VCE Psychology Unit 3 AOS 1
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Role of the nervous system
To receive information externally/internally, process information and coordinate responses to the information
Central nervous system
Consists of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing information and coordinating responses throughout the body.
Peripheral nervous system and role
Nerves outside the central nervous system
Transmits sensory information to the central nervous system and motor information from the brain to the muscles, organs and glands.
Role of the brain
Is responsible for processing sensory information from neural pathways and initiating motor movement.
Role of the spinal cord
Transmitting sensory information received from the PNS to the brain and motor information from the brain to muscles, glands and organs.
Nervous systems in Peripheral NS
somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
A component of the peripheral nervous system that:
Initiates voluntary muscle movement by relaying motor messages to muscles
Enables sensation by relaying sensory info from sensory receptors to CNS
Autonomic nervous system and functions
A component of the peripheral nervous system that:
regulates involuntary bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate, without conscious control.
Relays information from the central nervous system to internal muscles, glands and organs.
nervous systems in Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervou system
Enteric nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system and role
Part of the autonomic nervous system.
Immediately increases the bodily functions and activity at times of vigorous activity, stress or threat.
Activates FFF response
parasympathetic nervous system
Part of the autonomic NS
Gradually decreases bodily activity of visceral muscles, organs and glands to maintain homeostasis.
enteric nervous system
