Exam Three
1/120
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
If a species is oxidized, then …
it loses electrons
If a species is reduced, then …
it gains electrons
What is the redox reaction Mnemonic?
OIL RIG
Why do we care about redox reactions?
Corrosion
Photosynthesis
Batteries
Analytical Electrochemistry
What is a battery?
A device that stores electrical energy using chemical reactions. We set of redox reactions in separate cells that are compatible with manufacturing processes that give a useful amount of potential energy (voltage)
How is the chemical energy of a battery harvested?
By connecting the battery to a load in a circuit.
What is the most well known rechargeable battery?
The lithium ion battery that is actually not oxidized or reduced, acting as a positive charge compensation. The electrode materials have a layered structure.
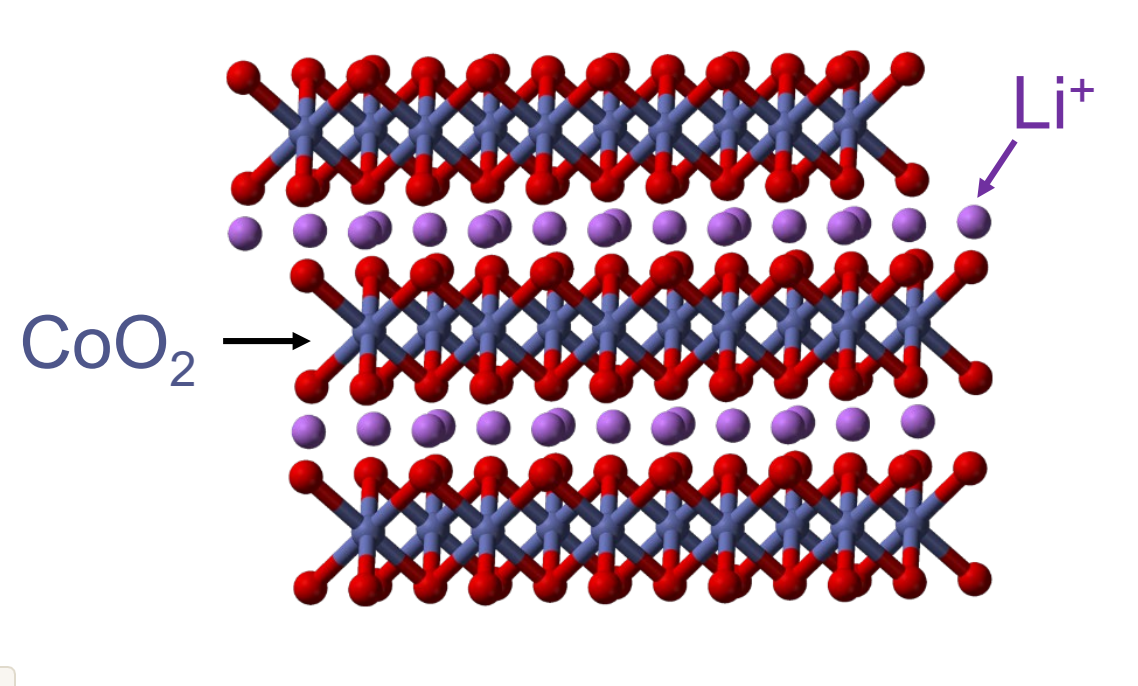
What is a galvanic cell?
A type of electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy into electrical energy through spontaneous redox reactions, typically consisting of two half-cells connected by a salt bridge.
Is the anode the oxidation or reduction reaction?
The anode is the site of oxidation in an electrochemical cell, where electrons are released.
Is the cathode the reduction or oxidation reaction?
The cathode is the site of reduction in an electrochemical cell, where electrons are gained.
What is the equation for the overall charge of a galvanic cell?
∆E = Ecathode - Eanode
The oxidizing agent is the species that is …
reduced in a chemical reaction, causing oxidation of another species.
The reducing agent is the species that is …
oxidized in a chemical reaction, causing reduction of another species.
The energy of an electron transfer reaction can be directly related to the voltage or electrical potential difference created in the system as represented by the equation ∆G = -nNFE. What is n?
charges per molecule or atom
The energy of an electron transfer reaction can be directly related to the voltage or electrical potential difference created in the system as represented by the equation ∆G = -nNFE. What is N?
Moles
The energy of an electron transfer reaction can be directly related to the voltage or electrical potential difference created in the system as represented by the equation ∆G = -nNFE. What is F?
Faraday’s Constant (Coulombs/mole) (9.649×104)
What is line notation of a galvanic cell?
A schematic representation of a galvanic cell that indicates the components of the cell and the direction of electron flow, typically written as anode | electrolyte | cathode.
Why do scientist coat silver electrodes with chloride?
To prevent corrosion and improve the stability of the electrode, as silver chloride is less reactive than silver.
Why do cells with cadmium metal and Silver chloride electrodes work, but the simpler cadmium and silver electrodes only work for brief period of tiime?
