Money Creation and the Federal Reserve System
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Money Creation
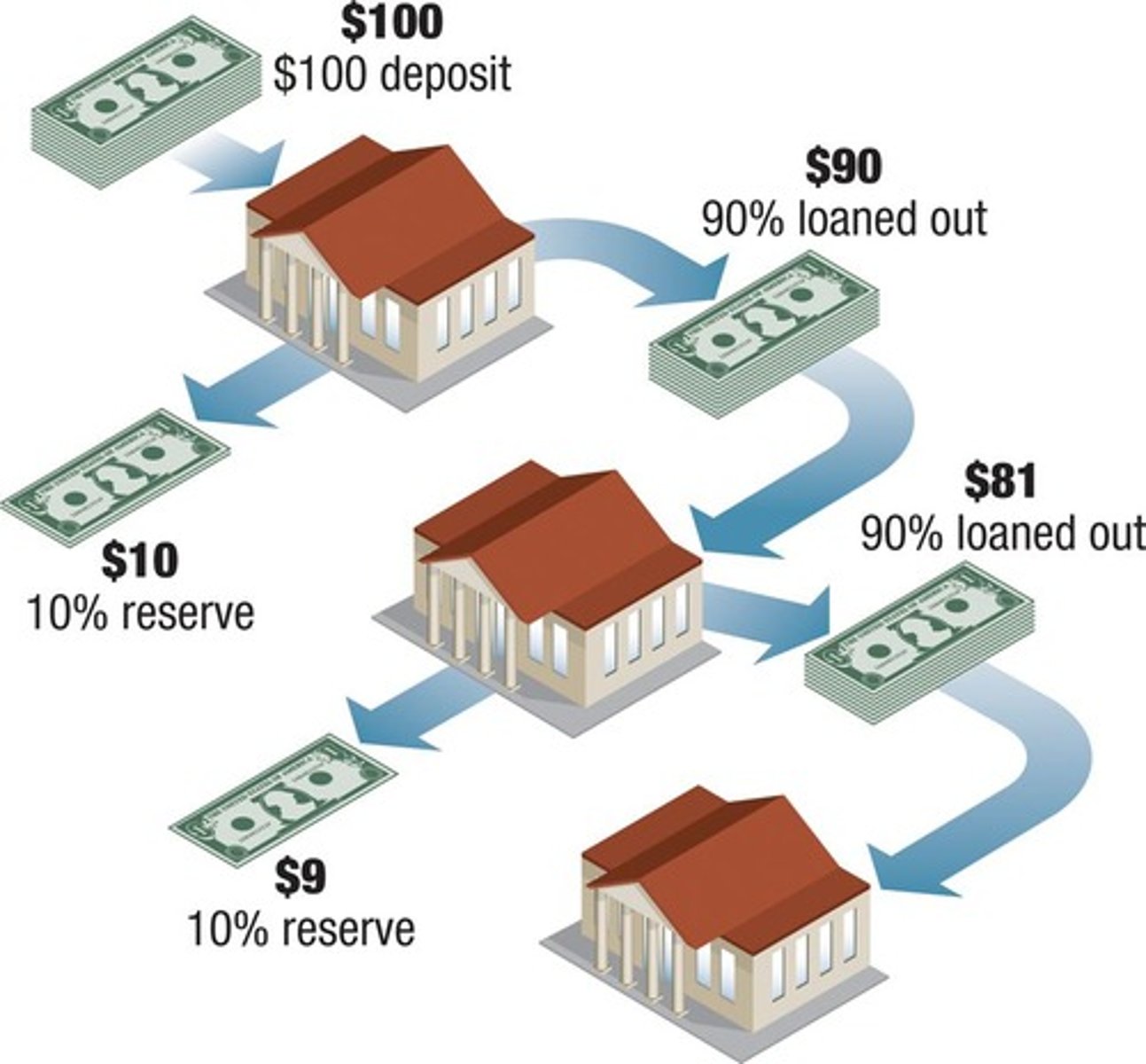
Money is created when financial institutions accept deposits and make loans.
Fractional Reserve Banking
A banking system where banks hold a fraction of deposits as reserves and lend out the rest.
Reserve Requirement
Required minimum portion of deposits a bank must hold as reserves.
Reserve Ratio
A bank's reserves as a percentage of its total deposits.
Money Multiplier
The factor by which initial new deposits can increase the money supply.
Monetary Base
The sum of total currency in circulation and reserves held by banks either in their vaults or on deposit at the Fed.
Actual Money Multiplier
The actual money multiplier in the United States is not much greater than 1 due to the tremendous amount of currency in circulation and reserves held by banks.
Cash Reserves
Cash held by banks in their vaults and ATM machines.
Reserves on Deposit at the Fed
Banks can deposit reserves at a Federal Reserve bank and earn interest.
