities)
* 90% of orgs offer this training
* personal skills: self awareness, knowing how to manage stress and solve problems
* interpersonal skills: managing conflict, communicating successfully
* derailment: managerial failure
* glass ceiling: barrier created by organizations that inhibits your ability to move up in an organization. women and minorities (aren’t always given the same developmental opportunities)
66
New cards
cultural diversity training (4,4)
* training designated to promote awareness of differences and appreciation of differences
* goal: reduce barriers that constrain employees contributions to org goals and personal development
* attitude and/or behavioral change
* expatriate training: training for employees given an international assignment
* includes diversity training
* specific information about host country: history, geography, culture, traditions
* high rate of failure for expatriates: people are not settling in and often come back to their original country
* family support critical factors
* goal: reduce barriers that constrain employees contributions to org goals and personal development
* attitude and/or behavioral change
* expatriate training: training for employees given an international assignment
* includes diversity training
* specific information about host country: history, geography, culture, traditions
* high rate of failure for expatriates: people are not settling in and often come back to their original country
* family support critical factors
67
New cards
sexual harassment training (2, 3)
* unwelcome sexual advances, requests for sexual favors, and other verbal and physical conduct of a sexual nature that impedes on one’s ability to work
* quid pro quo: “this for that”
* hostile environment: inappropriate culture
* sexual harassment is more about power than sex
* outcomes: understanding, more reporting, change in behavior
* quid pro quo: “this for that”
* hostile environment: inappropriate culture
* sexual harassment is more about power than sex
* outcomes: understanding, more reporting, change in behavior
68
New cards
executive coaching (6)
* individualized developmental process for business leaders provided by a trained professional (the coach)
* people come in, meet with an executive level individual, and focus on what individual executives are currently struggling with
* coach: external to organizations
* 93% of us based companies use coaching outcomes/benefits have more to do with the coach than with the person being trained
* more than counseling: active and direct role in preparing solutions and action plans.
* skills: interpersonal, communication leadership, cognitive, and self-management
* unlicensed and unregulated
* people come in, meet with an executive level individual, and focus on what individual executives are currently struggling with
* coach: external to organizations
* 93% of us based companies use coaching outcomes/benefits have more to do with the coach than with the person being trained
* more than counseling: active and direct role in preparing solutions and action plans.
* skills: interpersonal, communication leadership, cognitive, and self-management
* unlicensed and unregulated
69
New cards
team training (3)
* team: group of individuals who are working together interdependently toward a common goal
* taskwork vs. teamwork
* skills for effective teamwork: situational awareness, being adaptable, backup and feedback to each other
* taskwork vs. teamwork
* skills for effective teamwork: situational awareness, being adaptable, backup and feedback to each other
70
New cards
mentoring (2,3)
* when a more experienced employee advises a new person at the beginning of their career or time in the organization
* multiple phases
* psychosocial and job-related types of support
* formal vs. informal arrangements
* same sex/race
* multiple phases
* psychosocial and job-related types of support
* formal vs. informal arrangements
* same sex/race
71
New cards
other types of training (5)
* safety: some companies find this necessary
* cpr
* negotiation
* tabc: texas alcohol beverage commission
* food handler’s
* cpr
* negotiation
* tabc: texas alcohol beverage commission
* food handler’s
72
New cards
transfer of training
* extent to which trainees effectively apply KSAs acquired in a training context back on the job
* generalization: immediate transfer (less of a gap. on the job training facilitates, for example)
* maintenance: long-term transfer (after a while, are people still applying what they learned?)
* generalization: immediate transfer (less of a gap. on the job training facilitates, for example)
* maintenance: long-term transfer (after a while, are people still applying what they learned?)
73
New cards
training evaluation criteria: why evaluate?
* determine future use of training
* make decision about trainees: does learning new things facilitate your ability to be promoted get more responsibilities, etc?
* enhance scientific understanding of training process: how do we learn and retain information? documenting this process can facilitate changes in the future
* gather data for marketing training in future
* make decision about trainees: does learning new things facilitate your ability to be promoted get more responsibilities, etc?
