Human reproduction Biology 30
1/85
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
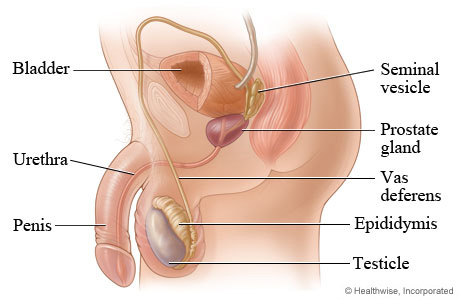
testes
male gonads that produce sperm and male sex hormone testosterone
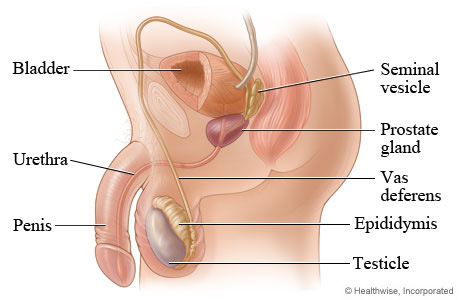
seminiferous tubules
long coiled tubes in which spermatogenesis occurs
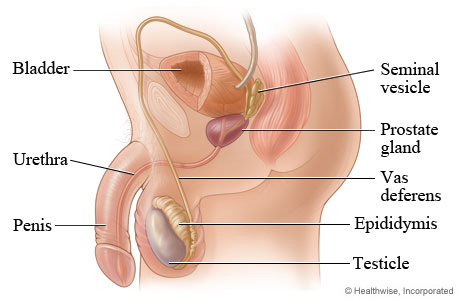
Sertoli cells
cells that make up the lining of the seminiferous tubules that supports spermatogenesis
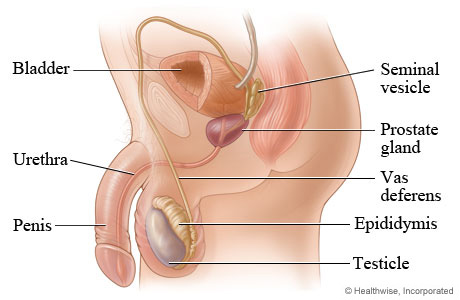
Interstitial cells
produces testosterone which promotes development of gametes and secondary sex characteristics
epididymis
site of the final stages of sperm maturation and storage of male gametes
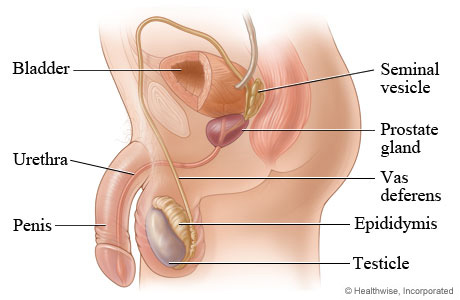
Ductus deferens(or vas deferens)
conducts sperm from epididymis to ejaclatory duct
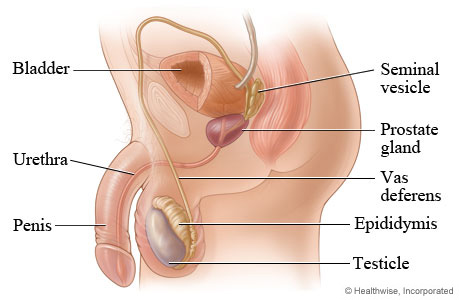
Seminal vesicles
produces fructose and fluid to semen
fructose is used as an external energy source
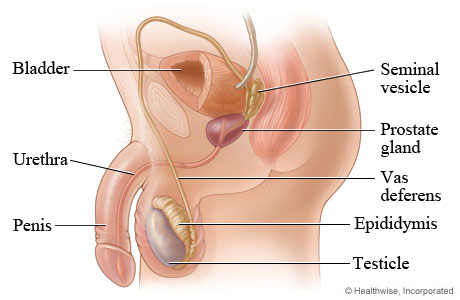
prostate gland
produces mucus(bulk of seminal fluid) and alkaline secretions
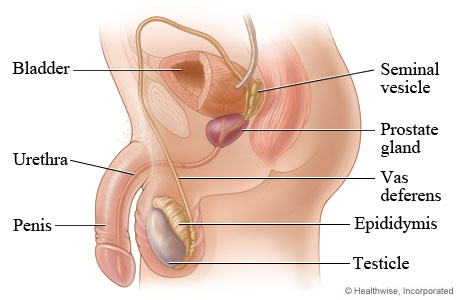
Cowper’s gland
produces a pre-ejaculate that neutralizes acids from any urine in the urethra prior to ejaculation
alkaline buffer provides some protection from acids in female reproductive tract
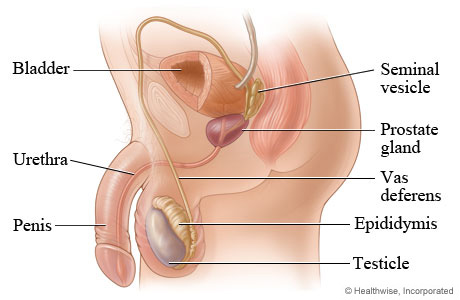
Urethra
Tube that conducts semen from the penis used for excretory function which conducts urine out of the body
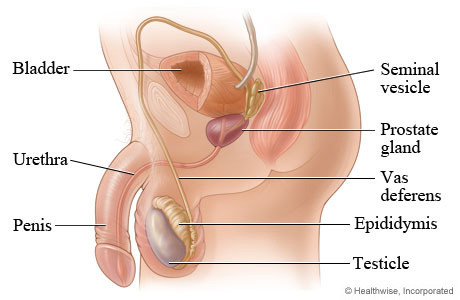
penis
carries semen into the female reproductive tract
spermatogenesis
process of spermatozoa production that occurs in between the sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubules under the influence of FSH
sertoli cells produce hormone inhibin to regulate pace of sperm production(negative feedback turning down LH and in turn testosterone)

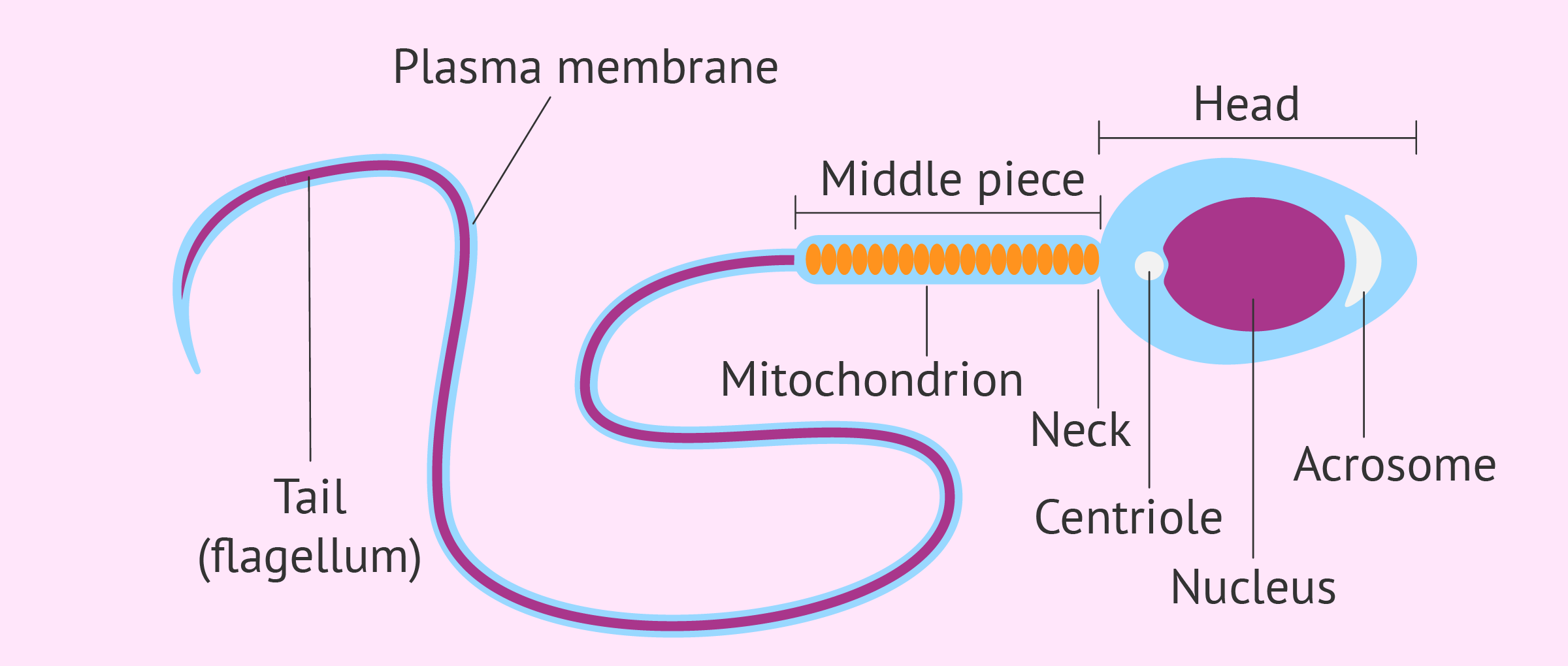
Parts of the spermatozoa
Head→has an enzyme cap called acrosome used to penetrate the egg and contains a nucleus with DNA(haploid-23 chromosomes)
