muscular system + skeletal system
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
what are the 3 main types of muscles in the muscular system?
skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
skeletal muscle characteristic(s); voluntary or involuntary?
skeletal muscle is composed of skeletal muscle tissue, nervous tissue, blood, and connective tissues. It is attached to bones of skeleton and is a voluntary muscle
cardiac muscle characteristic(s); voluntary or involuntary?
cardiac muscles makes up most of the wall of the heart and is responsible for the pumping action of the heart. It is an involuntary muscle
smooth muscle characteristic(s); voluntary or involuntary?
smooth muscle is in the walls of internal organs and is an involuntary muscle.
name 3 types of muscle coverings
epimysium, perimysium, endomysium
define epimysium
surrounds whole muscle
define perimysium
surrounds fascicles within a muscle
define endomysium
surrounds muscle fibers within fascicle
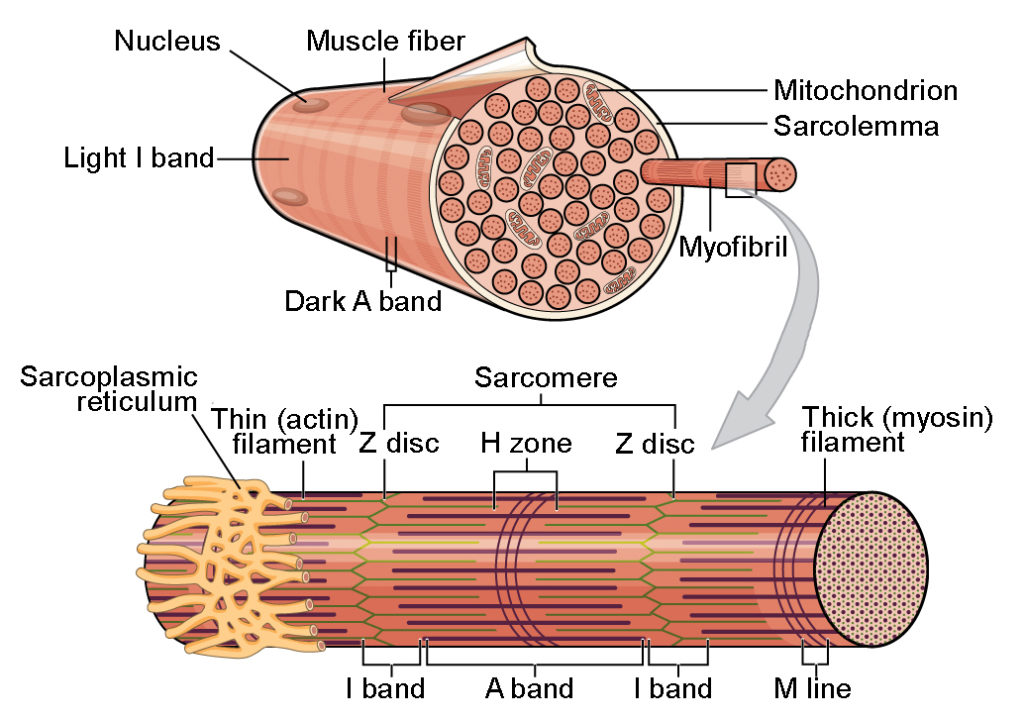
what are the main components of skeletal muscle fibers? what is its defining structure?
multimucleated sarcolemma
sarcoplasm
myofibrils
sarcomere
sarcoplasmic reticulum
defined by its striation pattern which is made by an arrangement of myofilaments and myofibrils
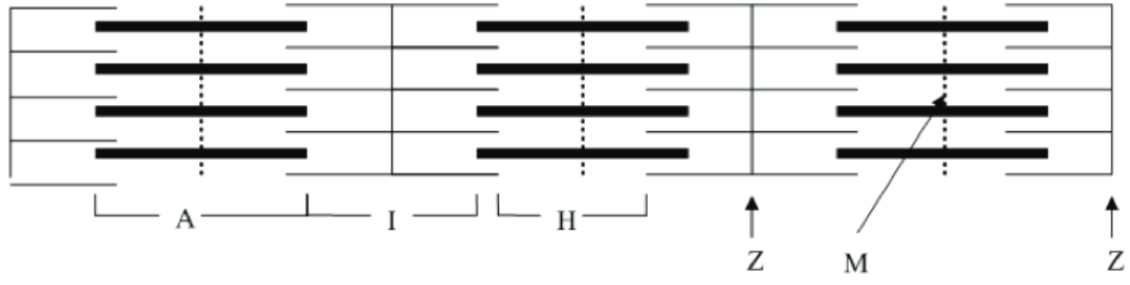
the what does the picture show? What do each letters represent?
the figure show components of a sarcomere. A band represents thin and thick filaments, I band represents thin filaments, H zone represents thick filaments, Z line represents Z disc, and M shows M line
what are thick filaments composed of? what is its function?
thick filaments are composed of myosin protein. The heads form cross-bridges

what are thin filaments composed of? what is its function?
thin filaments are composed of actin protein. they are associated with troponin and tropomyosin which prevent cross-bridge formation when the muscle is not contracting
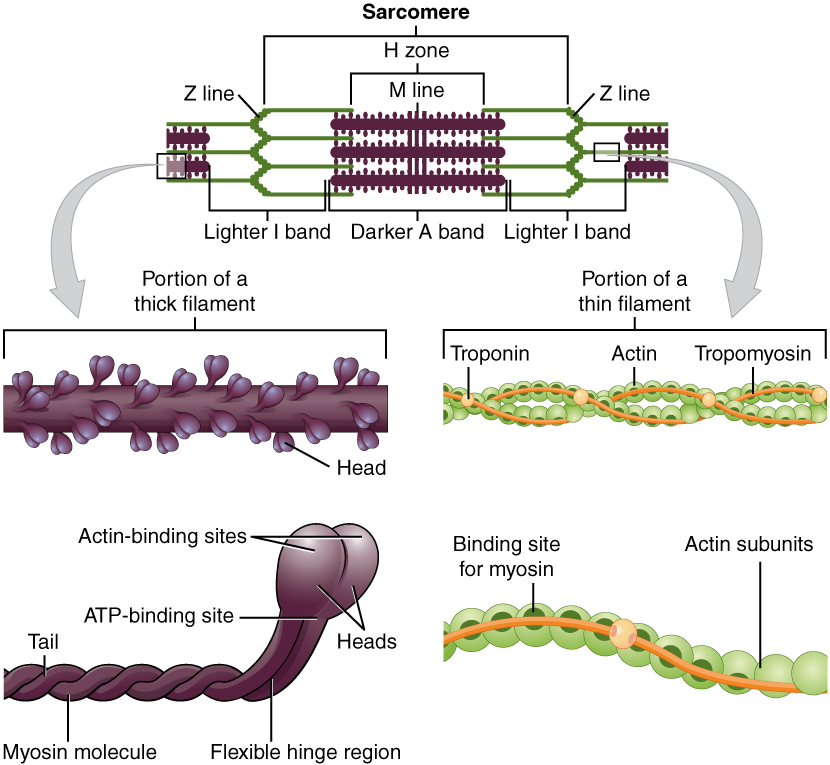
what is neuromuscular junction?
neuromuscular junction, aka myoneural junction, is a type of synapse. It’s a site where an axon motor neuron and skeletal muscle fiber interact. The skeletal muscle fibers will only contract when stimulated by a motor neuron.
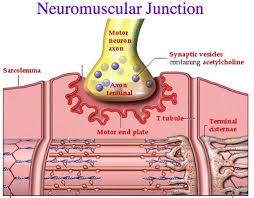
what are the components of a neuromuscular junction?
motor neuron
motor end plate
synaptic cleft
synaptic vesicle
neurotransmitters
what is the main neurotransmitter for muscle contraction?
acetylcholine
describe muscle contraction in terms of acetylcholine (ACh)
nerve impulse causes release of ACh from synaptic vesicles. ACh then binds to the ACh receptors on motor end plate. This binding causes changes in membrane permeability to Na+ and K+ ions, which generates a muscle impulse (action potential). The muscle impulse causes release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum, causing muscle contraction
what causes muscle contraction (in a chemical + biological sense)?
Ca+ is released into cytosol from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ca+ then binds to troponin to change its shape. (2) Each tropomyosin is held in place by a troponin molecule. The change in shape of troponin alters the position of tropomyosin. The binding sites on actin are now exposed, in which the myosin head bind to the exposed actin, creating cross bridges. (3,4)
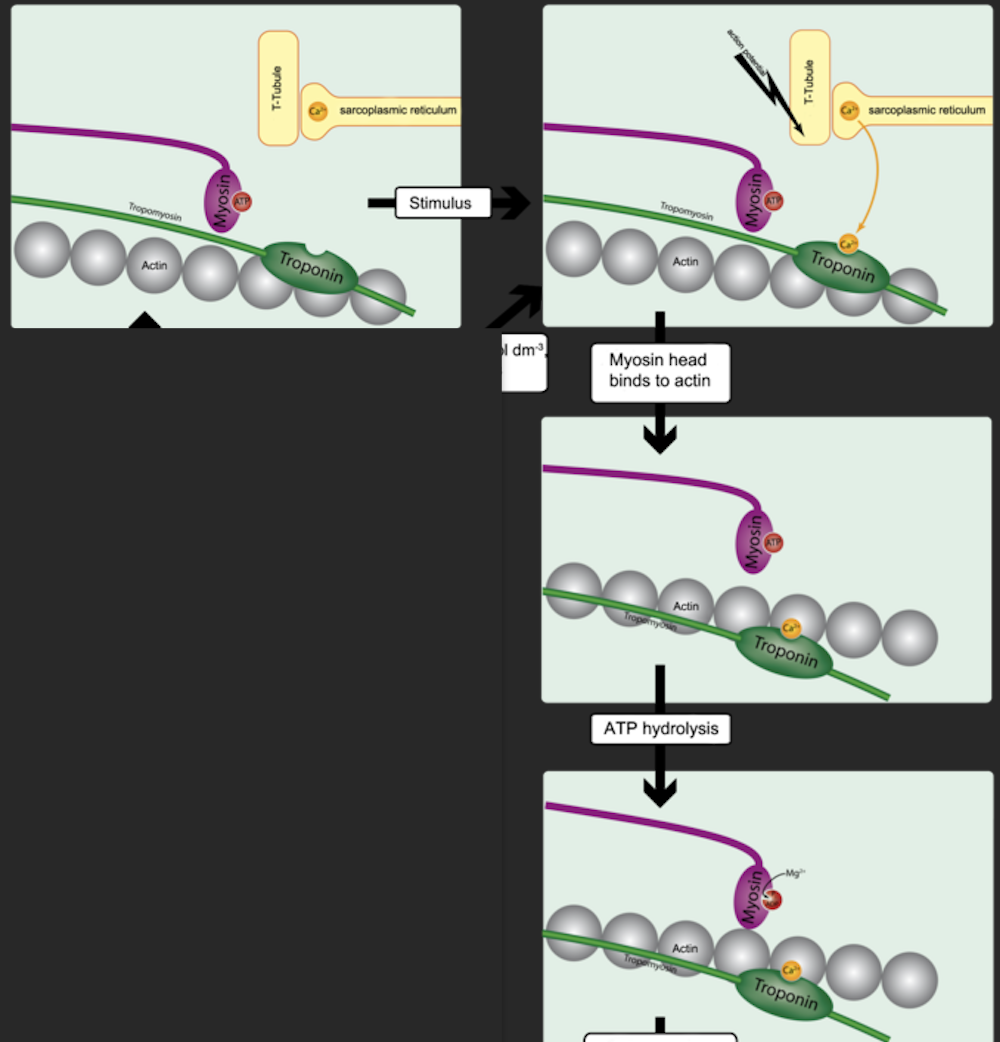
what is occurring during muscle relaxation? (chemically//biologically)
when neural stimulation of muscle fiber stops, acetylcholinesterase rapidly decomposes ACh remaining in the synapse. The decomposition of ACh causes muscle impulse to stop— stimulus to sarcolemma and muscle fiber membrane ceases. Ca+ pump moves back intro sarcoplasmic reticulum, and the troponin-tropomyosin complex covers binding sites on actin again. Myosin and actin binding are now prevented and muscle fiber relaxes.
