Anatomy Exam #2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/428
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
429 Terms
1
New cards
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
1. Support of the entire body
2. Protection of organs
3. Movement/attachment of muscles
4. Hemopoiesis
5. Energy metabolism
6. Mineral reserves
2. Protection of organs
3. Movement/attachment of muscles
4. Hemopoiesis
5. Energy metabolism
6. Mineral reserves
2
New cards
Viscera
Organs
3
New cards
Hemopoiesis
Blood cell production
4
New cards
Where do bones meet?
Joints
5
New cards
Are bones considered organs?
Yes, bones are made up of multiple types of tissues so they are considered organs
6
New cards
Is the skeletal system internal or external?
Internal
7
New cards
How many bones are there in an adult human body?
206
8
New cards
Skeletal System Parts
1. Bones
2. Cartilages
3. Joints
4. Ligaments
2. Cartilages
3. Joints
4. Ligaments
9
New cards
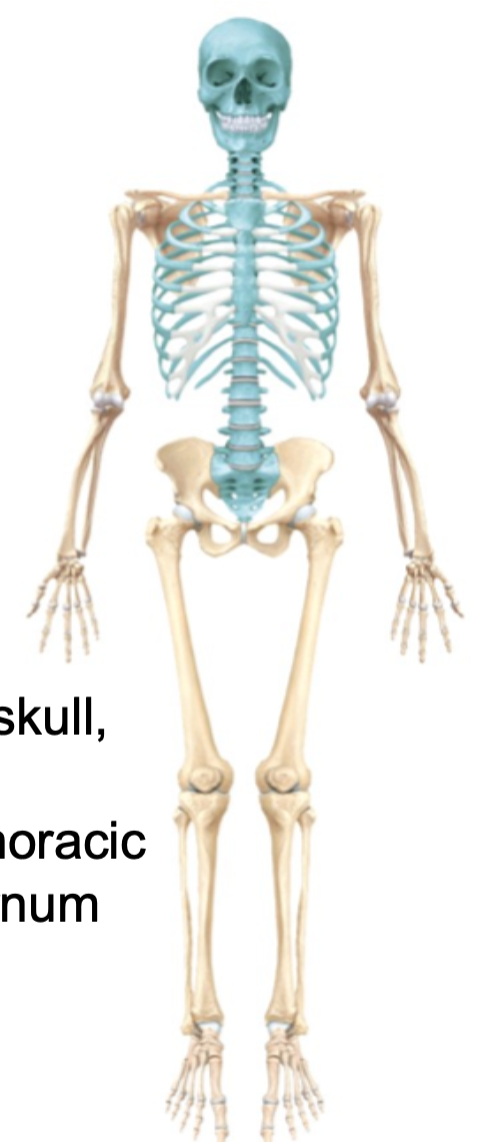
Axial Skeleton
1. Skull
2. Vertebral column
3. Thoracic cage (sternum and ribs)
4. Hyoid bone
5. Sacrum
6. Coccyx
7. Includes 80 bones all together
2. Vertebral column
3. Thoracic cage (sternum and ribs)
4. Hyoid bone
5. Sacrum
6. Coccyx
7. Includes 80 bones all together
10
New cards
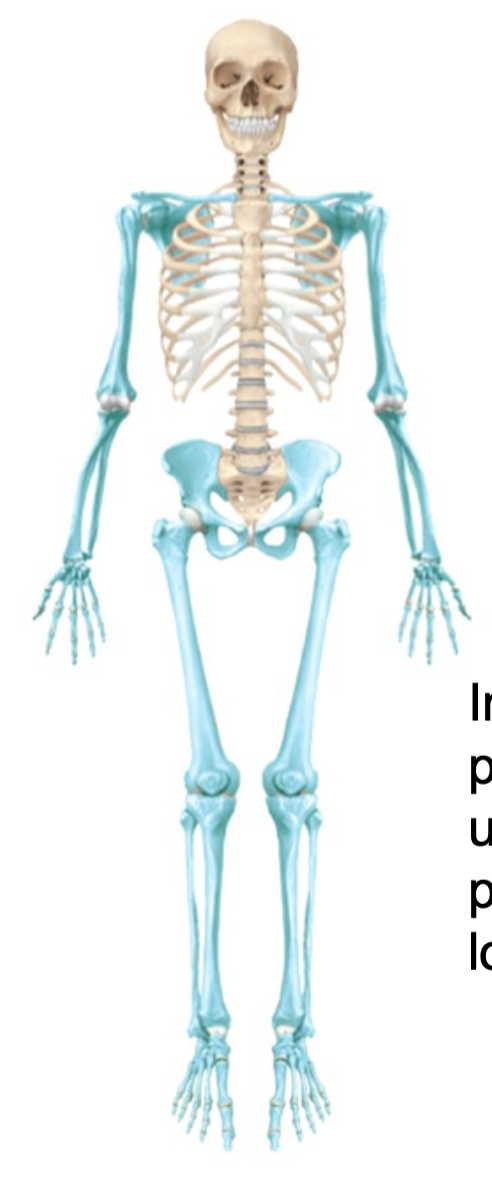
Appendicular Skeleton
1. Pectoral girdle
2. Upper limbs
3. Pelvic girdle
4. Lower limbs
5. Includes 126 bones all together
2. Upper limbs
3. Pelvic girdle
4. Lower limbs
5. Includes 126 bones all together
11
New cards
Axial Skeleton Function
1. Supports head, neck, and trunk
2. Protects brain, spinal cord, and thoracic organs
2. Protects brain, spinal cord, and thoracic organs
12
New cards
Appendicular Skeleton Function
Supports the attachment and functions of the limbs of the human body
13
New cards
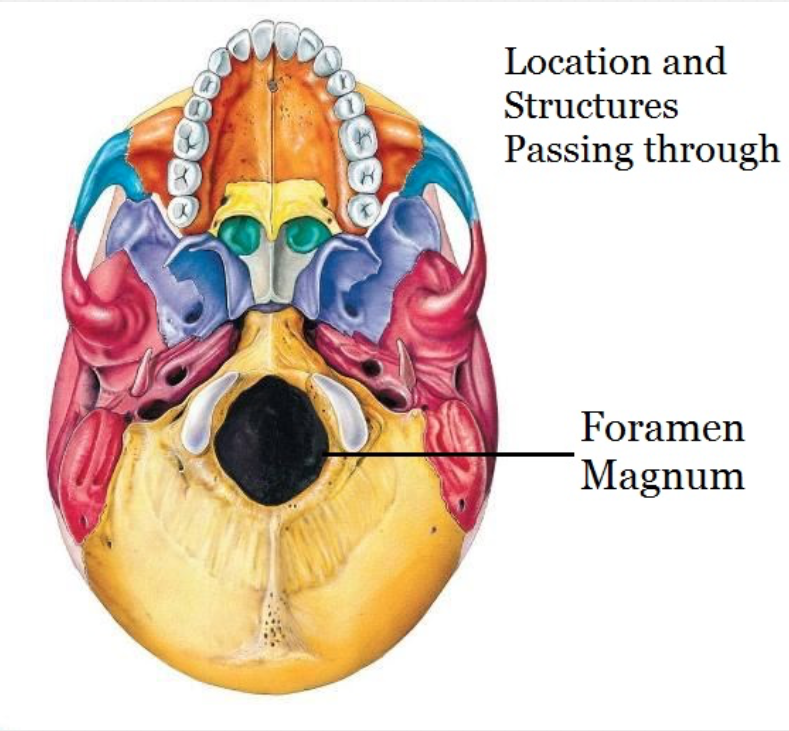
Foramen
1. AKA Foramina
2. A hole in a bone
- Typically for nerves or blood vessels
3. Examples; foramen magnum, infraorbital foramen