middle piece→contains large numbers of mitochondria to provide ATP for flagellum
tail(flagellum)-used to propel sperm through the female reproductive tract
Semen
a viscous fluid that consists of spermatozoa and secretions from the seminal vesicles, prostate,and cowper’s gland(accessory glands)
Semen functions
Produces protective mucus coating on sperm
Alkaline buffers to neutralize acids in male urethra(urine) and vagina
seminal vesicle produces a fructose rich fluid which nourishes the sperm
Follicle stimulating hormone(FSH) in males
stimulates the development of male sex organs
promotes spermatogenesis in males
Luteinizing hormone(LH)
stimulates production of testosterone by interstitial cells
hyper-secretion of testosterone has a negative feedback effects on LH
gametes
Specialized cells involved in sexual reproduction that are haploid
Gametes include sperm cells in males and egg cells in females
The male reproductive system
consists of the penis, scrotum, testes, an internal duct system, and accessory glands
the penis is a copulatory organ by which spermatozoa are placed in the female reproductive system
the scrotum covers and protects the testes and spermatozoic it maintains the testes’ proper temperature for spermatozoa production
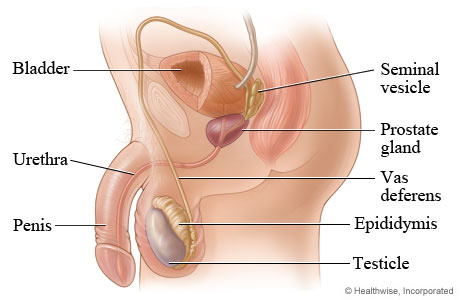
effects of Prostrate gland
enlarges slowly after age 40 and can cause difficulties due to enlarged state
enlarged state squeezes the urethra making urination difficult
testostorone
simulates production of spermatozoa
elevated levels influence male secondary sex characteristics
Andropause
caused by the decline of testosterone production(around age 40)
symptoms include: chronic fatigue, depression, loss of bone and muscle mass, and reduced sperm production
can be treated with hormone therapy
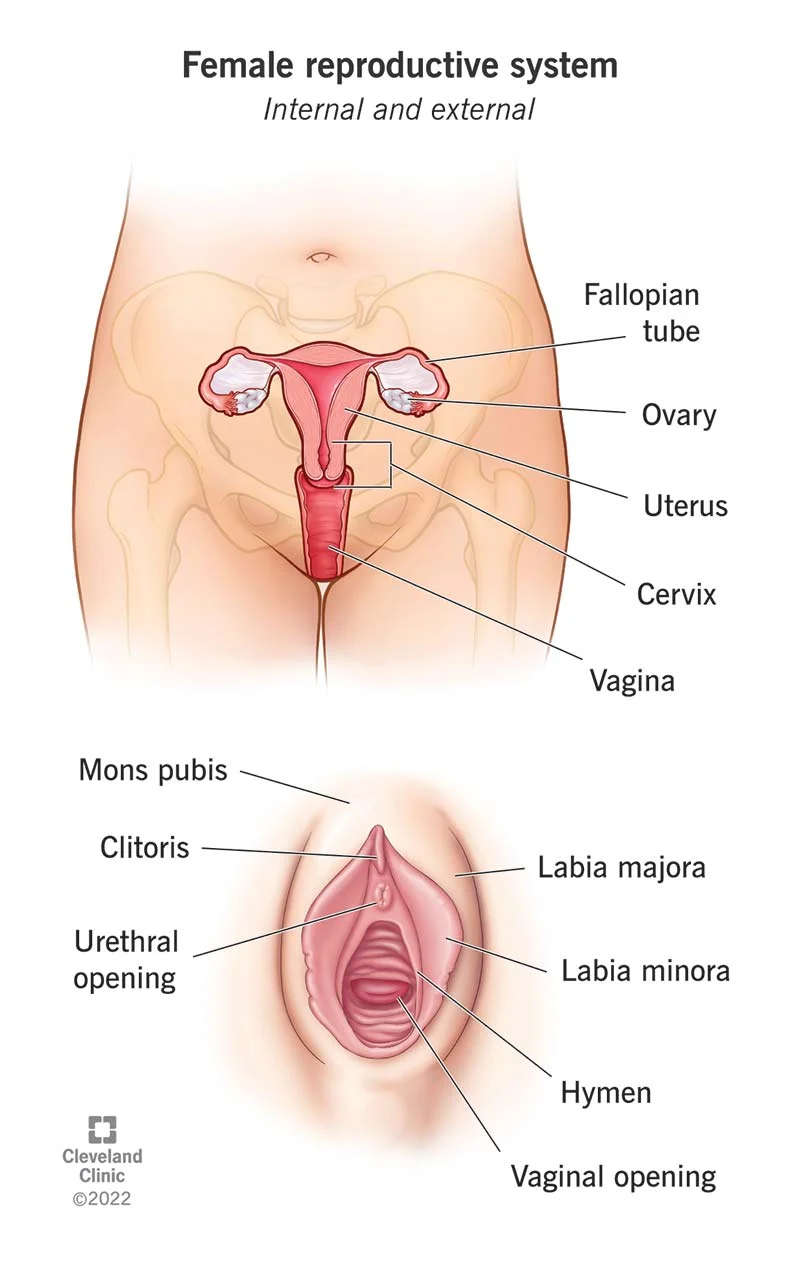
Ovaries
produce eggs and female sex hormones
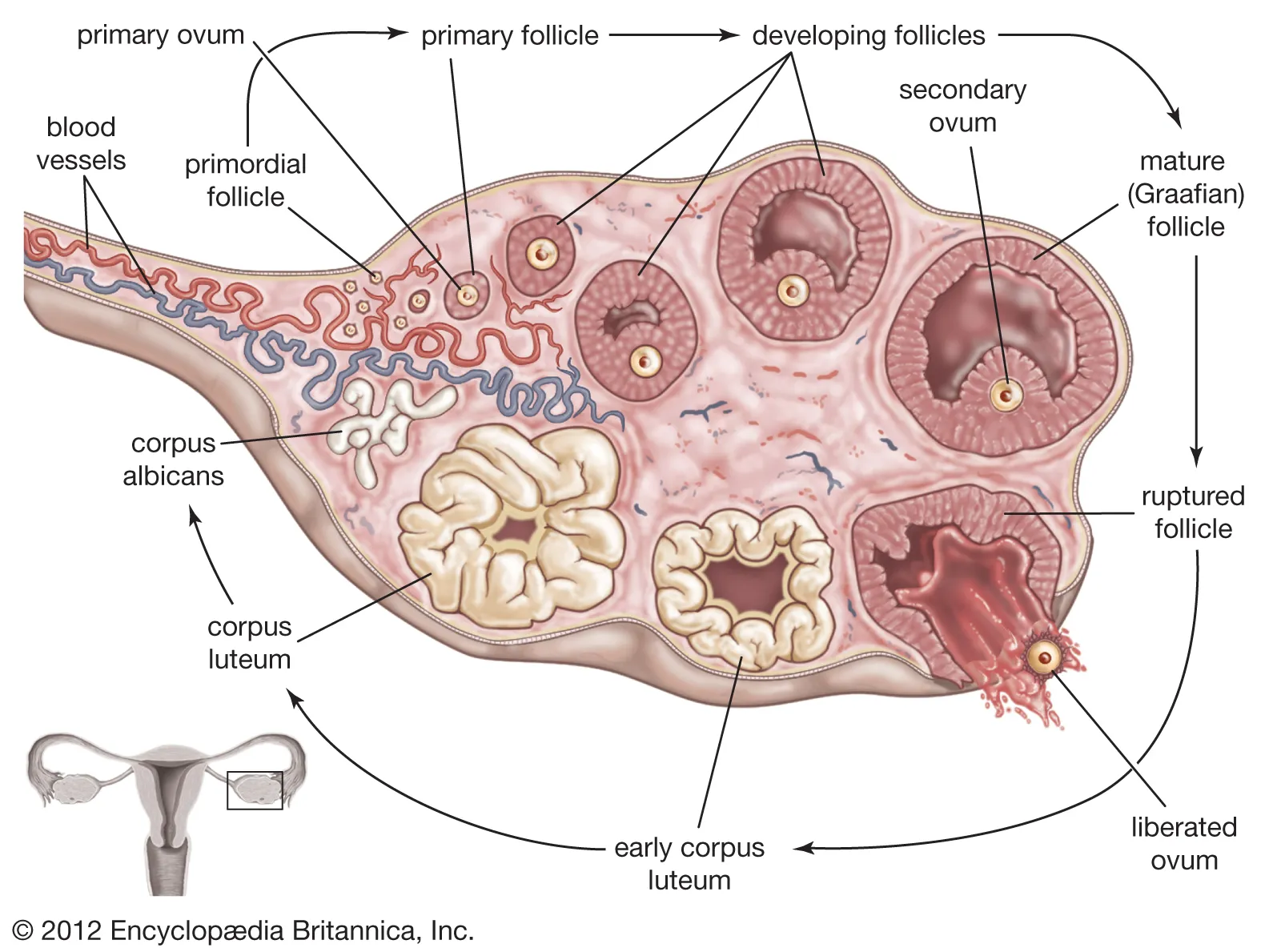
Follicles