Money Multiplier Calculation
1 ÷ (0.25 + 0.15) = 2.5 when the average percentage of deposits held in reserves is 25% and another 15% of the money supply is held as currency in circulation.
Federal Reserve System
The central bank of the United States, established by the Federal Reserve Act of 1913.
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
Determines the direction of monetary policy by targeting interest rates.
Federal Funds Rate
The interest rate that financial institutions charge each other for overnight loans used as reserves.
Lender of Last Resort
During an economic crisis, the Fed can provide loans when no one else can or will.
Tools of the Federal Reserve
Interest on reserve balances (IORB), discount rate, open market operations, reserve requirement.
Interest on Reserve Balances (IORB)
Interest paid on bank reserves held at the Fed.
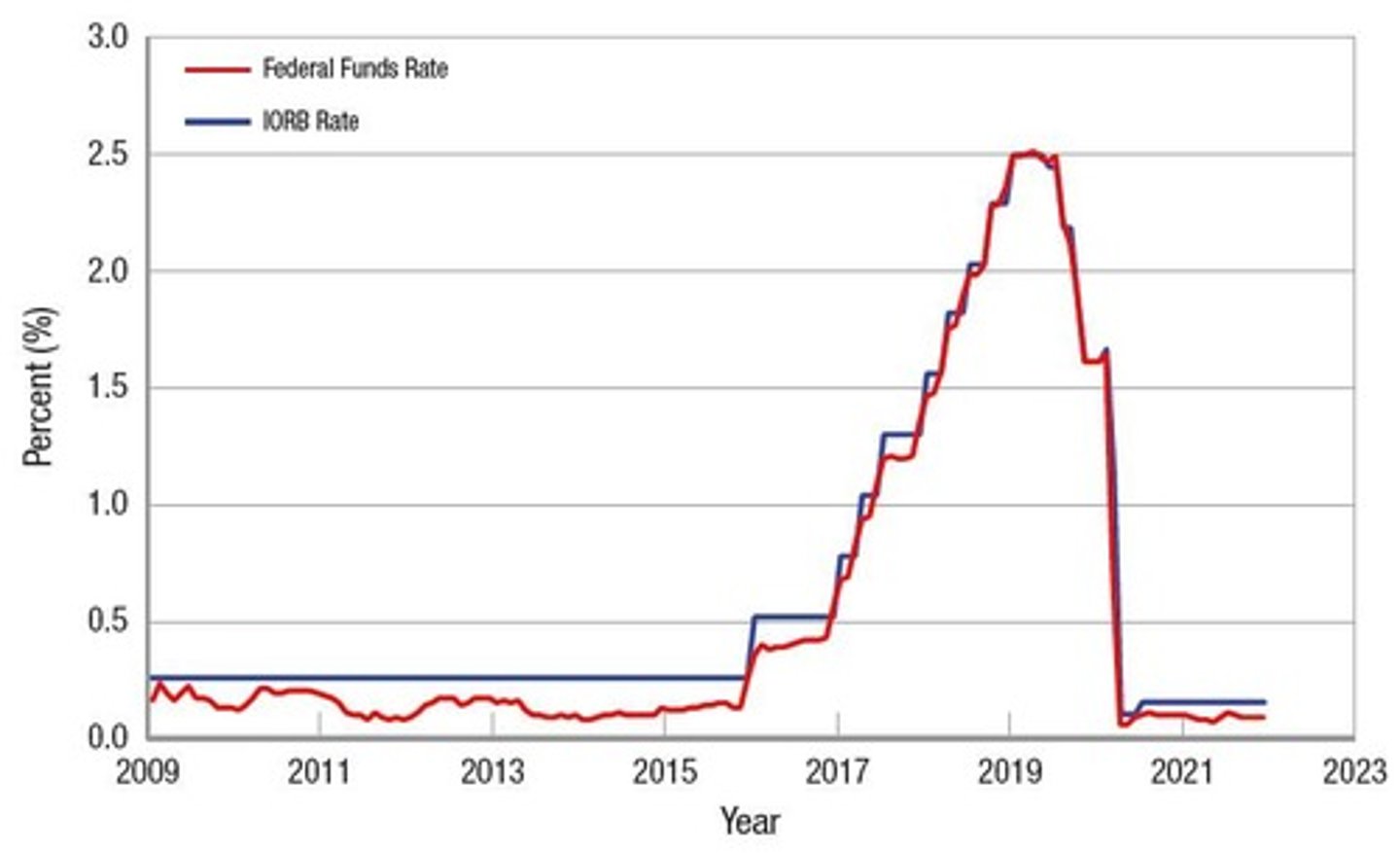
IORB Rate and Federal Funds Rate
The IORB rate creates a floor for the federal funds rate.
