Senses - Touch and Proprioception
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Somatosensory - Senses (7)
touch
pressure
vibration
proprioception
temperature
itch
pain
Sensor - Locations (3)
skin
muscles
joints
Receptors - Types (4)
thermoreceptor
meissner’s corpuscle
nociceptor
pacinian corpuscle
Thermoreceptor
senses temperature
Meissner’s Corpuscle
senses light touch
Meissner’s Corpuscle - Location
palm
soles of feet
eyelids
genitals
nipples
Nociceptor
senses pain
sensitive to stimuli that damage or threaten to harm tissue
Pacinian Corpuscle
senses deep touch or pressure or vibration
Pacinian Corpuscles - Location
dermis
deep tissue
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
12 cranial nerves
31 pairs of spinal nerves
Dermatome
sensory area on the body innervated by a specific spinal cord
Sensory Impulse Direction
northbound
Motor Impulse Direction
southbound
Somatosensory Afferent
conveys information from the skin surface to the central circuits
Peripheral Somatosensory Receptors (3)
mechanoreceptors
chemoreceptors
thermoreceptors
Mechanoreceptors
responds to mechanical deformation of the body by…
touch
pressure
stretch
vibration
Chemoreceptors
responds to substances released by the cells
including damaged cells following injury, or infection
Thermoreceptors
respinds to heat or cooling
Receptive Field
area of skin innervated by a single afferent neuron
distal parts have higher density of receptors than proximal parts
fields are smaller distally, and larger proximally
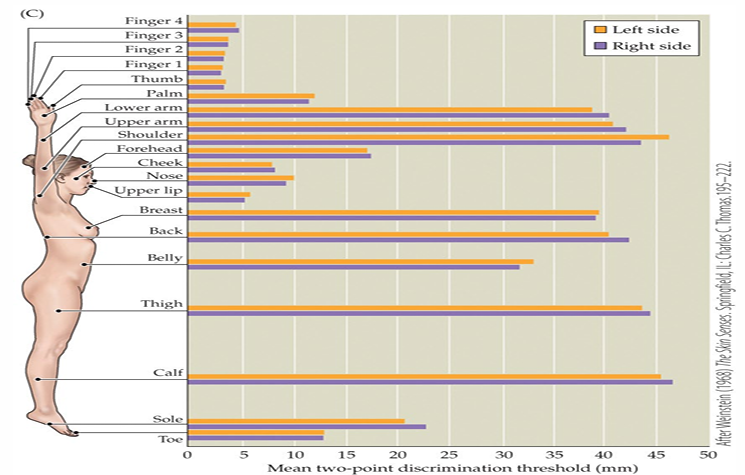
Proprioception Receptors - Location
muscle and joints to sense body position
sensory information sent by musculoskeletal system
Cutaneous Receptors - Responses
pain
temp
touch
vibration
discriminative touch
Cutaneous Receptors - Location
superficial and deep skin
Cutaneous Receptors - Types (6)
free nerve endings
merkel’s disc
meissner’s corpuscles
root hair plexus
ruffini corpuscles
pacinian
Free Nerve Endings
superficial skin touches
Merkel’s Disc
deep skin receptor
Root Hair Plexus
hair movement
Ruffini Corpuscles
intense pressure
C2 Dermatome
back of head
C3 Dermatome
back of neck
C6 Dermatome
outer arm
C7 Dermatome
middle finger
C8 Dermatome
inner arm
T1
armpits
T5
nipple
T10
umbilicus
L3 Dermatome
inner thigh/knee
L4 Dermatome
inner shank
L5 Dermatome
outer shank
S1 Dermatome
outer foot
S2 Dermatome
up posterior
lower extremity
S3,4,5 Dermatome
concentric circles around anus
Sensory Pathways (3)
conscious relay pathway
divergent pathway
nonconscious pathway
Conscious Relay Pathway
brings discriminative info about location to conscious awareness in cerebral cortex
light touch, proprioception, nociceptive, temperature
corresponds to somatotopic areas of brain
Divergent Pathway
bring info to brainstem and a cerebrum
does not correspond to somatotopic areas of brain
Nonconscious Pathway
brings movement related info to cerebellum
Tract, Column, lemniscus, Fascicle
bundle of axons in the CNS with the same origin and end point
Somatosensory Pathways
named for the origin and termination of the tract
contains 2nd neuron in series
Projection Neurons
neurons with long axons that connect distant regions of the nervous system
Sensory Pathways - Parts (3)
first order neuron
second order neuron
third order neuron
1st Order Neuron - Dorsal Column
sensory receptor → medulla (CNS)
located outside spinal cord in dorsal root ganglia