reproductive structure within the ovary where each follicle contains a single ovum surrounded by follicular cells that support ovum development
Fimbriae
finger-like tissues at the ends of the oviducts that sweep egg from ovary into oviduct
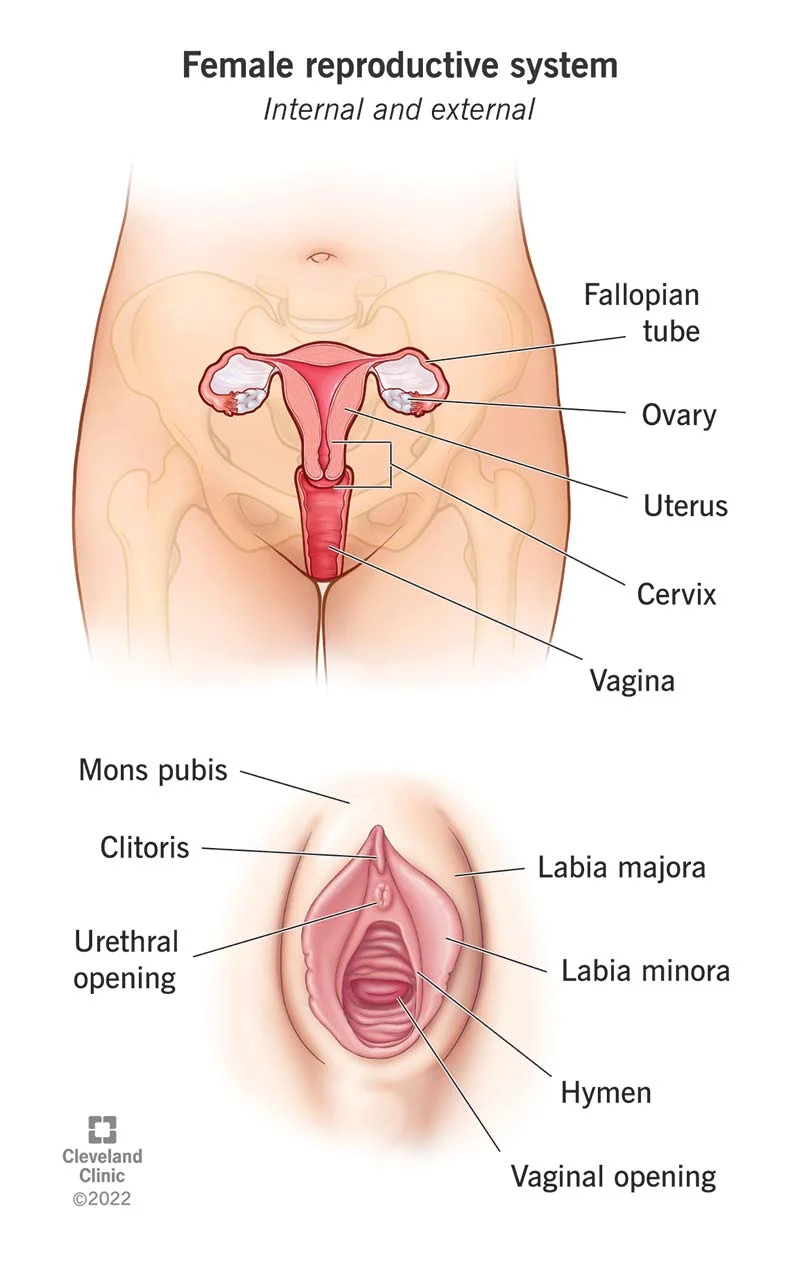
fallopian tubes(oviducts)
tube that connects the ovary to uterus also the site of conception
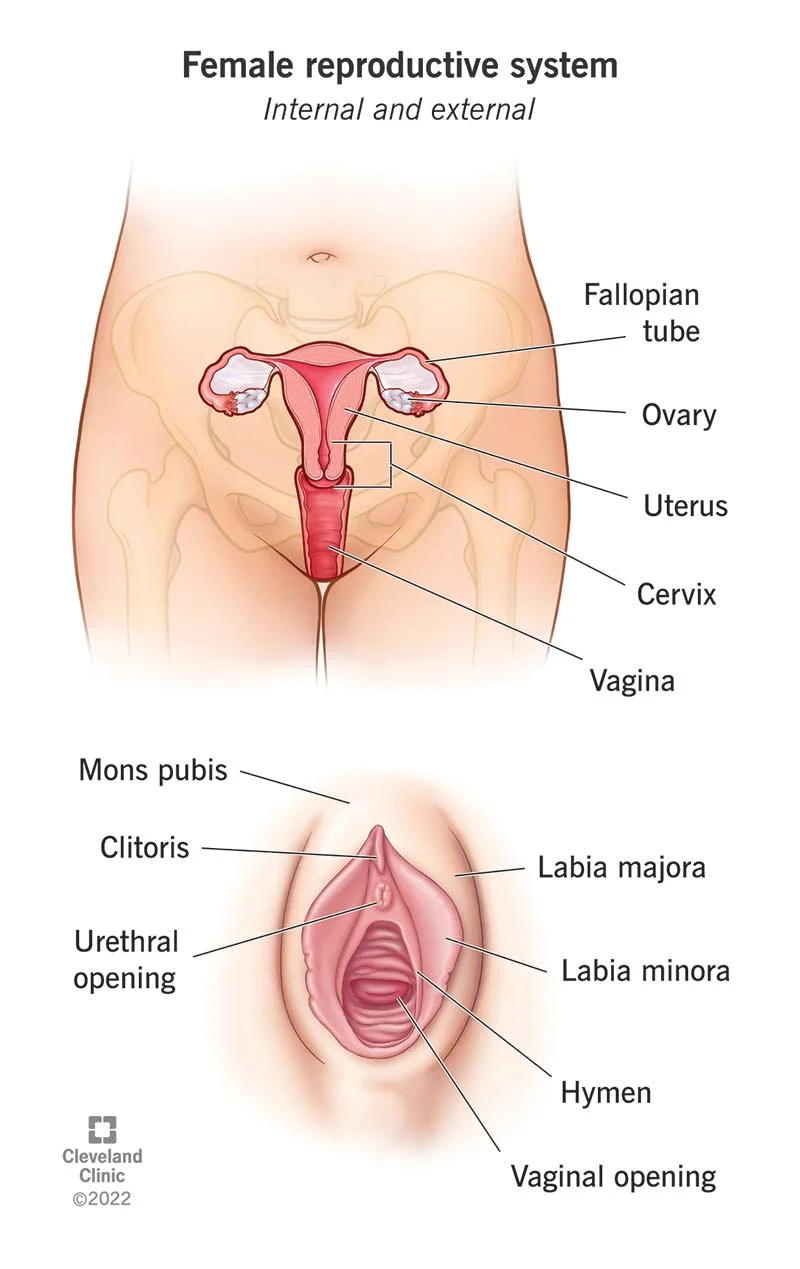
Uterus
shelters the developing embryo/fetus
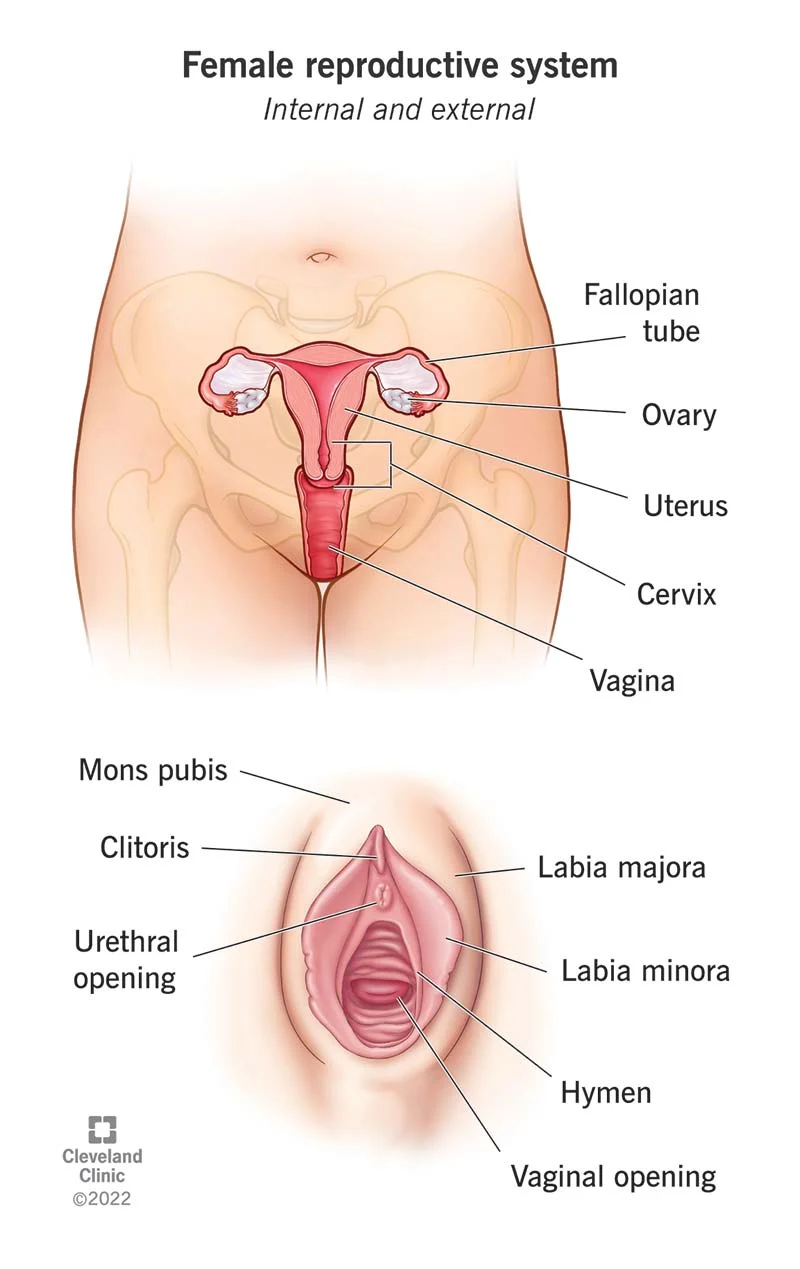
Endomentrium
the highly vascularized lining of the uterus that provides nutrients for the embryo/fetus
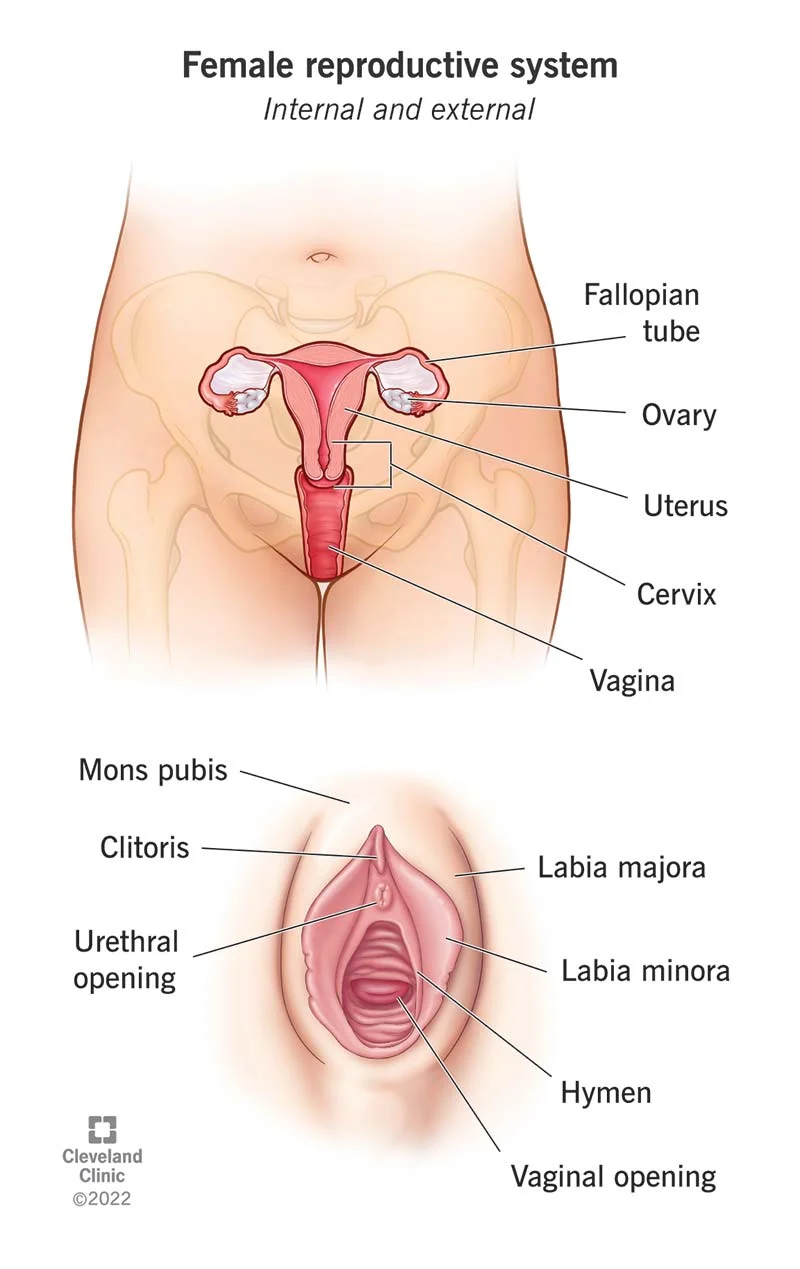
Cervix
ring of muscular tissue that is a opening to the uterus
prevents developing fetus from entering the birth canal prematurely
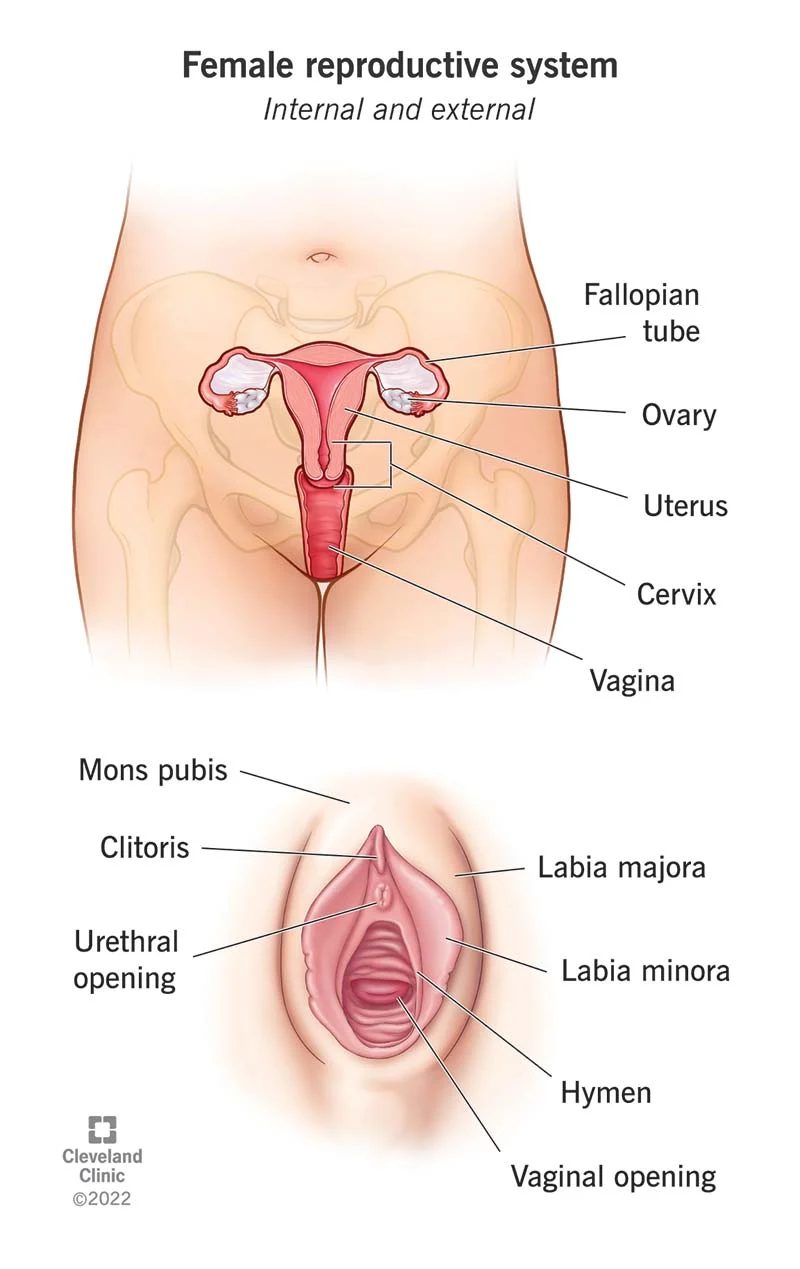
vagina
receives the penis during sexual intercourse and serves as the birth canal
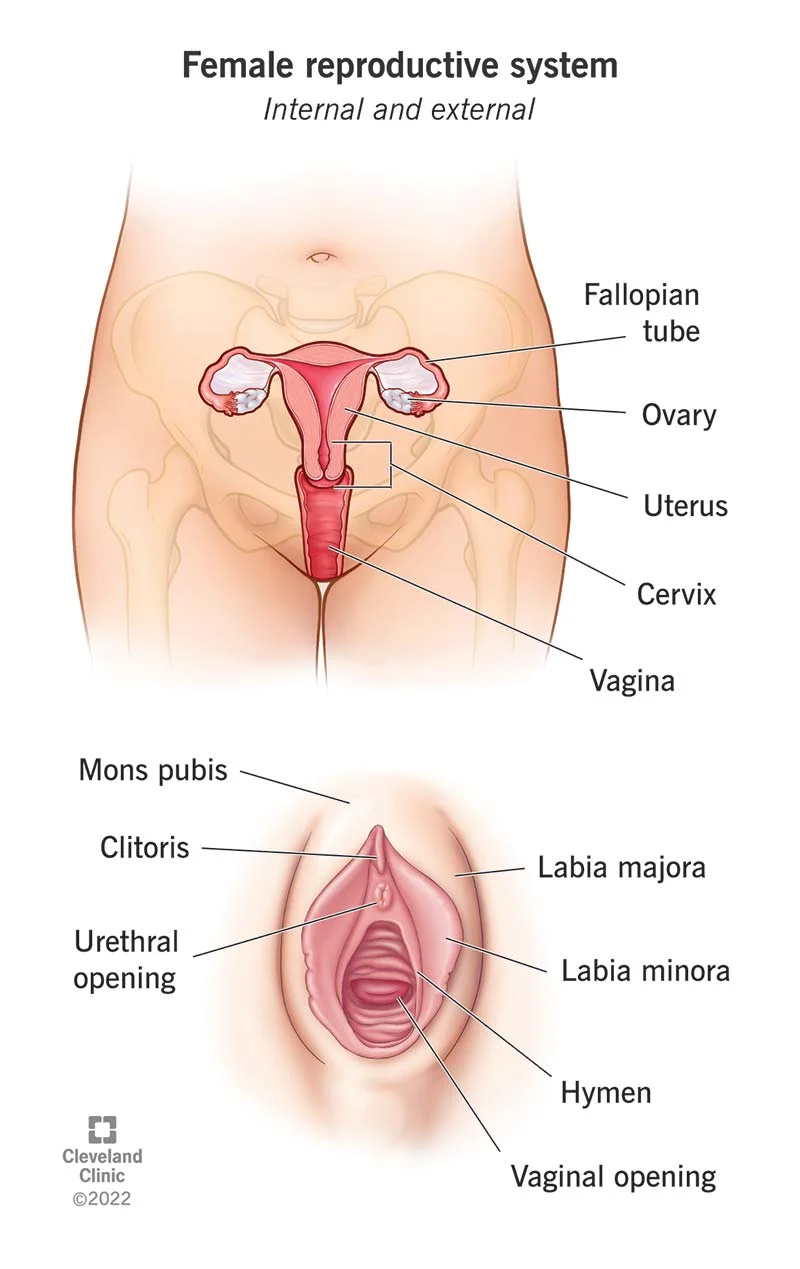
Vulva
external genitalia that includes the labia majora and the labia minora
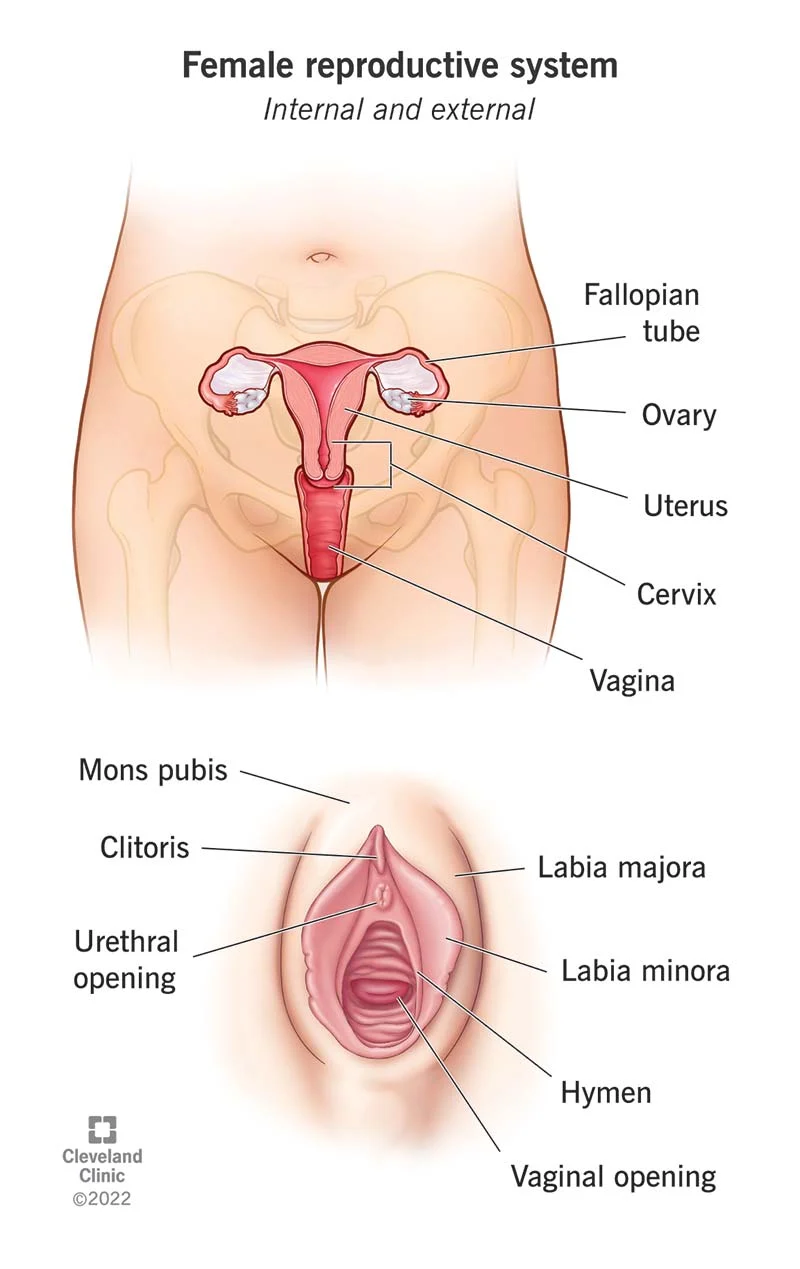
Oogenesis
the process of ova(egg) formation that begins while a woman is still undergoing fetal development
when a woman is born she already has all the eggs she will release over her reproductive life time
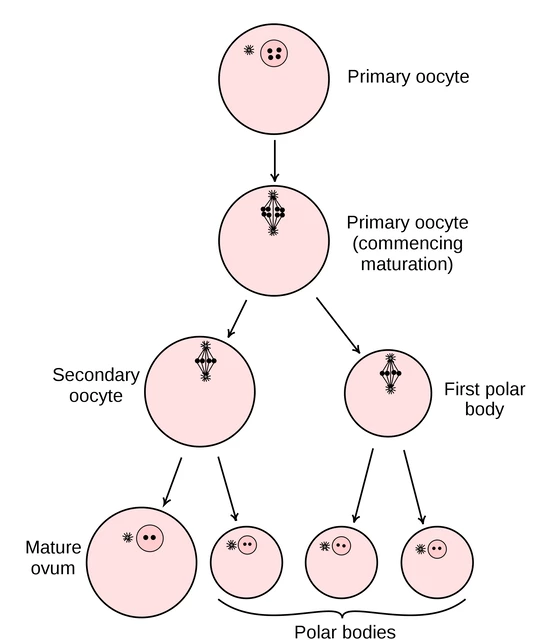
Ovum
Female reproductive cell released during ovulation, capable of being fertilized by sperm to form an embryo
has a large quantity of cytoplasm that contains nutrients from the first week of development before implantation
enveloped by successive protective layers sperm must penetrate
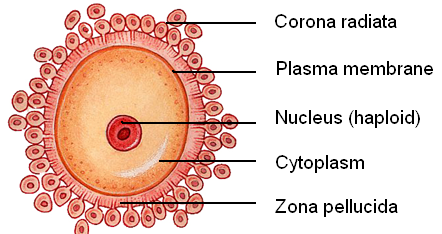
Follicle stimulating hormone(FSH) in Women
stimulates follicular growth and development in the ovaries which in turn secrete estrogen
Estrogen
stimulates endometrial growth during the 1st half of the reproductive cycle
increasing levels have negative feedback effect on FSH
Luteinizing Hormone(LH)
released just prior ovulation(with a burst of FSH) in the middle of the reproductive cycle causing ovulation
transforms ruptured follicle to become the corpus luteum