Cells with cadmium metal and silver chloride electrodes are more stable and less prone to corrosion, allowing for a longer operational lifespan compared to simpler cadmium and silver electrodes that can degrade quickly.
How do we avoid rapid degradation of electrodes?
Using a Salt Bridge
What is needed to build a galvanic cell?
Metals/Ions that transfer electrons
Typically Metal Electrodes
Dissolved salts of the metals
Salt Bridge with Inert Charge Carriers in Separate cells
What is the purpose of standard reduciton potential?
To measure the tendency of a chemical species to gain electrons and be reduced, helping to predict the direction of redox reactions. In a table these values are all wrote in the reduction form.
What do we mean by standard form in Standard Reduction Potential?
All atoms have an activity of one.
What does the standard reduction potential reference and what is the line notation for the system?
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode, Pt(s) l H2(g) l H+ (aq, Å=1) ll Ag+ (aq, Å=1) l Ag(s)
What is the purpose of a salt bridge?
To maintain a separation of electron transfer reactions into half-cells which allows exploitation of the chemically induced electrical energy.
True or False
The SHE has a potential of 0 arbitrarily.
true
When is a reaction spontaneous?
When Eºrxn > 0
What do we use to determine E-values under non standard conditions?
The Nernst equation is used to calculate E-values under non-standard conditions, allowing for adjustments based on concentrations and temperature.
What is the Nernst equation?
E = Eº - (0.05916V/n) • log(ÅBb/ÅAa)
Fill in the Blank:
A galvanic cell (also known as _______) uses a __________ reactions (∆G < 0) to generate electrical energy.
voltaic cells; spontaneous
What direction under standard conditions do the electrons flow?
From the anode to the cathode.
What does “n” represent in Nernst Equation?
The number of moles of electrons in the half reactions.
What is the Nernst Equation not at 25ºC?
E = Eº - RT/nF (ln(ABb/AAa)
What is the first step to solve the Nernst Equation?
Write the reduction half-reactions for both half-cells and find Eº for each. Mulitply the hal-reaction so that they contain the same number of electrons. When you multiply a reaction, you do not multiply Eº.
What is special about Eº when finding voltage?
It is an intensive property meaning that it does not depend on the amount of substance present.
What is the second step to solve the Nernst Equation?
Write a Nernst equation for the right half-cell attached to the positive terminal of the potentiometer (cathode). This is Ecathode.
How do you determine the Ecathode if this is unknown.
Use ∆G.
What is the third step to solve the Nernst Equation?
Write a Nernst equation for the left half-cell attached to the negative terminal of the potentiometer (anode). This is Eanode.
What is the fourth step to solve the Nernst Equation?
Find the net cell voltage by: E = Ecathode - Eandode (Anode reaction is reversed)
What is the fifth step to solve the Nernst Equation?
Write the net cell reaction by subtracting the anodic half-reaction from the cathodic half-reaction. This involves balancing the electrons and combining the half-reactions to show the overall reaction.
Why do galvanic cells produce electricity?
They are not in equilibrium?
What happens when a battery reaches 0V?
The chemical inside have reached equilibrium and the battery is “dead”.
When E=0 what happens with the Nernst Equation?
The Q is Equal to K therefore, K = 10nE/0.05916
If the standard hydrogen electrode is defined with an H+activity of 1.0, which means pH = what?
0
What are standard potentials defined for?
ph = 0
What are formal potentials for biochemistry defined for?
pH = 7
Which direction do electrons flow in electrochemistry?
From the more negative to the more positive electrode.
What is the purpose of a reference electrode in a three electrode cell?
To provide a stable voltage reference for measuring the potential of the working electrode.
If there is a change in concentration, binding, or chemical interactions, then …
more current is required
What is the amount of current supplied to a system directly proportional to?
The concentration
What is the first step to determine the Nernst Equation with activities?
Consider the µ for each cell
What is the second step to determine the Nernst Equation with activities?
Find Activity Coefficients
What is the third step to determine the Nernst Equation with activities?
Fill in the Nernst eq
What is electrolysis?
The foricng of e- transfer reactions in a non-spontaneous direction with an external power supply
What is an electrolytic cell?
An electrolytic cell is a device that uses electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions, typically involving the transfer of electrons during electrolysis. With both electrodes in the same containter.
In an electrolytic cell, what is the positive electrode?
anode
What does the electrode driven by the power supply serve as?
A tightly controlled reactant allowing us to carefully study e- reactions
In reality what else other than activities can affect the potential of a cell?
Ohmic potential, overpotential are both examples
What is a three-electrode cell?
A three-electrode cell is an electrochemical cell configuration that includes a working electrode, a reference electrode, and a counter electrode, allowing for precise measurement of the electrochemical reactions occurring at the working electrode.
What metal is the reference electrode typically?
A silver/silver chloride or calomel electrode.
What does the potentiostat circuit ensure?
The potentiostat circuit ensures that the potential difference between the working electrode and reference electrode remains constant, enabling accurate control of the electrochemical process.