* enhance scientific understanding of training process: how do we learn and retain information? documenting this process can facilitate changes in the future
* gather data for marketing training in future
74
New cards
training evaluation criteria: criteria levels (4)
* reaction: affective reactions. were you comfortable, did you like the trainer, activities, etc? surface level, yet most common (ex- smile sheets)
* learning: how much people are retaining (pre- training test and post-training test)
* behavioral: are you demonstrating the skills you learned in training?
* results: economic value of the training/ return investment
* learning: how much people are retaining (pre- training test and post-training test)
* behavioral: are you demonstrating the skills you learned in training?
* results: economic value of the training/ return investment
75
New cards
requirements for effective training (3)
* training tied to business strategy and objectives
* training is comprehensive and systematic
* top management committed: commitment to invest necessary resources to facilitate training
* training is comprehensive and systematic
* top management committed: commitment to invest necessary resources to facilitate training
76
New cards
workplace health and wellbeing
mental, emotional, and physical well-being of employees in relation to the conduct of their work
77
New cards
work-related stressors (8)
* physical
* task-related
* role
* social
* work-schedule
* career-related
* traumatic events
* stressful change processes
* task-related
* role
* social
* work-schedule
* career-related
* traumatic events
* stressful change processes
78
New cards
workplace safety (2,5)
* decreased likelihood of physical harm or danger while performing one’s job
* primary way in which we try to do this is by implementing certain controls
* elimination: take unnecessary dangerous things away
* substitution: replace hazard with something safer
* engineering controls: isolating people from the hazard, minimizing the opportunity for something dangerous to occur
* administrative controls: rules that prevent people from being exposed from certain hazards
* ppe: personal protective equipment. can make it a bit more challenging to carry out job
* primary way in which we try to do this is by implementing certain controls
* elimination: take unnecessary dangerous things away
* substitution: replace hazard with something safer
* engineering controls: isolating people from the hazard, minimizing the opportunity for something dangerous to occur
* administrative controls: rules that prevent people from being exposed from certain hazards
* ppe: personal protective equipment. can make it a bit more challenging to carry out job
79
New cards
workplace stress (apa 2022 work and well-being survey) (4,4)
* workers value employer mental health support
* flexible work hours
* workplace culture that respects time off
* ability to work remotely
* 4-day work week
* compensation not keeping up with inflation is a major concern
* workplace monitoring is common (and also a common source of stress)
* dei policies: more common in office settings than manual labor workplaces
* flexible work hours
* workplace culture that respects time off
* ability to work remotely
* 4-day work week
* compensation not keeping up with inflation is a major concern
* workplace monitoring is common (and also a common source of stress)
* dei policies: more common in office settings than manual labor workplaces
80
New cards
framework for mental health and well-being in the workplace (5)
* protection from harm: physical hazards, giving people the opportunity to rest and recover
* connection and community: work environment fosters positive social interactions and relationships
* work-life harmony: boundaries between work and life. flexibility over time and place where someone works. vacation time, providing autonomy on how to do your work, etc
* mattering at work: seeing the significance for your work to an organization. fair compensation
* opportunities for growth: ability to be promoted, gain new skills, etc. feedback, career training, etc
* connection and community: work environment fosters positive social interactions and relationships
* work-life harmony: boundaries between work and life. flexibility over time and place where someone works. vacation time, providing autonomy on how to do your work, etc
* mattering at work: seeing the significance for your work to an organization. fair compensation
* opportunities for growth: ability to be promoted, gain new skills, etc. feedback, career training, etc
81
New cards
task and role stressors (4)
* __*challenge*__ (not all stressors are a bad thing. job demands and characteristics that create positive feeling of achievement and succeeding) vs. __*hindrance*__ (demand or characteristic that is demotivating and problematic bc they hinder our abilities to be successful) stressors