corpus luteum releases estrogen and progesterone which prevents the shedding of the endometrial lining of the uterus
Menopause
marked by a time when a woman no longer menstruates
usually occurs around 50 years of age
women who have completed menopause are reproductively infertile
symptoms-hot flashes, mood swings, increased blood cholesterol, heat disease, etc
Hormone replacement therapy(HRT) to provie relief
Sexually transmitted infections
Infections transmitted through sexual contact, including HIV, chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and herpes
Can be prevented through condom use, regular testing, and vaccination (for HPV and Hepatitis B)
Symptoms may include genital sores, discharge, pain, and burning during urination.
Chlamydia
symptoms-unusual discharge from penis or vagina, burning sensation while urinating
effects on fertility/reproductive system:
women→can cause pelvic inflammatory disease(PID) which scars the oviduct. Increases susceptibility to HIV
treated with antibiotics
Gonorrhea
symptoms- burning sensation while urinating and thick greenish-yellow discharge
effects on fertility/reproductive system: lead to PID in women and can spread to the bloodstream
treated by antibiotics
Syphilis
occurs in 3 stages
infectious ulcerate sores(chancres) appear at site of infection
appears anywhere on body but mainly palms and soles of feet
infection affects cardiovascular and nervous systems. large infectious ulcers called gummas appear
treated by antibiotics
can infect developing embryos causing defects or stillbirth
genital herpes
symptoms-tingling sensation and blisters in boxer short area
effects on fertility/reproductive system: high risk of transmission from mother to unborn child. if the infant is infected blindness, neurological disorders, and death can occur
no cure, individual carries it for life
Human Papilloma Virus(HPV)
symptoms-flat or raised warts in genetial area