What do you call when a chemical reaction is fore to occur at an electrode by an imposed voltage?
Electrolysis
What does electrically biasing an electrode do?
It alters the electrode's potential to drive a reaction or control ion transfer.
If there is a negative bias at an electrode, then …
there are more reducing electrons leading to reduction
If there is a positive bias at an electrode, then …
there are more oxidizing electrons leading to oxidation
Even though the potential of an electrode is a range, what do all redox species have?
An intrinsic potential at which they exchange electrons with other species at equilibrium.
By changing the potential of an electrode what can we change?
The Fermi level or the change in the energy needed to facilitate electron transfer between species.
In a 3 electrode cell what is the working electrode?
The electrode where the analyte reaction occurs, typically the site of interest for measuring electrochemical activity.
In a 3 electrode cell what is the counter/auxillary electrode?
The electrode that completes the circuit by allowing current to flow, often used to balance the reaction occurring at the working electrode.
A 3 electrode system is just a feedback control system. What is that?
It is an electrochemical setup that regulates the potential of the working electrode through the measurement and adjustment of current, ensuring accurate and controlled analyte reactions.
In Amperometery, we record the current needed to maintain constant potential, what does this give us?
information about the electrons transfer reaction at the working electrode.
What is amperometry?
an electrochemical technique that measures the current generated by a redox reaction occurring at an electrode, providing quantitative information about the analyte concentration.
What is widely used in medicine and biology to measure dissolved oxygen?
Clark Oxygen electrode
What use biological components such as enzymes, antibodies, or DNA for a highly selective response to one analyte?
Biosensors
How does a molecule get to the electrode in a Rotating Disk electrode?
Through diffusion (concentration gradient), Convection (mixing, stirring), or Migration (attraction or repulsion)
How is diffusion limited surrent partially compensated for?
by using a roating disk electrode.
What are the applications of amperometry?
Sensing O2, measuring glucose levels, detecting neurotransmitters.
What can biomolecules be leveraged to do?
To improve analytical selectivity and sensitivity in biosensors.
In voltommetry what do we observe?
The current as a function of the applied potential, which helps to determine the concentration of analytes.
What is the potentiostat programmed to view during Voltammetry?
The sweep of the potential.
Why does the current of a system once a final voltage is reached not return to 0?
This occurs because of the presence of residual current due to irreversible reactions or capacitance effects in the system. Such as the depposition of a product on the electrode surface, which can maintain a non-zero current after the applied voltage sweep.
What is linear sweep voltametry?
A technique where the potential is linearly swept from a starting value to an endpoint, measuring the resulting current over time, often used to analyze electrochemical properties.
From both LSV and CV we get information about what?
The species diffusion, such as the diffusion limited current.
How do we “smooth” a curve in voltammetry?
By mixing the solution using a Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE)
Where does current and potential become directly proportional in voltammetry?
Near the reversible region of the voltammogram. (Slightly past the E{1/2} value of the redox couple.
What is the purpose of the Randles-Ševčǐk equation?
To relate the peak current to the concentration of the electroactive species in voltammetry.
What is the Randles-Ševčǐk equation?
IP = 0.4463 • nFAC • (nF𝓋D/RT)1/2 = 2.69 × 105 n3/2AC√D𝓋
What do we see from the Randles-Ševčǐk equation?
That a faster scan rate, 𝓋, means a higher current, IP
Using R.S. Eq. If we have IP, 𝓋, A, C, T, then…
we can measure the diffusion coefficient
There are two effects that happen at the surface of the electrode; Fardaic and Non-Faradaic Current. What is Faradaic Current?
Electron transfer reactions that occur at the electrode surface, resulting in measurable current due to the oxidation or reduction of a species.
What is non-faradaic current?
Current associated with analyte independently such as charging current or capacitive current.
What is cyclic voltammetry?
A technique used to study electrochemical reactions by cycling the potential of a working electrode and measuring the resulting current.
What information can be gathered from Cyclic Voltamettry?
Information about the Reversibility of a Reaction
The diffusion Coefficient
The formal potential E1/2 ≅ Eº’
The number of electrons
In a cyclic voltammetry system at 25ºC what is the ∆E or the Epa - Epc equal to?
57 mV/n for a one-electron transfer reaction at room temperature.
What is the average of the two electrodes in a cyclic voltammetry system equal to?
The average of the two electrodes is equal to the formal potential or E1/2.
What is Square-Wave Volttametry and what is the purpose?
an electroanalytical technique that combines features of both pulse and continuous voltammetry. Its purpose is to enhance sensitivity and resolution in the detection of analytes by applying square-wave potential pulses superimposed on a staircase waveform.
What do we observe during voltammetry?
The relationship between current adn potential during electron transfer reactions
What is a potentiostat used for?
To control potential while current is measured at the working electrode.
In voltammetry what is the data plotted as?
Curved of current versus potential.
What is the plot of current versus potential referred to as?
Voltammogram