1.2 A Nervous System Organization
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
neuron
excitable cells
gilal cells
non-excitable, mitotic support cells found in both the CNS and PNS (contain different kinds tho)
critical for normal function at neural synapses
what are the central and peripheral nervous systems made out of
nervous tissue
nervous tissue
neurons and gilal ccells
are there more gilal or neurons
glial cells account for about 1/2 of the entire volume of the nervous system
nerves
only found in the PNS are organs composed of clusters of numerous neuron axons
Central Nervous System
contain the brain and spinal cord
bbrain in regards to the central nervous system
site of thoughts and intelligence
processes information received and sends messages back to the body
Spinal cord in regards to the central nervous system
carries information between the brain and the body
musculoskeletal reflex center … like knee jerk
What protects the central nervous system
covered by connective tissue meninges
protected by skull and vertebrae
peripheral nervous system
nerves and ganglia
nerves in regards to peripheral nervous system
bundled axons which carry signals to and from the CNS
extended from brain or spinal cord
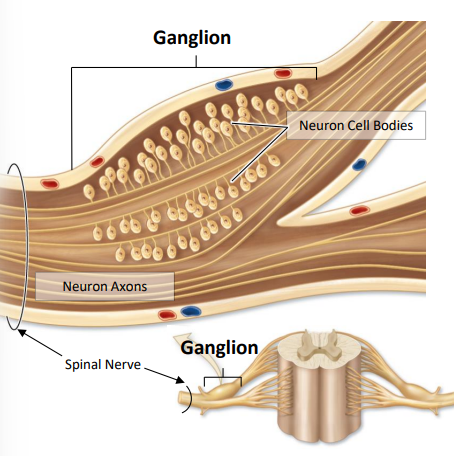
ganglia in regards to the peripheral nervous system
cluster of neuron cell bodies outside of the CNS
Nerve
an organized collective bundle of neuron axons that send signals throughout the PNS
How are nerves classified
structuarally by location or functionally based on the direction of signals they carry
types of nerves classified structurally by location
cranial nerves that extend from the brain
spindal nerves that extend from the spinal cord
nerves that are classified functionally based on the direction of signals they carry
sensory nerves
motor nerves
mixed nerves
sensory nerves
carry afferent sensory signals from the receptors throughout the body to the CNS (brain or spinal cord)
Motor nerves
carry EFFERENT motor signals from CNS (brain or spinal cord) to the effector ( skeletal muscles, smooth muscles and glands)
Mixed nerves
Carry both afferent sensory and efferent motor signals
all spinal nerves are mixed nerves
sensory signals are (afferent or efferent)
afferent - inward to cns
motor signals are (afferent or efferent)
efferent - outward
epineurium
connective tissue surrounding the outer nerve surface, protects the nervep
perineurium
connective tissue that surrounds and separates bundles of axons organized into fascicles
location of blood vessels supplying the nerve
endoneurium
connective tissue that surrounds and separates individual axons both unmyelinated or myelinated within fascicles
provides electrical insulation
Ganglion
localized cluster of neuron cell bodies and associated glial cells , found along the length of a nerve in PNS
Afferent Pathway branches
sensory nervous system to somatic and visceral sensory
efferent pathway branches
motor nervous system into somatic motor and autonomic motor - which further branches into sympathetic and parasympathetic division
Sensory nervous system
detects stimuli and transmits information from receptors to the CNS
detects stimuli and transmits information from receptors to the CNS
Somatic nervous system
branches from the sensory nervous system
sensory input that is consciously perceived from receptors
visceral sensory
branches from sensory nervous system
sensory input that is not consciously perceived from receptors of blood vessels and internal organs
Motor Nervous system
output
initiates and transmits information from the CNS to effectors
Somatic Motor
