01 Principles of Radiograph
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
RADIOGRAPH
a 2-dimensional representation of a 3-dimensional structure where the imaged produced is made up of multiple overlying structures
What are the advantages of a radiograph?
Being readily available
Being relatively cheap
Provides good anatomic resolution
What are the disadvantages of a radiograph?
Does expose the patient to radiation
It offers poor differentiation of soft-tissue structures
Not sensitive to subtle pathology
Enumerate rules to minimize errors when taking xrays
If possible, the patient should be awake
The X-ray beam must be perpendicular to the anatomic region being examined
The x-ray source should be the farthest possible distance from the region being examined (min distance: 2.75 m)
T
T/F: The greater the density of the tissue, the less penetration of x-rays there is and the whiter its image appears on the film
T
Xrays are based on the principle that different tissues have different densities and produce images in different shades of gray
XRAY
Part of the electromagnetic spectrum and have the ability to penetrate tissue to varying degrees
Radiographic density: foreign bodies (e.g., metals)
solid white
Radiographic density: contrast media
brigh white outline
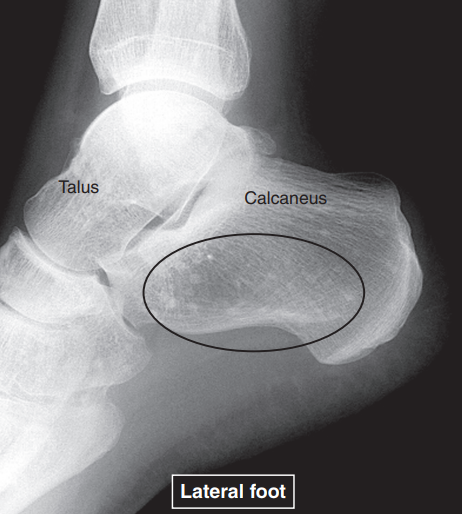
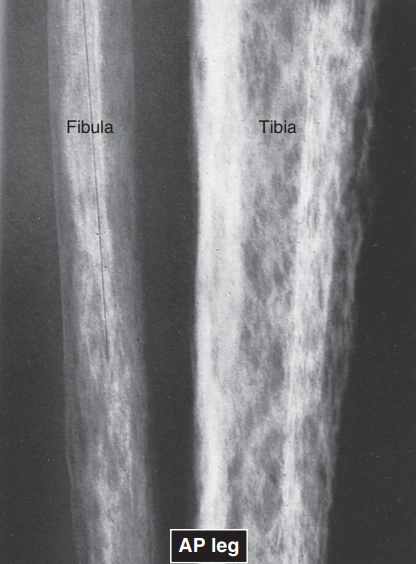
Radiographic density: bones
white
Radiographic density: soft tissues, water
gray
Radiographic density: fat
gray-black
Radiographic density: air or gas
black
What are the pitfalls of image interpretation?
Errors of observation, errors of interpretation
F
T/F: Non-radiologist cannot offer expertise from her or his own area of clinical specialty nor collaborate with the radiologist and others involved in the patient’s care.
SCLEROTIC
increased bone density
LYTIC
bone destruction
CORTEX
compact (dense) bone forming the bone surface
MEDULLA
trabecular bone in the bone marrow
ARTICULAR
refers to a joint (an articulation)
DEMINERALIZATION
decreased bone density (as occurs with osteomalacia/osteopenia/ osteoporosis)
ANKYLOSIS
fusion
OSTEO
prefix meaning bony
CHONDRO
prefix meaning cartilaginous
FIBRO
prefix meaning fibrous
ARTHRO
prefix meaning joint
SPONDYLO
prefix meaning spinal
DACTYL
prefix meaning digit
What does ABCS stands for in searching patterns for radiologic image interpretation?
Alignment, Bone desity, Cartilage space, Soft tissues
PAGET’S DSE
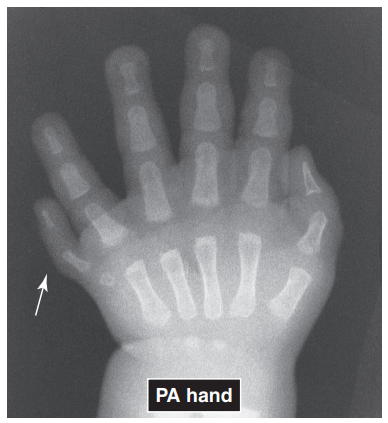
POLYDACTYLY
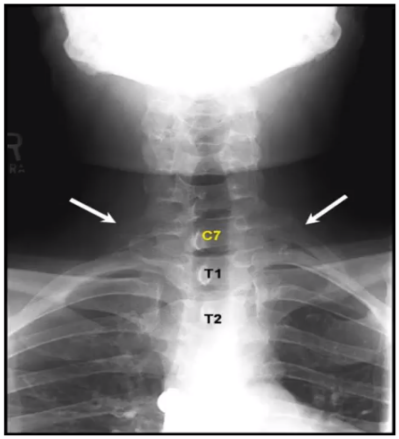
CONGENITAL ANOMALY - CERVICAL RIB
CONGENITAL DEFORMITY
CLEIDOCRANIAL DYSOSTOSIS
DEVELOPMENTAL DEFORMITY - SCOLIOSIS
T
T/F: The cortical outline of each bone should be smooth and continuous.