Monetary Policy Lags
Monetary policy is subject to information lags, recognition lags, decision lags, and implementation lags, with an average time for monetary policy to affect the economy being 12 to 18 months.
Janet Yellen
The first person to have held the three most prestigious economic posts in government: chair of the Council of Economic Advisers, chair of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors, and secretary of the U.S. Treasury.
Excess Reserves
The amount of reserves that banks hold above the required minimum.
Insolvent
A condition where an entity's liabilities exceed its assets.
Open Market Operations
The buying and selling of bonds in the open market by the Fed.
Discount Rate
The interest rate charged by the Fed to banks.
Arbitrage
The buying and selling of assets in different markets to profit from differences in price of the same asset.
Regional Federal Reserve Banks
Each Federal Reserve bank issues currency, marked by a letter (A to L) corresponding to its location.
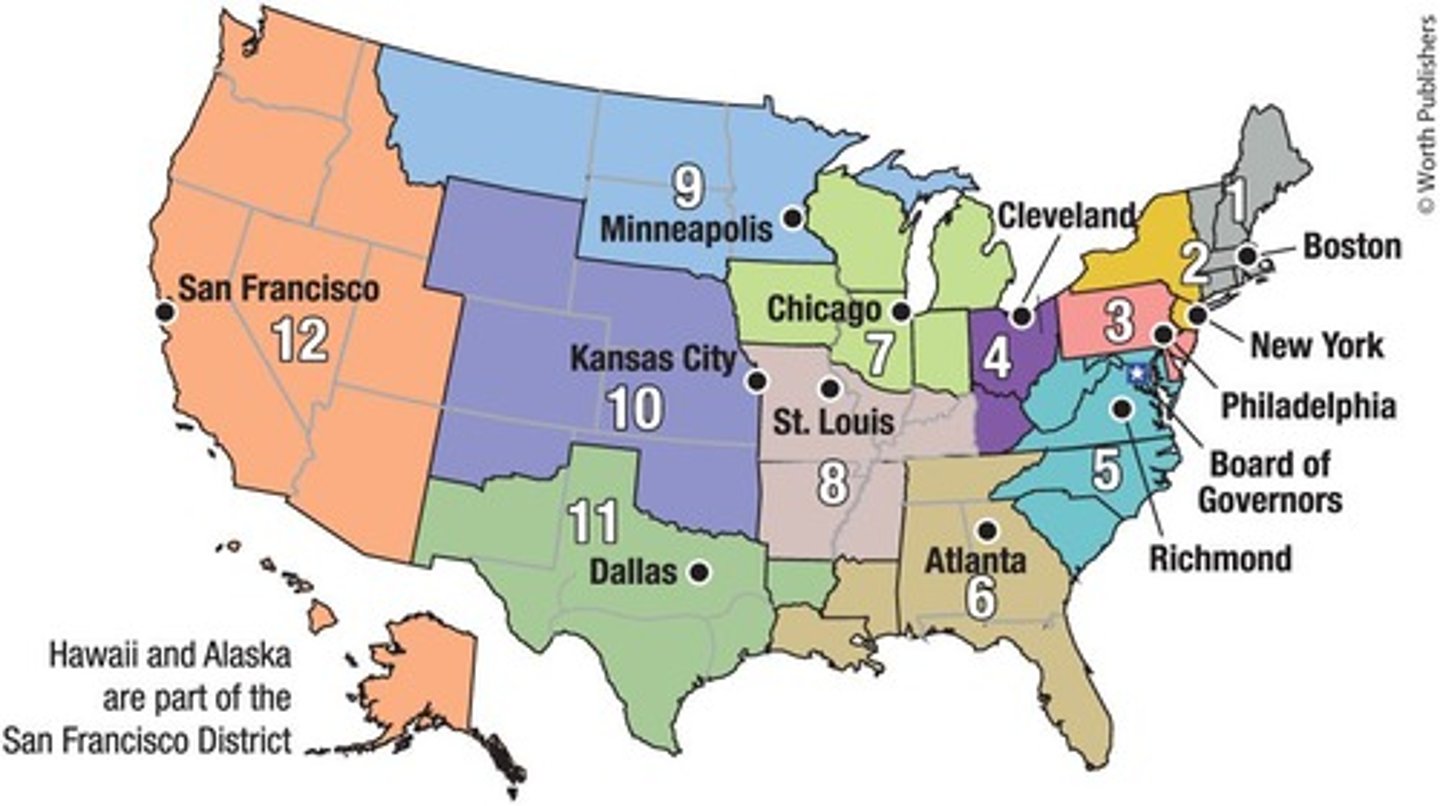
Functions of Regional Fed Banks
Provide a nationwide payments system, distribute coins and currency, regulate and supervise member banks, serve as the banker for the U.S. Treasury.