2. A hole in a bone
- Typically for nerves or blood vessels
3. Examples; foramen magnum, infraorbital foramen
14
New cards
Fossa
1. AKA fossae
2. A depression in a bone
3. Examples; mandibular fossa, lacrimal fossa
2. A depression in a bone
3. Examples; mandibular fossa, lacrimal fossa
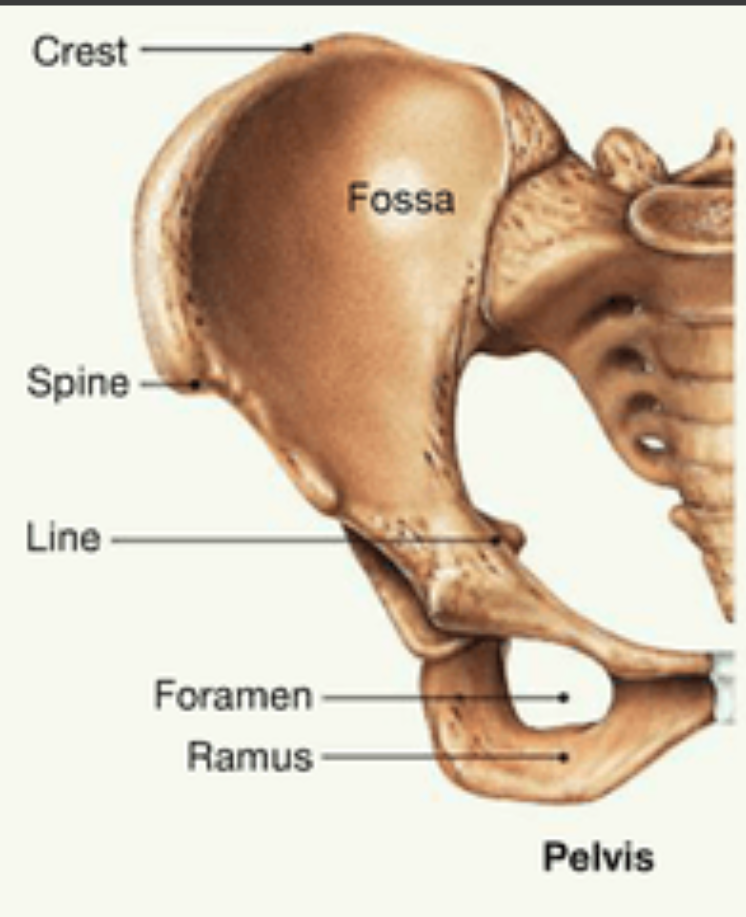
15
New cards
Process Bone Marking
1. Projection from bone
2. Narrow or wide
3. Protrudes from surrounding bone
4. Examples; styloid or mastoid process
2. Narrow or wide
3. Protrudes from surrounding bone
4. Examples; styloid or mastoid process
16
New cards
Meatus
1. A hole or tube-like structure
2. Passage or opening
3. Example; auditory meatus
2. Passage or opening
3. Example; auditory meatus
17
New cards
Canal
1. A groove or tube-like structure
2. Example; optic canal
2. Example; optic canal
18
New cards
Bone
1. Strong and stiff
2. Mineral reservoir
3. Muscle attachment sites
4. Protection
2. Mineral reservoir
3. Muscle attachment sites
4. Protection
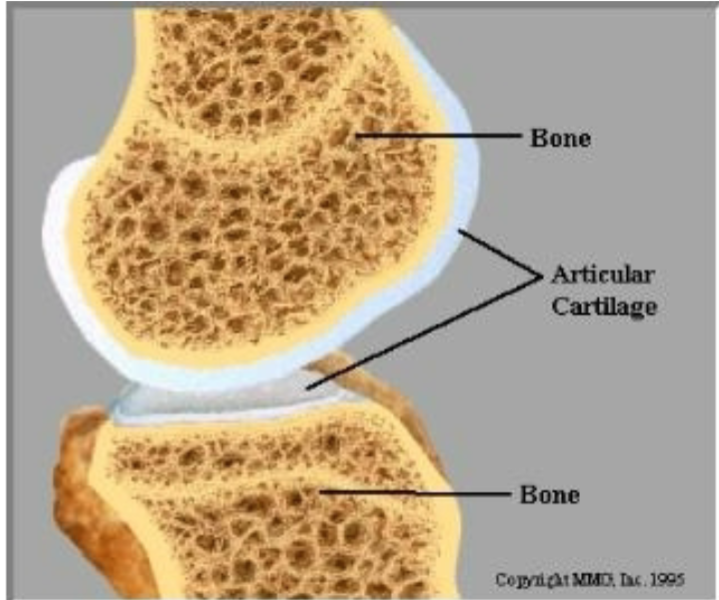
19
New cards
Cartilage
1. Flexible
2. Resilient (mostly water)
3. Resists tension and compression
2. Resilient (mostly water)
3. Resists tension and compression
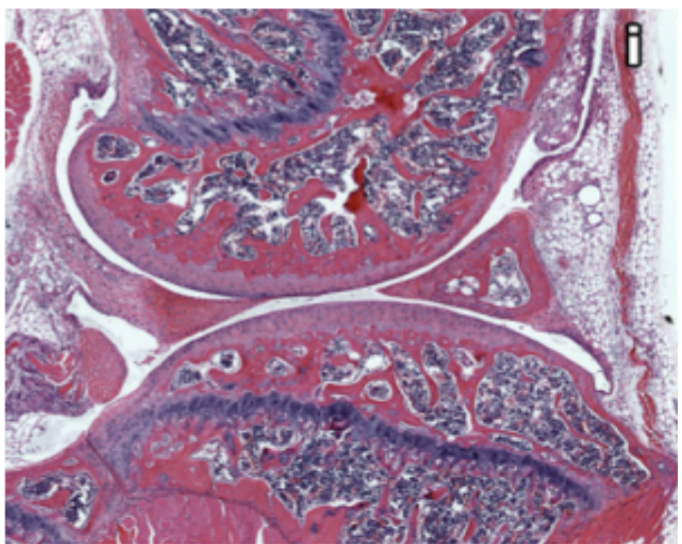
20
New cards
Cartilage Tissue Structure
1. Avascular
2. Cells are chondrocytes found in lacunae
3. Three types
- Hyaline
- Elastic
- Fibrocartilage
2. Cells are chondrocytes found in lacunae
3. Three types
- Hyaline
- Elastic
- Fibrocartilage
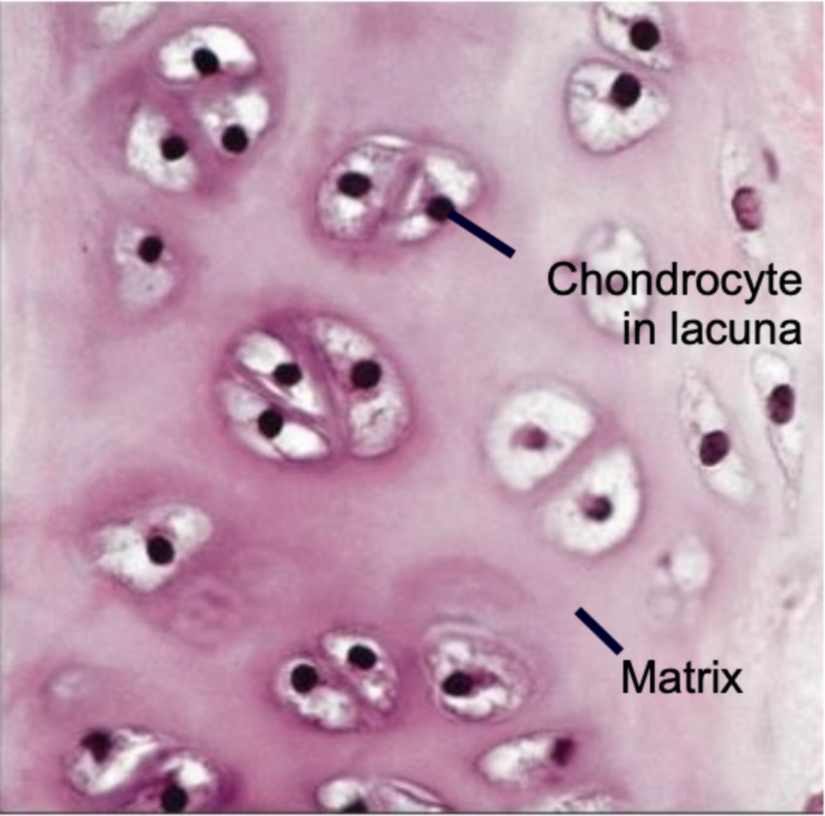
21
New cards
Avascular
No blood vessels
22
New cards
Cartilage Tissue Functions
1. Support soft tissues
2. Model for formation of bone
3. Gliding surface at articulations
2. Model for formation of bone
3. Gliding surface at articulations
23
New cards
Is cartilage soft bone?
NO
24
New cards
Hyaline Cartilage
1. Most common
2. Contains nearly invisible collagen fibers (fibrils)
3. Found in
- Ends of long bones
- Costal cartilages
- Articular joint cartilage