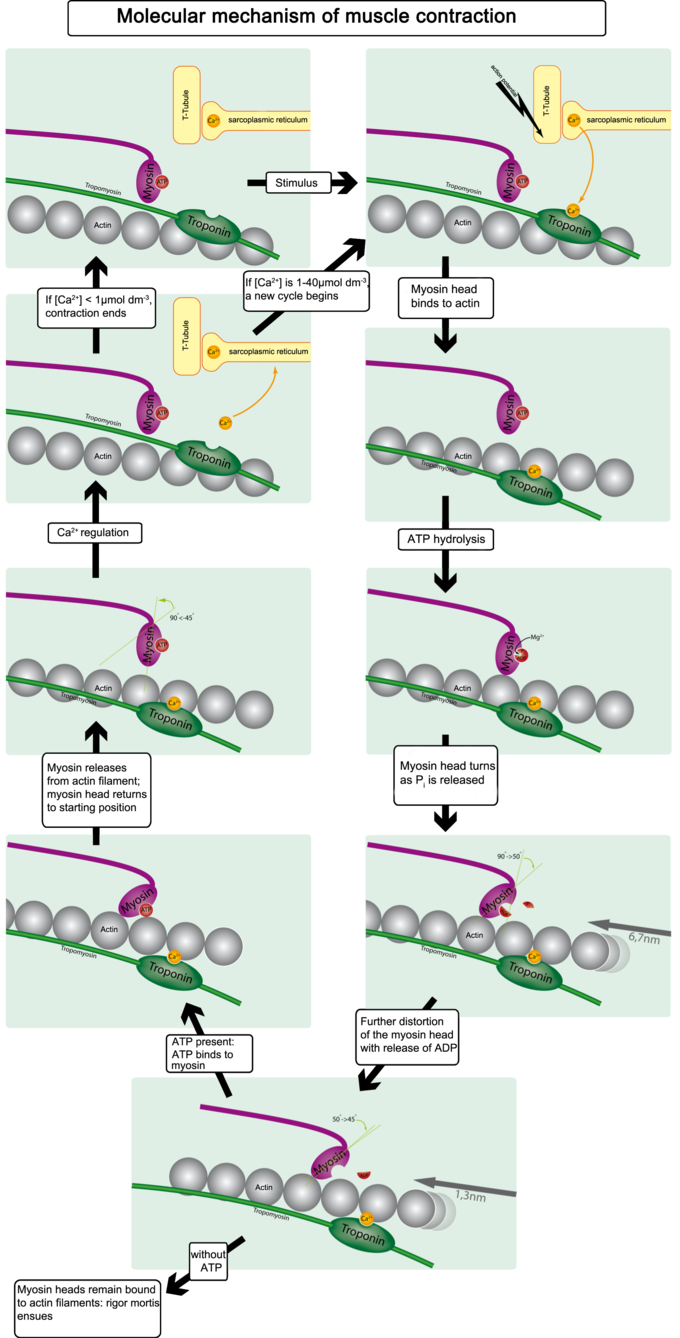
what is muscle fatigue and what causes it?
muscle fatigue refers to the inability to contract the muscle. It can be caused by decrease in blood flow, ion imbalances across the sarcolemma, loss of desire to continue exercise, and assimilation of lactic acid (though controversial)
what is muscle cramp and what are its causes?
muscle cramp refers to the sustained, involuntary contraction of a muscle. It may be caused by changes in electrolyte concentration in extracellular fluids in the area. Referred to as hypocalcemic tetany (low extracellular Ca2+)
function of the following muscle: frontalis
raises eyebrows
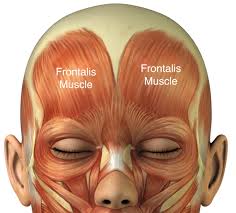
function of the following muscle: orbicularis oculi
blinks and closes eyes
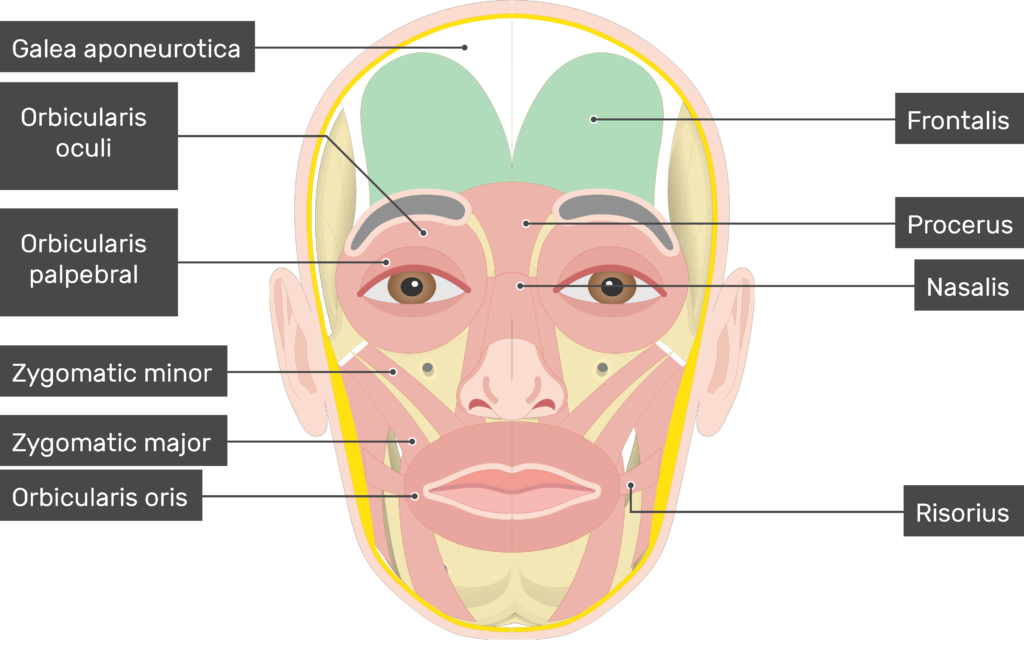
function of the following muscle: orbicularis oris
closes and protrudes lips (kissing muscle)
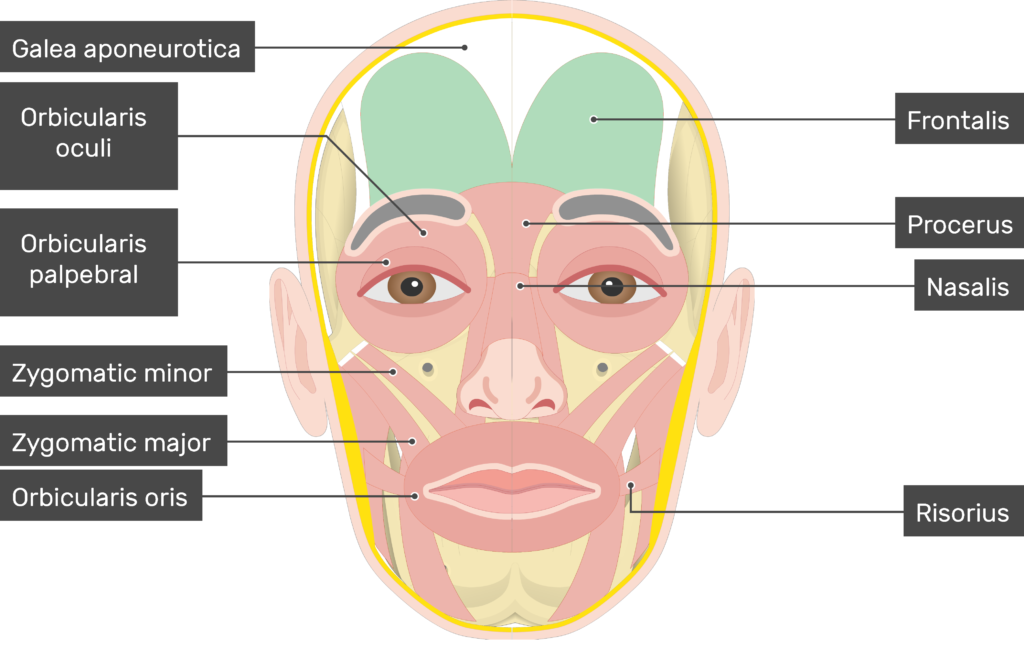
function of the following muscle: zygomaticus minor
elevates upper lip
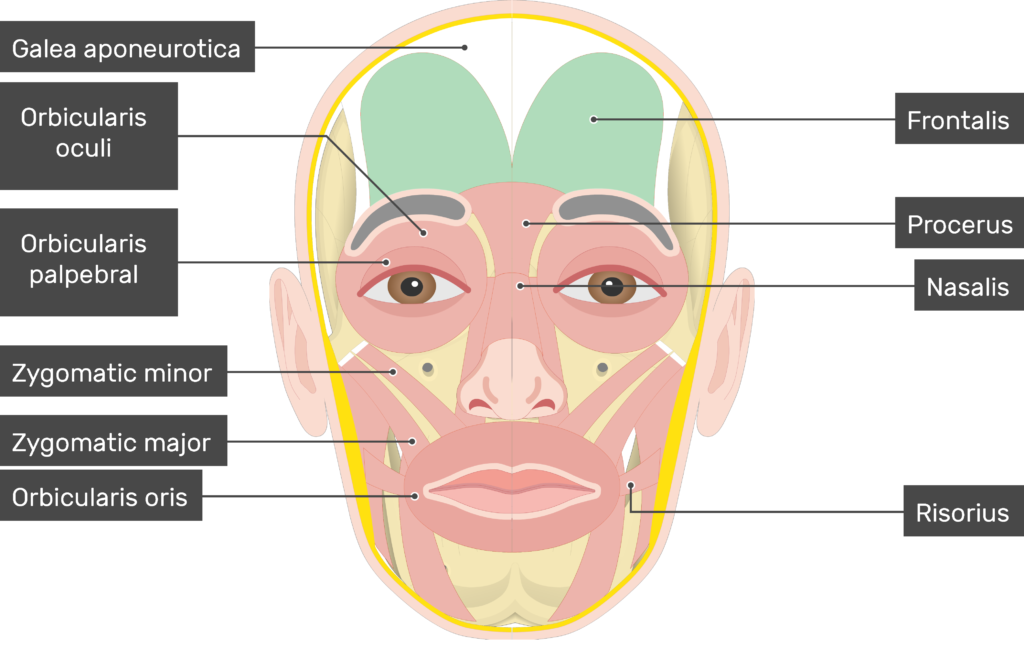
function of the following muscle:: zygomaticus major
raises corner of mouth (smile muscle)
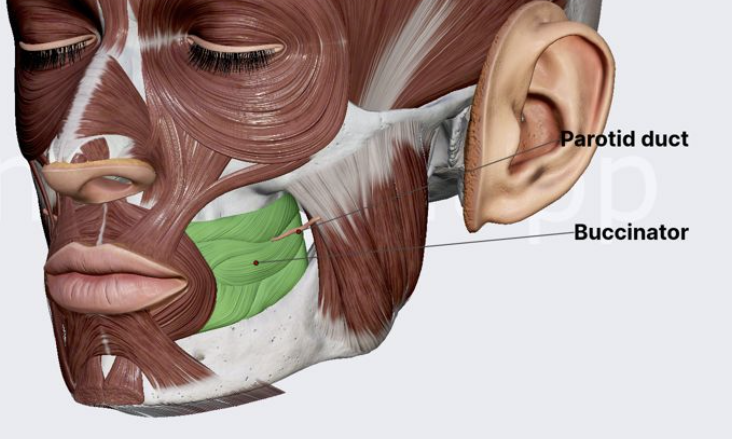
function of the following muscle: buccinator
compresses cheek (whistling muscle)
