Progressive Era STEM ECHS
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Progressive Movement
an early 20th century reform movement seeking to return control of the government to the people, to restore economic opportunities, and to correct injustices in American life

Social Gospel Movement
a 19th century religious movement based on the belief that Christians have a responsibility to help improve working conditions and alleviate poverty.

Settlement House Movement
built as a place where immigrants came to live. Instruction was given in English and how to get a job. Hull House was the first settlement house founded by Jane Addams in Chicago in 1889.

16th Amendment
Established a federal income tax.

17th Amendment
1913, provides for the direct election of US senators by the people rather than by state legislatures.

Prohibition
the banning of the manufacture, sale, and possession of alcoholic beverages.
The 18th amendment made prohibition the law. The 21st amendment ended prohibition.

Muckrakers
journalists who exposed the corrupt side of business and public life in the early 1900s.

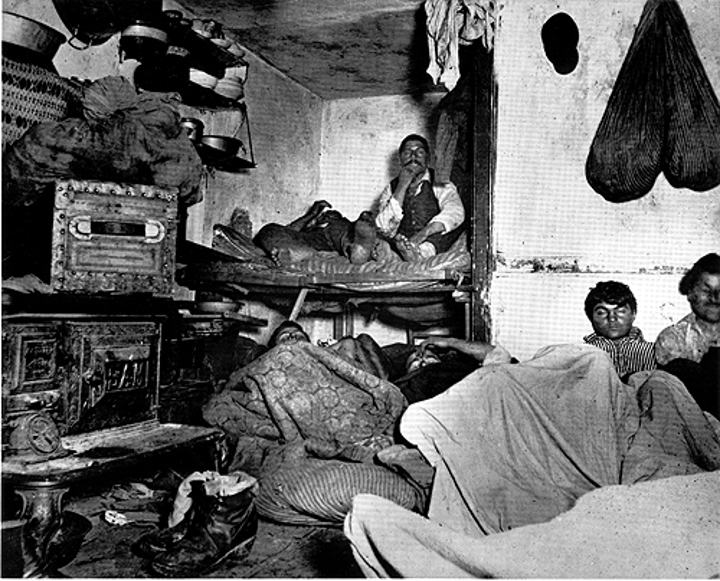
Jacob Riis
wrote "How the Other Half Lives" that told the public about the lives of the immigrants and those who lived in the tenement housing.

Upton Sinclair
wrote "The Jungle", that portrays the dangerous and unhealthy conditions prevalent in the meat packing industry at that time.

Populists
a movement that demanded that people have a greater voice in government and sought to advance the interests of farmers and laborers

National American Women's Suffrage Association (NAWSA)
An organization founded in 1890 to gain voting rights for women.

19th Amendment
1920, gives women the right to vote

Initiative
A procedure by which a law can be originated by the people rather than by legislatures

Referendum
A procedure by which a proposed law can be approved or denied by vote of the people.

Recall
A procedure for removing a public official from office by a vote of the people.

Secret Ballot
Allowed voters to cast a vote without election officials knowing who they voted for.

Direct primary
Voters, rather than politicians, would choose candidates for public office

