Functional Neuroanatomy Pt 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Functional divisions of the brain
parts of brain dedicated to specific fxns
not organised as individual centres but as parts of interacting networks
Ways to divide Cerebral cortex
phrenology
Broadmann areas
gyri and sulci
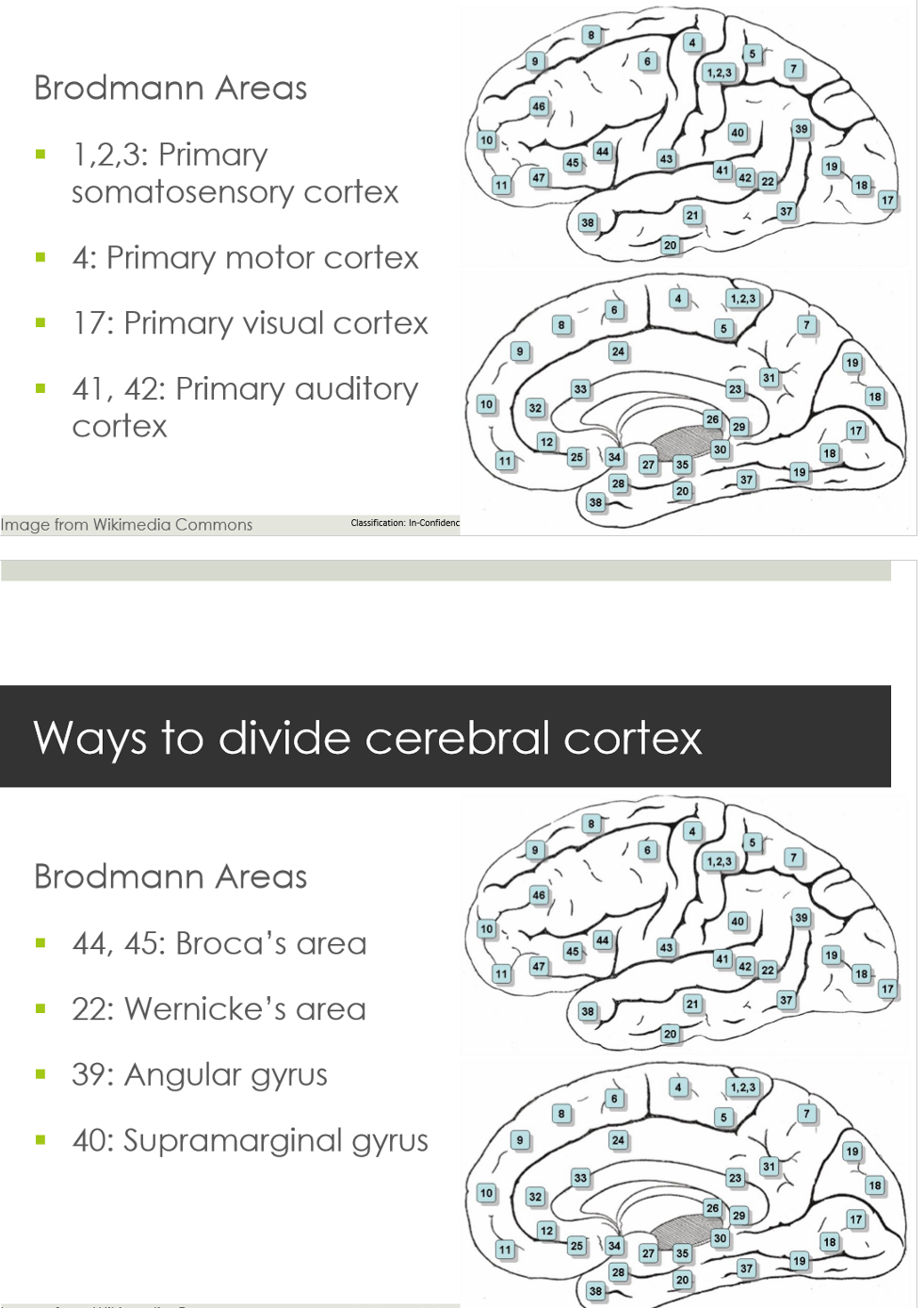
Broadmann Areas
brain divided into 52 areas
based on size, shape and type of neurons in cortex
Functional divisions of cerebral cortex
Primary areas
Association areas = secondary areas
Primary areas
± 10% of cortex
Primary motor area
Primary sensory areas
Primary motor area (M1)
responsible for execution of motor tasks
located in precentral gyri in frontal lobes (BA4)
control of the skeletal muscles on the contralateral side of the body
source of descending motor pathways projecting to lower levels of nervous system
contains motor homonculus
Primary sensory areas
precise relationship with specific body areas
receive sensory info from receptors in periphery
little interpretation of meaning
Primary somatosensory area (S1)
located in postcentral gyri in parietal lobes (BA 1,2,3)
contralateral representation
contains sensory homunculus
Primary auditory area (A1)
Heschl’s gyrus in temporal lobe (BA 41, 42)