effects on fertility/reproductive system: some forms are linked to cervical cancers tumor formations on vulva, vagina,anus, and penis
HIV/AIDS Infection
symptoms destroy helpers t-cells in the body and make the body susceptible to more infections
effects on fertility/reproductive system: children born to mothers with this infection have a high likelihood of infection
shortened as human immune-deficiency virus
tretament→drug therapy
menstrual cycle
last 28 days in humans and can be divided into two cycles:
Ovarian cycle
Uterine cycle
Ovarian cycle
describes the events leading to the development and release of the second oocyte
influences pituitary hormone release and anatomical changes in the ovary’s
involves follicular stage(days 1-13) and luteal stage(days 15-28)
Follicular stage(day 1-13)
follicles begin to grow and mature under the influence of FSH
as follicles develop they release estrogen which causes a decrease in FSH secretion
day 13 elevated estrogen levels cause a release of GnRH
this triggers a spike in LH and FSH that results in the expulsion of the secondary oocyte on day 14(ovulation)
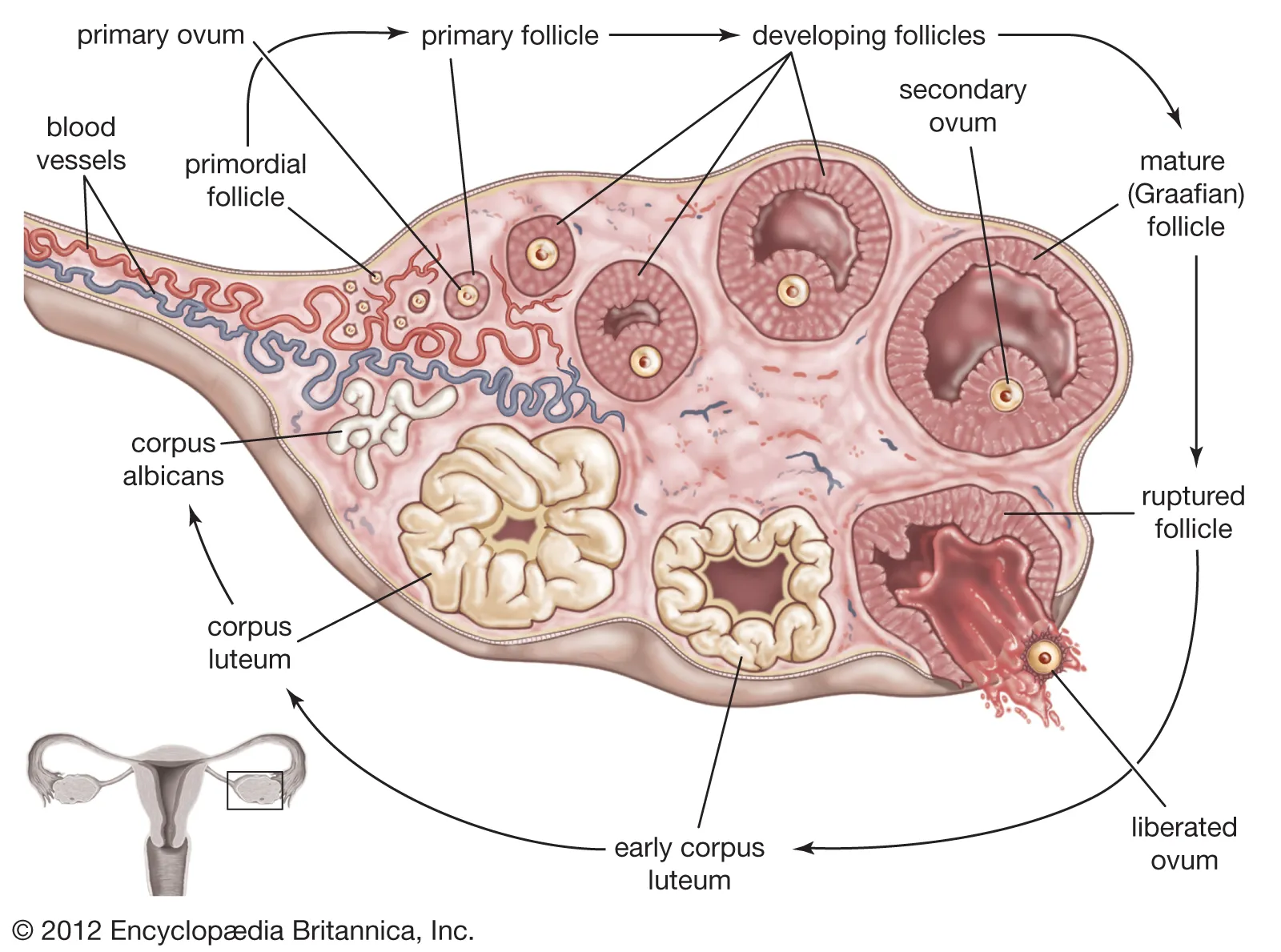
Luteal stage(day 15-28)
ruptured follicle becomes the corpus luteum which secretes estrogen and progesterone which halts the growth/maturation of the follicles
prevents the shedding of the endometrial lining in uterus to prepare for possible implantation
LH begins to decline during days 21-28 which causes the corpus luteum to degenerate
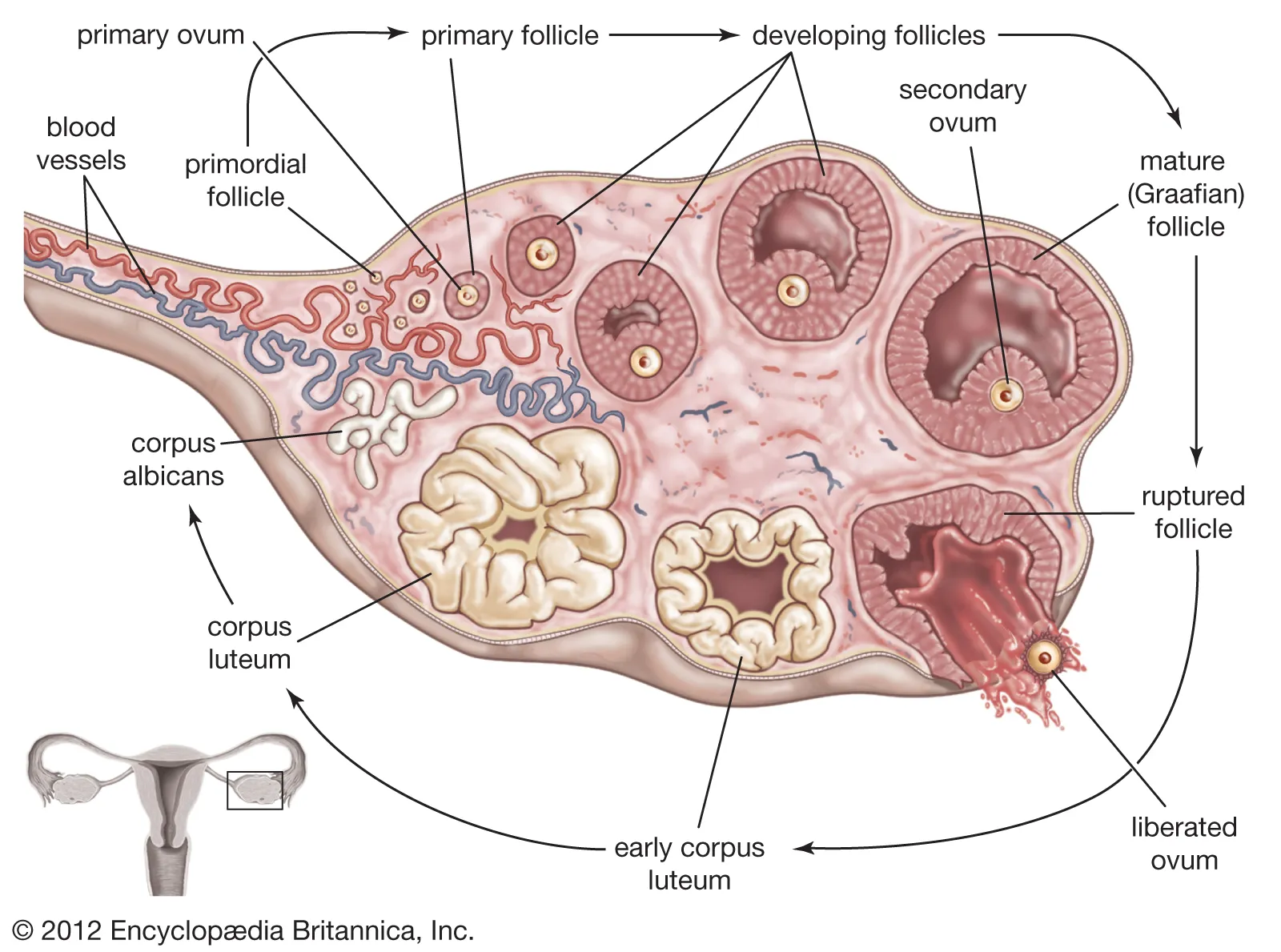
uterine cycle
describe events that take place in the uterus to prepare for potential implantation
during days 1-7 the endometrial lining is shed(flow phase)
new endometrial lining begins to grow during days 8-14 under the influence of estrogen from follicles in the ovary
endometrium thickens and becomes vascularized(grows blood vessels) during days 14-21 due to progesterone and estrogen a fertilized egg can now reach the uterus
Days 22-28 endometrium begins to degrade as progesterone and estrogen secretion from corpus luteum declines
fertilization