* role conflict: tension due to incompatible role demands (intrarole- withing the role, responsibilities conflict) (interrole- external roles vs roles as employees conflict)
* role ambiguity: uncertainty about the behavior to exhibit in a role or boundaries around a role
* role overload: feeling overwhelmed from having too many roles or responsibilities
* role conflict: tension due to incompatible role demands (intrarole- withing the role, responsibilities conflict) (interrole- external roles vs roles as employees conflict)
* role ambiguity: uncertainty about the behavior to exhibit in a role or boundaries around a role
* role overload: feeling overwhelmed from having too many roles or responsibilities
82
New cards
covid-19 specific stressors (5,2)
* unemployment and reduced work
* travel restrictions limiting work
* potential exposure to the virus from coworkers and customers
* additional requirements and responsibilities
* cleaning
* testing
* alternative ways of doing things
* travel restrictions limiting work
* potential exposure to the virus from coworkers and customers
* additional requirements and responsibilities
* cleaning
* testing
* alternative ways of doing things
83
New cards
workplace trends (6)
* more women working
* more single parents
* more dual-career couples
* aging parents: employers have increasing responsibilities for taking care of their elder parents
* increasing technologies (“electronic leash”)
* older people working longer: extending official retirement age, people stay in the workforce longer
* more single parents
* more dual-career couples
* aging parents: employers have increasing responsibilities for taking care of their elder parents
* increasing technologies (“electronic leash”)
* older people working longer: extending official retirement age, people stay in the workforce longer
84
New cards
work schedules (4)
* majority of u.s. workers are paid by the hour
* 82% of hourly workers report fluctuations in weekly work hours
* schedule unpredictability is very stressful, challenging for nonwork life, and for economic stability
* clopening: some employees are responsible for opening and closing
* 82% of hourly workers report fluctuations in weekly work hours
* schedule unpredictability is very stressful, challenging for nonwork life, and for economic stability
* clopening: some employees are responsible for opening and closing
85
New cards
shift work (6,3)
* often 24-hour day divided into 3 8-hr shifts
* 7am-3pm (day)
* 3pm-11pm (swing/afternoon)
* 11pm-7am (night)
* service-oriented occupations and food service
* problems with psychological and social adjustment
* shift rotations particularly problematic: backwards rotations are most problematic
* educational programs for shift workers and their families
* shift length experiment: conducted w/ police force, randomly assigned officers to different shifts (8, 10, or 12). fatigue, safety, organizational metrics. 10 hr shift associated with most positive outcomes
* 7am-3pm (day)
* 3pm-11pm (swing/afternoon)
* 11pm-7am (night)
* service-oriented occupations and food service
* problems with psychological and social adjustment
* shift rotations particularly problematic: backwards rotations are most problematic
* educational programs for shift workers and their families
* shift length experiment: conducted w/ police force, randomly assigned officers to different shifts (8, 10, or 12). fatigue, safety, organizational metrics. 10 hr shift associated with most positive outcomes
86
New cards
work-nonwork research (7)
* domains: Work, Home, School, Church, etc.
* roles: Employee, Spouse, Parent, Child, etc.
* work-family balance
* work-family conflict (WFC)
* work-family enrichment
* both directions (work-> family; family->work)
* negative outcomes associated with WFC
* children create the biggest conflict between work and family
* supportive supervisor is key
* roles: Employee, Spouse, Parent, Child, etc.
* work-family balance
* work-family conflict (WFC)
* work-family enrichment
* both directions (work-> family; family->work)
* negative outcomes associated with WFC
* children create the biggest conflict between work and family
* supportive supervisor is key
87
New cards
family-related employment laws: pregnancy discrimination act
a woman who is pregnant or had an abortion cannot be fired, refused job, promotion, or forced to go on leave because of pregnancy & are entitled to their job upon return (but not special treatment unless a medical disability is proven). pregnancy is the most common discrimination charge during selection (interview)
88
New cards
family-related employment laws: family medical leave act
