LSU BIOL 4215 Salmonella: Invasion and Evasion
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Salmonella
gram negative pathogen- outbreakes often caused by contaminated food
InvA
a gene that allows Salmonella cells to invade epithelial cells through an Injectisome. Making them inv+.
FlhA
a gene involved in the assembly of flagella
interesting relationship found between InvA and FlhA
InvA is homologous to FlhA
pathogenicity islands
refers to gene clusters responsible for virulence
SPI-1 and SPI-2
salmonella pathogenicity islands that each encode a separate type III secretion system
Injectisome
mechanism for injecting toxins into host cells
Flagella
whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
TIIISS
one of the bacterial secretion systems used by bacteria to secrete their effector proteins into the host's cells to promote virulence and colonisation, type of injectisome
cryoelectron tomography
can provide images of multi- protein complexes/structures by EM and computer rendering in 3D
discovered through cryoelectron tomography about TIIIS
TIIIS structural similarities across species
use of TIIISS by pathogens
moves proteins called effectors into host cells
animal pathogens that use type III secretion machinery
salmonella, E.coli, Shigella flexneri, pseudomonas aeruginosa, yersinia pestis, chlamydia trachomatis
though many animal pathogens use type 3 secretion, why do they have different effects on host cells?
the specificity of the pathogens effect on the host cell lies in the nature of the secreted effectors
How many proteins are injected into host cells by salmonella?
over 40
Salmonella effectors mechanisms of host manipulation (9)
modulation of GTPases, Repurposing of host enzymes, phosphorylation, ubiquitylation, Ribosylation, Acylation, Acetylation, Proeolysis, GlcNAcylation
Phosphorylation
The metabolic process of introducing a phosphate group into an organic molecule.
Ubiquitylation
Process by which one or more ubiquitin molecules are attached to a protein substrate molecule, which often results in the degradation of the tagged protein
GlcNAcylation
the post-translational, covalent attachment of a single N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) to Ser or Thr residues of proteins
Ribosylation
The transfer of ADP-ribose from NAD+ onto Arginine, Glutamate, or Aspartate residues.
-catalyzed by ribosyltransferase
Acylation
When an acyl group (-COR) is added to a molecule
Acetylation
addition of acetyl group
Proteolysis
the breakdown of proteins or peptides into amino acids by the action of enzymes
What awas discovered in the 1988 study by Finlay, Gumbiner, and Falkow
The researchers observed that bacterial entry was associated with dramatic reorganization of host cell actin cytoskeleton, leading to membrane ruffling at the site of bacterial contact. The salmonella actively invades epithelial cells
Required for Salmonella invasion
TIIISS
SopE
Salmonella effector required for membrane rufflign and invasion
actin polymerization
Process of actin monomers forming filaments.
Membrane ruffling requires
actin polymerization
Actin
A globular protein that links into chains, two of which twist helically about each other, forming microfilaments in muscle and other contractile elements in cells; component of cytoskeleton
How does SopE promote actin polymerization?
activates members of the Rho family of GTPases, particularly Rac1 and Cdc42, which are key regulators of actin cytoskeleton dynamics.
G proteins
A class of proteins that reside next to the intracellular portion of a receptor and that are activated when the receptor binds an appropriate ligand on the extracellular surface.