Primary visual area (V1)
In occipital lobes (BA 17)
Olfactory area
involved in smell sensation
Gustatory area
involved in taste sensation
Lesion in primary areas
complete or partial deficit in corresponding motor or sensory modality
clearly defined deficits
e.g. reduced perception of stimuli, weakness
Association areas
specific areas adjacent to primary motor and sensory area
receive input from primary areas
higher order processing
larger association areas = broader fxn
Unimodal
primarily receives input from a single sensory area
Heteromodal
receives input from multiple sensory or multimodal areas
Association areas in frontal lobe
Premotor area
Supplementary motor area
Broca’s area
Prefrontal area
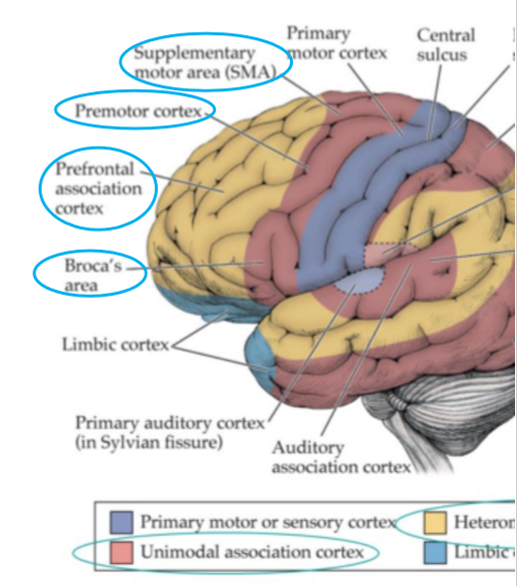
Premotor cortex
= motor association area
anterior to primary motor area
planning of voluntary movement
integration and interpretation of motor info
contains motor maps for movement of larger muscle groups
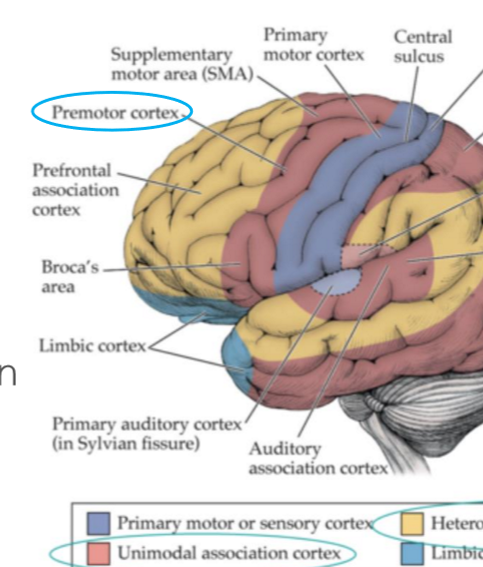
Supplementary motor area (SMA)
anterior to M1 & superior to premotor area (medial surface)
maps for postural stabilization
initiation of speech
Broca’s Area
(BA 44 & 45)
in dominant hemisphere (usually left)
pars triangularis & opercularis of IFG
programs speech movements and phoneme sequencing