- Respiratory structures (larynx, trachea)
- Fetal/embryonic skeleton
2. Contains nearly invisible collagen fibers (fibrils)
3. Found in
- Ends of long bones
- Costal cartilages
- Articular joint cartilage
- Respiratory structures (larynx, trachea)
- Fetal/embryonic skeleton
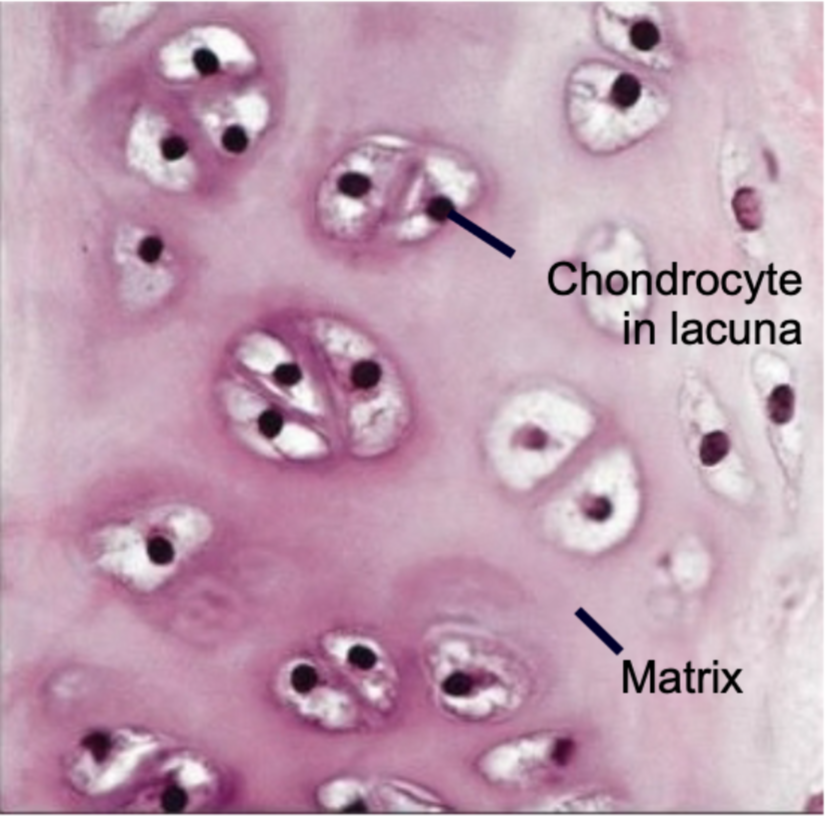
25
New cards
Elastic Cartilage
1. Similar to hyaline cartilage
2. Contains lots of elastic fibers
3. VERY resilient and flexible
4. Tolerates repeated bending
5. Found in
- Pinna (outer ear)
- Epiglottis
2. Contains lots of elastic fibers
3. VERY resilient and flexible
4. Tolerates repeated bending
5. Found in
- Pinna (outer ear)
- Epiglottis
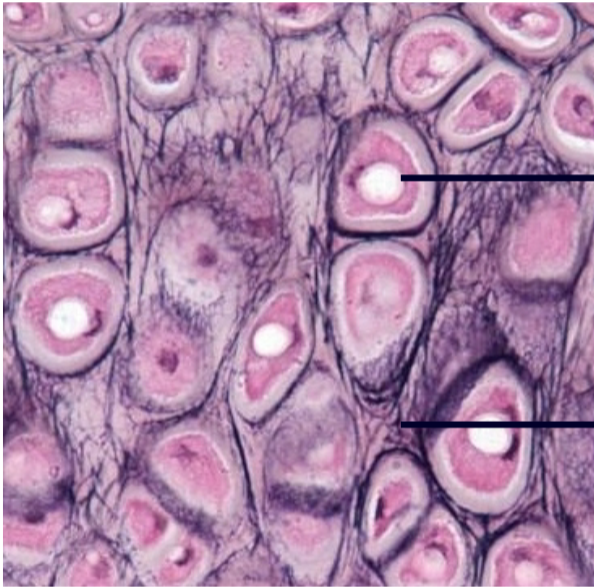
26
New cards
Fibrocartilage
1. Contains little ground substance
2. Matrix has thick, dense collagen fibers
3. Resists strong compression
4. Found in
- Intervertebral disks
- Knee joint
- Pubic symphysis
- Meniscus
2. Matrix has thick, dense collagen fibers
3. Resists strong compression
4. Found in
- Intervertebral disks
- Knee joint
- Pubic symphysis
- Meniscus
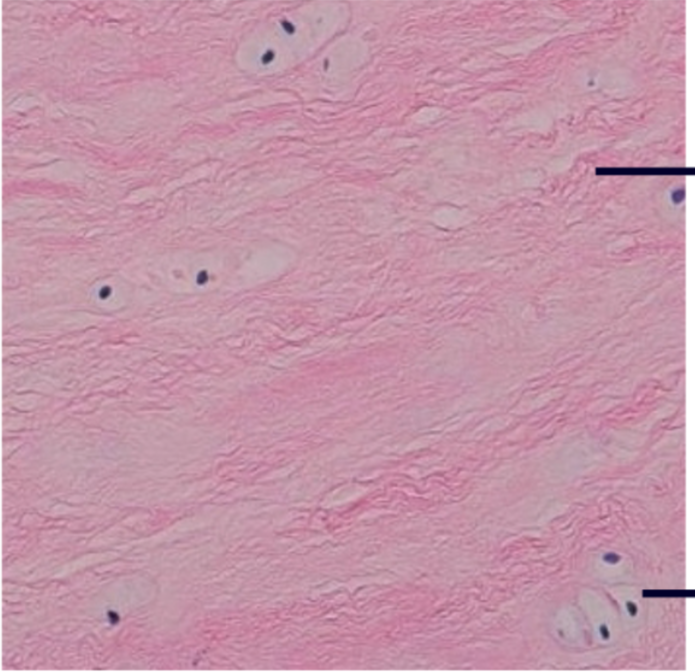
27
New cards
Cartilage Locations Diagram
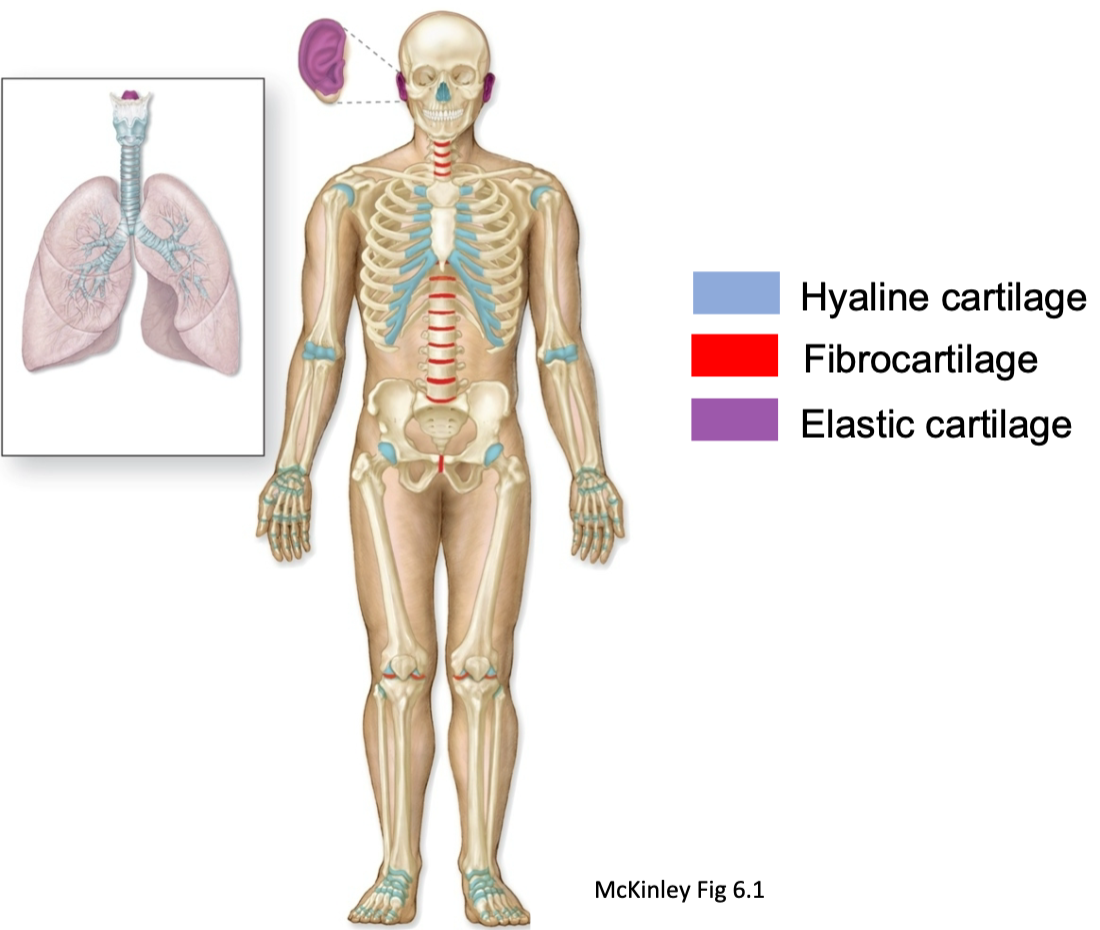
28
New cards
Fibril
1. Very thin fibers
2. Found in hyaline cartilage
2. Found in hyaline cartilage
29
New cards
Bone Tissue
1. Very little fluid
2. Resists compression and tension; very strong
3. Well vascularized
- Heals/remodels easily
4. Organic and inorganic materials
5. Osteocytes in lacunae
2. Resists compression and tension; very strong
3. Well vascularized
- Heals/remodels easily
4. Organic and inorganic materials
5. Osteocytes in lacunae
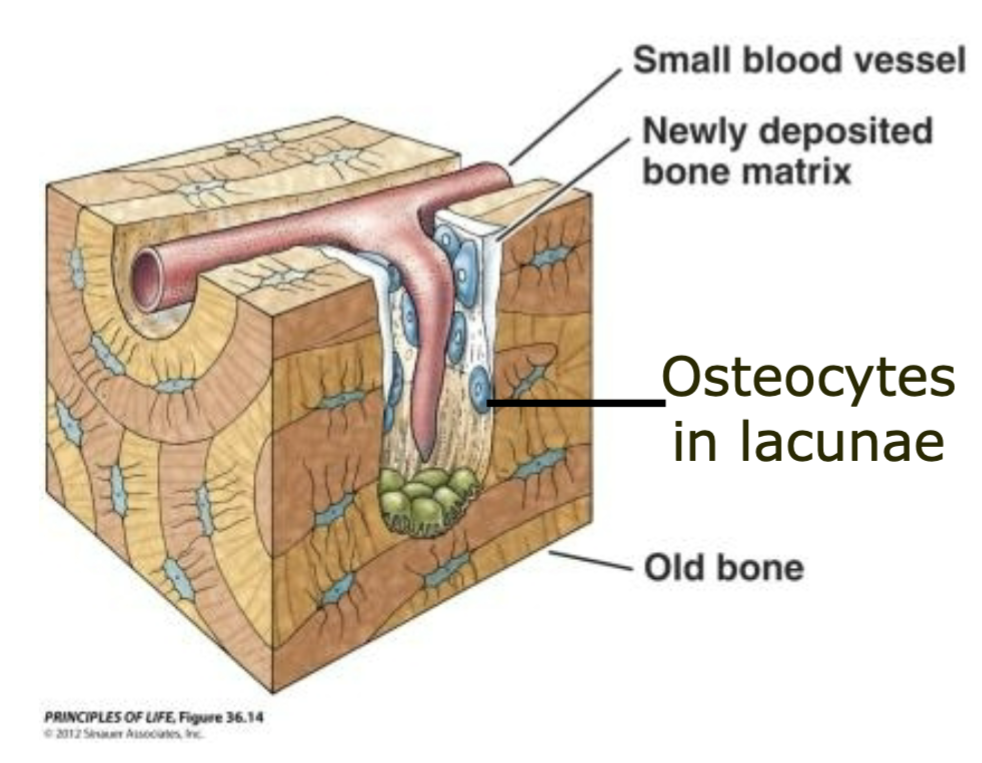
30
New cards
Lacunae
Contains osteocytes
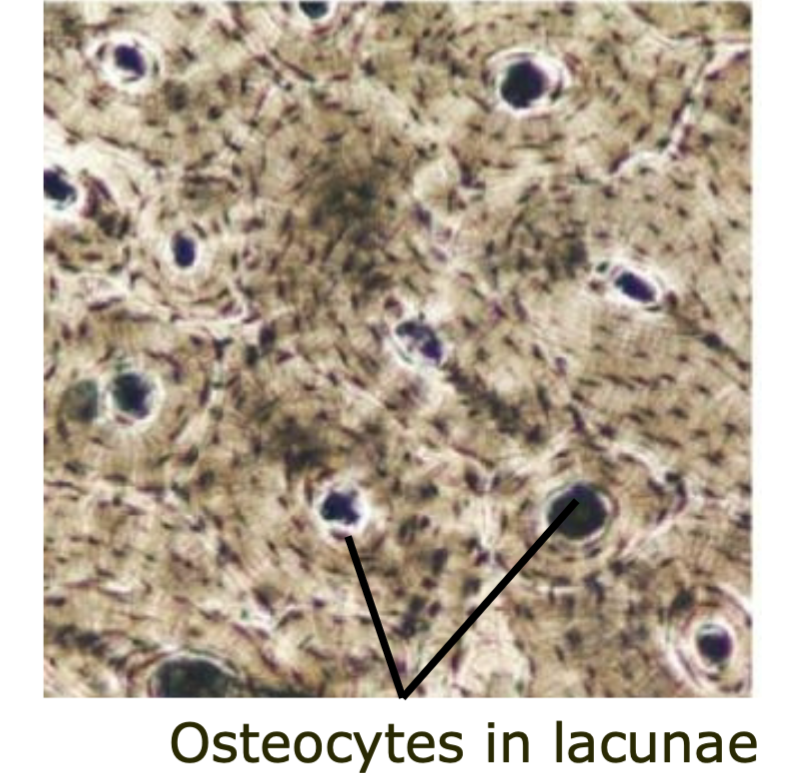
31
New cards
Osteocytes
1. Found in lacunae
2. Mature bone cells
3. Can also be osteoblasts and osteoclasts
2. Mature bone cells
3. Can also be osteoblasts and osteoclasts
32
New cards
What is the extracellular matrix of bones?