function of the following muscle: masseter
closes jaw (chewing muscle)
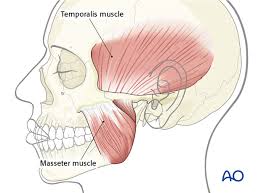
function of the following muscle:: temporalis
closes jaw (another chewing muscle)
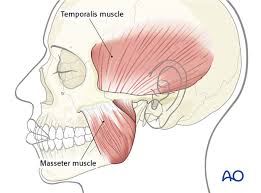
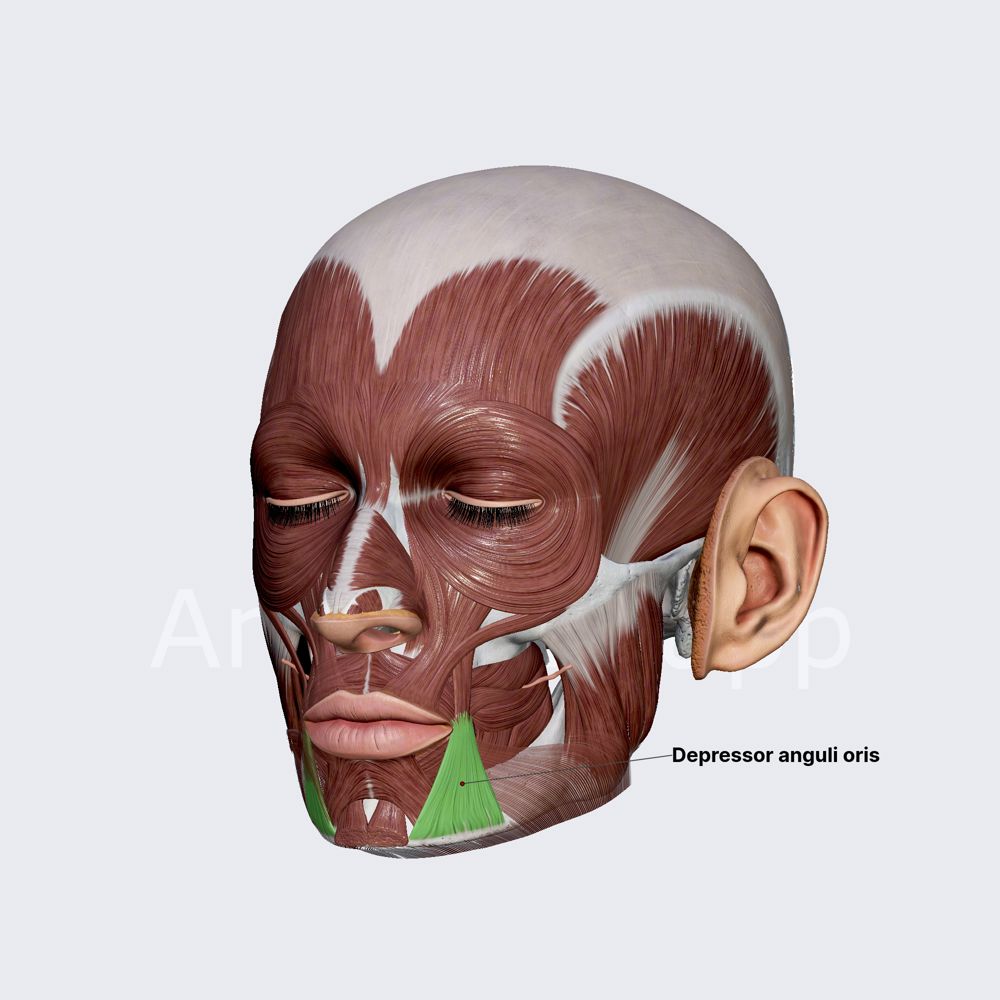
function of the following muscle: depressor anguli oris
pulls down on corners of mouth (frown muscle)
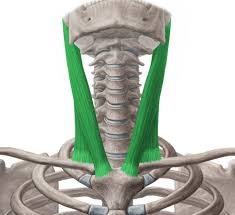
function of the following muscle: sternocleidomastoid
flexes neck + rotates head (from sternum to clavicle to mastoid)
function of the following muscle: platysma
pulls corners of mouth inferiorly and widens it (may convey a look of sadness or fright)
function of the following muscle: pectoralis major
adducts and medially rotates the arm
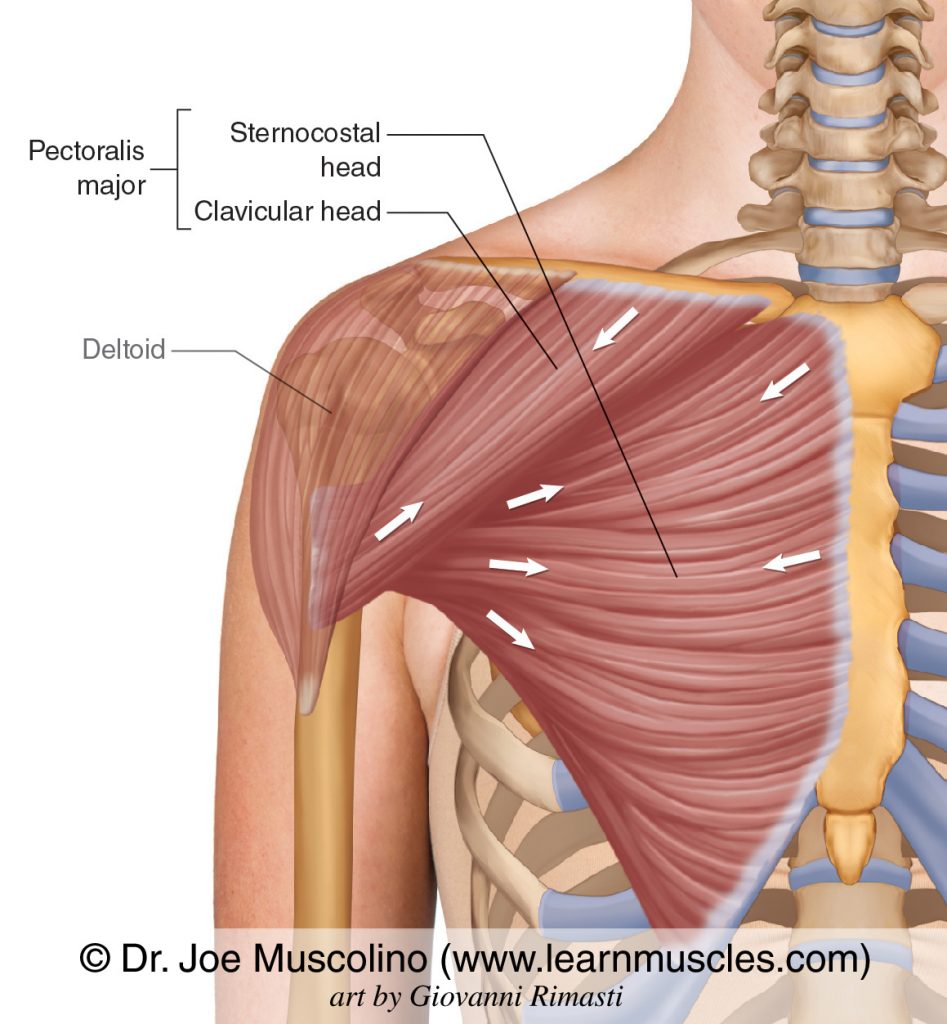
function of the following muscle: pectoralis minor
pulls scapula anteriorly and down

function of the following muscle: internal intercostals
depress ribs, decrease size of throracic cavity when exhaling
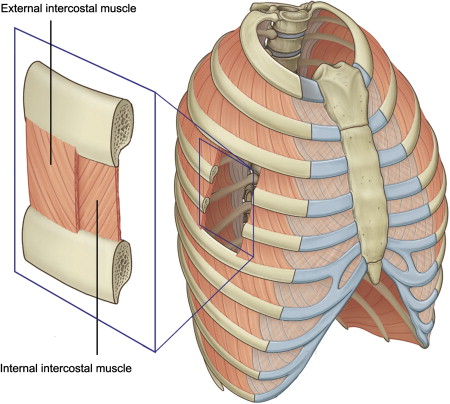
function of the following muscle: external intercostals
lift ribs, increase size of throracic cavity when inhaling

function of the following muscle: rectus abdominis
flexes vertebral column