Pendleton Act
created a Civil Service Commission that gave exams and selected government employees based on merit. Replaced the "Spoils System".
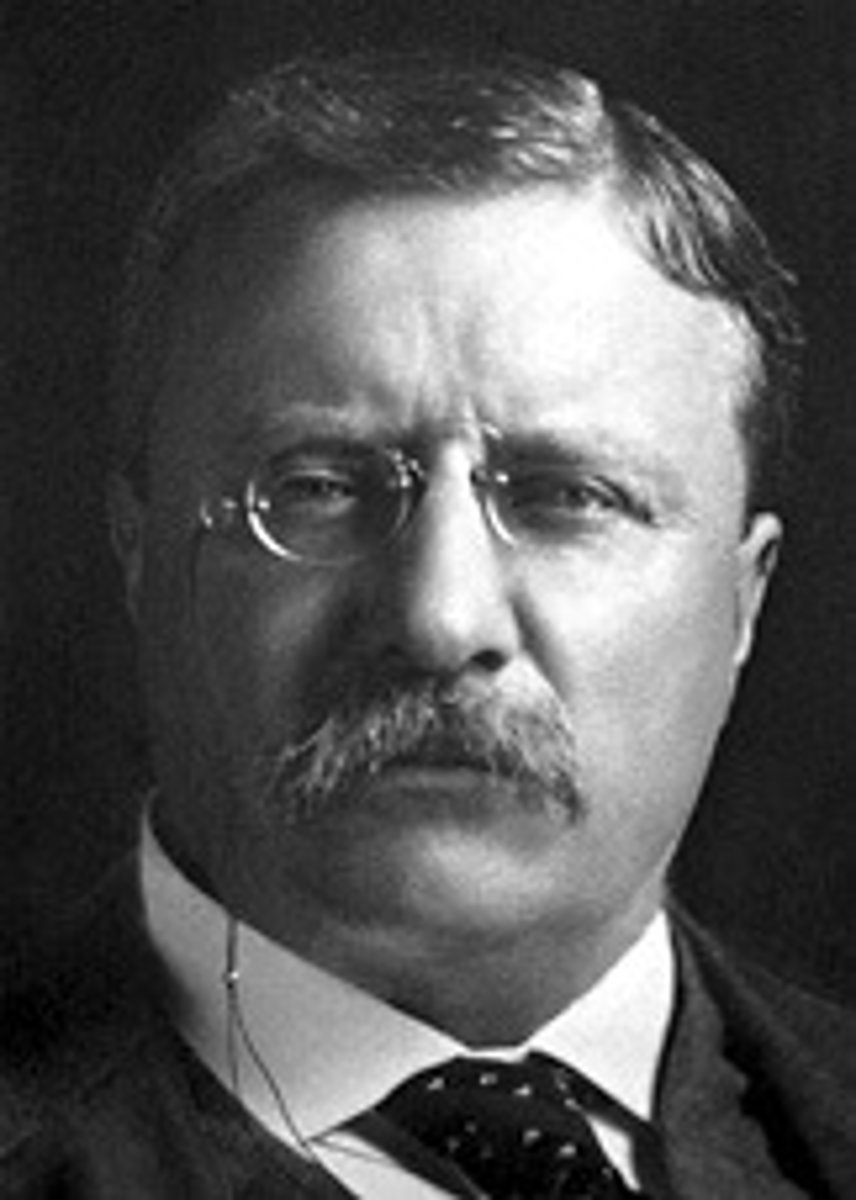
"Trustbuster"
Nickname for Teddy Roosevelt who broke up many monopolies and trusts.