1. Organic
- Fibers (lots of collagen)
- Ground substance
2. Inorganic
- 65% mineral salts
- Calcium phosphate
- Fibers (lots of collagen)
- Ground substance
2. Inorganic
- 65% mineral salts
- Calcium phosphate
33
New cards
Osteoblast
1. A cell from which bone develops
2. Builds new bone
2. Builds new bone
34
New cards
Osteoclast
1. Cells that breakdown and consume bone tissue
2. Break down or consume bone
2. Break down or consume bone
35
New cards
Intramembranous Ossification
1. The process of forming bones within a membrane
2. Forms
- Flat bones
- Bones of the skull
- Clavicle
- Maxillae
- Zygomatic mandible
2. Forms
- Flat bones
- Bones of the skull
- Clavicle
- Maxillae
- Zygomatic mandible
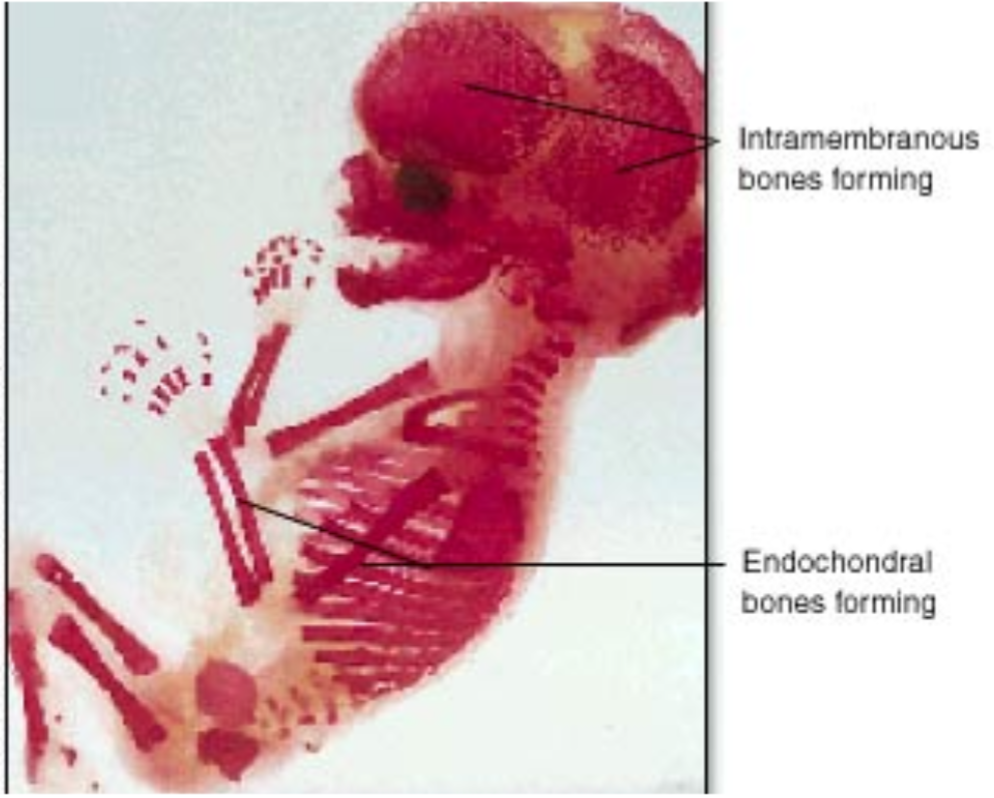
36
New cards
Endochondral Ossification
1. The process of forming bones most bones go through
2. Forms
- Long bones of the axial skeleton
- Appendicular skeleton
2. Forms
- Long bones of the axial skeleton
- Appendicular skeleton
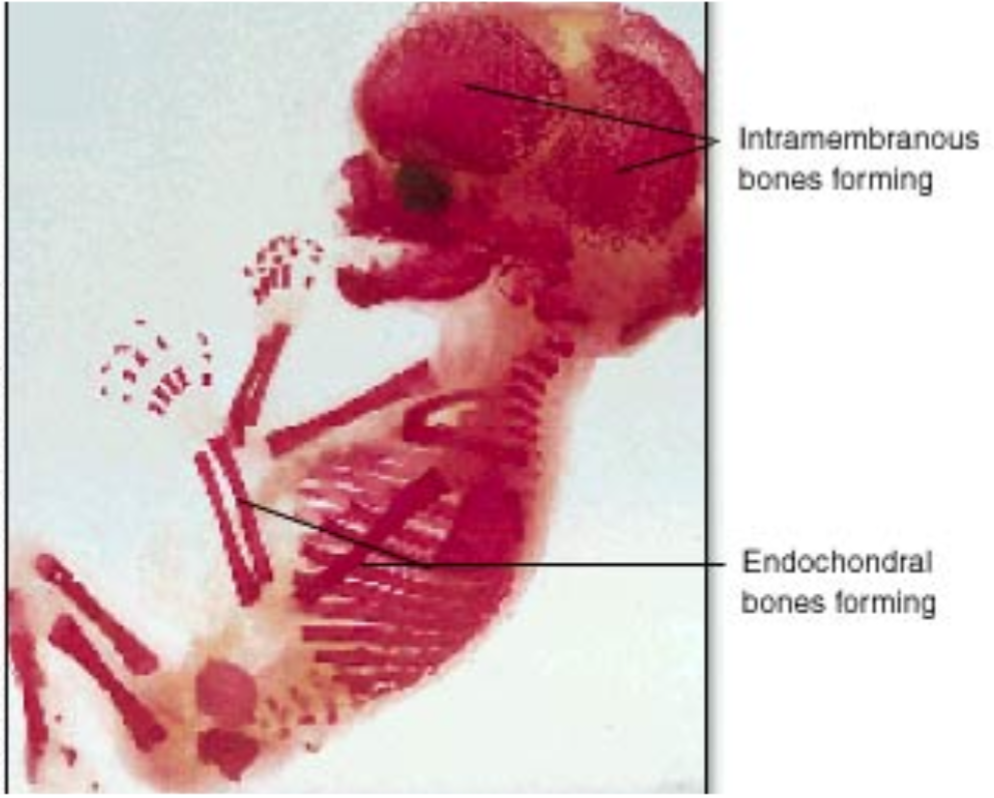
37
New cards
Endochondral Ossification Steps
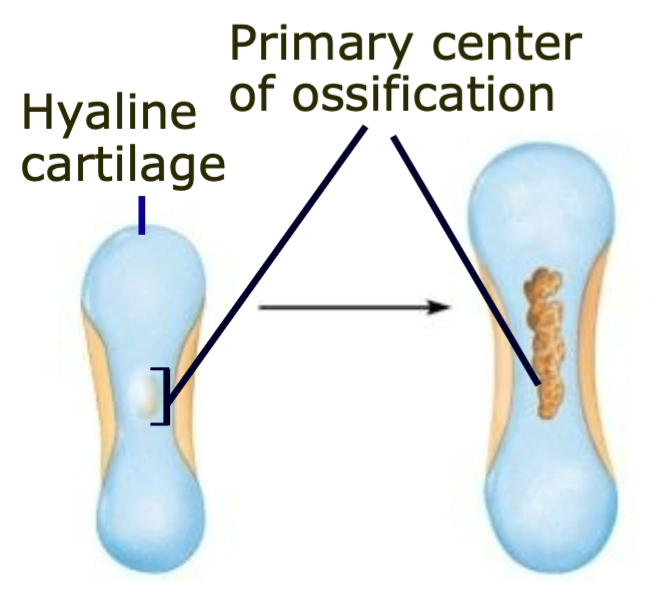
1. Skeleton begins as hyaline cartilage model
2. Primary center of ossification appears in diaphysis and bone replaces cartilage
3. Secondary center of ossification form in epiphyses