function of the following muscle: transverse abdominis
compress abdomen

function of the following muscle: trapezius
elevation and upward rotation of scapula (extends neck)
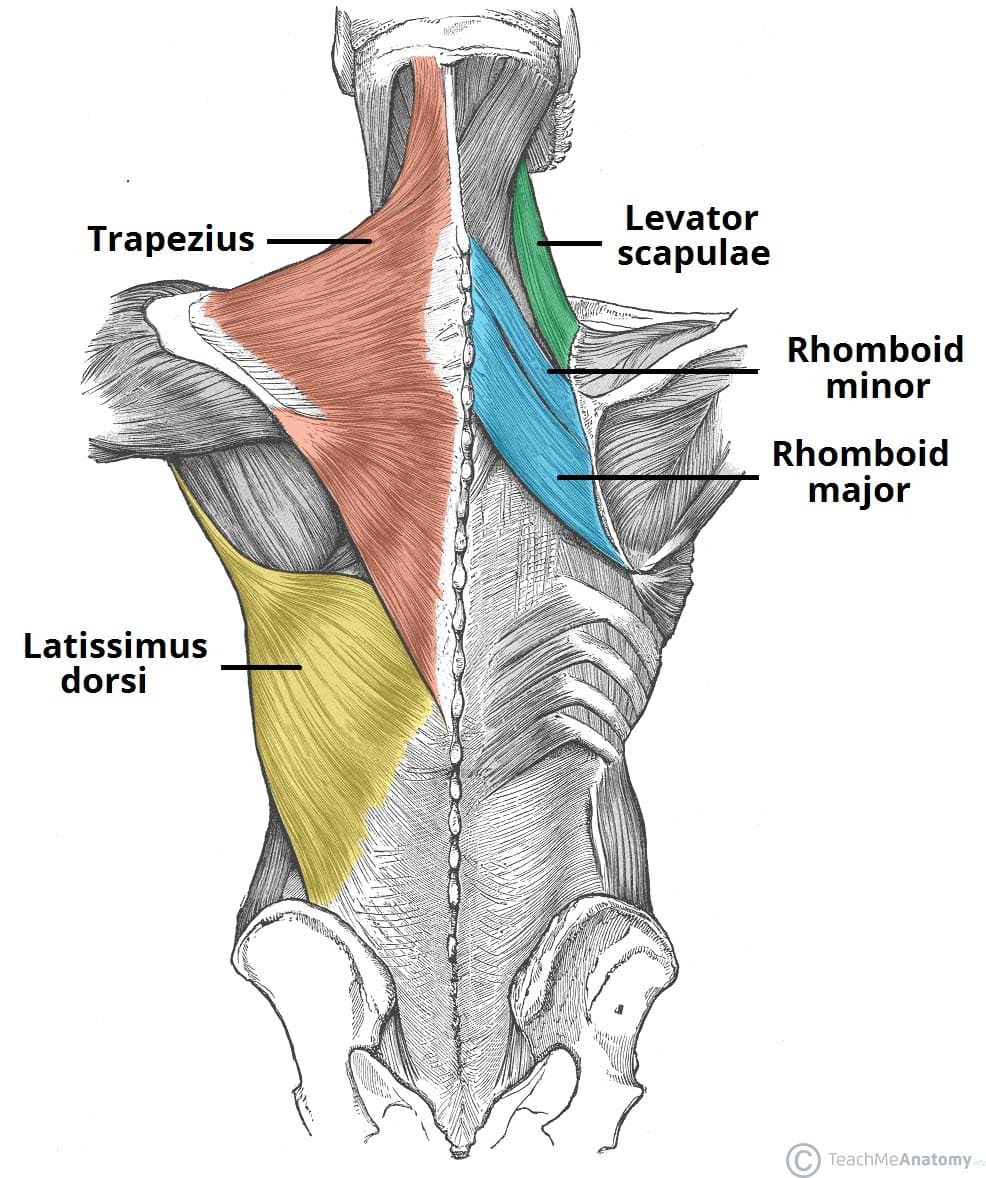
function of the following muscle: levator scapulae
elevates the scapula (shrugging shoulder)
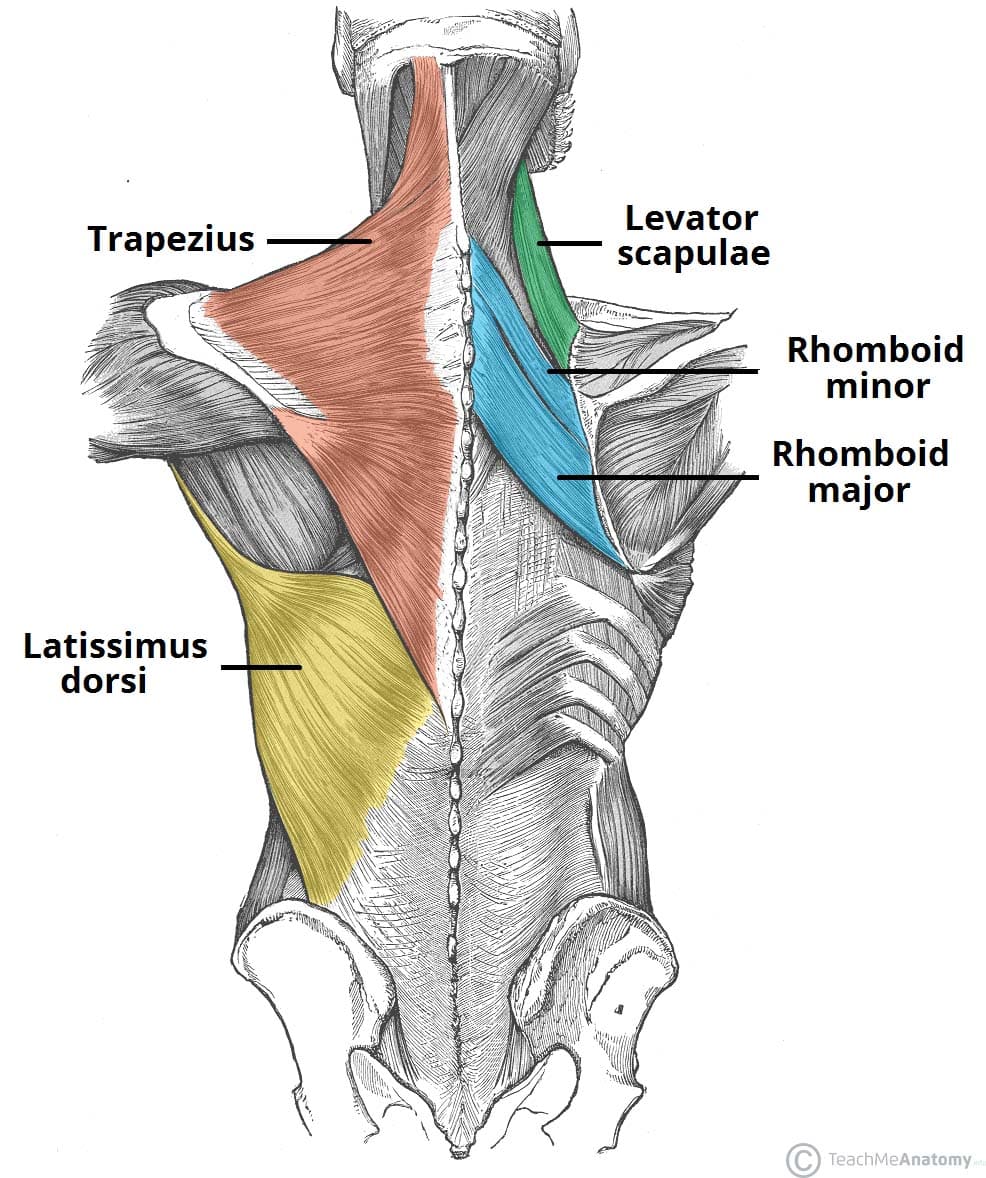
function of the following muscle: rhomboideus major
retraction of scapula (pulls shoulder together)

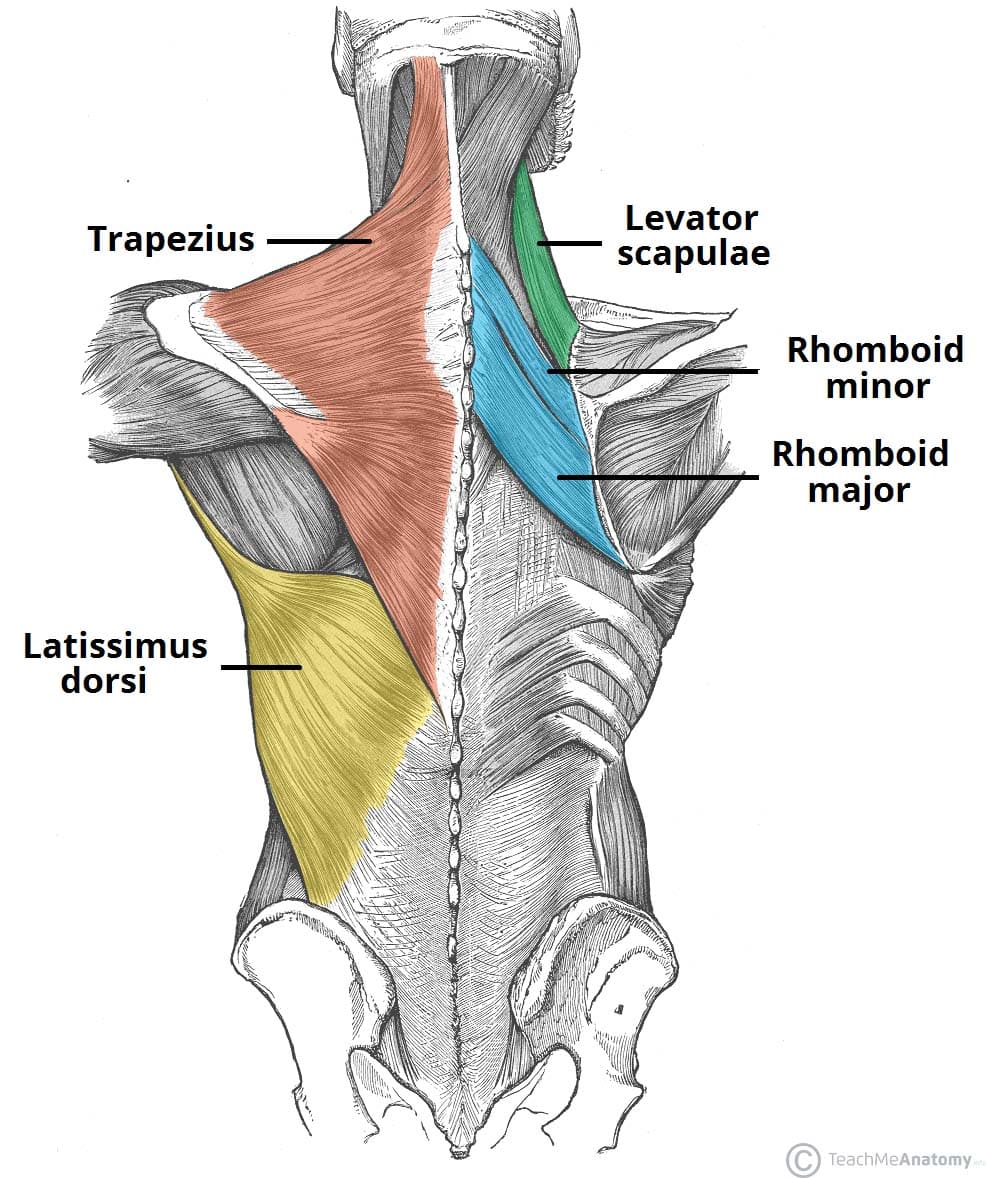
function of the following muscle: rhomboideus minor
retraction of scapula, superior to rhomboideus major
function of the following muscle: teres major
adduction of arm
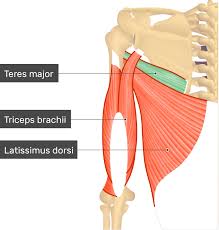
function of the following muscle: infraspinatus
external rotation of humerus
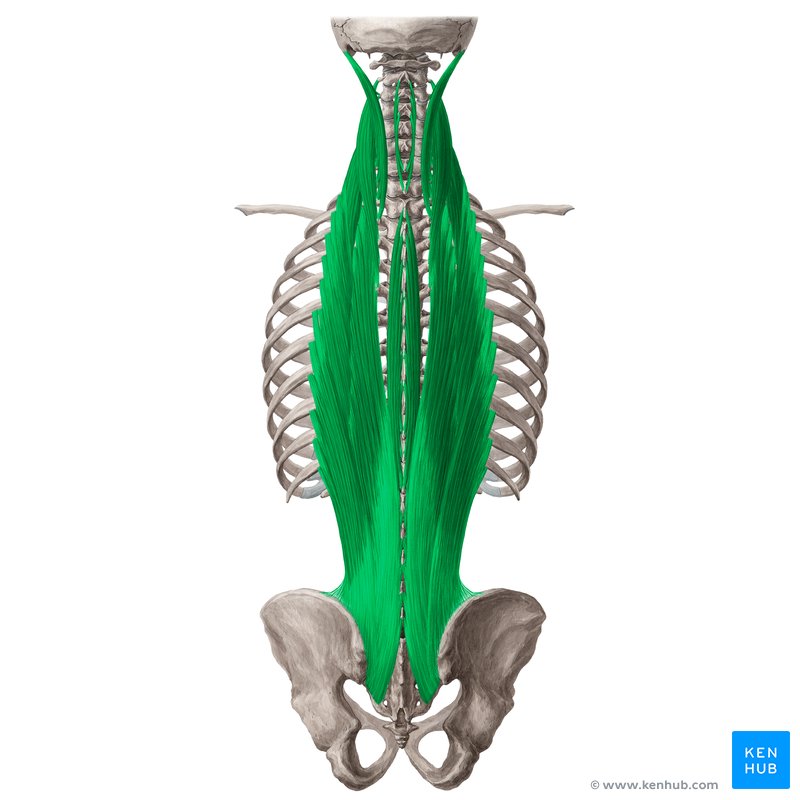
function of the following muscle: erector spinae
a group of muscles that extend the vertebral column and allow for side to side rotation
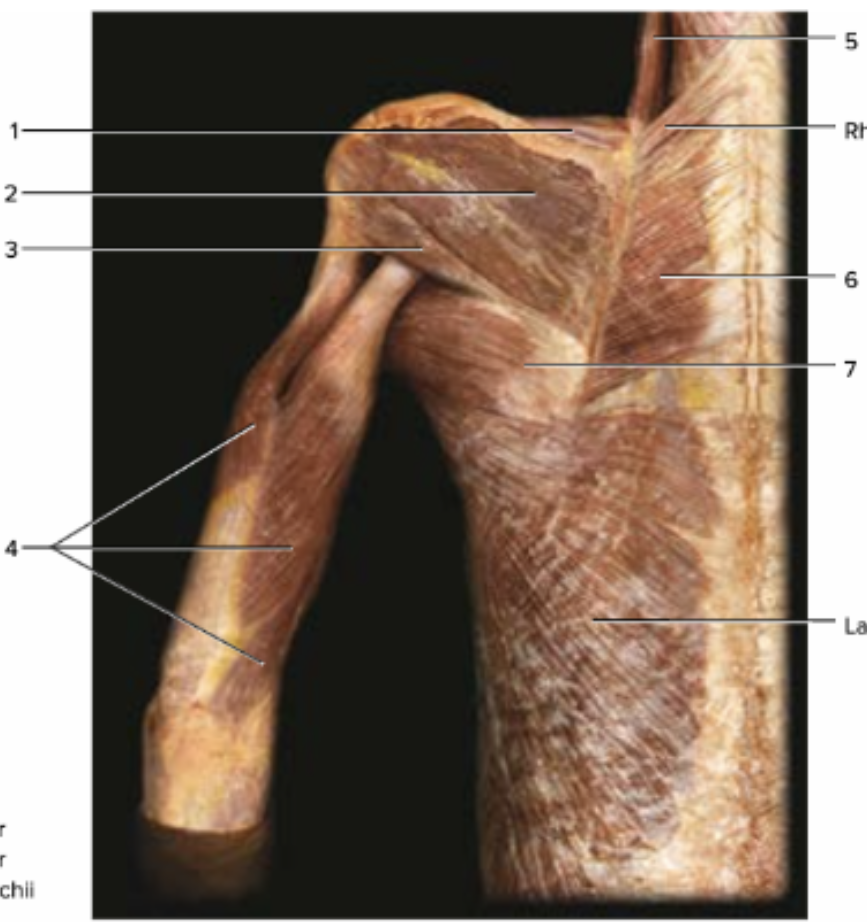
label 1-7. word bank: infraspinatus, levator scapulae, rhomboid major, supraspinatus, teres major, teres minor, triceps brachi
1: supraspinatus, 2: infraspinatus, 3: teres minor, 4: triceps brachii, 5: levator scapulae, 6: rhomboid major, 7: teres major