the fusion of male and female gametes to form a single zygote. Conception typically takes place in the oviducts closest to the ovary
enzymes in acrosome digest an opening through the protective layers(corona radiate and zona pellucida) to deliver male nucleus to the ovum structure-a zygote
12-24 hrs for male and female chromosomes to align before the first mitotic cell division occurs
Steps leading to fertilization
the ovum is released from the ovary and swept into the oviducts
after fertilization the ovum has a viable lifespan of 24 hours
peristaltic contractions of the oviduct and cilia sweep the ovum towards the uterus which can take 4-7 days for the ovum to meet the uterus
2. millions of sperm cells exist the male urethra per ejauculation
most are killed in the acidic environment of the vagina and in the passage through the cervix
only few make it to the oviduct containing the ovum
structure of the egg including the corona radiata, zona pellucida, and vitelline membrane assist as well
when the sperm meets the egg there is a 12-24 period where maternal and paternal chromosomes align in preparation for the first miotic division
this forms a zygote with 43 chromosomes
process of cleavage
after an egg has been fertilized it travels toward the uterus with the goal of implantation
zygote divides rapidly many times producing smaller cells each time
at 32 cell stage, the structure is called a morula
morula reaches the uterus in 3-5 days after conception, then begins to absorb fluid which fills the centre
cell division without the enlargement of cells is called cleavage which produces daughter cells
process of implantation
the morula reaches the uterus within 3-5 days after fertilization and is now called a blastocyst(the structure that implants in the endometrium)
between days 5-7 after fertilization, the blastocyst attaches to the endometrium
trophoblast releases enzymes that digest some of the endometrium allowing it to sink into its lining(causes spotting)