motor output that is consciously or voluntarily controlled… effector is skeletal muscle
e
effector of somatic motor
skeletal musclea
autonomic motor
motor output that is not consciously or is involuntarily controlled
effectors are cardiac muscle smooth muscle and glands
effectors of autonomic motor
cardiac muscle smooth muscle and glands
sympathetic division
branches from motor nervous then autonomic motor
best known for fight or flight or freeze stress response
parasympathetic division of autonomous motor
often referred to as the resting and digesting branch due to its role maintaining homeostasis
structural classification of neuron types
multipolar, bipolar, unipolar and anaxonic
multipolar neuron
most common type of neuron
includes all motor neurons and most interneurons
multiple processes extend directly from neuron cell body (soma)
typically has multiple dendrites and one axon
includes all motor neurons and most interneurons
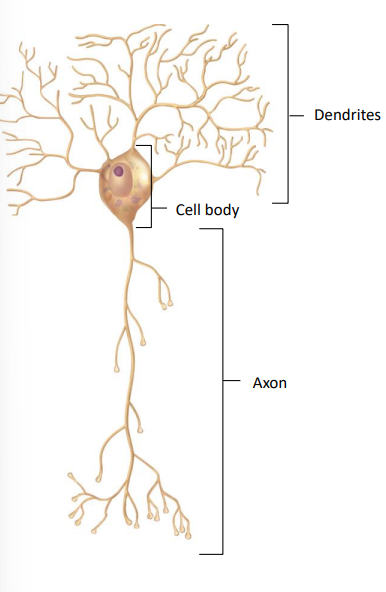
what is the most common type of neuron
multipolar neuron
what are all motor neurons and most interneurons
multipolar neurons
bipolar neuron
limited locations
found in some special senses like retina and olfactory epithelium in nose
two processses extend directly from cell body - one dendrite and one axon
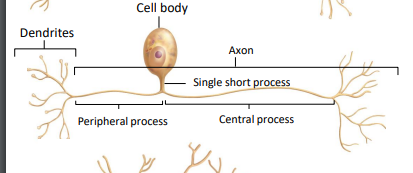
Unipolar neuron
most sensory neurons
dendrites directly to peripheral process of axon… single short process extends directly from the cell body and forms a T intersection with the two processes (peripheral and central) of one long axon.
anaxonic neuron
interneurons
lacks an axon; processes are only dendrites that extend from cell body
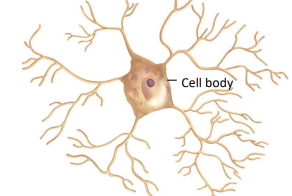
sensory neurons
receive somatic and visceral sensory input
conduct action potential signals to the CNS
most sensory neurons are unipolar with receptive region and cell body in PNS and axon ends in the CNS
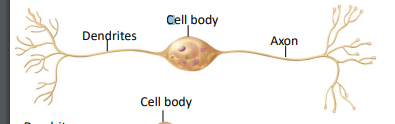
dendrites
receive nerve impulses… transferring them from synapse to the cell body
axons
long thread like portion of a nerve that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body
Interneuron (association neurons)
receives signals from sensory neurons and sends signals to motor neurons
locate entirely in the CNS
typically multipolar or anaxonic neurons
motor (association) neuron
conducts motor output from cns to effectors in the PNS…
innervates both somatic and autonomic effectors
multipolar neurons
Types of synapses
electric and chemical synapses
electrical synapse
fastest type of synapse
junction between two neurons that allow for the two way transmission of electrical signals
presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons bound together by gap junctions
chemical synapses
most common type of synapse
presynaptic neuron’s axon terminal produces signal iin the formaof a neurotransmitter
post synaptic neuron recieves signal as a neurotransmitter binds to receptors and causes a postsynaptic potential … either depolarization or hyperpolarization)
types of axonal transport
retrograde and anterograde
anterograde transport
moves newly synthesized material toward synaptic knobs
retrograde transport
moves used material from axon for breakdown and recycling in celll body
Fast axonal transport
approx 400 mm/day
involves movement along microtubules powered by motor proteins that split ATP
anterograde transport of vesicles, organelles, glycoproteins
retrograde transport of used vesicles, potentially harmful agents
slow axonal transport
result from the flow of axoplasm
anterograde transport of enzymes, cytoskeletal components, new axoplasm