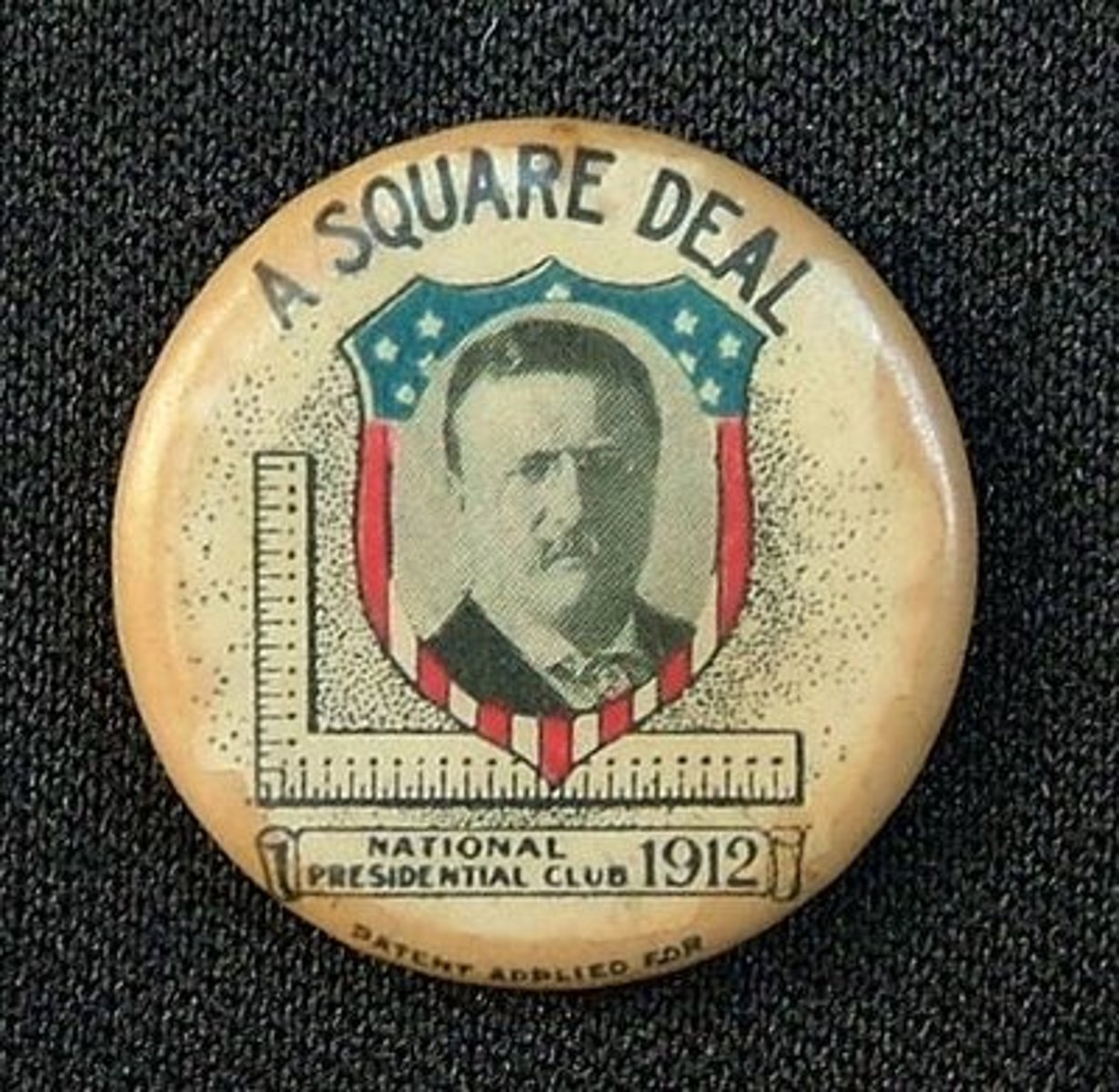
"Square Deal"
Teddy Roosevelt's progressive plan; involved trust-busting and conservation projects.