First TIIISS effector to have a function assigned to it
SopE
Structural basis for reversible activation of a Rho protein by SopE
SopE has no amino acid similarity with any known GEF, binds Cdc42 differently from any known GEF
Inactive Rho=
less actin polymer
active Rho
more actin polymer
how does salmonella alter host cell shape
by activating and deactivating small GTPases
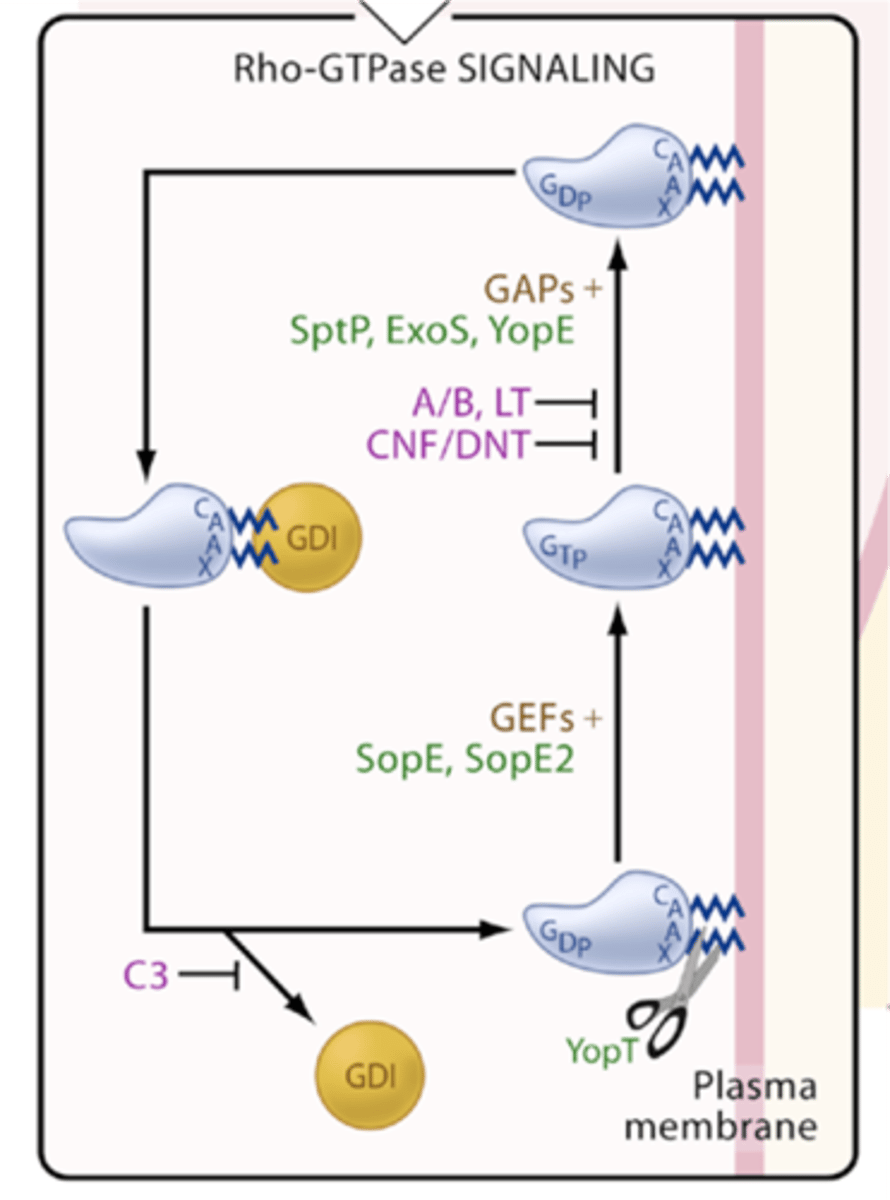
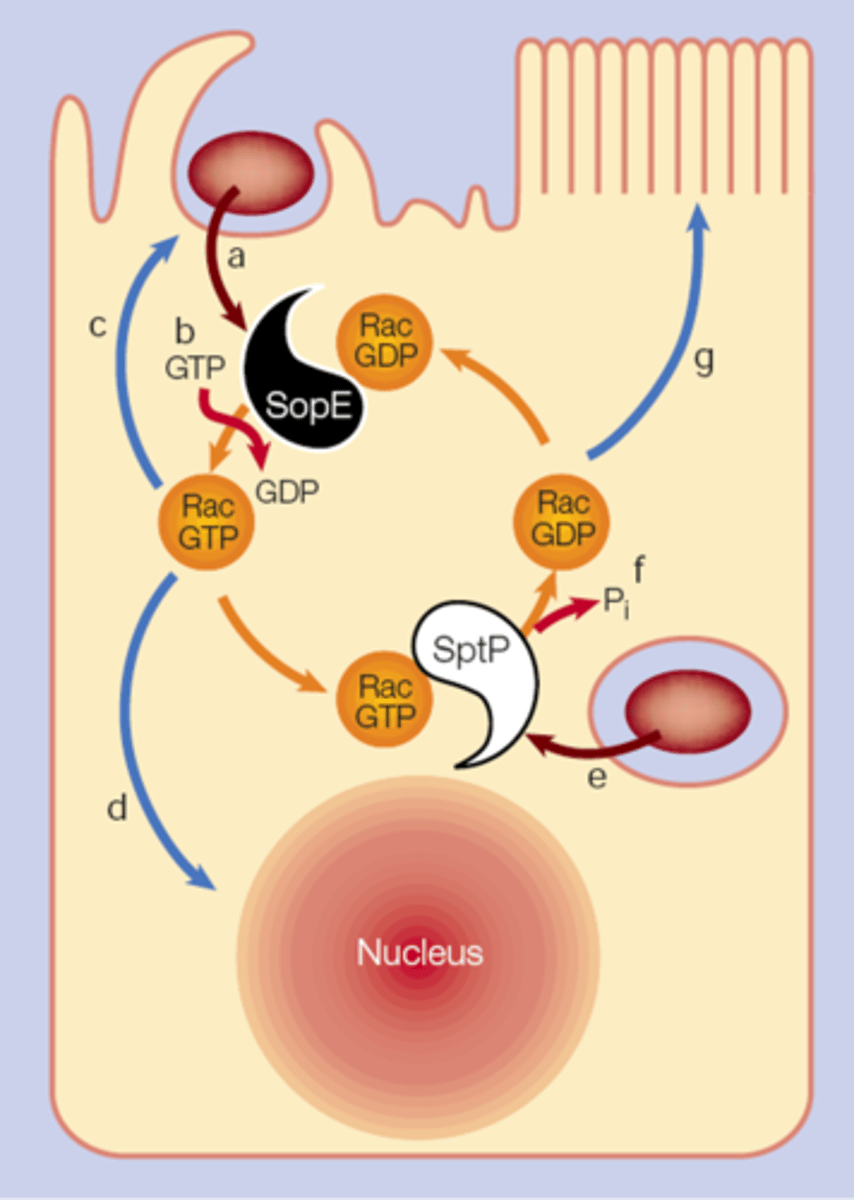
Explain steps of Salmonella altering cell shape
SopE protin into cytoplasm, binds to Rac
SopE acts as guanin-nucleotide exvhange factor to favour GTP form of Rac
Rac stimulates membrane ruffling
bacterial uptake
SptP protin binds to GTP Rac, restoring GTPase activity
Cell shape is restored
