Topic 22 definitions
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the key characteristics of Clade Bilateria?
: Bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, anterior-posterior differentiation, coelom (usually), digestive tract with two openings; includes protostomes and deuterostom
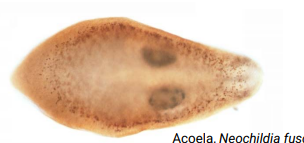
What defines Phylum Acoela as the most basal bilaterians?
No body cavity, flat body, minimal cephalization, no brain, mouth but no gut cavity or anus.
What defines Clade Lophotrochozoa?
Molecular phylogeny; includes diverse body plans with no single defining characteristic. Some have a lophophore, others a trochophore larva.
What is a lophophore?
A fan of ciliated tentacles surrounding the mouth used for feeding.
What is a trochophore?
A free-swimming larval stage with bands of cilia, found in some lophotrochozoans.
What are general features of Phylum Platyhelminthes?
No coelom, incomplete gut, no circulatory or gas-exchange system, dorsoventrally flattened.
What distinguishes Catenulida from Rhabditophora?
Catenulida are simple "chain worms"; Rhabditophora includes diverse free-living and parasitic species.
Characteristics of free-living Rhabditophora (planarians)?
Cephalized, eyespots, centralized nerve network, gastrovascular cavity with one opening.
How do parasitic rhabditophorans differ from free-living forms?
Have suckers/hooks, tough coverings, complex life cycles with intermediate and definitive hosts.
Define intermediate host.
Host where asexual reproduction occurs.
Describe a tapeworm’s body structure.
Scolex (hooks and suckers) and a chain of proglottids (reproductive segments).
What is a proglottid?
A reproductive segment of a tapeworm containing sex organs.
What phyla are united in Syndermata?
Rotifers (free-living) and acanthocephalans (vertebrate parasites).
Key traits of Phylum Brachiopoda?
Shelled, filter-feeding lophophorates; resemble bivalves but have dorsal/ventral shell
Key traits of Phylum Ectoprocta?
Colonial, sessile filter feeders with CaCO₃ exoskeleton; have retractable lophophores and U-shaped
What are the three main parts of a mollusc’s body
Muscular foot, visceral mass, and mantle.
What is the function of a radula
Rasping feeding organ used to scrape food.
What is a mollusc’s mantle?
Tissue that secretes the shell and forms the mantle cavity.
Characteristics of Class Polyplacophora?
Chitons with multiple shell plates; marine grazers.
Characteristics of Class Gastropoda?
Coiled shell (except slugs), pronounced cephalization, radula, some terrestrial; move with foot.
Characteristics of Class Bivalvia?
Two-part shells, filter feeders, no radula, reduced cephalization.
Characteristics of Class Cephalopoda?
Tentacles from foot, beak, closed circulatory system, advanced brain and eyes, no external shell.
Main features of segmented worms (Annelida)?
Segmented body, hydrostatic skeleton, closed circulatory system, coelom, cephalization.
Features of Clade Errantia?
Mobile, marine predators with parapodia and chaetae, good sensory structures.
Features of Clade Sedentaria
Less mobile, often filter feeders or substrate dwellers, hermaphrodites, direct development.
What are parapodia?
Paired appendages with chaetae used for locomotion or respiration.
What are chaetae?
Bristle-like structures made of chitin.
Features of earthworms and leeches?
Earthworms: ingest soil, have chaetae. Leeches: parasites/predators, no chaetae or parapodia.