Prefrontal area
anterior to premotor area
role in executive functions, working memory and personality
Association areas in the parietal lobe
somatosensory association cortex
posterior parietal cortex
multimodal association area
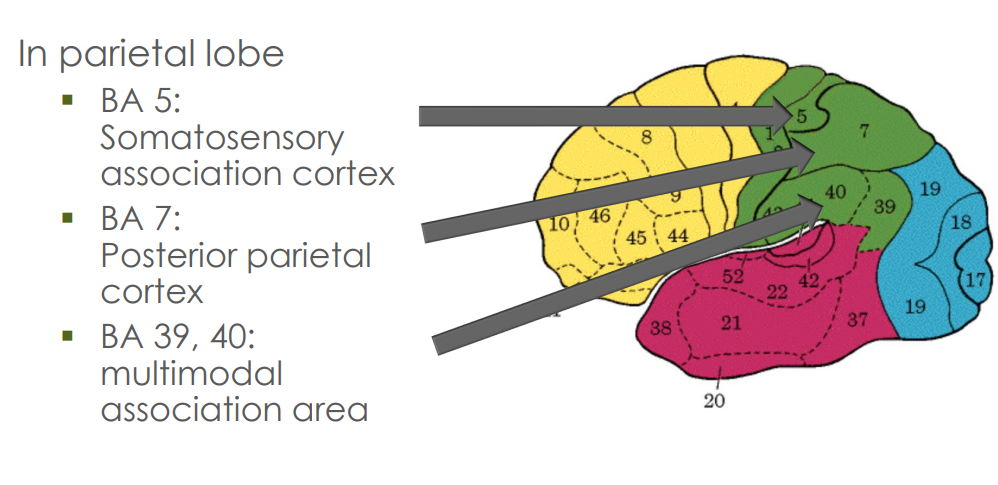
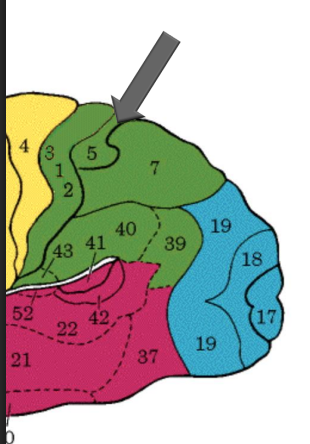
Somatosensory association cortex
BA 5
adjacent to primary somatosensory area
interpretation of sensory info
lesion can result in astereognosia (inability to recognize objects by touch)
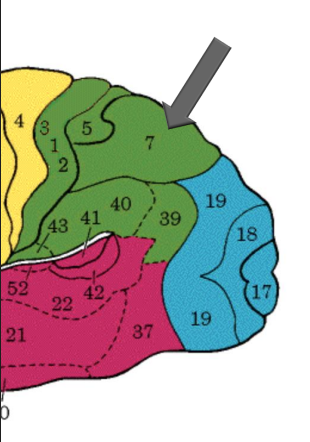
Posterior parietal cortex
BA 7
Somatosensory & visual integration
Visuospatial perception & attention
Representation & manipulation of objects
Perception of movement
Lesions may result in:
Neglect syndrome
Apraxia
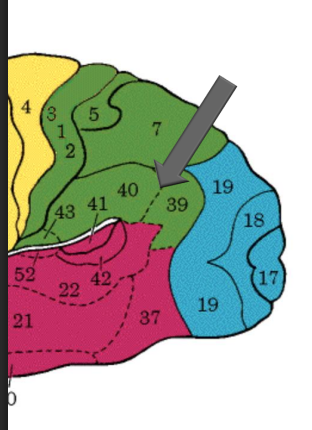
Inferior parietal cortex
BA 39, 40
Multimodal association cortex
visual, auditory & somatosensory info
Role in receptive language in dominant hemisphere
phonology, reading, spelling
Role in spatial & symbolic representation of abstract concepts
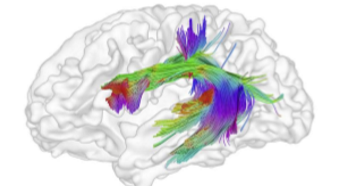
Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus/Arcuate fasciculus
Important tracts connecting inferior parietal cortex (IPC) to inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) and superior temporal gyrus (STG)