connects to 2nd order in the gray matter of spinal cord
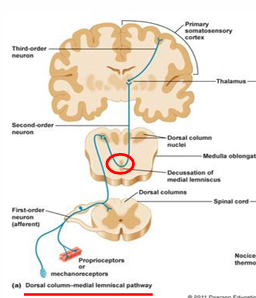
2nd Order Neuron - Dorsal Column
medulla (CNS) → somatosensory thalamus
located in brainstem
can decussate from one side of the CNS to the other
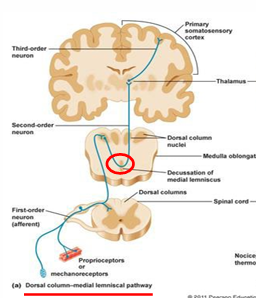
3rd Order Neuron - Dorsal Column
thalamus → cerebral cortex (primary somatosensory cortex)
located in post central gyrus
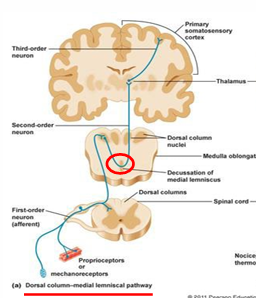
Dorsal Column/Medial Lemniscus Pathway
carries sensation of
touch
conscious proprioception (1/3 head and rest of body)
visceral pain
in the grey matter of the spinal cord
Dorsal Column/Medial Lemniscus Pathway - Cunate Tract
upper limb
trunk
neck
Dorsal Column/Medial Lemniscus Pathway - Gracile Tract
lower limbs
Anterolateral Columns/Spinal Thalamic Pathway
carries sensation of
pain
temp
crude touch (discriminative)
in the white matter of the spinal cord
Crude Touch
nociception & temperature
Nociception
fast, discriminative, lateral or spinothalamic
have c-fibers (unmyelinated) and fibers (myelinated)
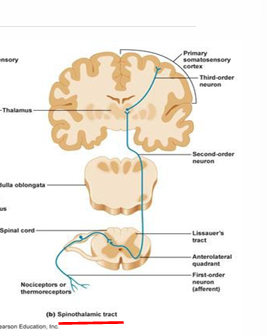
1st Order Neuron - Anterior Column
sensory receptor → dorsal anterior horn
located in white matter of spinal cord
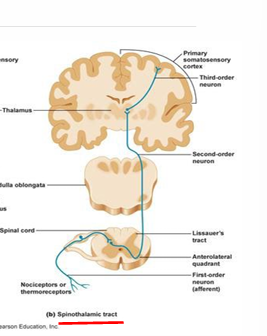
2nd Order Neuron - Anterior Column
decussates at midline
dorsal anterior gray horn → thalamus
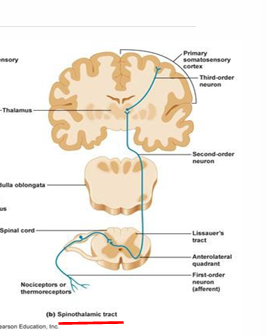
3rd Order Neuron - Anterior Column
thalamus → cerebral cortex
Proprioception
sense that brings awareness to our body’s position in space
Kinesthesia
awareness of body’s movement in space
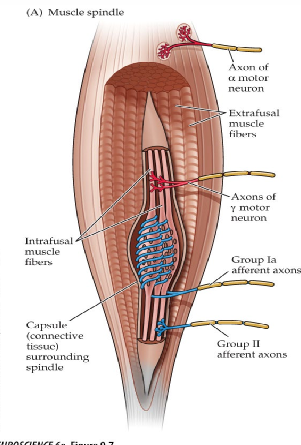
Muscle Spindle
collection of muscle fibers, sensory endings, and motor endings
Sensory Endings
respond to stretch (muscle length)
Afferents - Type 1 A
monitors quick and tonic stretch of a muscle spindle
monitors velocity of change in muscle length
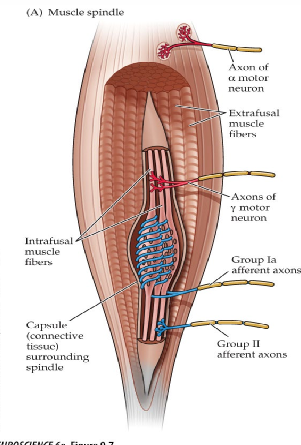
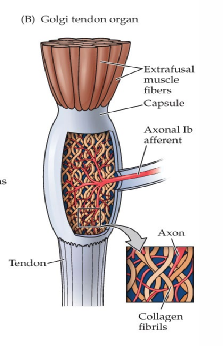
Afferents - Type 1 B
monitors stretch and tension in tendons
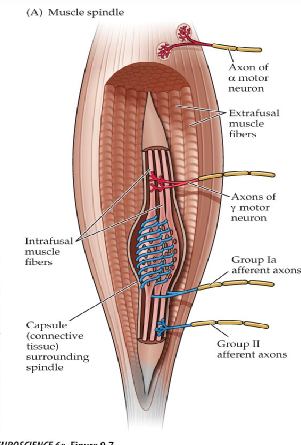
Afferents - Type 2
monitors tonic stretch of muscle
Golgi Tendon Organ (GTO)
provides information about tension in tendons
affected by tension with passive stretch and active contraction
Joint Receptors
responds to mechanical deformation of the capsule and ligaments
Joint Receptors - Types
Ruffini’s Endings (Type 2)
Pacinian Corpuscles (Type 2)
Ligament Receptors (Type 1b)
Free Nerve Endings
Joint Receptor - Ruffini’s Corpuscles
Type 2
signals extreme joint range movement
respond more to passive than active movement
Joint Receptor - Pacinian Corpuscles
Type 2
respond to movement but not when joint position is constant
Joint Receptor - Free Nerve Endings
respond to inflammation
Proprioceptive Pathways (2)
unconscious pathway
conscious pathway
Proprioceptive Pathway - Unconscious
uses spinocerebellar tracts
ends up in cerebellum
'“righting reactions”
Proprioceptive Pathway - Conscious Pathway
uses dorsal column pathway to thalamus
ends up in parietal cortex
ends up in brain making specific decisions to acts
Diabetes
dysfunction in proprioceptive neurons (especially in ankle)
leads to ataxia
Sense of Touch Disorders
diabetes
alcoholism
autoimmune diseases
exposure to toxic chemicals
vitamin deficiency
heart and blood medications
traumatic brain injury
spinal cord injury
brain and spine cancers
ischemia of the spine and brain