implantation is completed 10-14 days after conception and the nestling of the blastocyst into the endometrium is called implantation
parts of blastocyst
trophoblast-outer shell of cells
chorion-will form extra-embryonic membranes(formed from trophoblast cells)
the interior cluster of cells form the inner cell mass which will become the embryo
Human chorionic gonadotropin(hCG)
secreted by the trophoblast to act like LH(which promotes the maintenance of the corpus luteum) and releases progesterone and estrogen
progesterone and estrogen maintain the endometrium and prevent menstruation
hCG stops being released when the placenta is fully formed(3 months) as the placenta produces its own progesterone and estrogen
Corona radiata
the follicular cells that nourished the ovum during development in the ovary
Zona pellucida
specialized layer that can change from flexible jelly-like layer to hard impenetrable barrier once breeched by the sperm
Gastrulation
Process during embryonic development where a blastula transforms into a gastrula
space forms between the inner cell mass and trophoblast(amniotic cavity) which is surrounded by a membrane called the amnion
Cells migrate and rearrange to form three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
makes the beginning of morphogenesis
embryonic development weeks 1-4
2nd week:
space forms between the inner cell mass and the trophoblast called the amniotic cavity and is filled by amniotic fluid
3rd week:
mesoderm forms notochord which acts as the framework of backbone and skeleton
nervous system starts to develop into tube from ectoderm above notochord
heart starts forming and beating day 18
4th week:
blood cells form and fill new formed blood vessels
lungs,kidney, arm/leg buds, head, eye, ears, nose all began to from and appear
morphogenesis
process by which an organism develops its shape and form during embryonic development
involves the coordinated movements, differentiations, and growth of cells, tissues, and organs to create the final structure of an organism.