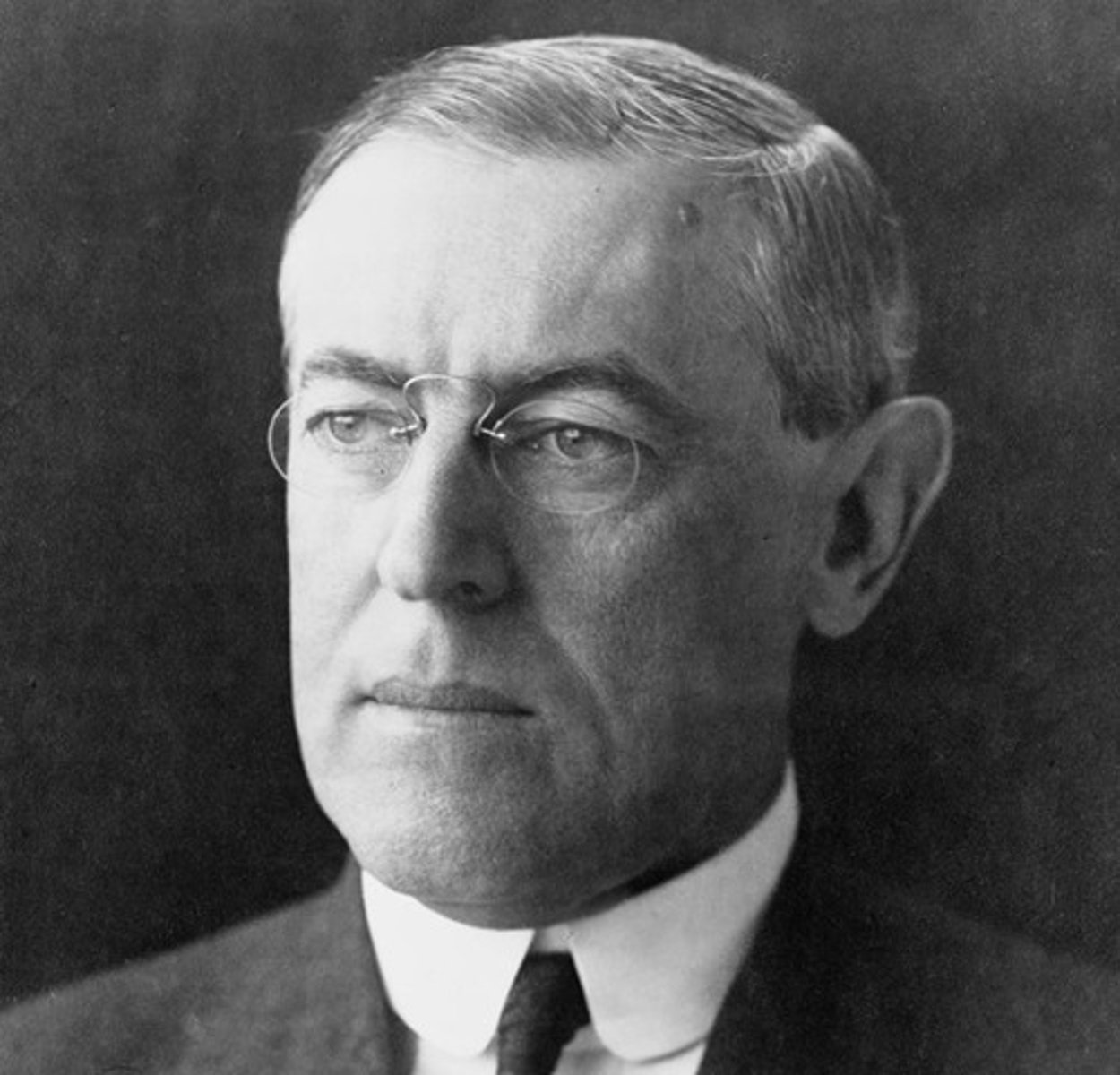
"New Freedom"
Wilson's progressive plan; involved financial reform, increased government regulation of business.

Interstate Commerce Commission (1886)
A federal regulatory agency that governed over the rules and regulations of the railroad industry.