HEEL SPUR
IMPACTION
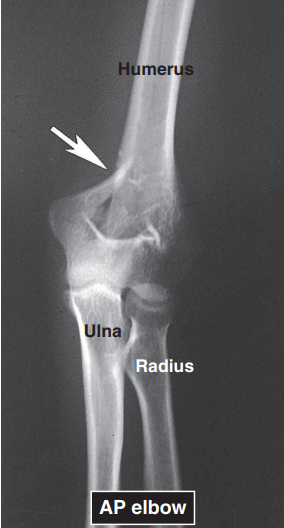
AVULSION FRACTURE
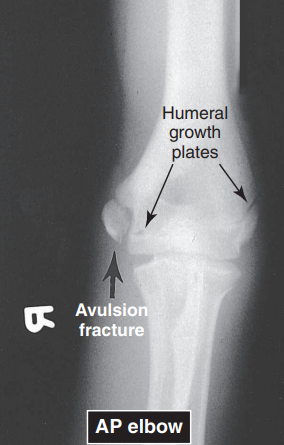
ANT DISLOCATION OF GH JOINT
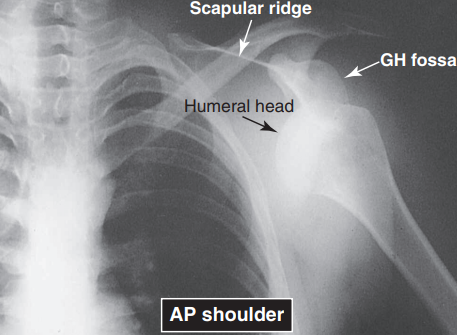
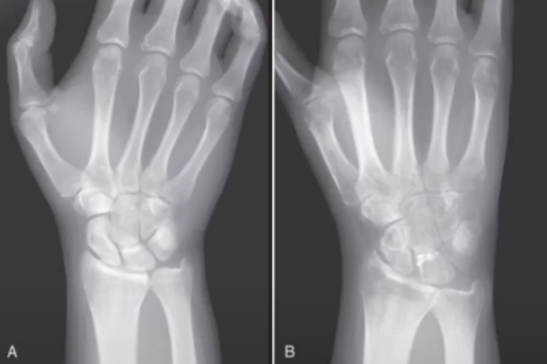
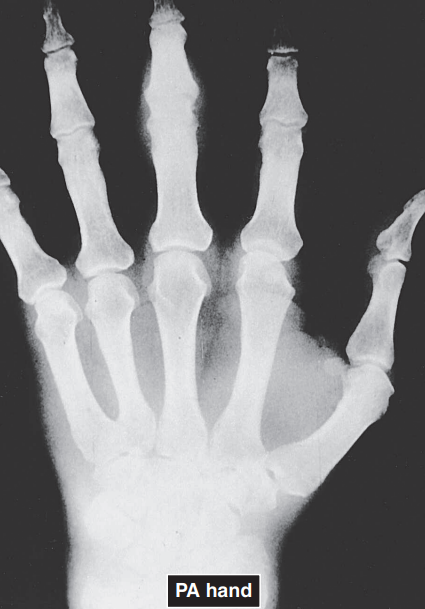
RA OF THE HANDS
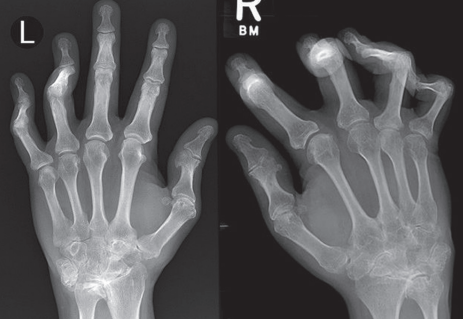
OSTEOPOIKILOSIS
overall increase in skeletal density
OSTEOMALACIA
overall decrease in skeletal density
OSTEOPOROSIS
FLUFF TRABECULAE
random proliferation of both osteoblastic and osteoclastic activity; seen in the skull of a patient with Paget’s disease and in hyperparathyroidism
HYPERTHYROIDISM
SMUDGED AND INDISTINCT TRABECULAE
a characteristic of osteomalacia
COARSENING OF TRABECULAE
often seen in patients with chronic renal failure and osteoporosis
LACY, DELICATE APPEARANCE OF TRABECULAE
secondary to thalassemia (Cooley’s anemia)
COOLEY’S ANEMIA OR THALASSEMIA
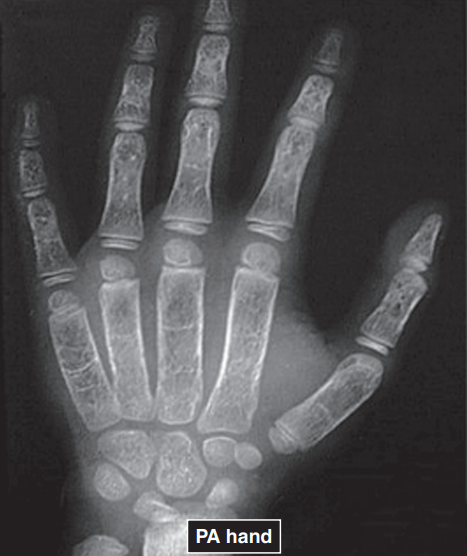
SCLEROSIS