label 1-4. word bank: brachioradialis, flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus
1: brachioradialis, 2: flexor carpi radialis, 3: flexor carpi ulnaris, 4: palmaris longus
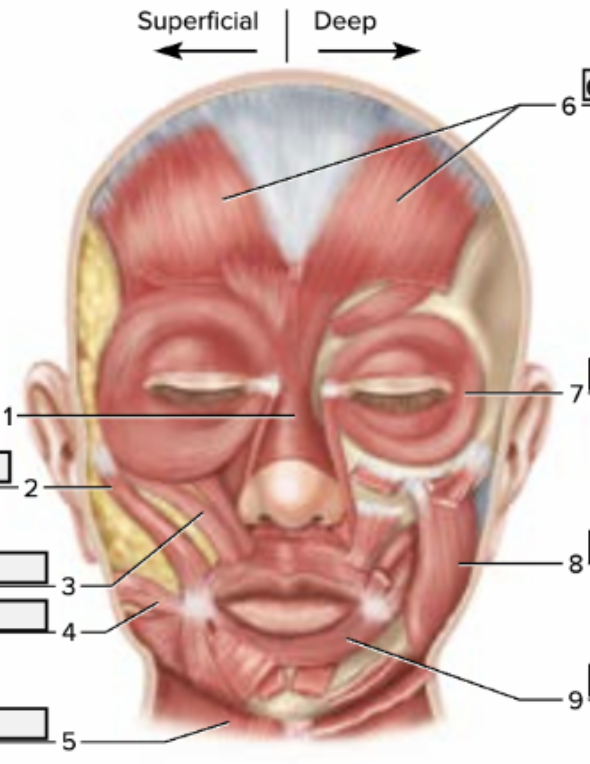
label 1-9
1: nasalis, 2: zygomaticus major, 3: zygomaticus minor, 4: risorius, 5: platysma, 6: epicranius, 7: orbicularis oculi, 8: masseter, 9: orbicularis oris
function of the following muscle: deltoideus
adducts the arm
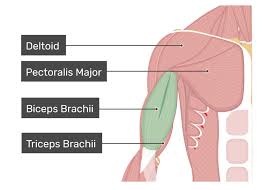
function of the following muscle: biceps brachii
flexes the elbow and supinates the forearm

function of the following muscle: brachialis
flexes the elbow
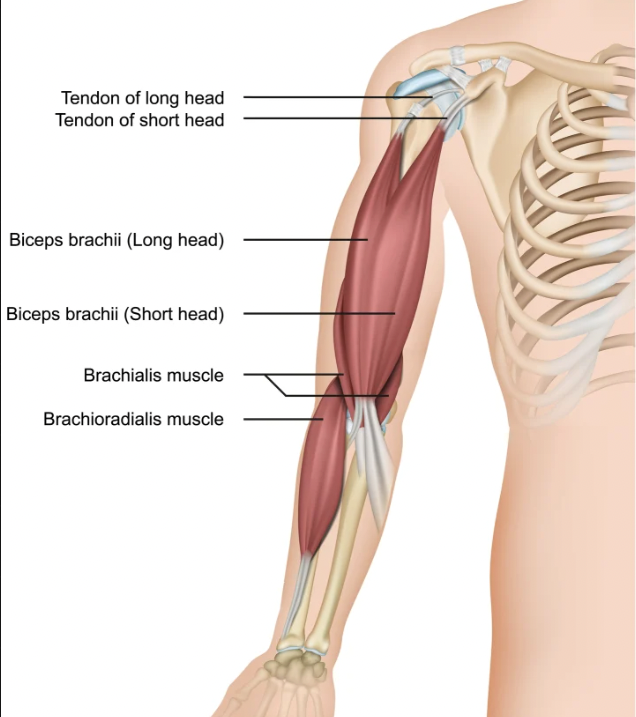
function of the following muscle: brachiaoradialis
flexes the elbow
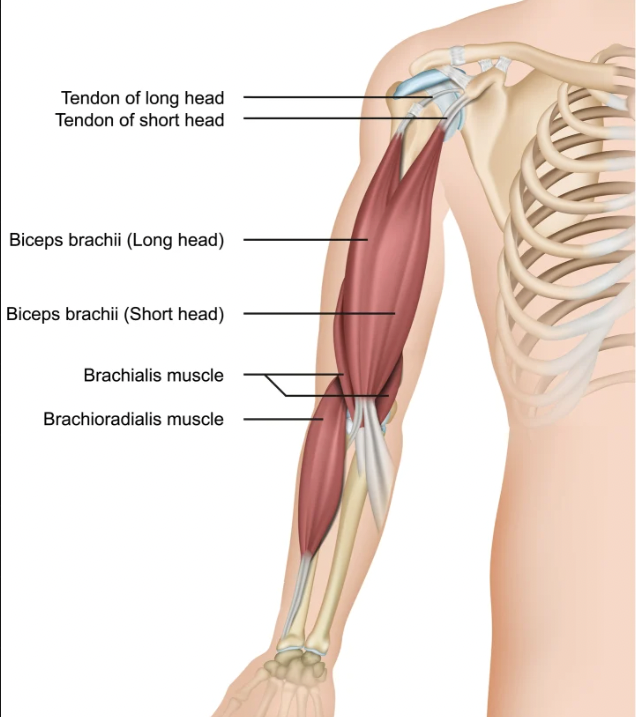
function of the following muscle: triceps brachii
extends the elbow
what are the 4 flexors of the hand and wrist
flexor carpi, flexor digitorum, flexor pollicis longus, palmaris longus
function of the following muscle: rectus femoris
extends lower leg, straightens knee
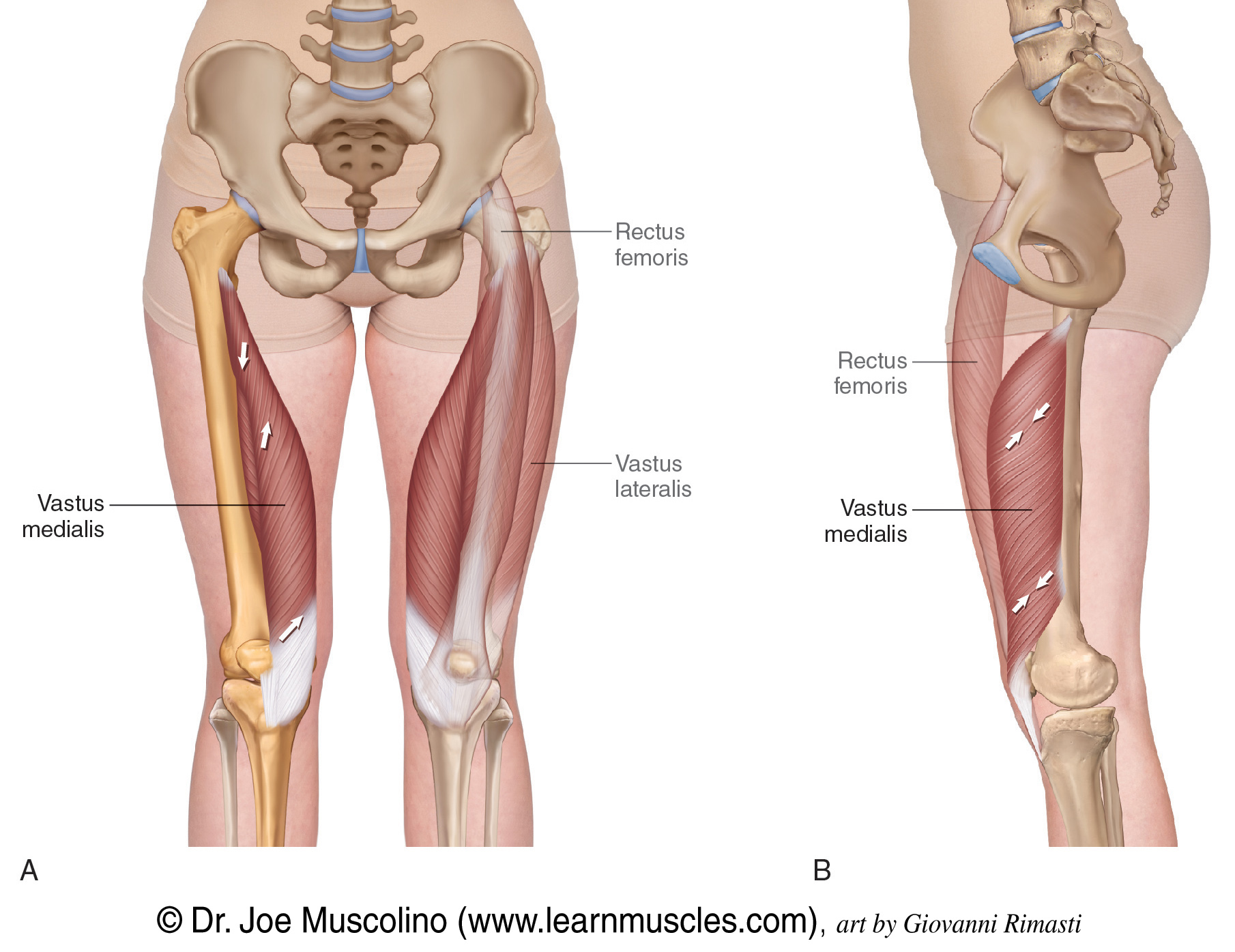
function of the following muscle: vastus lateralis
extends lower leg, straightens knee
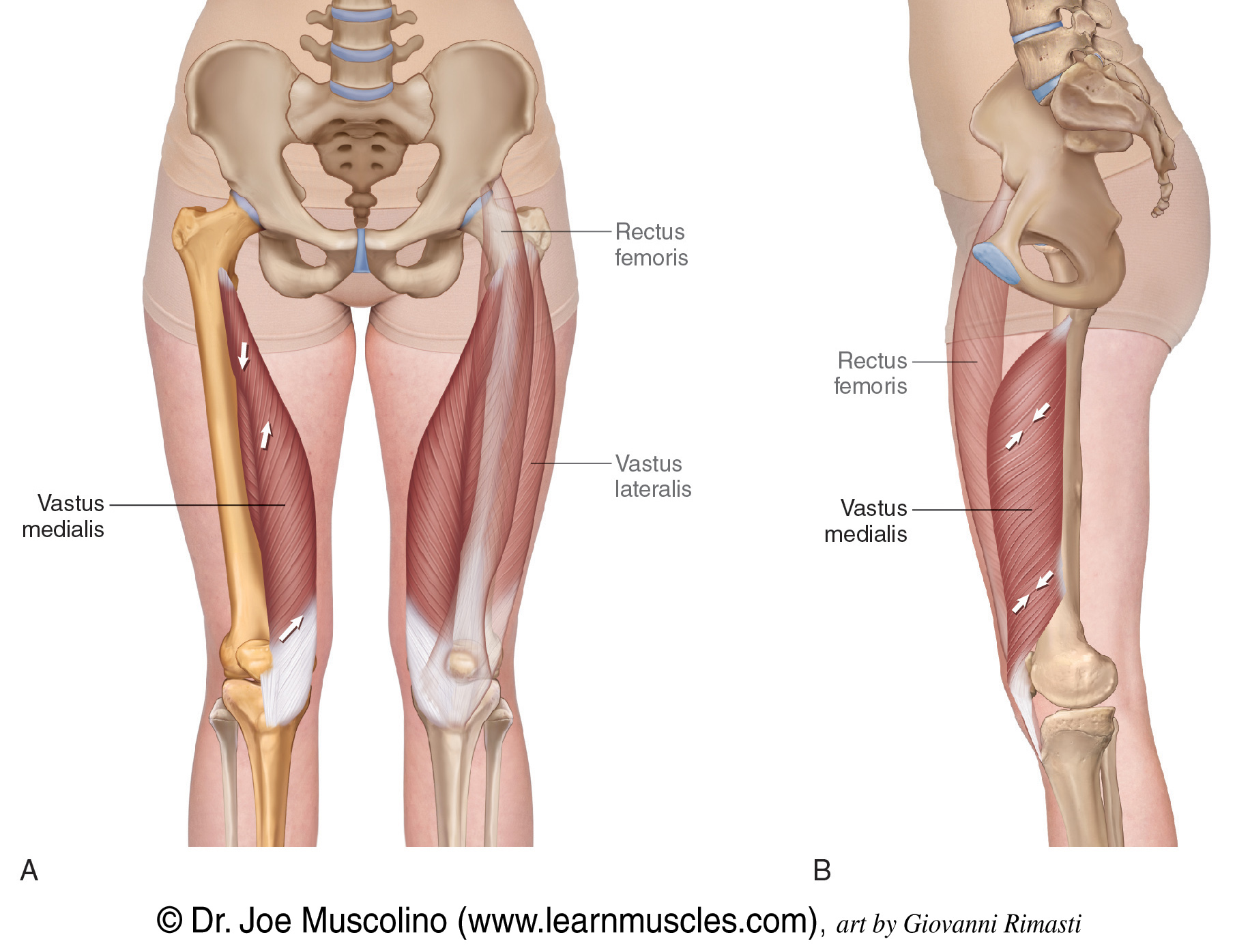
function of the following muscle: vastus medialis