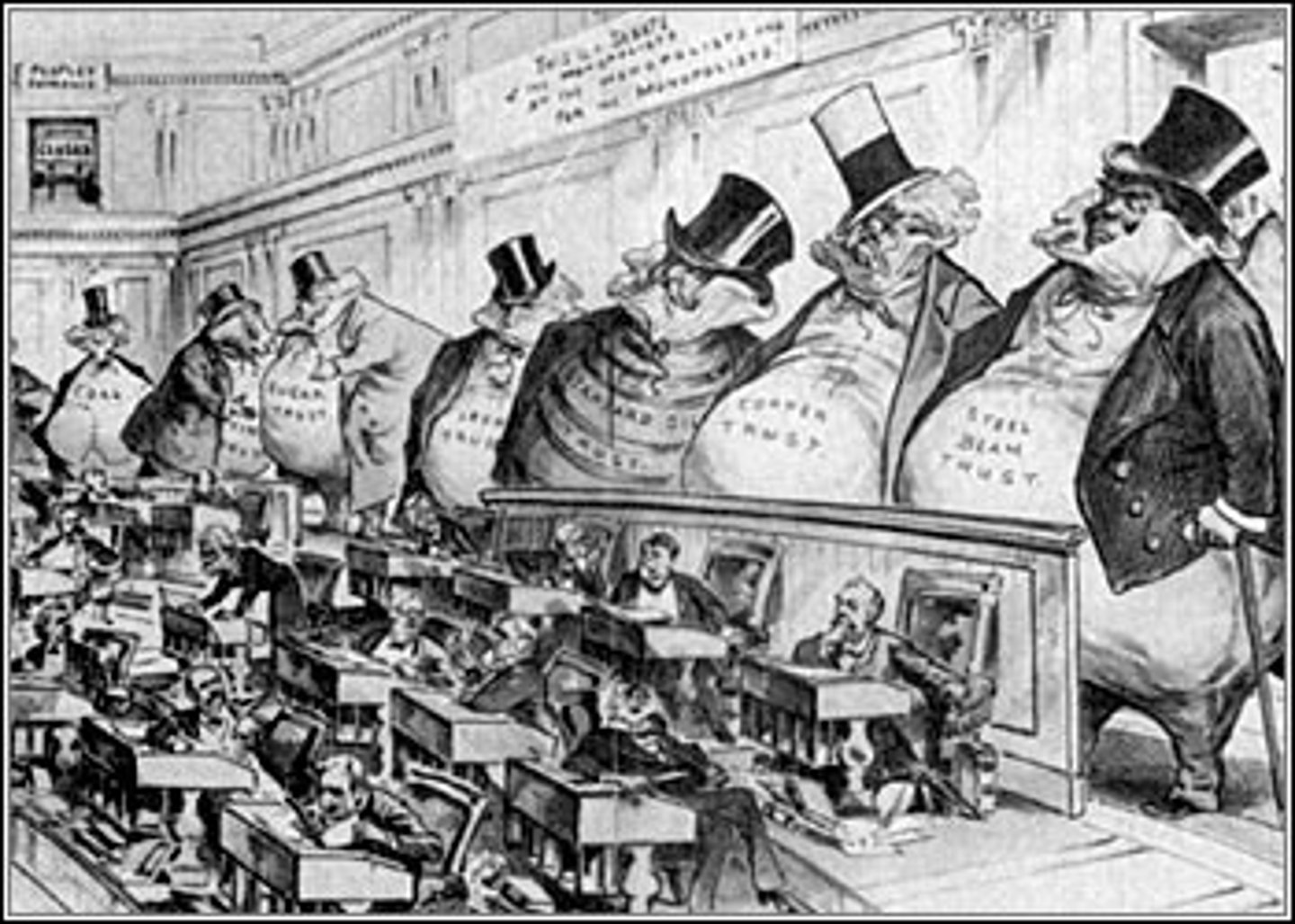
Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890)
A law that was intended to prevent the creation of monopolies by making it illegal to establish trusts that interfered with free trade.

Clayton Anti-Trust Act
1914, a law that made certain monopolistic business practices illegal and protected the rights of labor unions and farm organizations.

Pure Food and Drug Act & Meat Inspection Act
-Halted the sale of contaminated food and drugs and to ensure truth in labeling.
-established strict cleanliness requirements for meat-packers and created a federal meat-inspection program.