Proteins that mimic active G-protein created by bacterium
Map (EPEC), IpgB (Shigella), SifA (Salmonella)
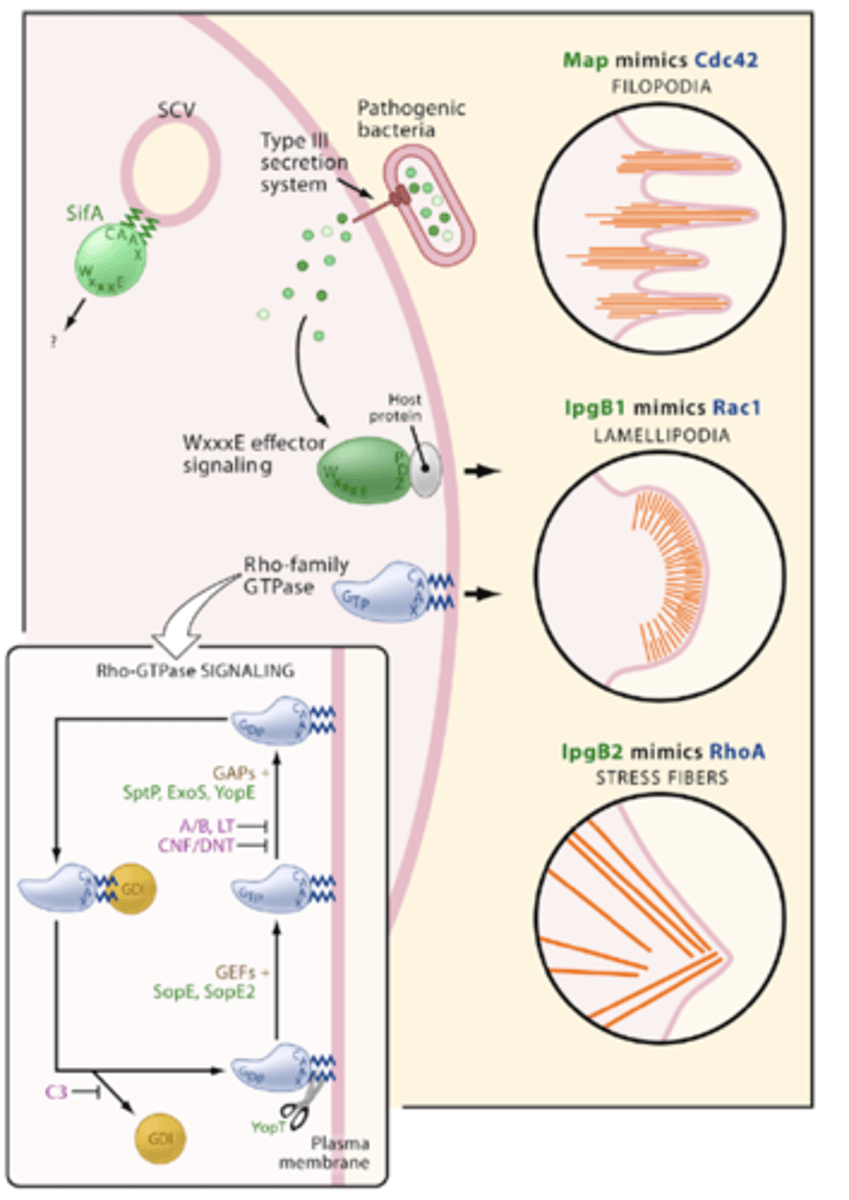
WxxxE motif
a conserved sequence that function as guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for Rho GTPases.
Yersinia pestis
plague, spread by fleabite or inhaled, systemic infection
Yersina pestis virulance
resistant to phagocytosis and macrophages, replicate extracellularly