extends lower leg, straightens knee
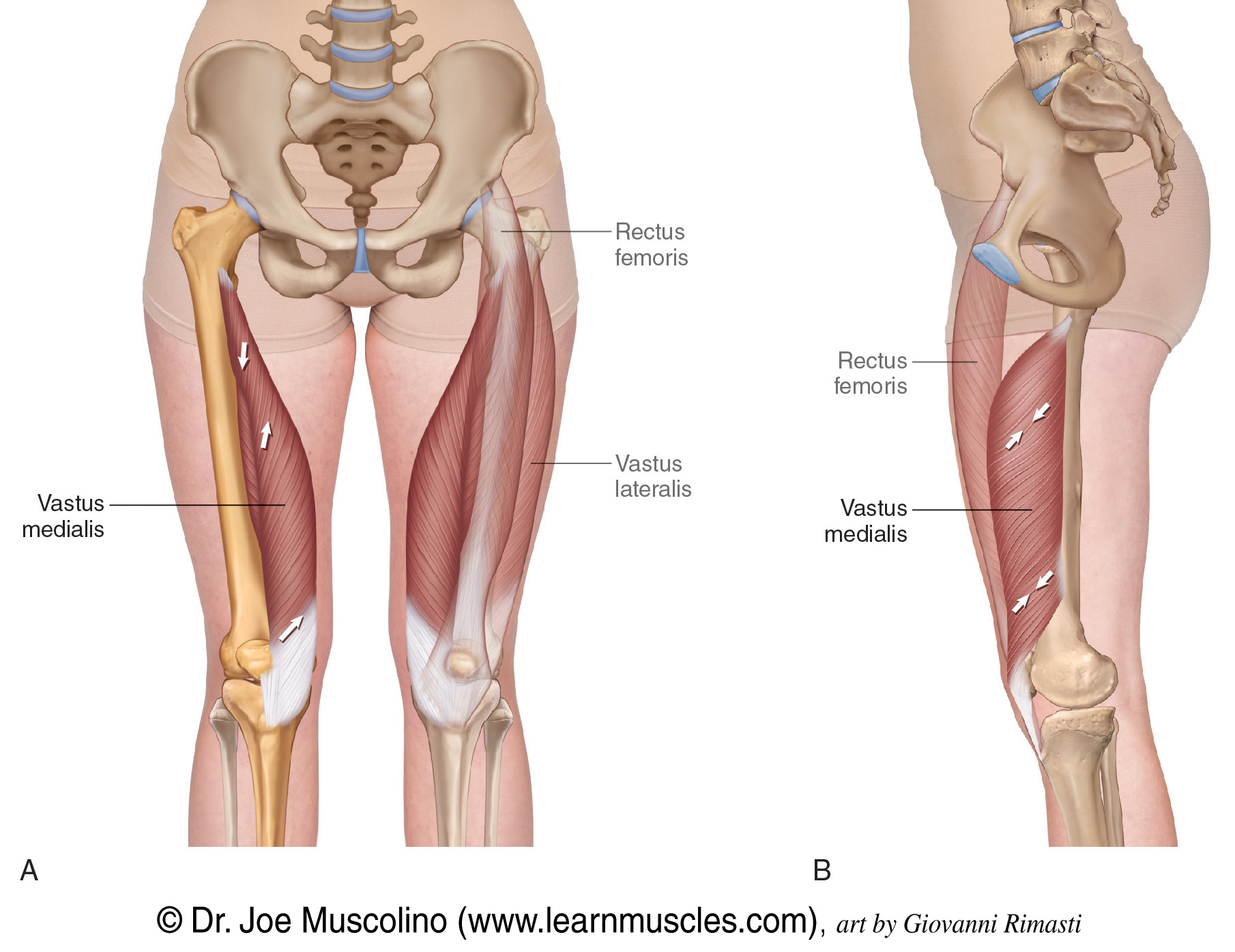
function of the following muscle: sartorius
flexes thigh
function of the following muscle: tibialis anterior
dorsiflexes and inverts the foot

function of the following muscle: fibularis longus
plantar flexion and eversion of the foot
semitendinosus (hamstrings)
flexes leg, bends knee
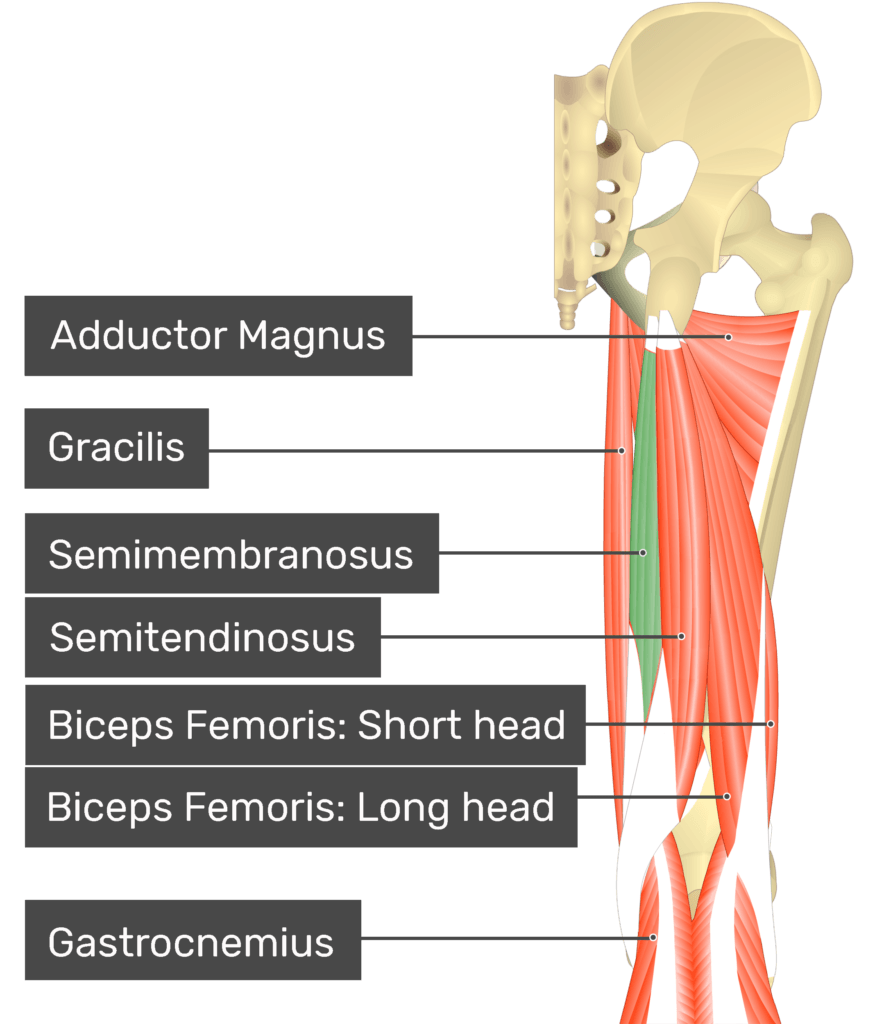
function of the following muscle: semimembranosus
part of hamstringsl flexes leg, bends knee
function of the following muscle: soleus
plantar flexes the foot and flexes the knee
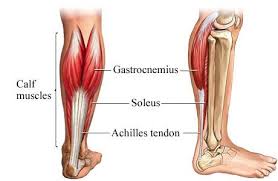
function of the following muscle: gastrocnemius
plantar flexes the foot and flexes the knee
function of the following muscle: gluteus maximus
extends and laterally rotates thigh at hip, abducts the thigh
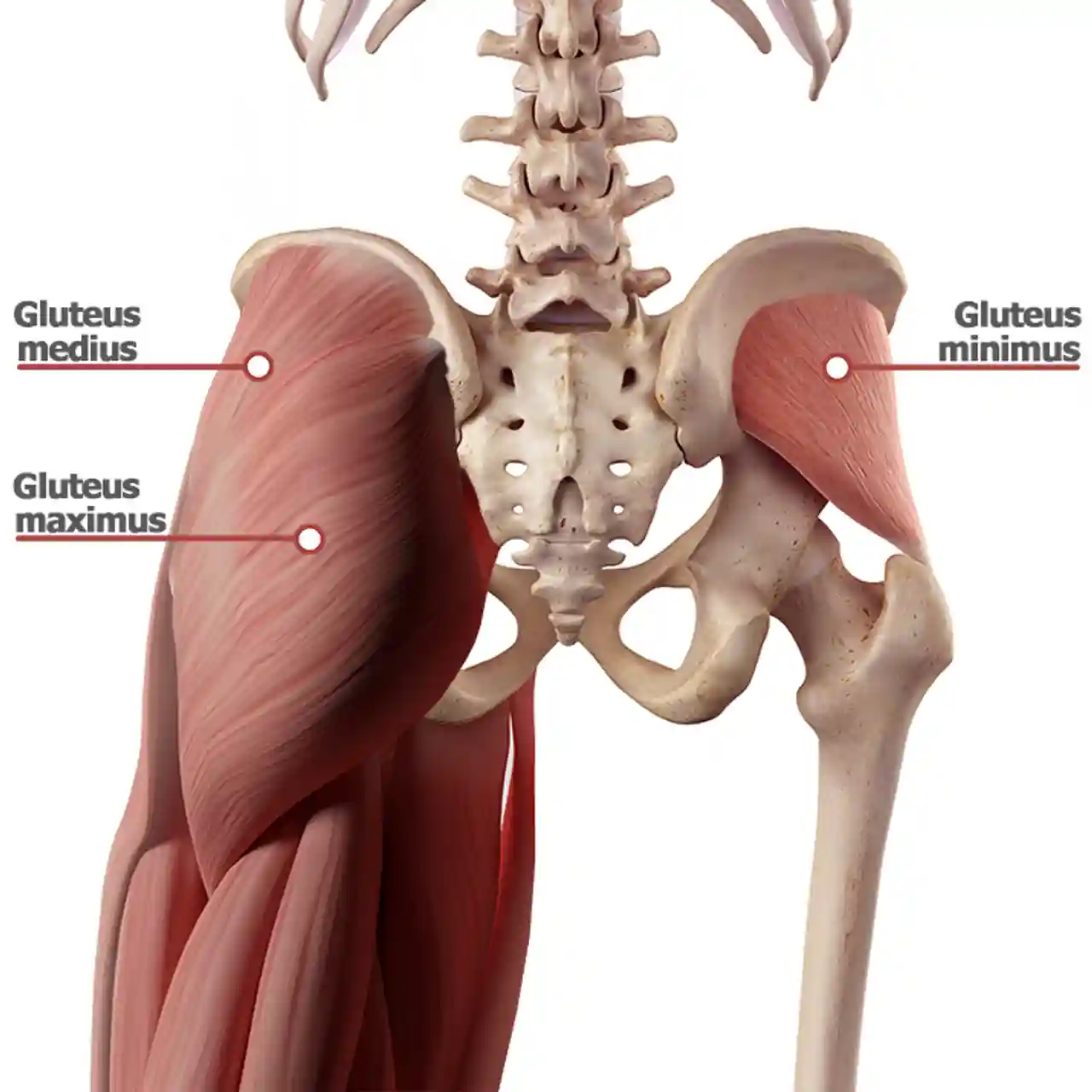
function of the following muscle: gluteus medius
abduction of thigh at hip, medial and lateral rotation of thigh
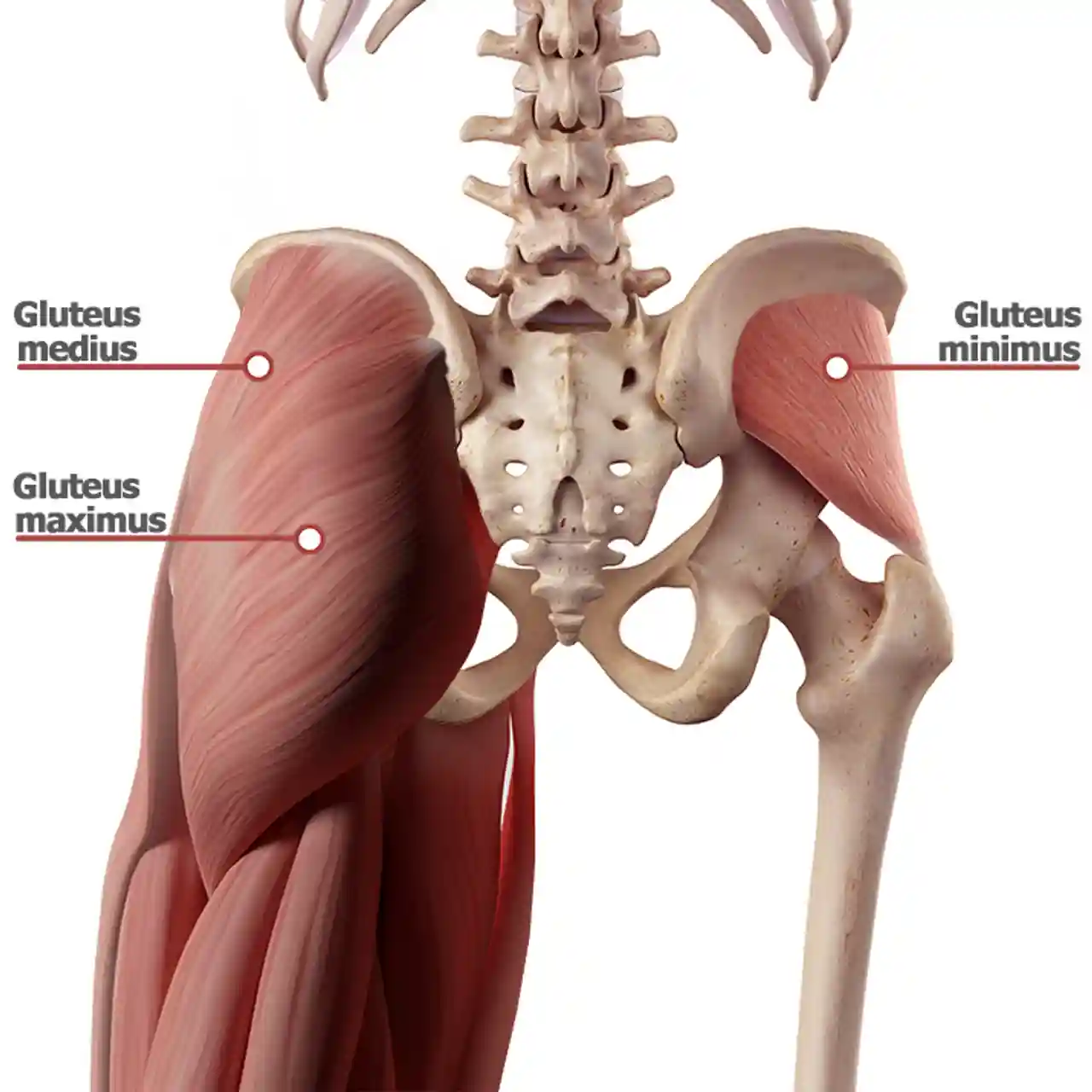
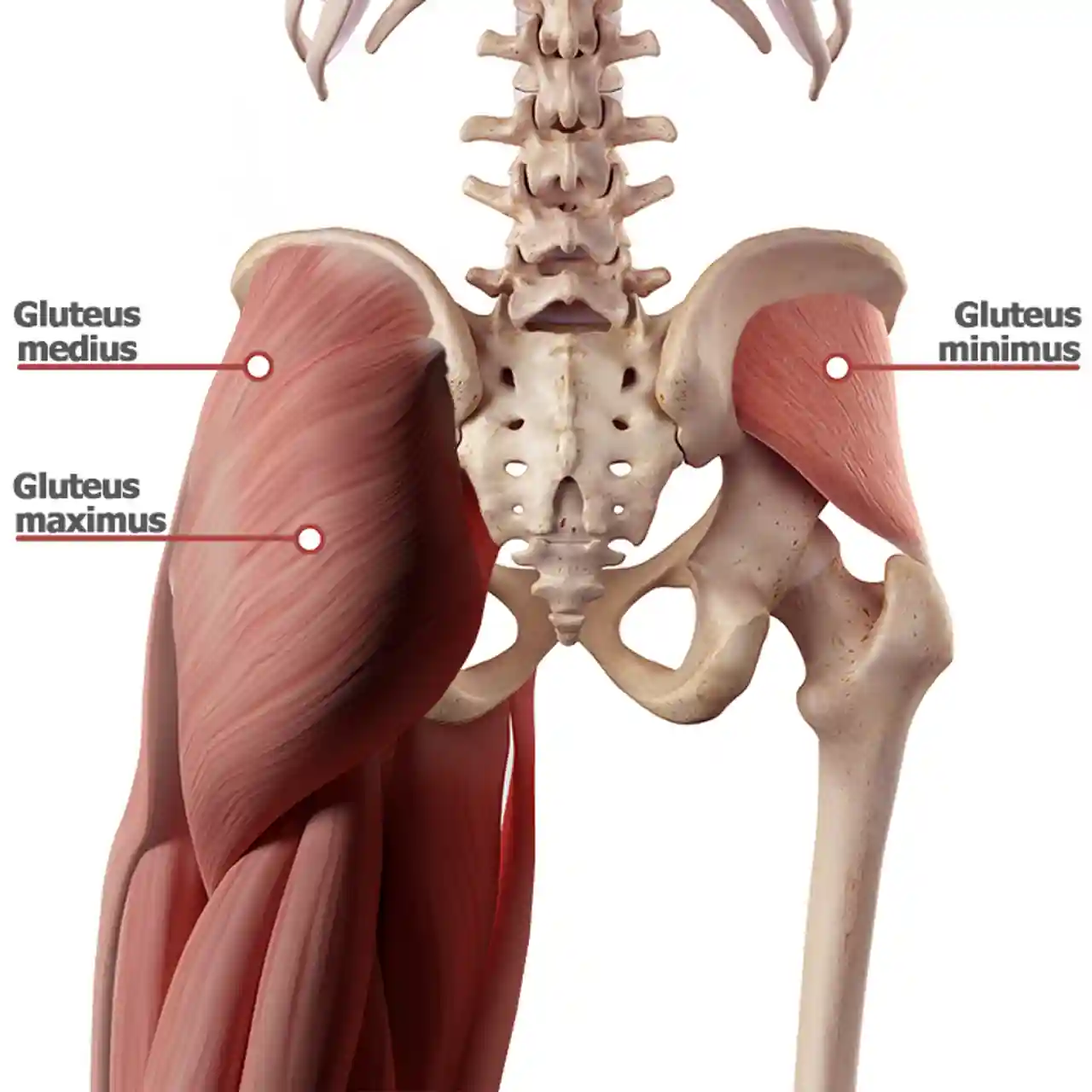
function of the following muscle: gluteus minimus
deepest gluteus, abduction of thigh at hip, medial rotation of thigh
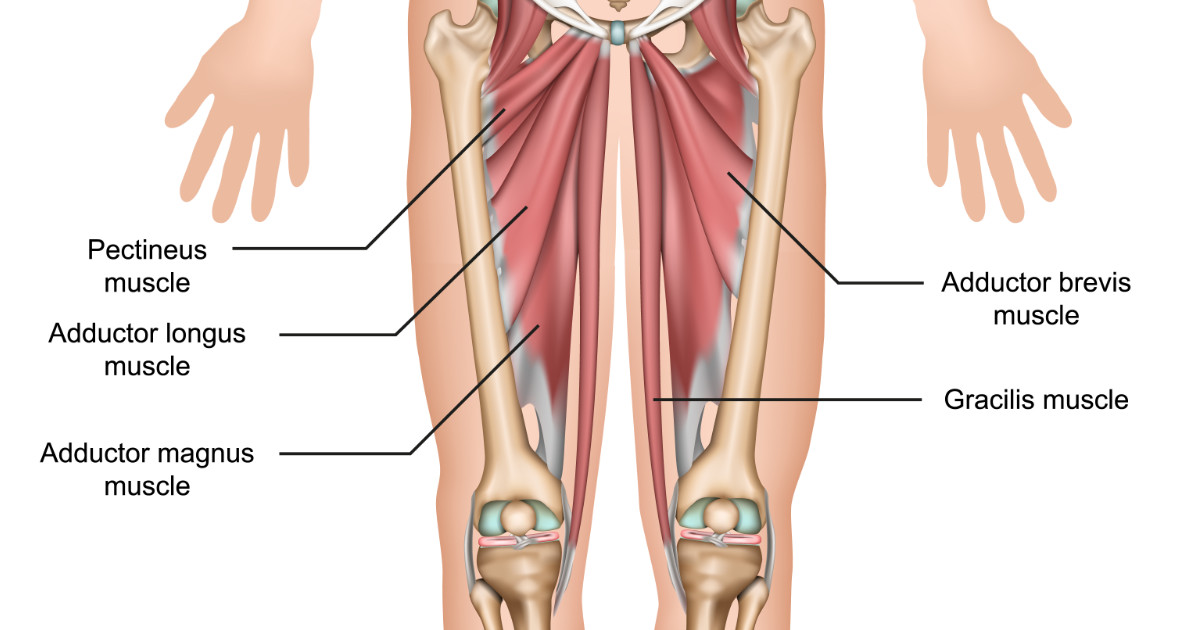
what are the 5 specific adductor muscles of the hip?