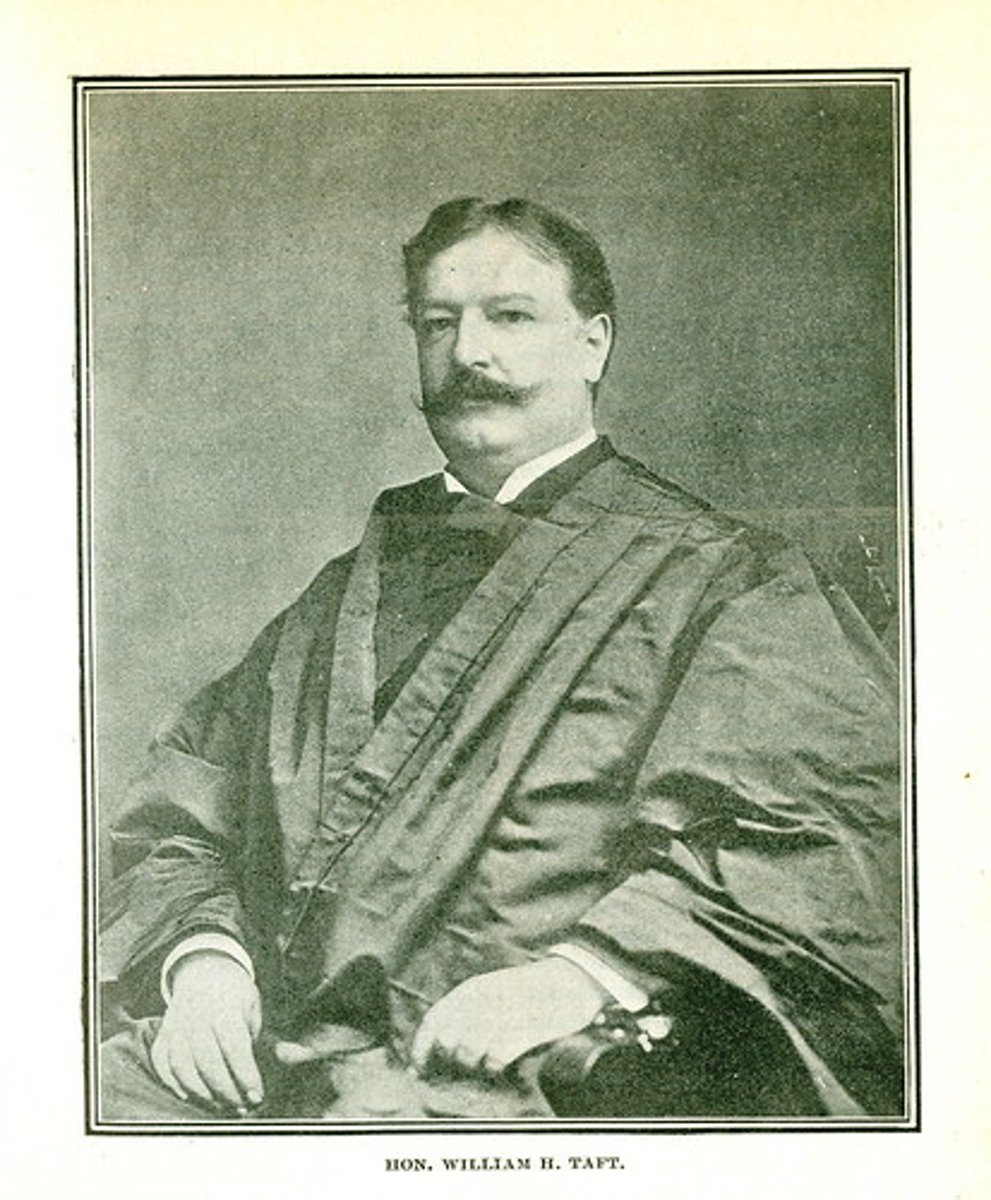
William Howard Taft
Elected President in 1908; supported safety standards for mines and railroads; supported 16th amendment; disappointed progressives in the areas of tariffs and conservation.

Federal Reserve Act
Established the modern banking system to regulate the money supply, set interest rates, etc.

Federal Trade Commission
A federal agency established in 1914 to investigate and stop unfair business practices. Created to enforce the Clayton Act.

Plessy v. Ferguson
The supreme court ruled that separation of the races in public accommodations was legal, thus establishing the "separate but equal" doctrine.

"Jim Crow" Laws
Laws enacted by southern state and local governments to separate white and black people in public and private facilities.

Booker T. Washington
founded the Tuskegee Institute to equip African Americans with teaching diplomas and useful skills in the trades and agriculture.

W.E.B. DuBois
Co-founded the NAACP to help secure legal equality for minority citizens. Argued African Americans should be given equal rights immediately

National Association of the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP)
An organization founded in 1909 to promote full racial equality.

Populist party platform (1892)
- unlimited coinage of silver to raise farm prices
- single term limit for presidents
- direct elections of senators
- secret ballots
- shorter work days

William Jennings Bryan
Democratic nominee for president in 1896 and 1900, supported by Populists. He argued for the free coinage of silver.