4. Skeleton grows via division of cartilage (and bone) cells until maturity
5. Epiphyseal (growth) plates ossify
2. Primary center of ossification appears in diaphysis and bone replaces cartilage
3. Secondary center of ossification form in epiphyses
4. Skeleton grows via division of cartilage (and bone) cells until maturity
5. Epiphyseal (growth) plates ossify
38
New cards
Primary Center for Ossification
1. Appears in diaphysis
2. Bone replaces cartilage
2. Bone replaces cartilage
39
New cards
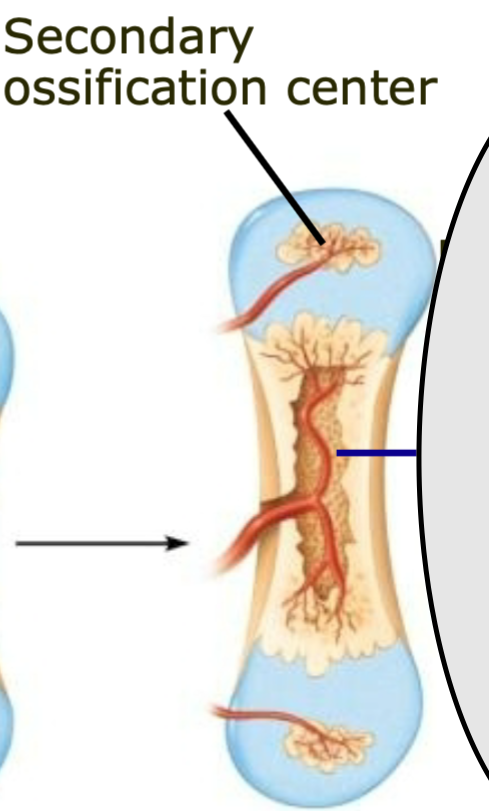
Secondary Center for Ossification
1. Forms in epiphyses
2. Skeleton continues to grow via division of cartilage (and bone)
cells until maturity
2. Skeleton continues to grow via division of cartilage (and bone)
cells until maturity
40
New cards
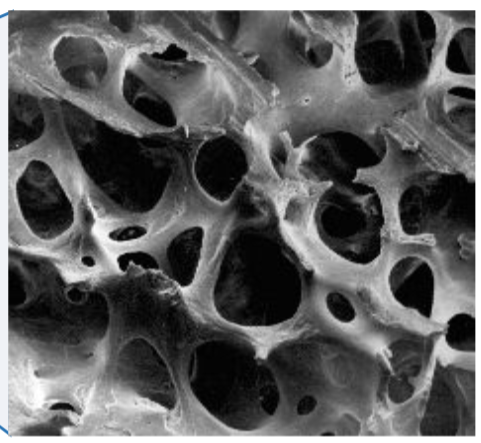
Spongy Bone (trabecular bone)
1. Internal (deep) portion of bones
2. Surrounded by marrow
3. Typically near joints
4. More air pockets than compact bone
5. Good shock absorption
2. Surrounded by marrow
3. Typically near joints
4. More air pockets than compact bone
5. Good shock absorption
41
New cards
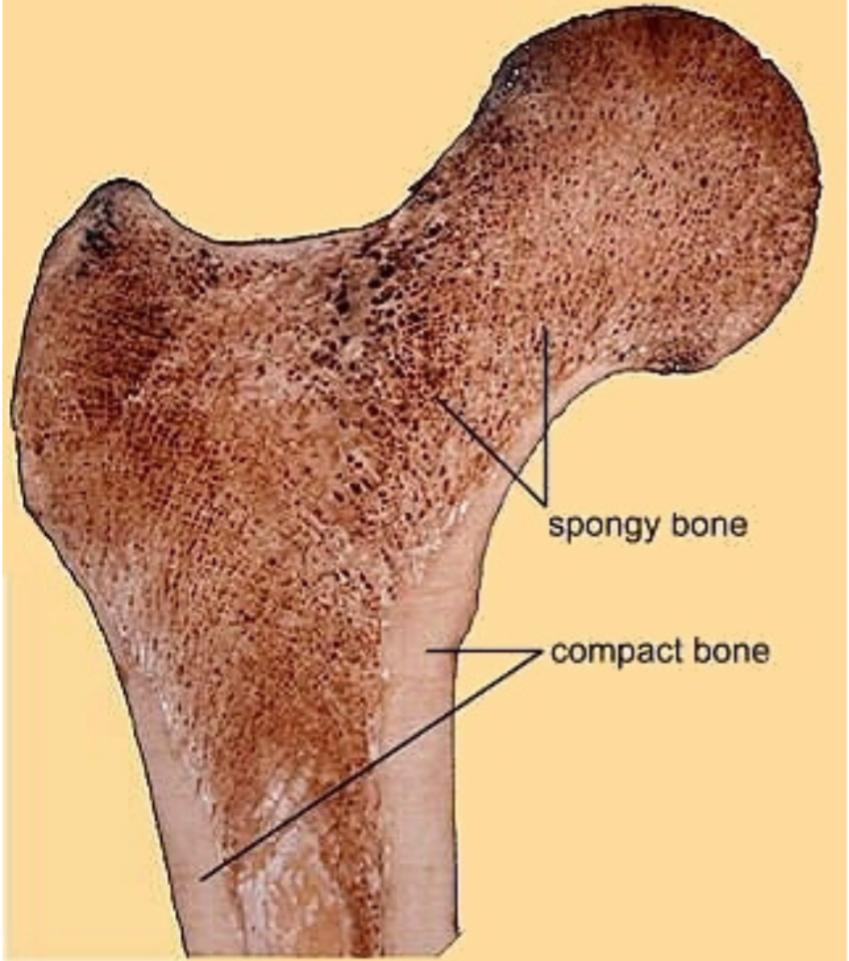
Compact Bone (cortical bone)
1. External (superficial) portion of bones
2. Smooth
3. Dense
4. Strong
5. Rigid
2. Smooth
3. Dense
4. Strong
5. Rigid
42
New cards
Compact Bone Structure