adductor longus, adductor brevis (under longus), adductor magnus, pectineus, gracilis
actions are coordinated between what muscles?
flexors and extensors
which muscles are activated by eliciting a stretch response in the patellar tendon?
knee flexors (hamstrings) and knee extensors (quadriceps)
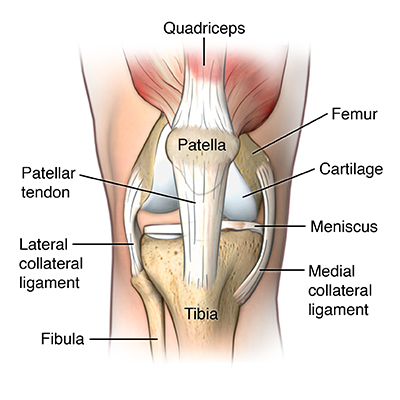
characteristics + function of muscle spindle
the muscle spindle contains intrafusal fibers and a stretch receptor. Its activation leads to muscle contraction
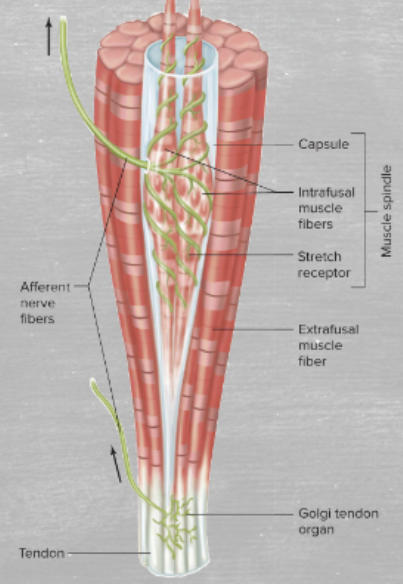
characteristics and function of golgi tendon organ
the golgi tendon organ is within the tendon, rather than the muscle, and contains the stretch activator. Its activation leads to muscle relaxation
define hypertrophy and hyperplasia
hypertrophy refers to the increase in the size of fibers. hyperplasia refers to the increase in the number of fibers
what causes hypertrophy?
Hypertrophy is caused by increased protein synthesis driven by mechanical tension, metabolic stress, and muscle damage.
define Physiological Cross-Sectional Area (PCSA)
physiological cross-sectional area refers to the number of sarcomeres in parallel, and is related to maximum tension
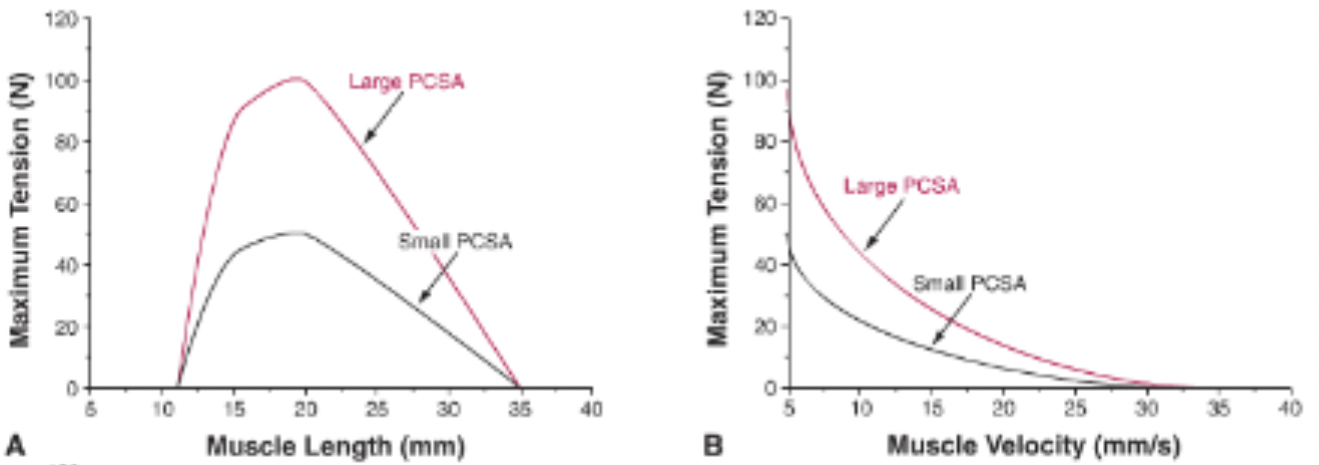
what is Normalized Fiber length?