Third party movements
- examples: Populists, Bull Moose
- influence: major parties will usually adopted third party ideas if they draw significant support (ex: direct election of senators)
- third parties never win presidential elections, but may draw votes away from another party

Ida Tarbell
muckraker that wrote "History of the Standard Oil Company" to show how Rockefeller's power was based on unfair business practices. Her book eventually brought down Standard Oil

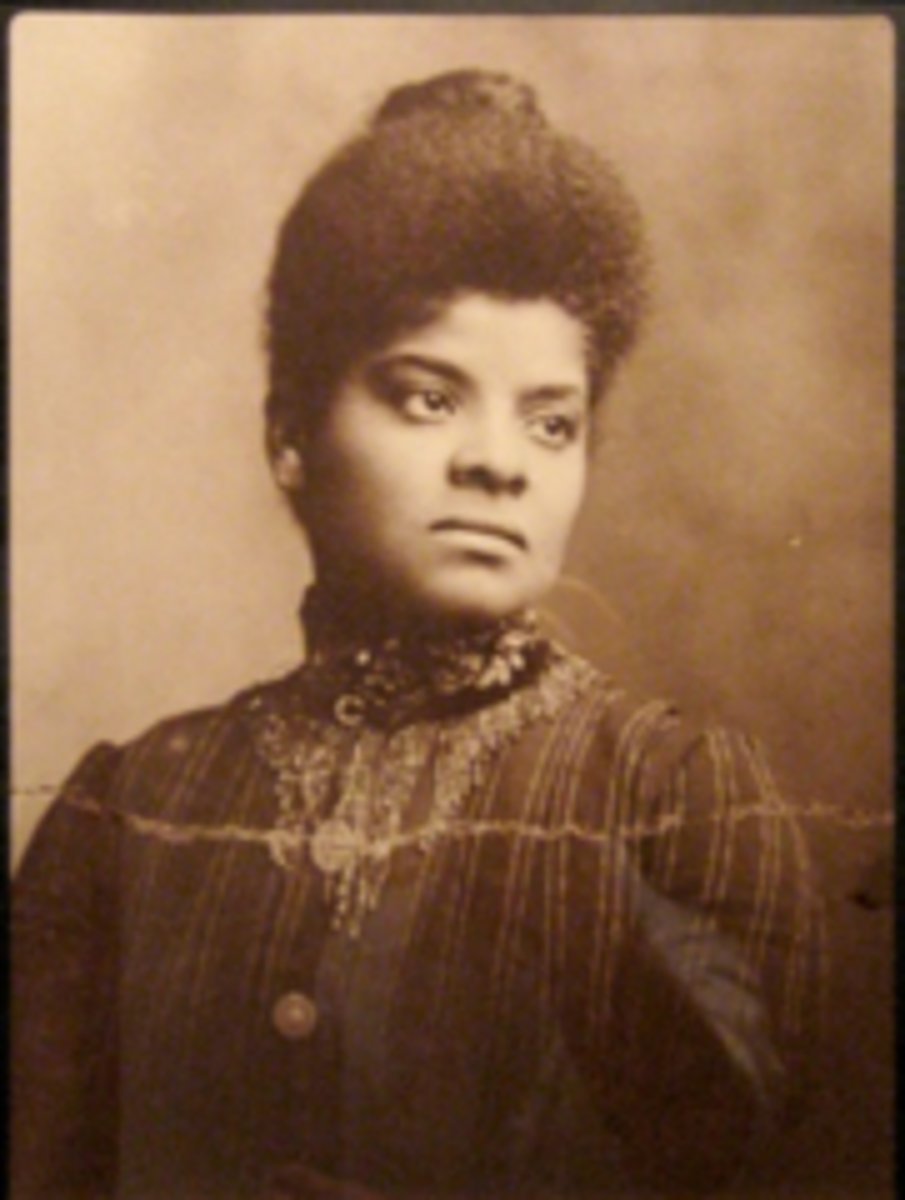
Ida B. Wells
co-founded NAACP, leading voice in social reform for African-Americans, spoke out against and led an anti-lynching campaign across the country