connects frontal, parietal and temporal lobes
how Wernicke’s and Broca’s area are interconnected
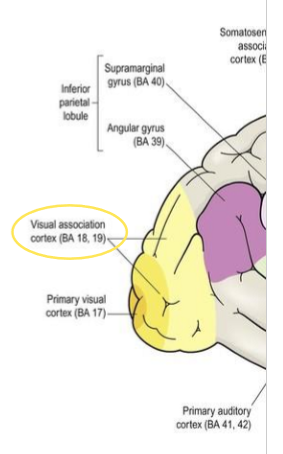
Visual association cortex
in occipital lobe
surrounding primary visual cortex on medial surface and extending onto lateral surface
interpretation of what we see
dorsal stream - where? location & movement of objects
ventral stream - what? form and colour of objects
Association areas in temporal lobe
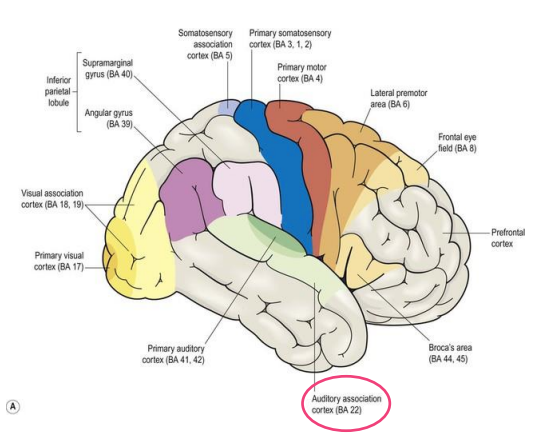
auditory association cortex
fusiform gyrus
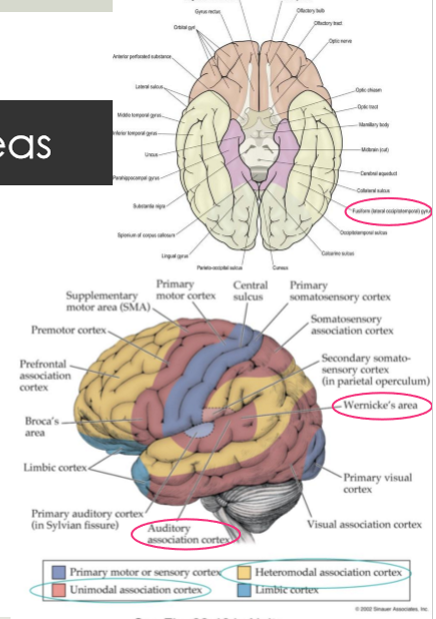
Auditory association cortex
Distinguish sounds as speech, music or noise
Wernicke’s area
superior temporal gyrus
assigning meaning to symbols
comprehension of language: spoken, written & gestures
Fusiform gyrus/occipitotemporal gyrus
Inferior surface of temporal lobe
Synthesizes & elaborates complex aspects of info
e.g., link visual object/word/face to meaning
Lesions in association areas
more complex result
e.g., higher cognitive ability, personality
Example
visual agnosia following lesion in fusiform gyrus
can see object & can describe it but don’t know what it is
may be able to recognise it using touch, smell, …
prosopagnosia: visual agnosia for faces