normal local increases in bone density seen in areas subjected to increased physical stress, such as the weight-bearing areas of joints; actually signs of repair-extra bone is deposited to fortify bony architecture to withstand the forces of weight-bearing
EXCESSIVE SCLEROSIS
evident in normal conditions: at the site of a healing fracture as callus is formed and new bone is remodeled
may also be seen in abnormal conditions: degeneration of an osteoarthritic joint
DJD OF THE KNEE
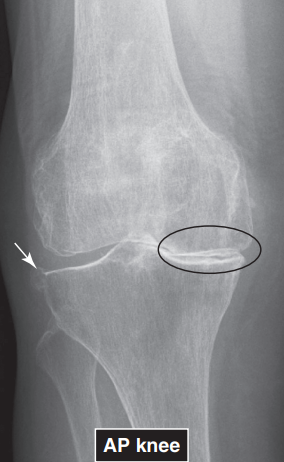
REACTIVE SCLEROSIS
present when the body acts to surround and contain a diseased area, such as a tumor or infection
OSTEOMYELITIS
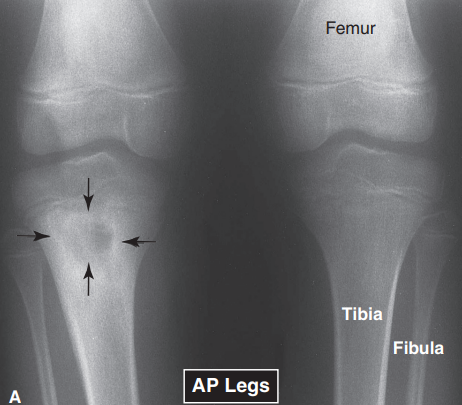
F, should be decreased
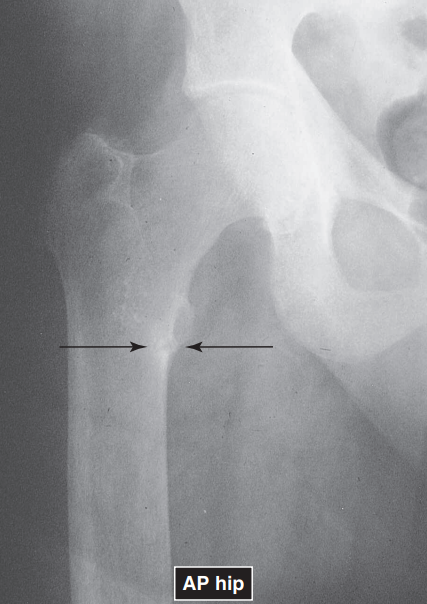
T/F: An increased joint space implies that the cartilage or disk is thinned down as a result of degenerative processes.
DEGENERATIVE DISK DISEASE
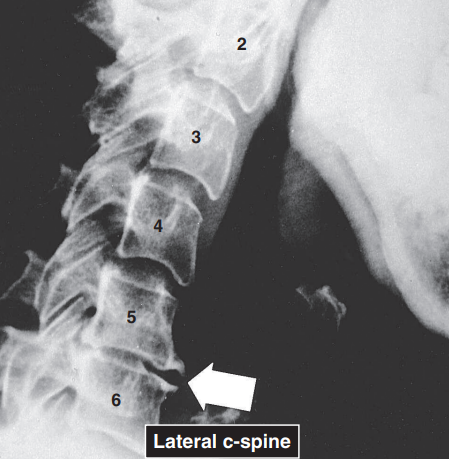
T
T/F: In the inflammatory arthritides such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, no reparative sclerosis is seen in the subchondral bone. Rather, erosions of the subchondral bone form radiolucencies at the joint margins.