Regulates gastrointestinal functions, controlling processes such as digestion, absorption, and gut motility, often referred to as the "second brain" due to its autonomy.
Conscious responses
Voluntary reactions to stimuli that involve awareness and intention, such as moving your hand to grab a glass.
Unconscious responses
Involuntary reactions to stimuli that occur without conscious awareness
Spinal reflex
An Involuntary, automatic response to a stimulus that involves neural information only reaching the interneuron in the spinal cord through the sensory pathway first and then activating a motor neuron to produce a quick reaction, bypassing the brain.
Eg. touching a hot pan
Visceral muscles
muscles involved in the activity of internal organs and glands like the intestines (also called smooth muscles)
skeletal muscles
muscles attached to bone and require motor messages to function
sensory neurons
Neurons that receive and carry sensory information from external and internal environments to the central nervous system
afferent
neural pathways that lead to the central nervous system and brain
motor neurons
Neurons that carry information from the central nervous system to skeletal muscles, organs and glands to stimulate activity
efferent
neural pathways that direct information away from the central nervous system towards relevant organs, glands, and muscles
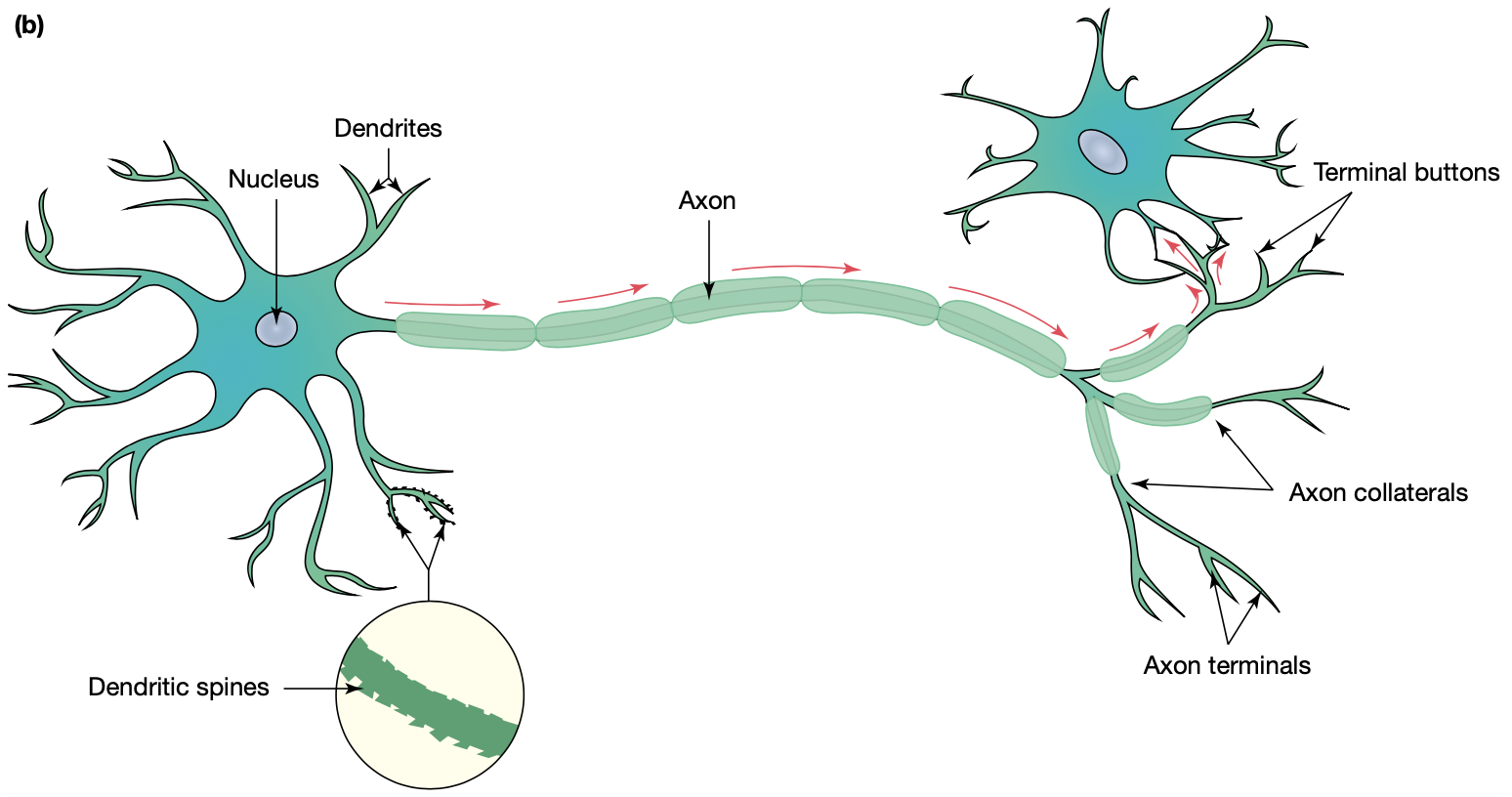
soma
cell body
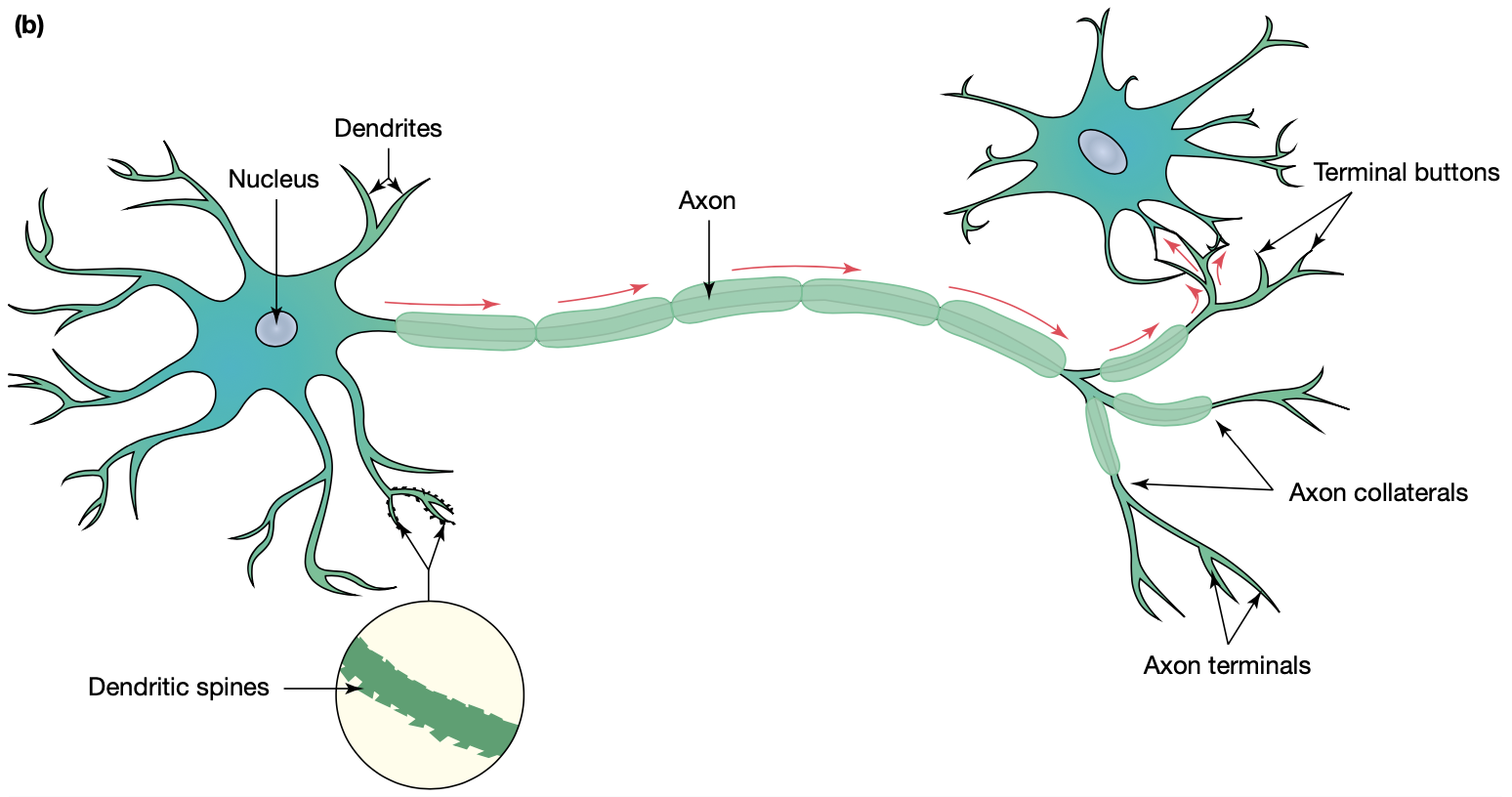
dendrites
transmit information to the soma
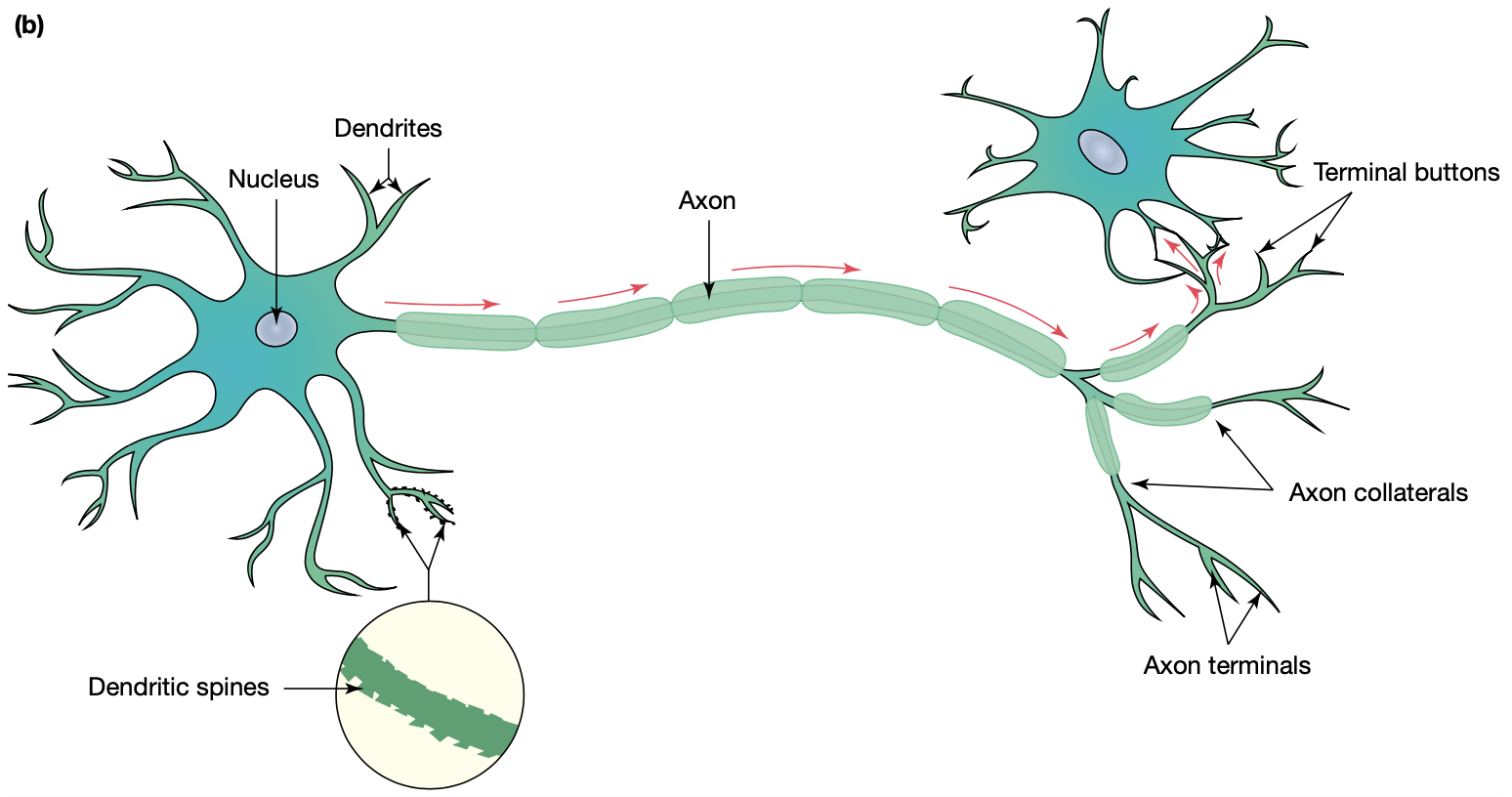
axon
transmits information from the soma to the axon terminals
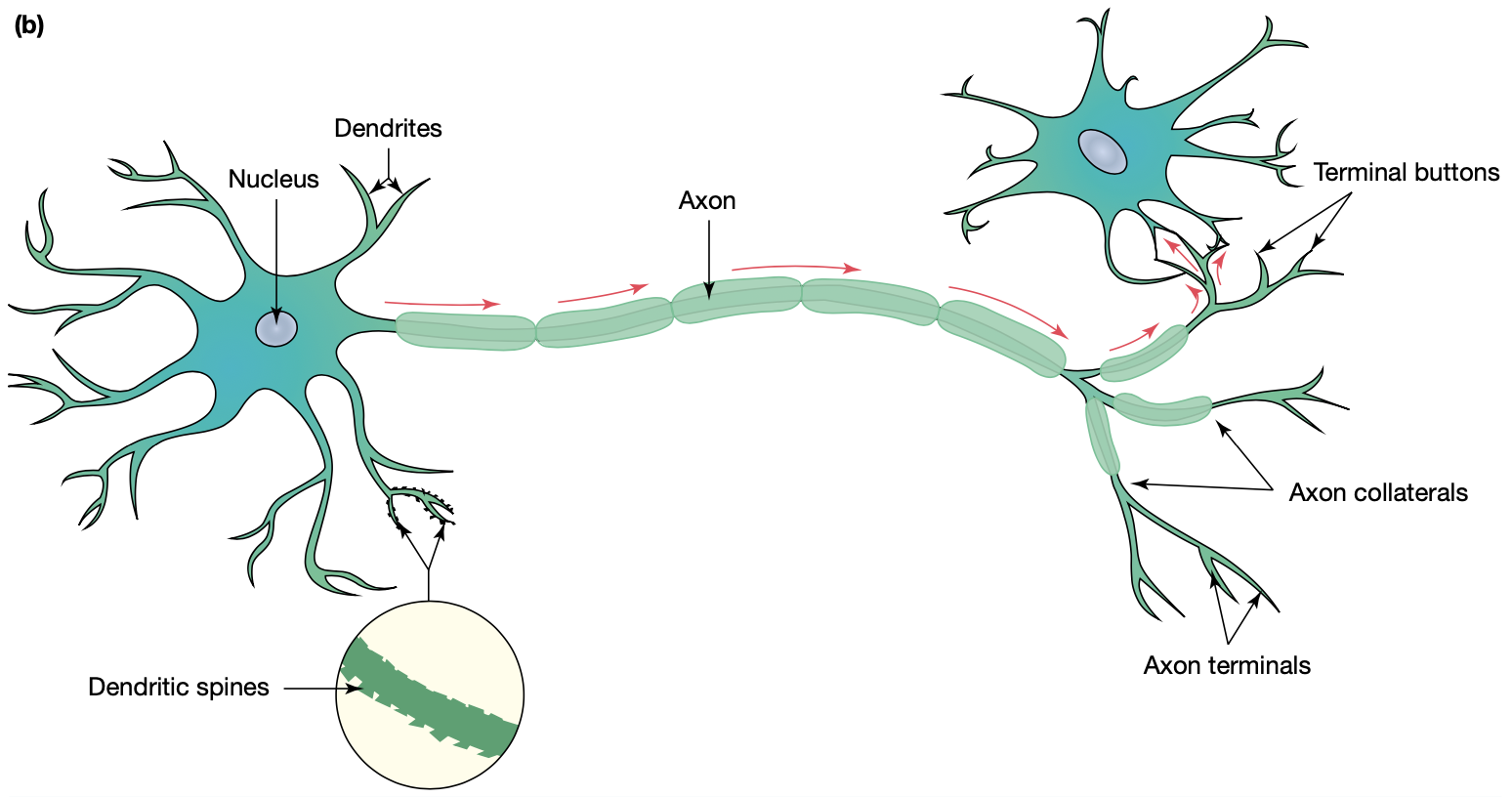
axon terminal
branches at the end of the axon that
‘synapse’ with other cells
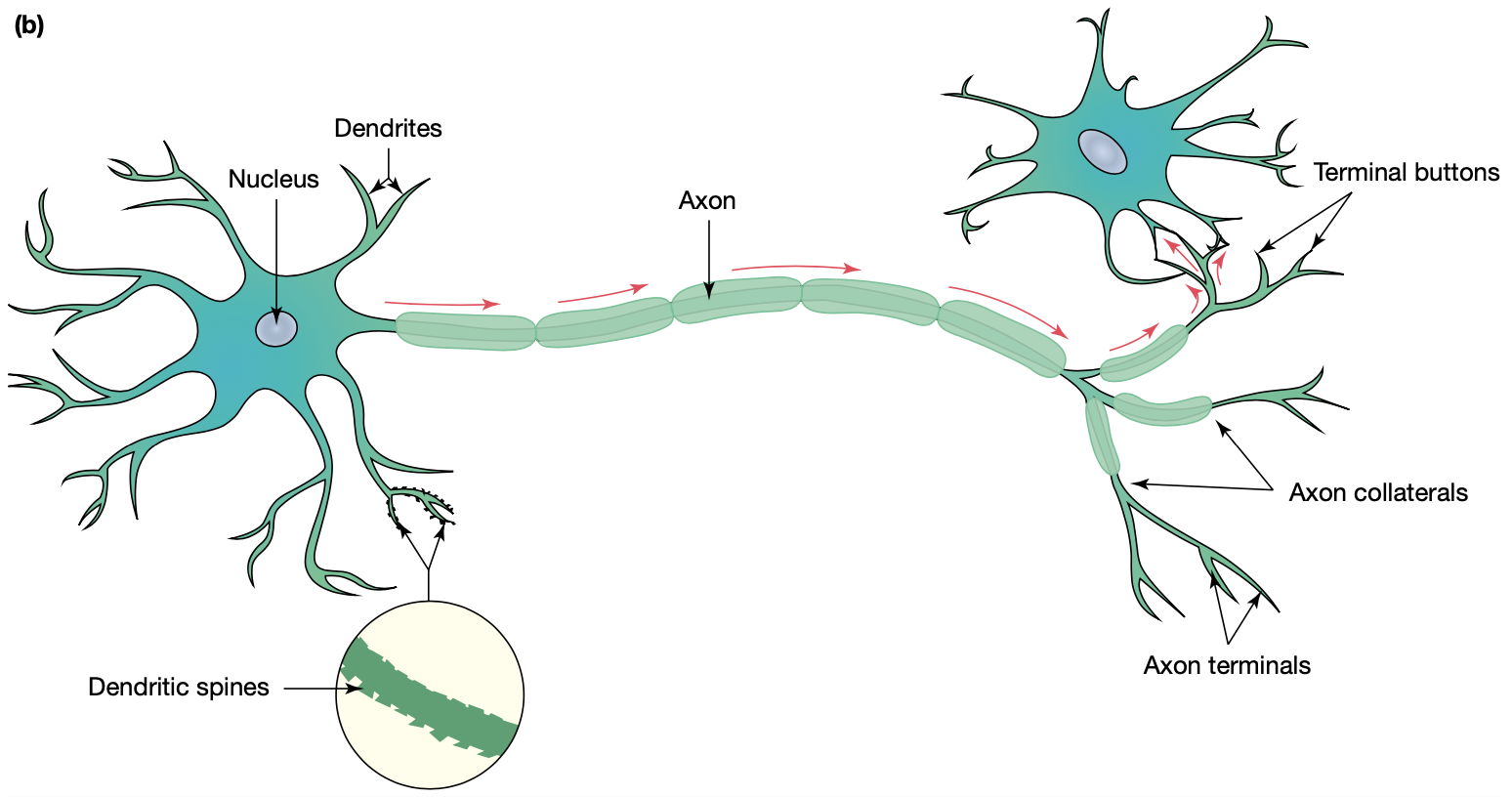
myelin
fatty substances that insulates axon allowing messages to travel faster
neurotransmitters
chemical substances that carry messages to other neurons, glands and muscles
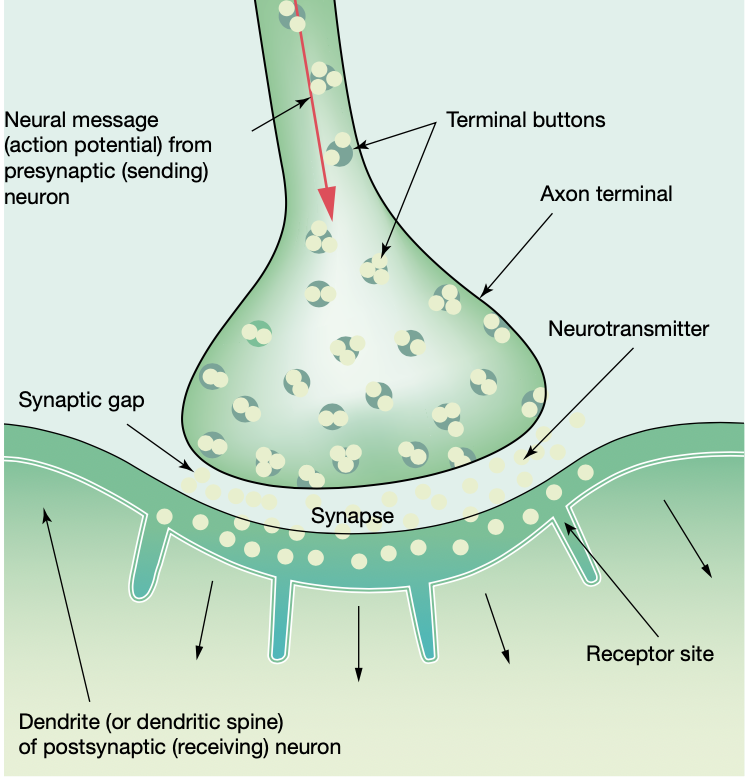
synapse
site where neuron communication occurs