Normalized Fiber length refers to the number of sarcomeres in series, and is related to the maximum velocity and muscle excursion
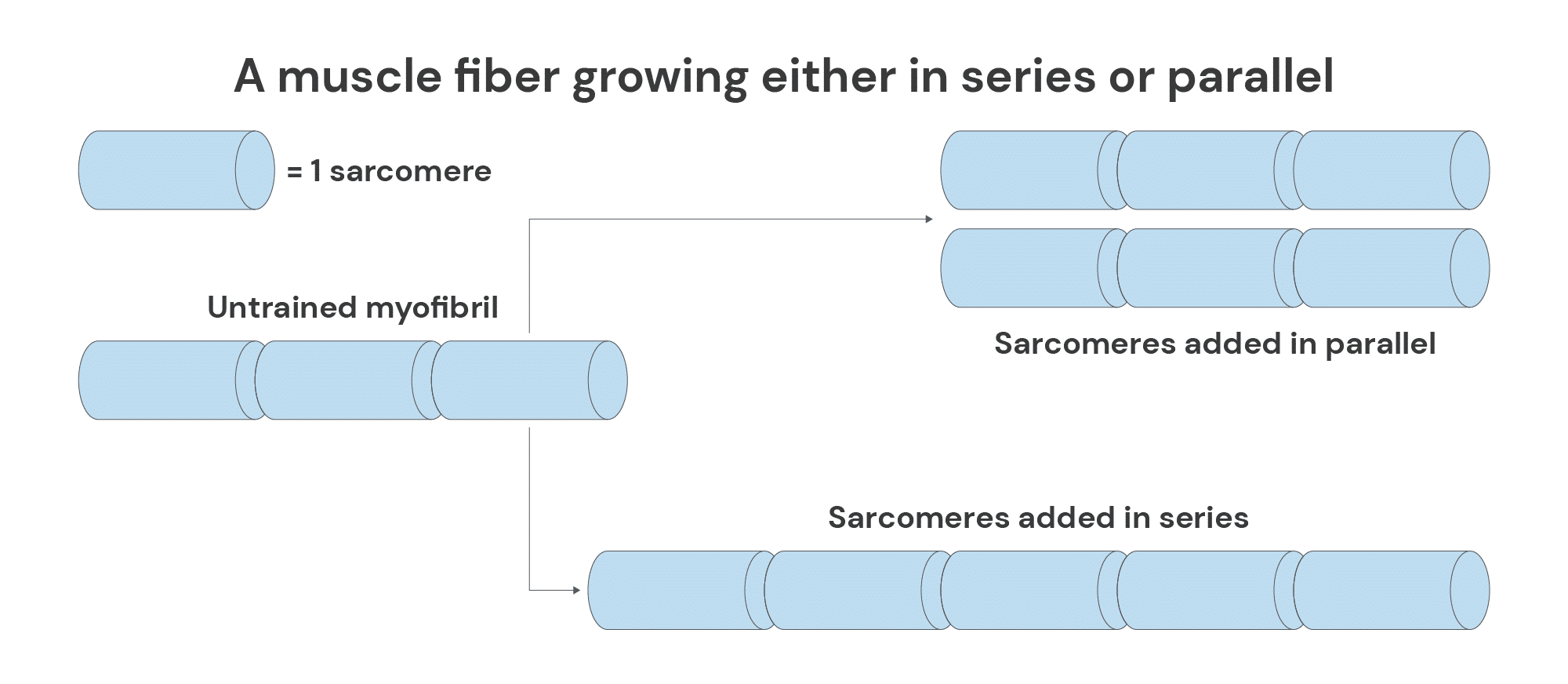
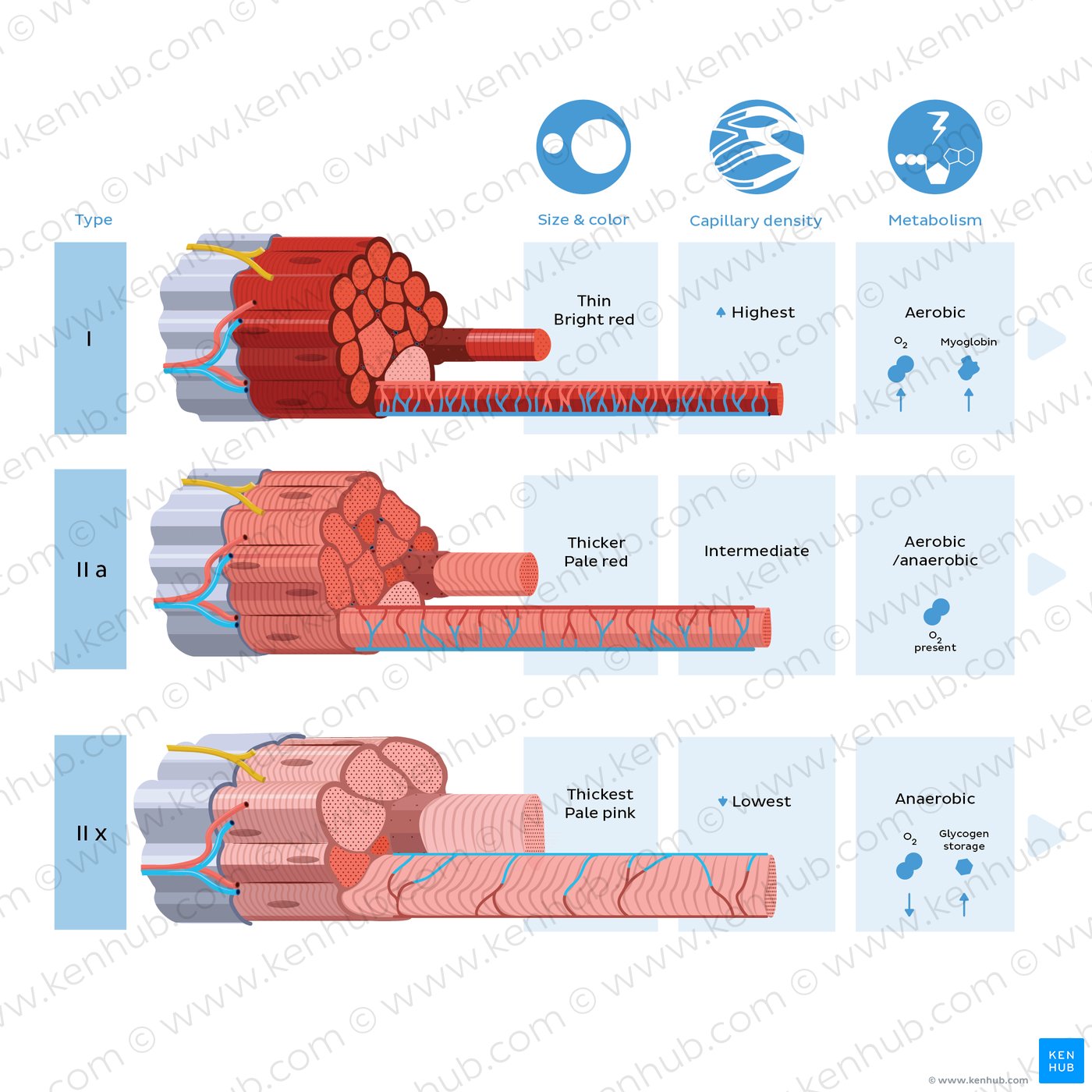
what fiber characteristics/structures are seen in fibers that promote velocity?
fibers that promote velocity are often long (series sarcomeres) and run parallel to the muscle axis (low), and contain fast-twitch fibers and high amounts of myosin ATPase— Type 1
what fiber characteristics/structures are seen in fibers that promote tension?
fibers that promote tension are often short (parallel myofibrils) and angled relative to the tendon (high), and contain slow/intermediate fibers and low amounts of myosin ATPase. They maximize the number of actin-myosin cross-bridges. — Type 2
muscle motor units are recruited from ___ to ___. explain.
small to large; the small, type I slow-oxidative fibers are recruited first, but if they can’t produce enough force, larger motor units are recruited
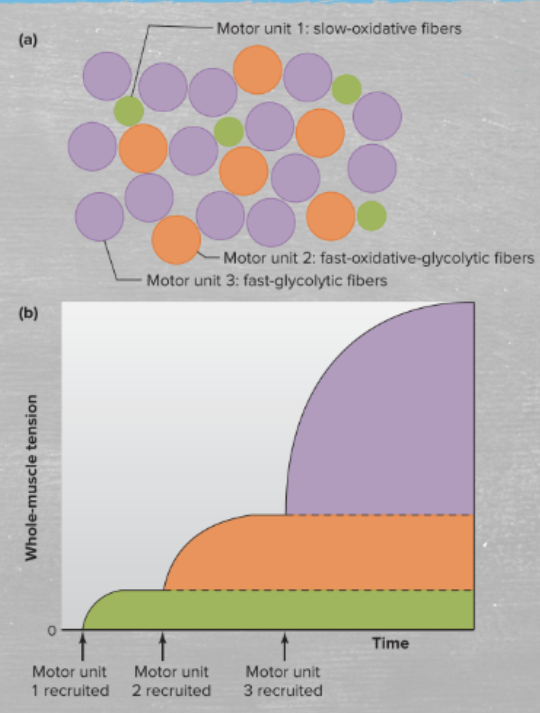
what are the 3 muscle fiber types?
slow oxidative fibers
fast-oxidative-glycolytic fibers
fast-glycolytic fibers
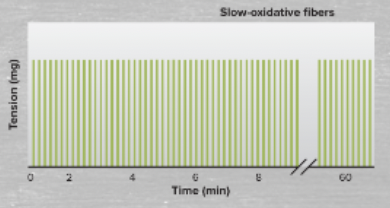
define/characterize slow-oxidative fibers
slow-oxidative fibers are fatigue resistant and part of the small motor units
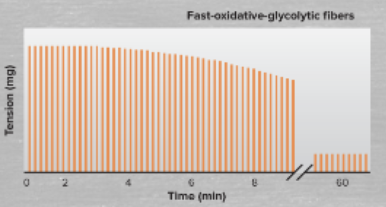
define/characterize fast-oxidative-glycolytic fibers
fast-oxidative-glycolytic fibers have intermediate fatigability, and are part of the intermediate sized motor units
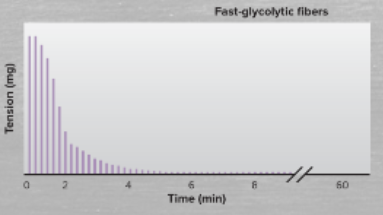
define/characterize fast-glycolytic fibers
fast-glycolytic fibers are easily fatigable and are part of large motor units
getting energy from glycolysis vs oxidative phosphorylation
glycolysis can proceed anaerobically and is fast, but inefficient. Glucose can be accessed for a few minutes internally via glycogen or indefinitely via circulation.
Oxidative phosphorylation is efficient, but requires oxygen (aerobic) and is slow. It is fueled by intenral glycogen/amino acids, or glucose/fatty acids via circulation.
If ATP is low, what acts as a rapid backup system that replenishes ATP during high, intensity, short-duration exercise?
creatine phosphate
what are 2 major uses of ATP in the skeletal muscle?
ATP is used by myosin to energize cross-bridges and by SERCA to pump Ca2+ back into SR
What causes rigor mortis?
In rigor mortis, the lack of ATP results in actin and myosin filaments remaining locked in a contracted state, and calcium into the muscle cells prevent the muscles from releasing this contraction.
active tension depends on what?
active tension depends on filament overlap
what are the 3 types of contractions?
concentric, isometric, and eccentric
force increases with what?
force increases with stimulation frequency
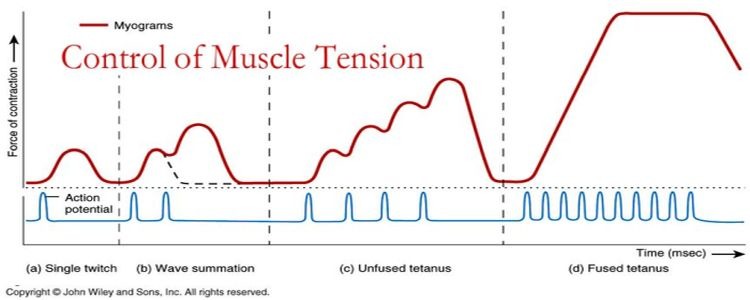
define twitch and tetanus
twitch refers to the force generated from single stimulation. tetanus refers to a twitch series when the next stimulus occurs after full relaxation.
Fused tetanus is when the next stimulus occurs before any relaxation. Unfused tetanus is when the next stimulus occurs during relaxation
define eccentric muscle contraction (lengthen/shorten, movement, cause)
eccentric muscle contraction refers to the lengthening of the muscles and involves lowering movements. Resistance is greater than the force produced, causing the muscle to lengthen under tension
This movement increases strength and muscle damage
(e.g. lowering dumbbell, lowering down to squat)
define concentric muscle contraction (lengthen/shorten, movement, cause)
concentric muscle contraction refers to shortening of the muscles and involves lifting movements. This occurs when the muscle produces more force than resistance.
This movement build power
(e.g. pushing up, lifting dumbbells, standing up from squat)
define isometric muscle contraction (lengthen/shorten, movement, cause)
isometric muscle contraction refers to no movement of the muscle. This is when resistance equals force produced and the muscle generates force without changing length.
This movement improves stability and joint strength
(e.g. holding dumbbell, plank, holding squat)
what are some possible consequence for a muscle that loses fast fibers?
inability to sprint, jump, lift heavy weights, slow reflexes
passive vs active tension
passive tension is the force generated by stretching a muscle to its resting length or beyond, resulting from the elastic resistance of non-contractile tissues. ‘
active tension is the force generated by muscle contraction through actin-myosin cross-bridge cycling stimulated by the nervous system.
order from largest to smallest: myofibril, muscle, sarcomere, muscle fascicle, muscle fiber,
muscle, muscle fiber, muscle fascicle, myofibril, sarcomere