GOUT AT IP JOINT
GROSS MUSCLE WASTING
may suggest a primary muscle disease, paralysis, inanition associated with severe illnesses, or disuse atrophy secondary to trauma
DISUSE ATROPHY OF QUADS
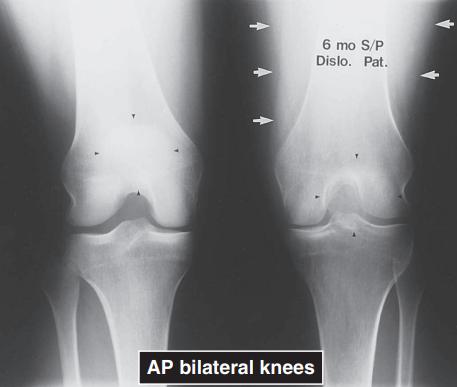
GROSS SWELLING OF MUSCLES AND SOFT TISSUES
may be indicative of inflammation, edema, hemorrhage, or tumor
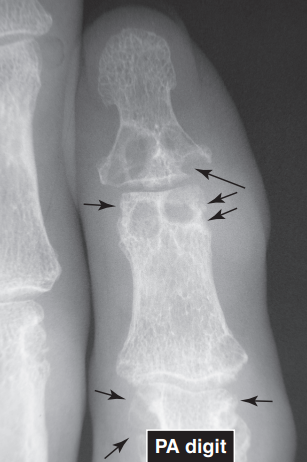
RA OF THE HAND
T
T/F: Loss or displacement of fat pads and lines is usually due to swelling and is a clue to an adjacent abnormality.
F, should be pronator quadratus
T/F: Displacement of the pronator teres fat line at the wrist usually indicates a wrist fracture.
T
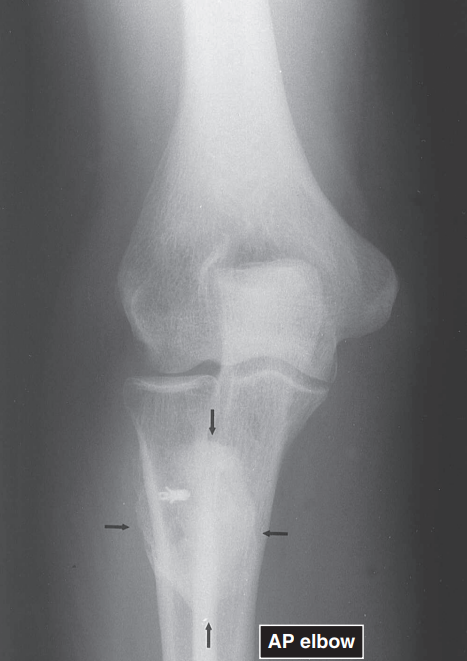
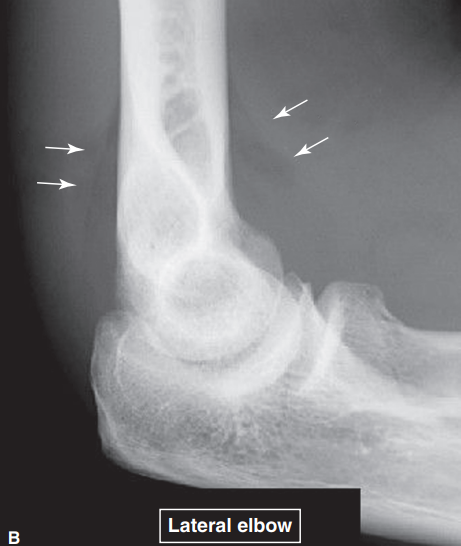
T/F: Displacement of the fat pads at the elbow (from the olecranon fossa posteriorly and from the coronoid and radial fossa anteriorly) often indicated hemarthrosis associated with fracture.
POSITIVE FAT PAD SIGN OR SAIL SIGN
SOLID
This reaction indicates an indolent (slow-growing) process; seen in fracture healing and chronic osteomyelitis.
LAMINATED OR ONIONSKIN
This reaction indicates repetitive injury, as in the battered child syndrome. It is also associated with sarcomas such as Ewing’s sarcoma.
SPICULATED OR SUNBURST
This reaction is almost always associated with malignant bone lesions, such as osteogenic sarcomas, and is less frequently seen in metastatic squamous cell tumors.
CODMAN’S TRIANGLE
A piece of periosteum elevated by abnormal conditions ossifies in a triangular shape. This may be present in a variety of conditions, including tumor, subperiosteal hemorrhage, and battered child syndrome.
GAS IN SOFT TISSUES
in soft tissues, this is an indication of gas-forming organisms,as in gangrene or trauma
CALCIFICATION
may be the result of trauma whereby hemorrhage has coagulated and calcified
MYOSITIS OSSIFICANS