private sector employers with 50 or more employees must provide up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in case of birth; adoption; foster care; care for spouse, parent, or child; & own health (with medical certification)
89
New cards
family-friendly initiatives (4,2)
* dual career job placement assistance
* flexible work arrangements
* flex place (telecommuting, satellite workplaces)
* flex time (compressed work weeks, job sharing)
* on-site or near-site childcare and elder care centers
* family leave, lactation room/breaks
* flexible work arrangements
* flex place (telecommuting, satellite workplaces)
* flex time (compressed work weeks, job sharing)
* on-site or near-site childcare and elder care centers
* family leave, lactation room/breaks
90
New cards
benefits of work arrangements in place and time (3,2,3,1)
* organization: attract and retain quality employees, cost savings & reduced turnover, address challenges of the globalization of business
* job/coworkers: increase productivity, decrease workplace accidents
* employees: greater control over where, when and how their work gets done, less likely to miss work die to illness or nonwork demands, and improvements in will-being
* community: employees can be involved in community, school and, family events taking place during traditional work and commuting hrs
* job/coworkers: increase productivity, decrease workplace accidents
* employees: greater control over where, when and how their work gets done, less likely to miss work die to illness or nonwork demands, and improvements in will-being
* community: employees can be involved in community, school and, family events taking place during traditional work and commuting hrs
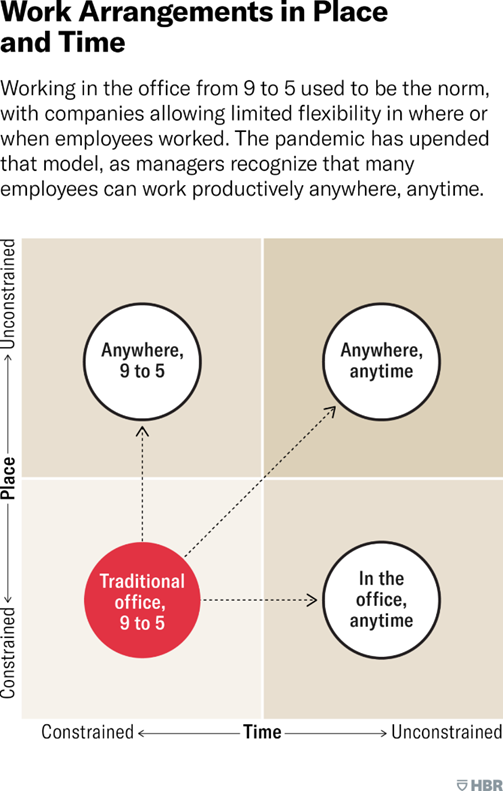
91
New cards
flextime
work schedules that gives workers some discretion over arrival and departure times. there are core hours during which everyone must be at the office, and it is most common among managerial and professional specialty occupations and sales work
* helpful to working moms and dual career couples because it alleviates problems with other commitments
* outcomes: less lateness, absenteeism, and turnover; more satisfaction and productivity. benefits lower level employees the most, but can be detrimental to team functioning
* helpful to working moms and dual career couples because it alleviates problems with other commitments
* outcomes: less lateness, absenteeism, and turnover; more satisfaction and productivity. benefits lower level employees the most, but can be detrimental to team functioning
92
New cards
compressed workweek
people work more hours per day but fewer days per week. there has been an uptick lately (15% of us employers offer this option)
* outcomes: more time for recreation, second job, family, etc, increase in job satisfaction, doesn’t reduce absenteeism, fewer productive hours, increased worker fatigue
* outcomes: more time for recreation, second job, family, etc, increase in job satisfaction, doesn’t reduce absenteeism, fewer productive hours, increased worker fatigue
93
New cards
flexplace
working in another location (telecommute, telework, WFH, remote work). people telework because of commuting commuting, some jobs don’t require you to be physically there, etc.
* outcomes: eliminating physical and temporal boundaries between home and work can be problematic, some researchers argue that if poorly implemented, this can have negative consequences
* outcomes: eliminating physical and temporal boundaries between home and work can be problematic, some researchers argue that if poorly implemented, this can have negative consequences
94
New cards
family-friendly backlash: grover and crooker
conducted research on family-responsive hr policies. found that it results in higher org commitment, lower turnover intensions, and that response varied depending on the parental status of employees
95
New cards
family-friendly backlash: rothausen et al.
found possible resentment by childless workers and workers who do not use the on-site childcare
96
New cards
psychological effects of unemployment (3)
* latent consequences of unemployment: loss of imposition of a time structure, regular shared experiences and contact with people outside of the family. goals and purposes, personal status and identity and the enforcement of activity are all negatively impacted
* uncertainty and loss of control leads to problems with psychological and physical health, life satisfaction, wage penalty, changes in personality, etc.
* intervention programs focus on self-esteem, optimism, control and job-seeking skills
* uncertainty and loss of control leads to problems with psychological and physical health, life satisfaction, wage penalty, changes in personality, etc.
* intervention programs focus on self-esteem, optimism, control and job-seeking skills