neurotransmission
communication between neurons by neurotransmitters binding to receptor sites of the post-synaptic neuron.
excitatory neurotransmission
excites postsynaptic neurons to promote activity
inhibitory neurotransmission
blocks or prevents post synaptic neuron firing
glutamates
main excitatory neurotransmitter increases likelihood of post synaptic neuron firing and is involved in learning and memory.
gaba
primary inhibitory neurotransmitters in central nervous system that makes postsynaptic neurons less likely to fire.
interneuron
neurons that relay information between sensory and motor neurons
sensory receptors
sensory nerve endings that when stimulated, produce an afferent or sensory impulse
synaptic vesicle
a membrane- bound sphere filled with neurotransmitter molecules
synaptic gap
the space between the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron and the membrane of the post-synaptic neuron
receptor site
a membrane protein on the dendrites of neurons that receive and detect specific neurotransmitters
neuromodulators
a subclass of neurotransmitters that alter the strength of neural transmission by increasing or decreasing the responsiveness of neurons to neurotransmitter signals
dopamine
a multifunctional neurotransmitter with both excitatory and inhibitory effects, is involved in many central nervous system functions such as movement, pleasure, attention, mood, cognition and motivation
reward pathway
a group of structures in the brain that are activated by rewarding or
reinforcing stimuli
serotonin
an inhibitory neurotransmitter that also acts as a neuromodulator, influencing a variety of brain activities
serotonin pathway
serotonin’s neuromodulatory system, which originates in the brainstem and extends to almost all areas of the cerebrum including the cerebral cortex
synaptic plasticity
changes that occur in the synapse between neurons leading to the strengthening or a weakening of neural connections.