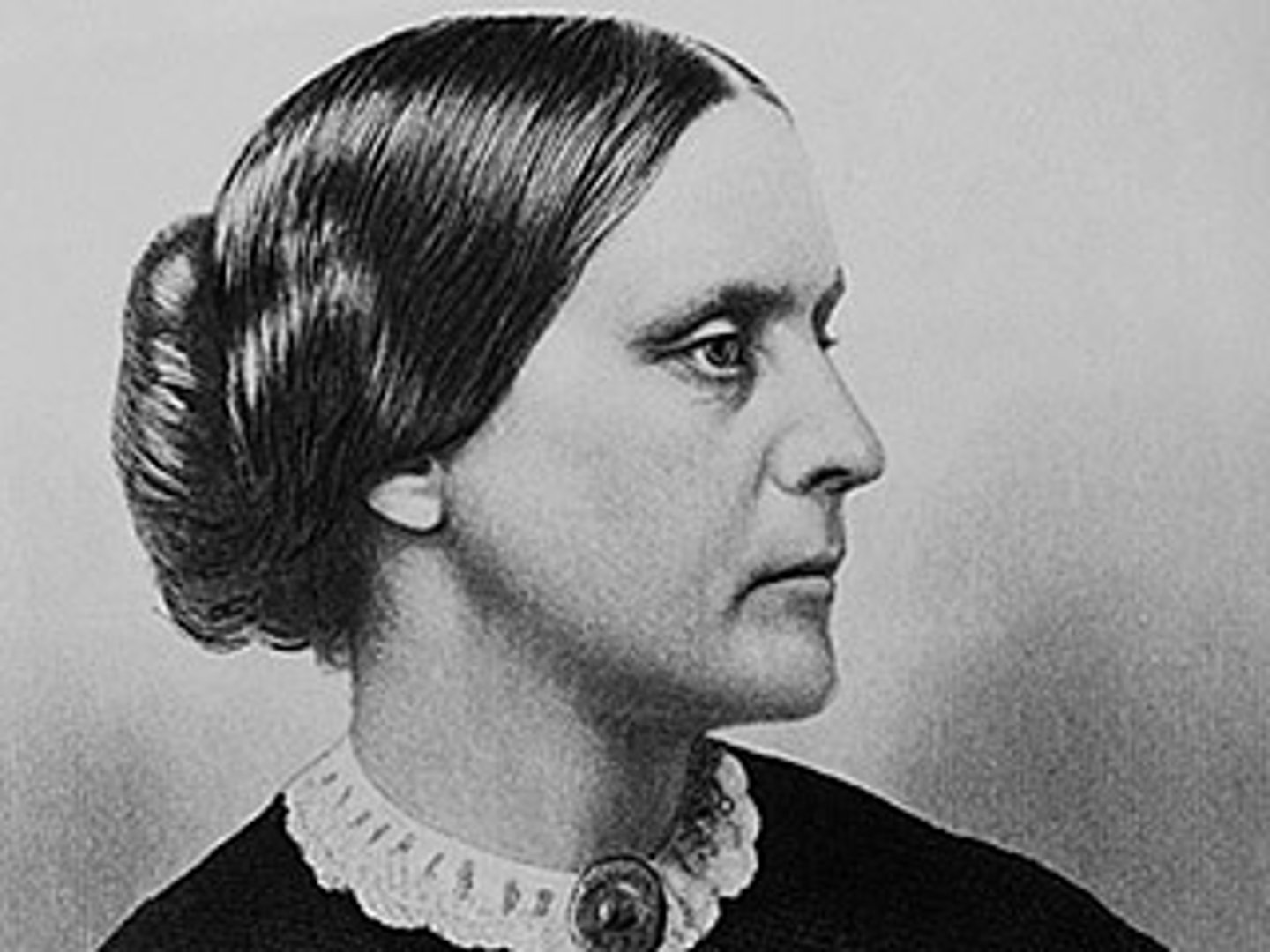
Susan B. Anthony
Leader of the women's rights movement. She got arrested for voting illegally.

Robert La Follette
Wisconsin's progressive governor that "cleaned up" state government from corruption and big business