Contain osteons
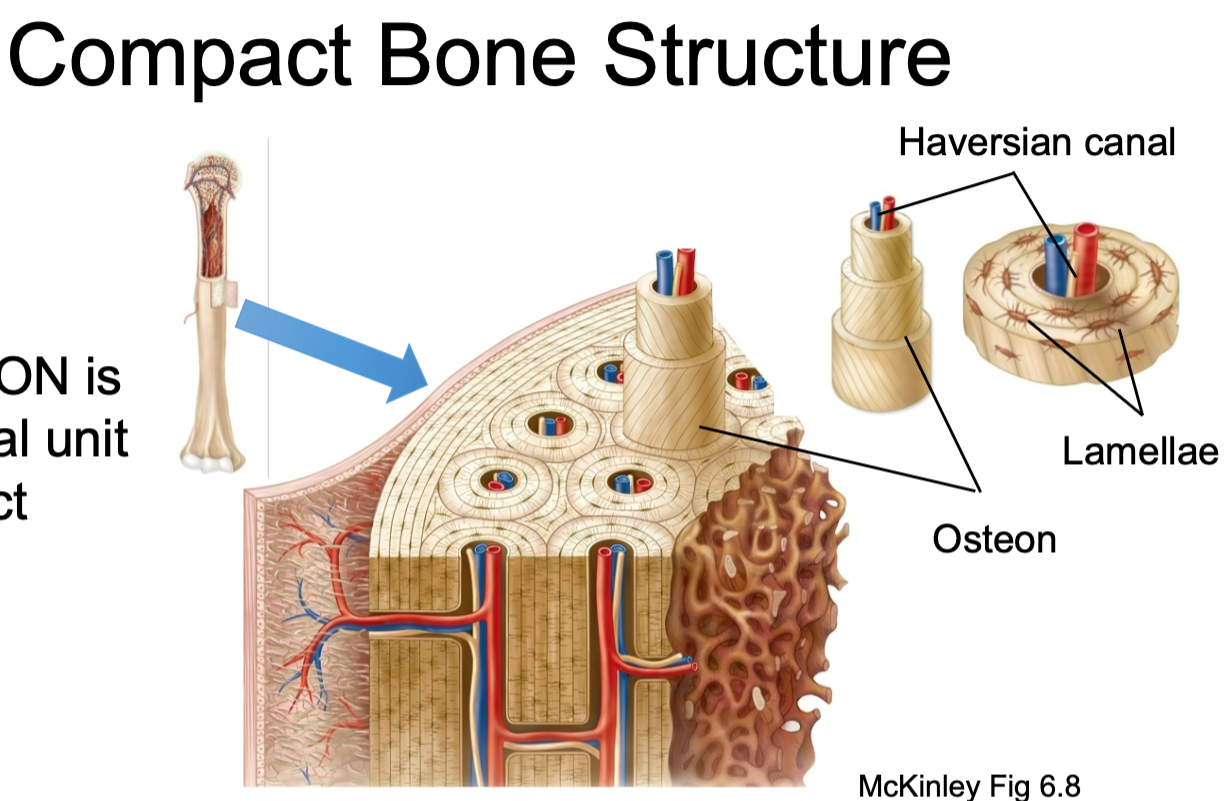
43
New cards
Osteon
1. Structural unit of compact bone
2. Made up of concentric tubes called lamellae
3. Oriented parallel to the long axis and main compression stresses
4. Haversian (central) canal runs through core
2. Made up of concentric tubes called lamellae
3. Oriented parallel to the long axis and main compression stresses
4. Haversian (central) canal runs through core
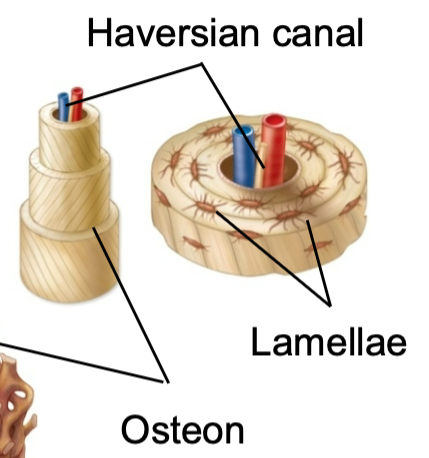
44
New cards
Haversian (central) Canal
1. Found in compact bone
2. Located inside osteons
3. Provides
- Blood supply
- Nutrients
- Nerves
2. Located inside osteons
3. Provides
- Blood supply
- Nutrients
- Nerves
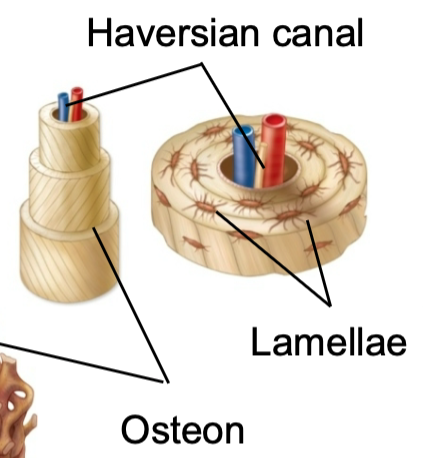
45
New cards
Lamellae
1. Found in compact bone
2. Concentric tubes that make up osteons
2. Concentric tubes that make up osteons
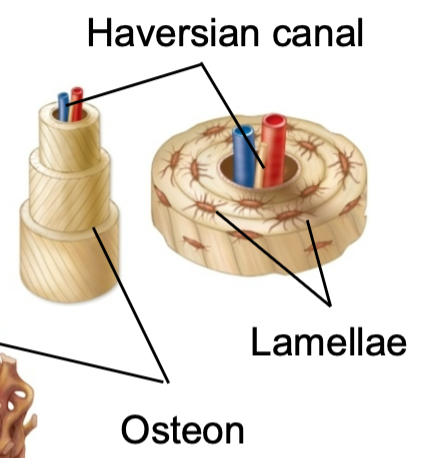
46
New cards
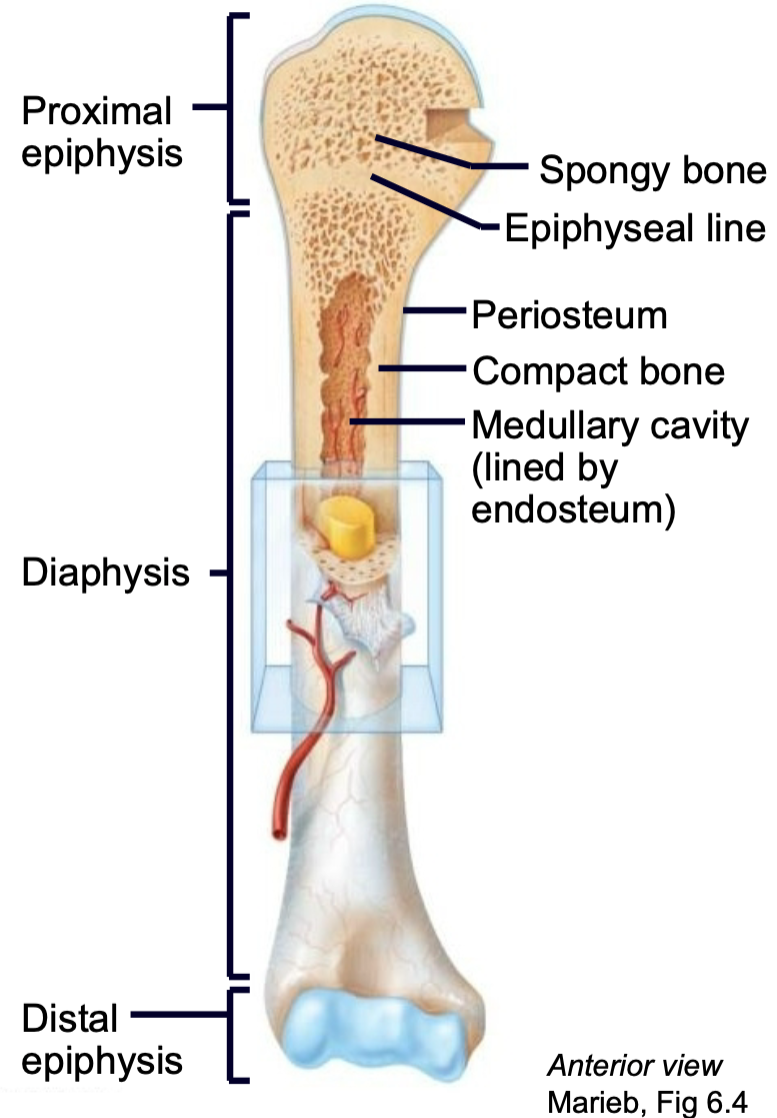
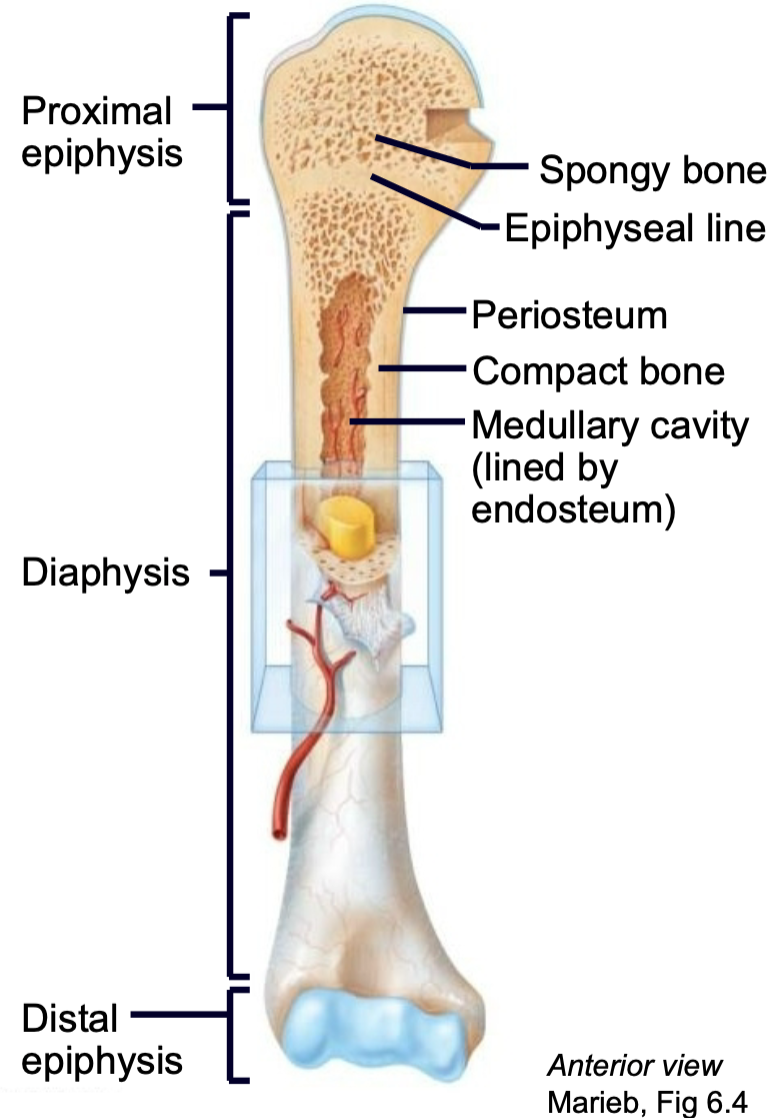
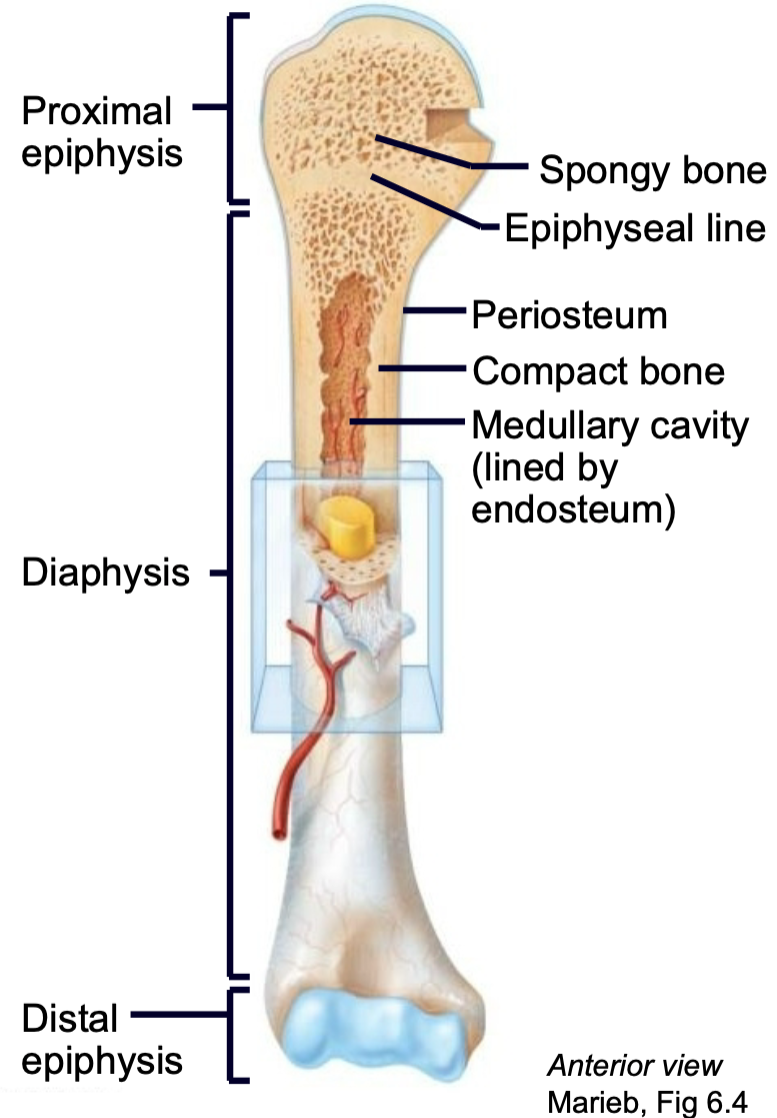
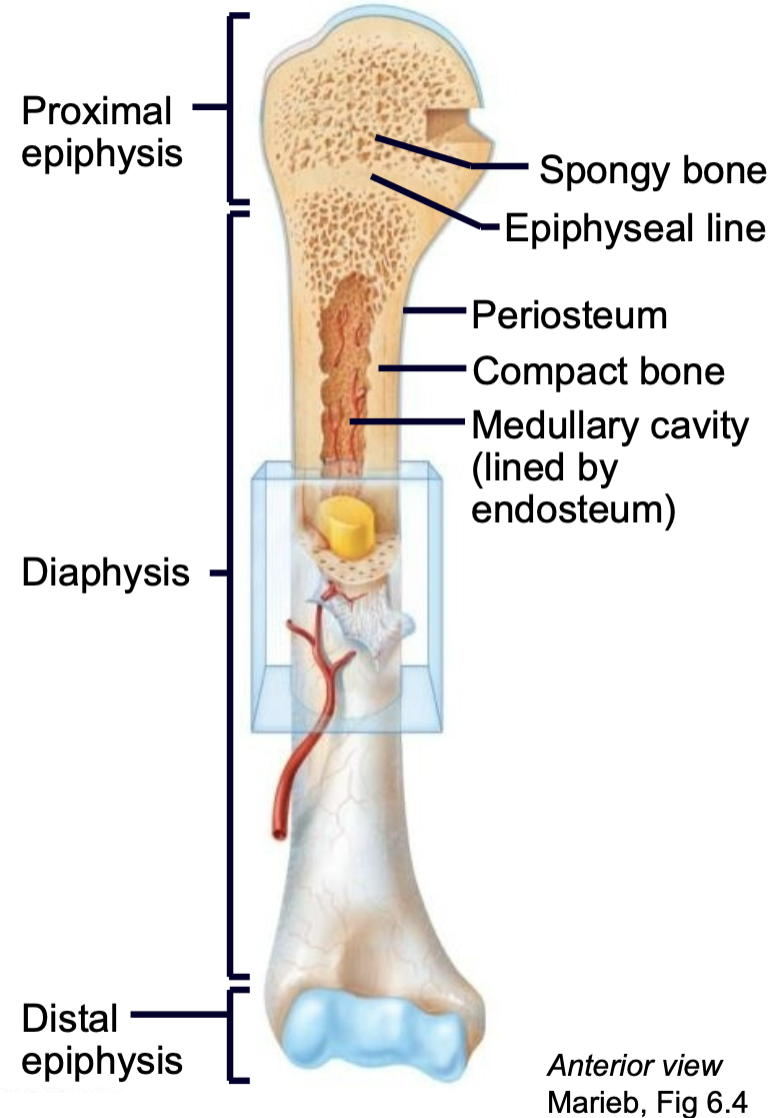
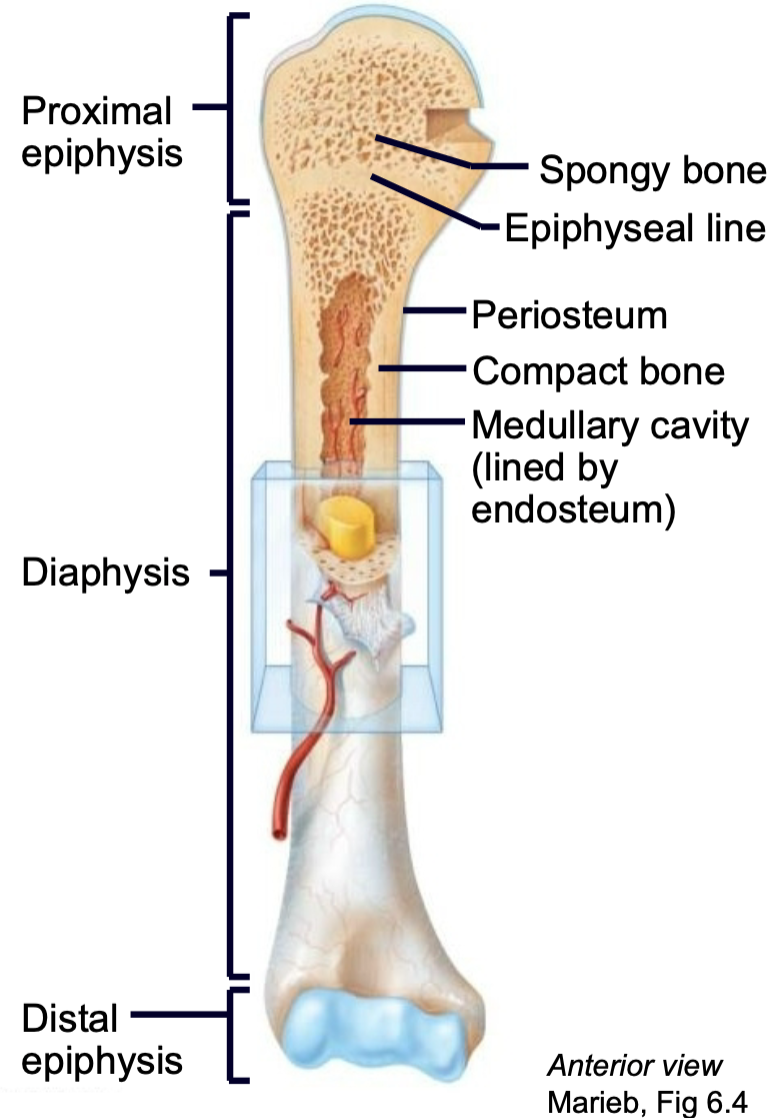
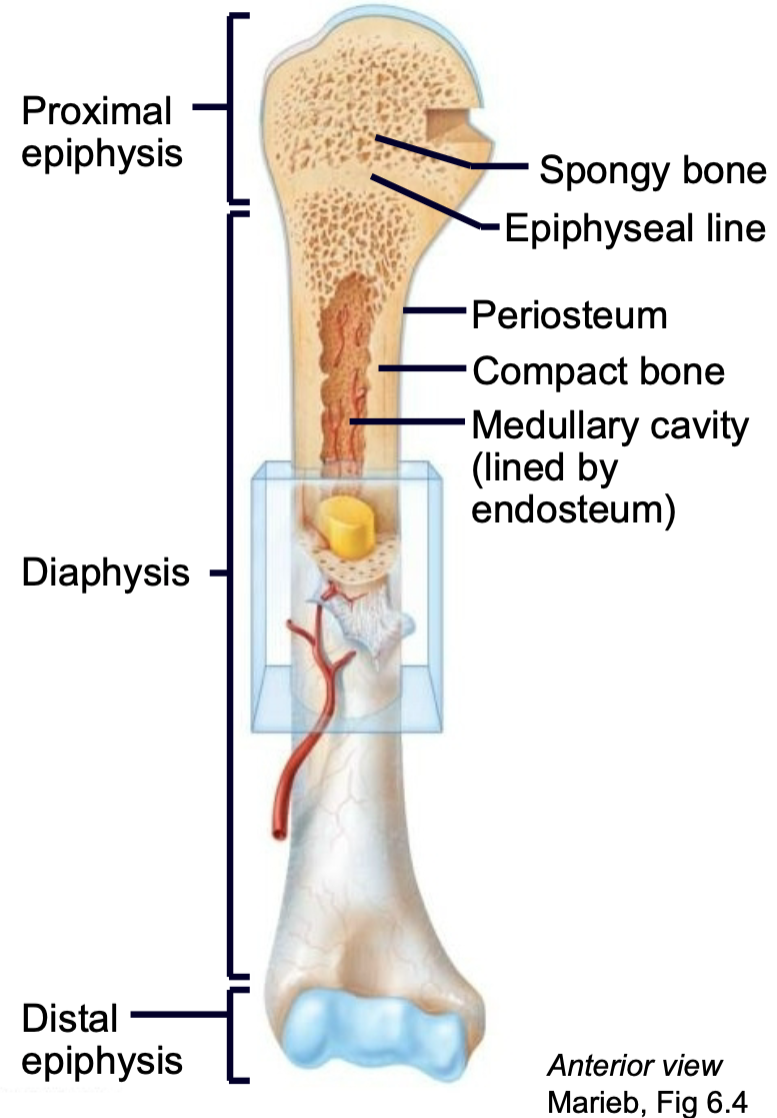
What is the structure of a long bone?
1. Epiphysis
2. Epiphyseal line
3. Diaphysis
4. Compact bone
5. Spongy bone
6. Periosteum
7. Endosteum