Plasmid encoded type III secretion system
How many were killed by black death in the 14th century
50 million people
YopE is a GAP
inactivating a G protein and turning off phagocytosis in immune cells
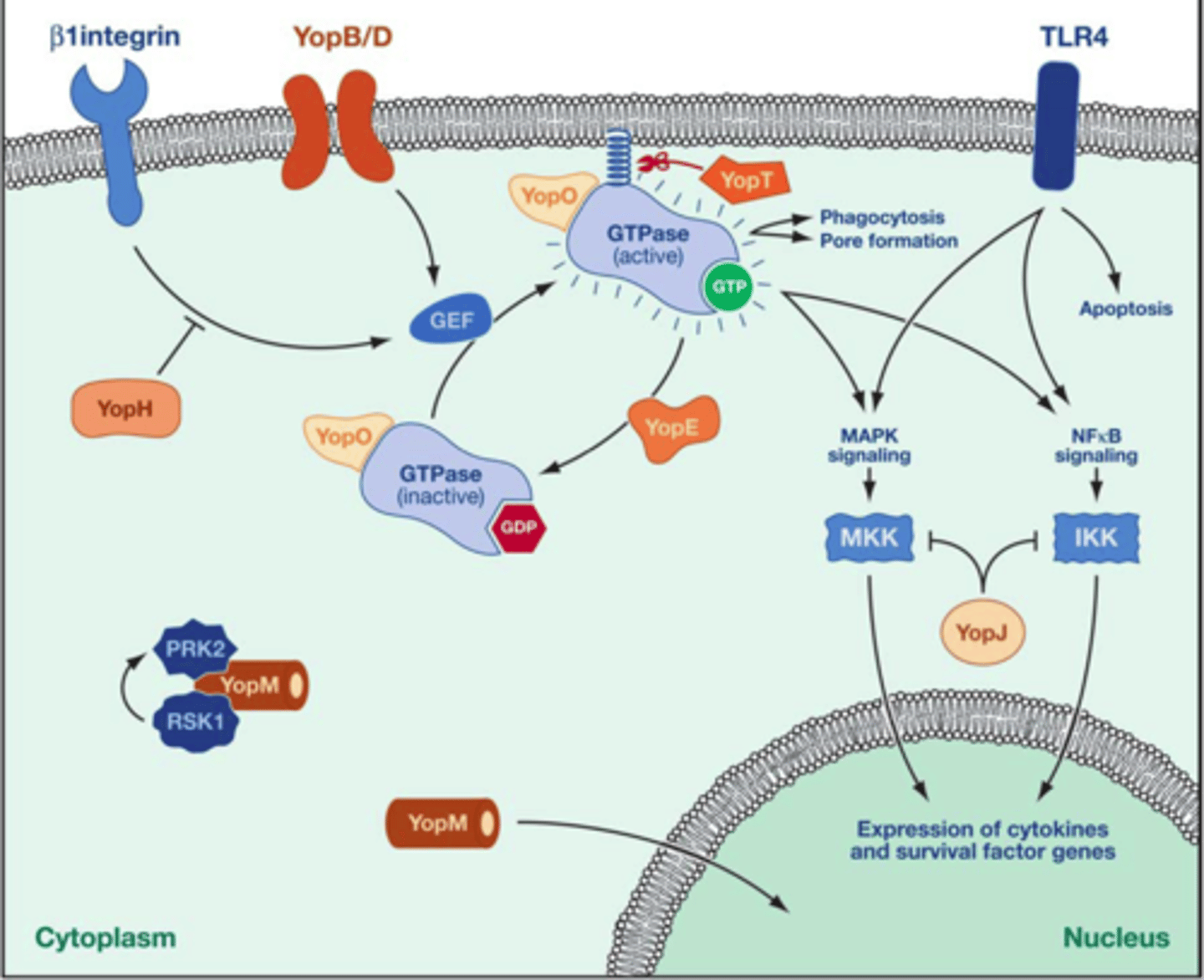
Yersinia Strategy
remain extracellular, avoid phagocytosis
THe MAP kinase pathway is also targeted by
T3SS effectors