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
the relatively permanent strengthening of synaptic connections as a result of repeated activation of a neural pathway
Long-term depression (LTD)
the relatively permanent weakening of synaptic connections as a result of repeated low- level activation
sprouting
the growth of axon or dendrite fibres at the synapse
dendritic spines
a dendrite fibre that grows by sprouting on the post-synaptic neuron
filigree appendages
a fibre that sprouts from the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron
synaptogenesis
the formation of new synapses that result from sprouting
rerouting
the formation of new neural connections to establish alternative neural pathways
pruning
the removal of excess neurons and synaptic connections to increase efficiency of neuron transmissions
stressor
any event that causes you stress
stress
a state of mental, emotional, physiological tension resulting from a stressor
internal stressor
cause of stress that comes from within the individual and can be psychological or biological
external stressor
cause of stress that comes from outside the individual and can be environmental or sociocultural
acute stress
stress that usually occurs because of a sudden threat and only lasts for a short time
chronic stress
stress that lasts for a long time and can be detrimental to long term health
Flight or fight or freeze response
an automatic biological response to a perceived stressor that increases our chances of survival in our environment
cortisol
a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that regulates a wide range of bodily processes, including metabolism, and is released in response to stress
appraisal
the process of categorising an event on the basis of its perceived significance and how it may affect our wellbeing
General adaptation syndrome
a biological model of stress that proposes
we have a non-specific biological response to stress that occurs in three stages
Alarm reaction stage
the first stage of the general adaptation syndrome, in which we become aware of the stressor.
Consisting of two phases: shock and countershock
Shock
the first phase of the alarm reaction of the GAS, where the body’s ability to deal with the stressor falls below normal
Countershock
the second phase of the alarm reaction of GAS, where the body’s ability to deal with the stressor rises above normal
Resistance stage
the second stage of GAS, where the stressor persists, and the body’s resources are maximised to cope and adapt over time
Exhaustion stage
the third stage of GAS, where the continued depletion of energy stores and high levels of cortisol decrease resistance to the stressor and supress the immune system
Transactional model of stress
a model that suggests a stress response is only elicited if an event is perceived to exceed our ability to cope and is based on our appraisal of the situation
Primary appraisal
when an individual determines whether a situation or event is significant to them and stressful or not
Irrelevant
when an event is not stressful: the event has no implications for an individual’s wellbeing because nothing will be gained or lost, or they are not invested in the situation
Benign/positive
when an event is not stressful: it is perceived as having a positive outcome for an individual. It either maintains or enhances their wellbeing
Threat
event is stressful: the anticipated harm/loss in the future because of an event
Harm/loss
event is stressful: the damage to the individual that has already occurred as a result of a stressor
Challenge
the event is stressful and significant but there is potential for personal gain or growth from it
Secondary appraisal
when the event is stressful and an individual considers the available resources and their own coping strategies, to decide the best way of dealing with a stressor
coping
the things we do to manage and reduce the stress we experience
coping strategy
a method that we use to manage or reduce the stress produced by a stressor
Coping flexibility
the ability to modify our coping strategies to adapt and meet the demands of different stressful situations
context specific effectiveness
when a coping strategy matches or is appropriate to the stressful situation
approach strategy
an effort to confront a stressor and deal directly with it and its effects
avoidance strategy
an effort to avoid a stressor and not deal directly with it and its effects
Differences of Neurotransmitters and Neuromodulators
Neuromodulators:
release into multiple synapses effecting multiple post-synaptic neurons
influences responsiveness of neurons to NT signals
release slower but have longer lasting effect
Neurotransmitters:
effect one or two post-synaptic neurons
increase or decrease likelihood of firing
release faster but have shorter effect
Effects of cortisol
Increases metabolism
Energises body
Suppresses immune system functioning
Depletes bodily resources
- increased vulnerability to diseases; colds, hypertension, diabetes
Gut-brain axis
Bidirectional communication link between CNS and ENS via Vagus Nerve
Explanatory power of GAS
Strengths
- identifies physiological processes
- suggests stress weakens ability to resist infection
Limitations
- overlooks individual differences
- research done on rats
Explanatory power of Lazarus and Folkman's Transactional Model of stress and coping
Strengths
- identifies psychological processes
- provides different methods of coping
limitations
- ignores physiological processes
- subjective therefore hard to test