8. Medullary cavity
9. Nutrient arteries
10. Articular cartilage
2. Epiphyseal line
3. Diaphysis
4. Compact bone
5. Spongy bone
6. Periosteum
7. Endosteum
8. Medullary cavity
9. Nutrient arteries
10. Articular cartilage
47
New cards
Epiphysis
End of a long bone
48
New cards
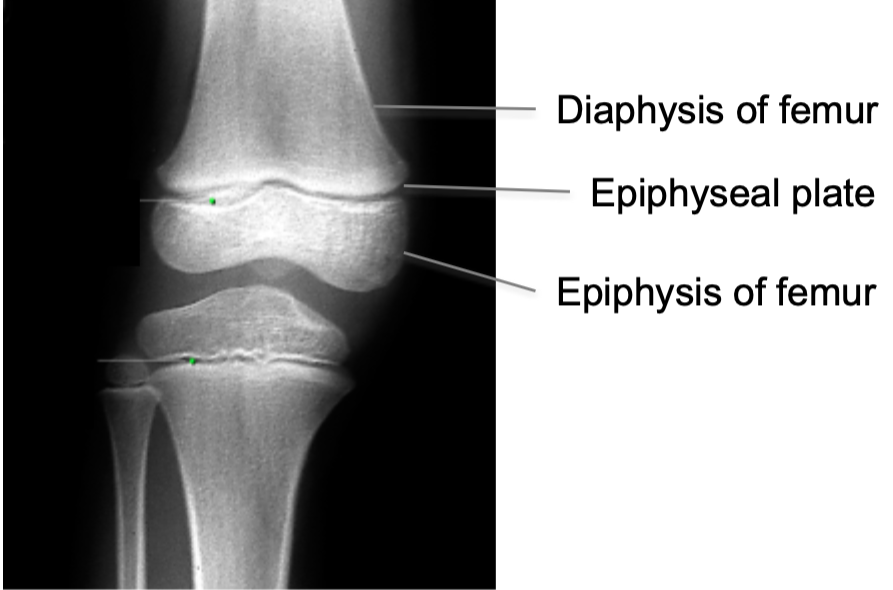
Epiphyseal Line/Plate
1. AKA Growth plate
2. Hyaline cartilage plate
3. Found in epiphysis at each end of a long bone
4. In people who have stopped growing, the plate is replaced by an epiphyseal line
2. Hyaline cartilage plate
3. Found in epiphysis at each end of a long bone
4. In people who have stopped growing, the plate is replaced by an epiphyseal line
49
New cards
Diaphysis
Shaft of long bone
50
New cards
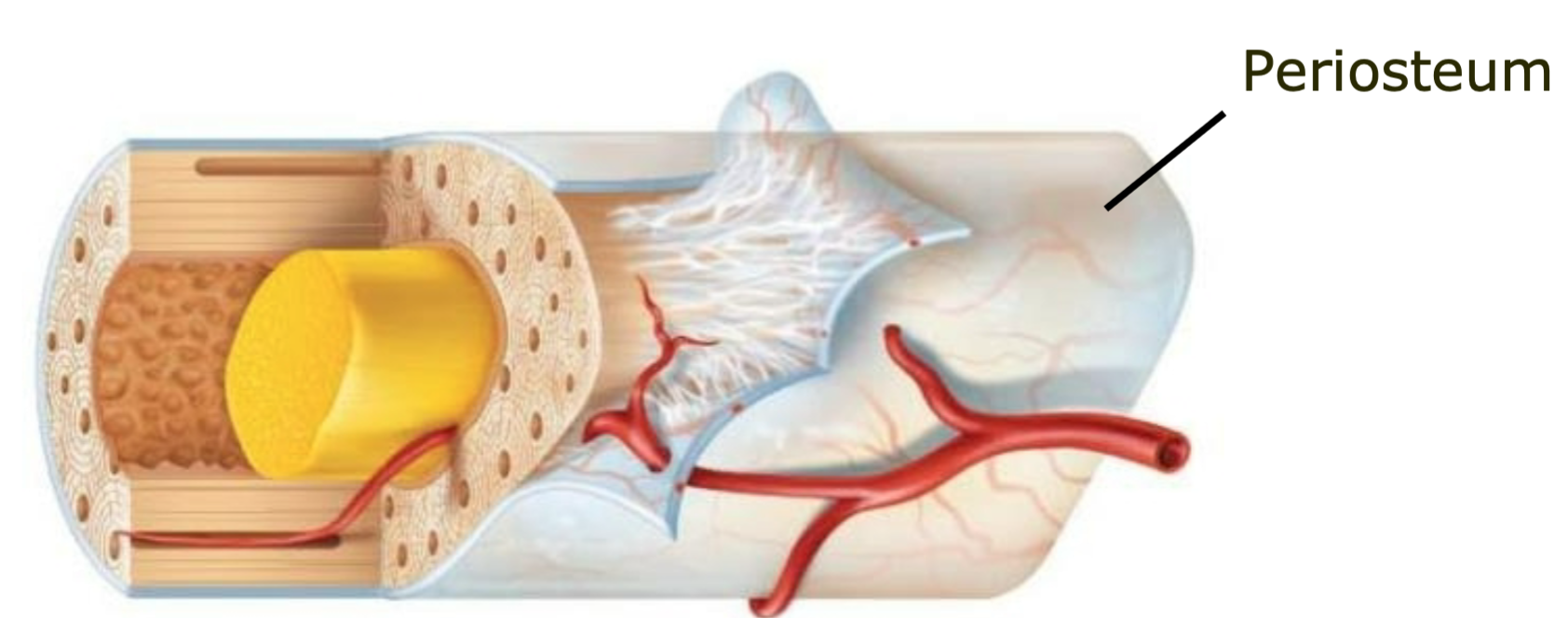
Periosteum
1. Outer membrane on bone long bone
2. Well supplied with nerves and blood vessels
3. Provides a place for tendons and ligaments to attach to bone
2. Well supplied with nerves and blood vessels
3. Provides a place for tendons and ligaments to attach to bone
51
New cards
Endosteum
1. Vascular membrane
2. Lines internal cavity of long bones
2. Lines internal cavity of long bones
52
New cards
Medullary Cavity
1. Bone marrow
2. Lined by endosteum
2. Lined by endosteum
53
New cards
What is the structure of flat, irregular and short bones?