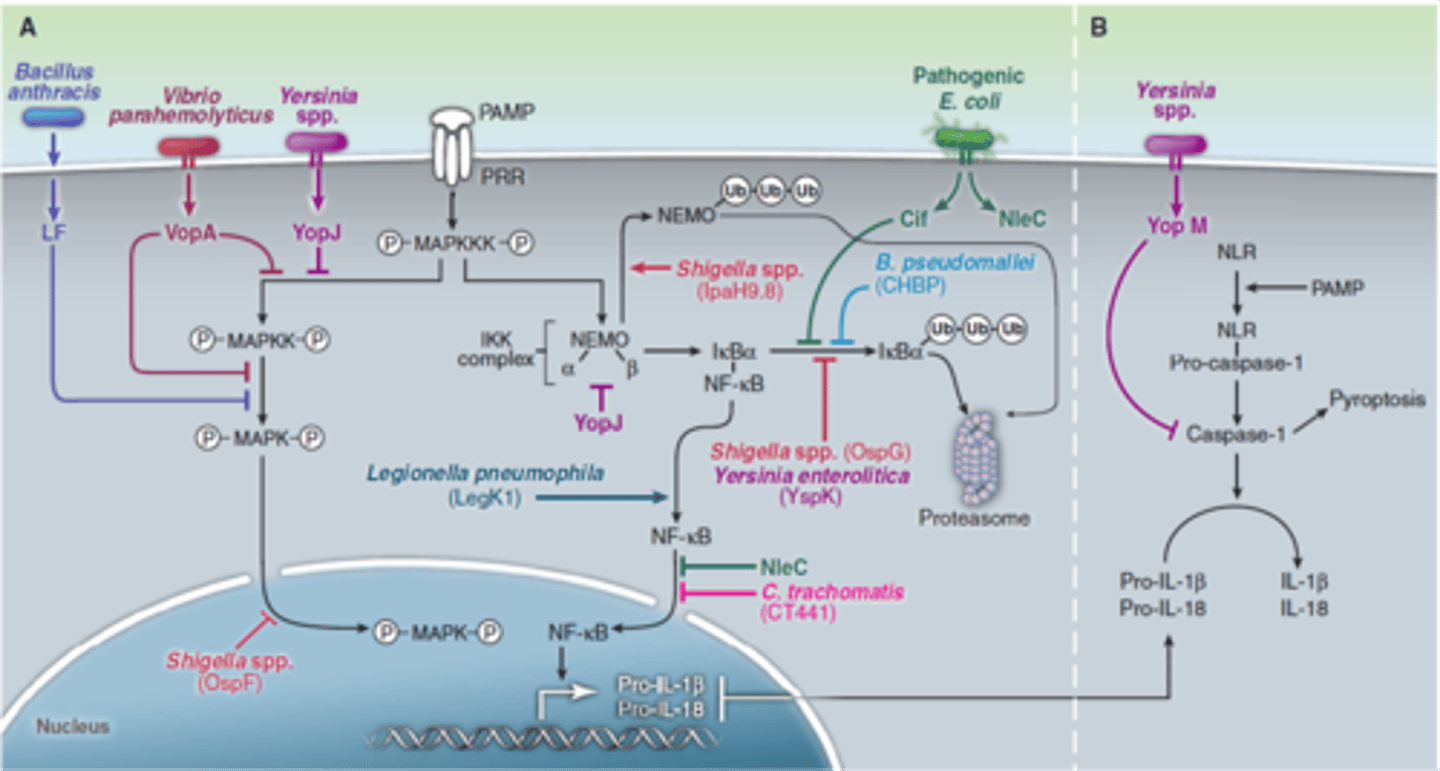
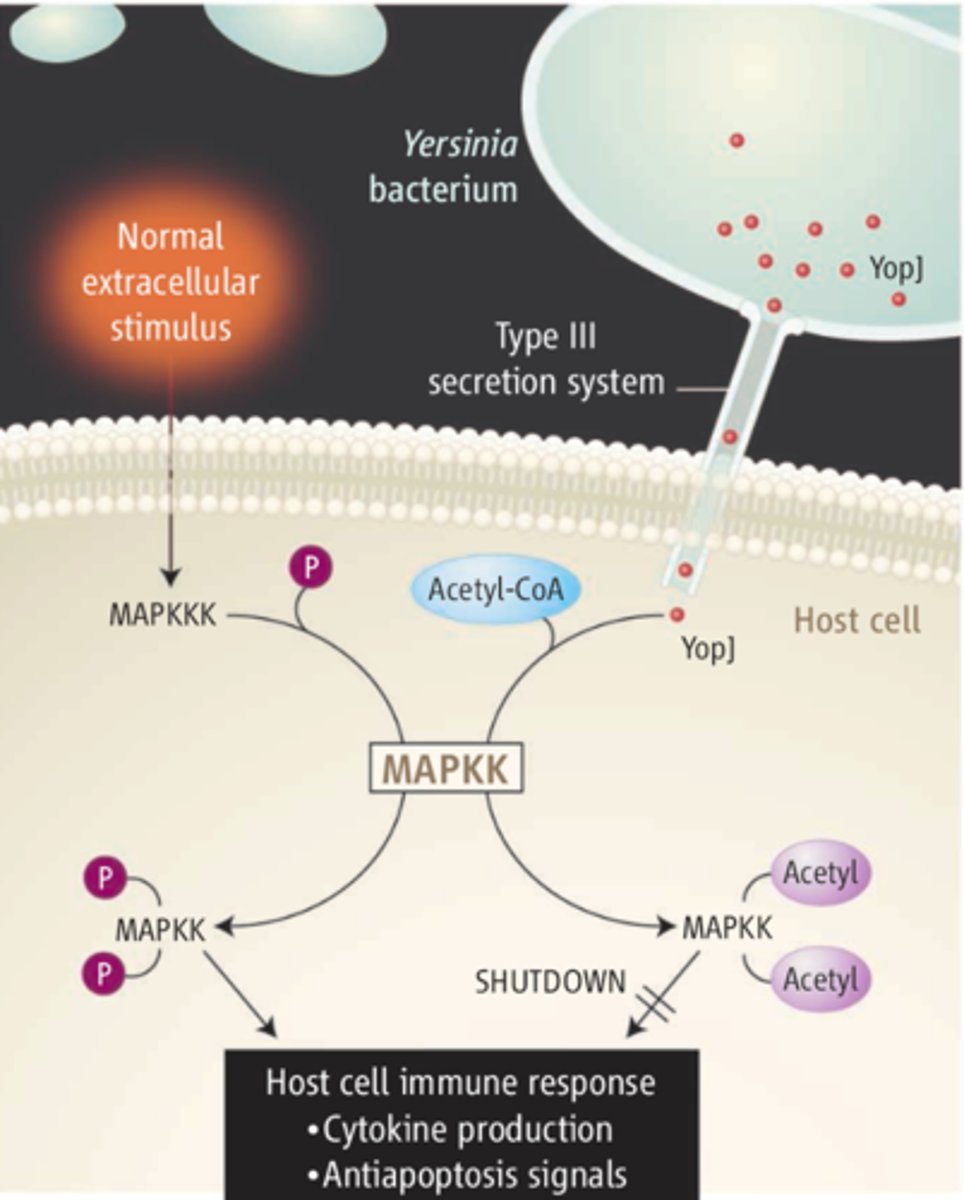
How odes Yersinia YopJ inhibit kinase activation
inhibites mitogen-activated protin kinase (MPK) and nuclear tacter kB(NFkB) signaling pathways used in innate immune response by preventing activation of family of MAPK kinases
How does YopJ act as acteyltransferase