Morphogens, signaling molecules, and gene expression play crucial roles in morphogenesis.
Abnormalities in morphogenesis can lead to developmental disorders or birth defects.
three embryonic layers
ectoderm→outer skin including hair, nails, sweat glands, mammary glands, nervous system
Mesoderm→lining of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, body cavities, connective tissue(blood,bone,muscle)
Endoderm→lining of respiratory system, digestive tract, urinary bladder, most internal organs
Embryonic development weeks 5-8
5th week:
head has grown and is larger than the rest of the body
eyes are open but not fully developed
6th week:
limbs lengthen and move
gonads produce hormones that influence external genital anatomy
7th-8th week:
embryo has distinct human features
organs are formed directed by the CNS
eyes, nostrils and developed but shut or sealed
end of 8th week:
90% of organs are formed and will continue to enlarge and mature until birth
Amnion
thin transparent membrane that fills iwth amniotic fluid and protects the embryo/fetus from physical trauma
also allows freedom of movement and prevents limbs from sticking to the body
Yolk sac
contributes to the formation of the digestive tract
produces embryonic blood cells and future gonads
allantois
forms the umbilical cord(2 arteries 1 vein) and eventually becomes part of the urinary bladder
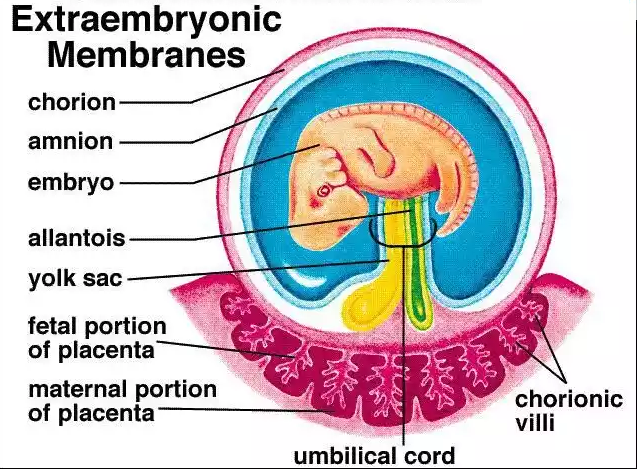
Placenta
Organ in pregnant mammals that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall, allowing for nutrient and waste exchange between mother and baby
made of maternal and fetal tissues(inter-digitated)
fully formed at 10-12 weeks gestation
chorionic tissues make up half of the placenta
transports and stores nutrients(proteins, Fe, Ca) to be released to fetus in the event the mother cannot fully provide
transports fetal waste to mother’s blood, antibodies from mother to fetus, and gives O2 to baby while also taking Co2 from baby
Parturition(labour)
begins with uterine contractions that start as light 20-30 second long contractions and growing in frequency
onset labour is strong contractions lasting 40 seconds or longer 15-20 mins apart
cervical stretching signals release of oxytocin which initiate intensity of contractions
Stages of labour
dilation stage:
uterine contractions/oxytocin cause the cervix to dilate an eventually cause the amniotic sac to break and amniotic fluid to be released(2-20 hrs)
Expulsion stage:
strong contractions push the baby through the birth canal
baby’s head rotates allowing the body to pass through the birth canal(30 min-2 hrs)
Placental stage:
shortly after the baby is delivered the placenta and umbilical cord are delivered(afterbirth)
Caesarean section
surgical procedure where baby is removed through an incision in the mother’s abdomen
required if baby is not in correct head down position and cannot be turned, mother has infectious STI, mother has narrow plevis
First trimester
first 8 weeks fall under embryonic development
during the last 4 weeks:
growth in body length accelerates and growth of head slows
end of 12th week→cartilage begins to calcify into bone and genitalia can distinguish the sex of the fetus
Second trimester
weeks 13-24 and the physical signs of pregnancy(morning sickness, baby bump) begin to show
the baby brain grows rapidly and the nervous system starts to fully function
mother feels fetal movement
fine soft hair and oily secretions protect and cover the developing skin which appears wrinkled as the fetus has no stored fat
third trimester
weeks 25-38 where fetal brain cells from rapidly
testes descend into scrotum for males
layers of subcutaneous fat collects under the skin
digestive and respiratory systems are the last to mature
Teratogen
agent that causes a structural abnormality due to exposure during pregnancy
especially significant during the first 9 weeks when the developing embryo/fetus are highly sensitive to environmental factors
Cigarettes→smoking or second-hand smoke can cause underweight babies, stillbirths, reduced intellectual ability
Alcohol→fetal alcohol syndrome(FAS), decreased weight/height, facial malformations
Drugs→eg.thalidomide, causes deformations
xrays, pollutants, and large amounts of vitamins(vitamic c) also
Lactation
The production and secretion of milk from the mammary glands, typically occurring in female mammals after giving birth
Prolactin
the hormone needed for milk production that is not secreted during pregnancy due to being suppressed by high levels of estrogen and progesterone
before birth the breasts secretes colostrum→watery, yellowish fluid similar to milk but contains more protein and less fat. Alos rich in antibodies
Process of breast feeding
baby suckling stimulates the release of milk from the mother’s breast. baby stimulates nerve endings in nipple and areola sending impulses to hypothalamus, then the posterior pituitary to release oxytocin
oxytocin causes contracts of mammary lobules that contain alveoli(sacs with milk) which results in the flow of breast milk
if suckling does not occur milk productions stops
sterile
permanent condition where a person cannot have children
Infertile
condition that causes someone to have very low reproductive potential. sometimes it can be corrected
surrogacy
when a woman is contracted to carry a baby for them
genetic surrogate→mother uses her own eggs(artificial insemination)
gestational surrogate→genetically unrelated to the child(in-vitro fertilization)
Artificial insemination
a reproductive technique used to assist in achieving pregnancy.
involves the introduction of sperm into a woman's reproductive system, bypassing natural fertilization.
can be done using fresh or frozen sperm, and it is commonly used in cases of male infertility, single women, or same-sex couples
Superovulation
process that stimulates the release of multiple eggs a sa result of hormone treatment
often used prior to IVF
Surgical sterilization
surgical form of making someone sterile either a tubal ligation(women) or vasectomy(men)
Tubal ligation→cutting the oviducts and tying off the ends to prevent egg from reaching the uterus and sperm from reaching the egg
vasectomy→vas deferens is cut and tied so that semen deos not contain sperm(gametes)
Emergency contraception
Method used to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex or contraceptive failure
it contains higher doses of hormones (like progestin) to inhibit ovulation, fertilization, or implantation.
Inhibin
produced by sertoli cells in response to elevated spermatogenesis and reduces the secretion of FSH from anterior pituitary gland
In-vitro fertilization(IVF)
technique in which the ovum is fertilized by the sperm outside of the body. the resulting embryo is reintroduced to the uterus
Steps of IVF
stimulation(superovulation)-fertility drugs causes the ovaries to produce more than one egg a month
egg retrieval-follicular aspiration, removes eggs from womans body
Insemination and fertilization-sperm is placed with best quality eggs an undergoes insemination(mixing sperm to egg) than
Embryo culture-fertilized egg divides and becomes an embryo
embryo transfer-multiple embryos placed into uterus 3-5 days post egg retrieval and fertilization(may result in multiple pregnancies)