uses acetyl-coenzyme A to modify serine and threonine residues in activation loop of MAPKK6, blocking phosphorylation
What type of pathway is a common target for T3SS effectors
MAP kinase pathways
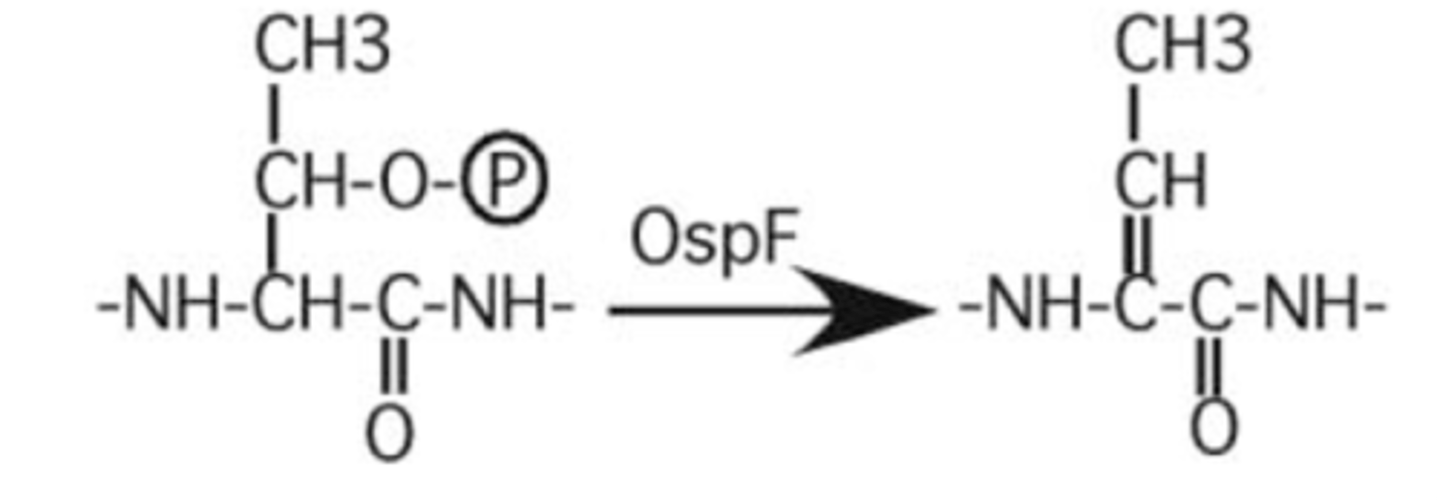
How does phosphothreonine lyase activity (ex. Shigella OspF) prevent re-phosphorylation?
removes phosphates from MAPK threonine residues
A potential target for virulence drugs
TIIISS