1. Compact bone with periosteum on the outside
2. Spongy bone with endosteum on the inside
3. Contain marrow but DO NOT have a marrow cavity
2. Spongy bone with endosteum on the inside
3. Contain marrow but DO NOT have a marrow cavity
54
New cards
Closure of Epiphyseal Plates
1. Cartilage is gradually replaced by bone tissue on both sides of
the epiphyseal plate (primary and secondary center of ossification)
2. Centers of ossification meet at the epiphyseal plate
3. Growth stops
the epiphyseal plate (primary and secondary center of ossification)
2. Centers of ossification meet at the epiphyseal plate
3. Growth stops
55
New cards
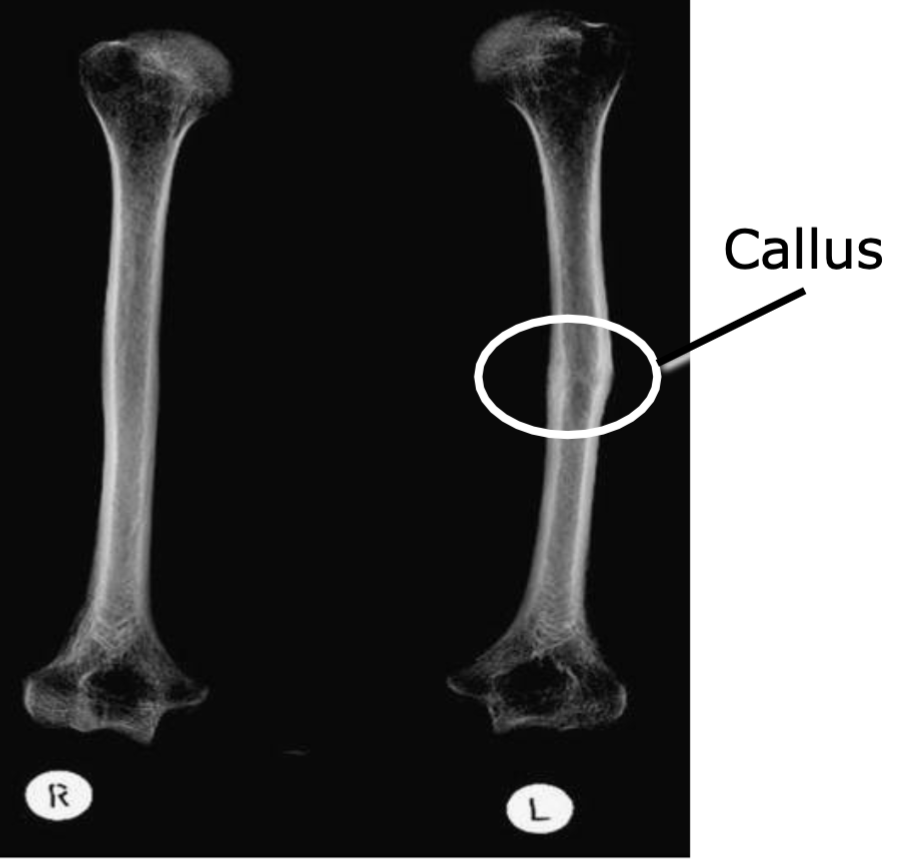
Bony Callus
1. If injured, cells tend to overgrow at an injury site
2. Forms a bony callus from the overgrowth of the osteoblasts
2. Forms a bony callus from the overgrowth of the osteoblasts
56
New cards
How often do bones go through remodeling?
1. Bone continually undergoes remodeling
2. This is when cells break down/build bone
2. This is when cells break down/build bone
57
New cards
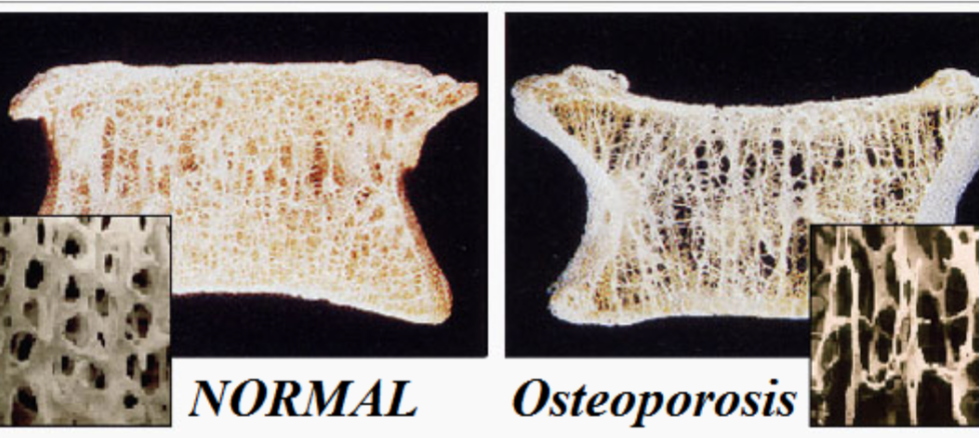
Osteoporosis
1. Results from an imbalance of bone remodeling
- More bone is broken down than new bone is built
2. Seen after menopause
- Women don’t absorb as much calcium so osteoclasts break bone down to release the calcium into the bloodstream
3. Common with compression fractures
- More bone is broken down than new bone is built
2. Seen after menopause
- Women don’t absorb as much calcium so osteoclasts break bone down to release the calcium into the bloodstream
3. Common with compression fractures
58
New cards
What does bone development and growth look like BEFORE week 8 of life?
Skelton made of hyaline cartilage or mesenchyme
59
New cards
What does bone development and growth look like AFTER week 8 of life?
Bone tissue begins to replace most cartilage or mesenchyme
60
New cards
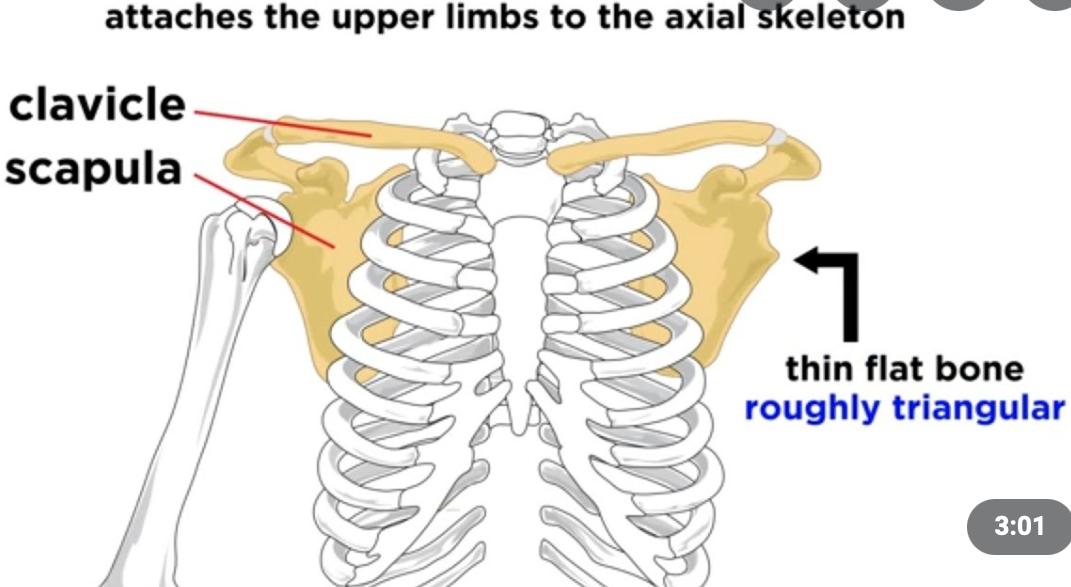
Pectoral Girdle
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Left/right scapulae
3. Left/right clavicles
2. Left/right scapulae
3. Left/right clavicles
61
New cards
How are the scapulae attached to the axial skeleton?
1. Scapulae do NOT join to the axial skeleton at all
2. Their articulation with the clavicle is very loose
3. They are attached to the axial skeleton by way of associated muscles and ligaments
4. This provides a highly flexible system
2. Their articulation with the clavicle is very loose
3. They are attached to the axial skeleton by way of associated muscles and ligaments
4. This provides a highly flexible system
62
New cards
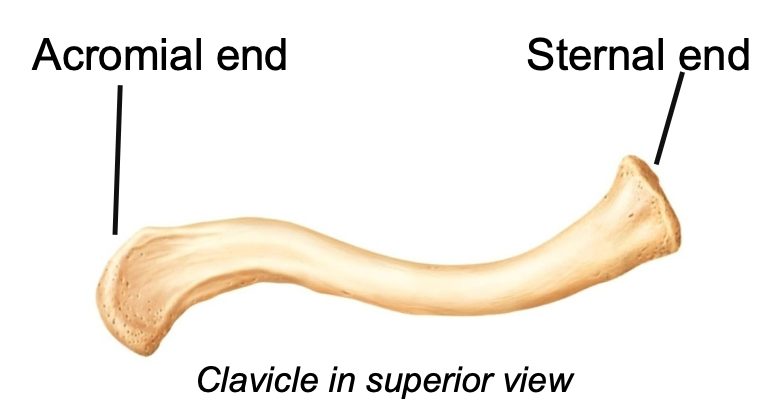
Clavicle
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Located in pectoral girdle
3. "Collarbone"
4. Provides muscle attachment
5. Acts as brace for the scapula and arms
6. S-shape makes it prone to fracturing near the curves
2. Located in pectoral girdle
3. "Collarbone"
4. Provides muscle attachment
5. Acts as brace for the scapula and arms
6. S-shape makes it prone to fracturing near the curves
63
New cards
What does the acromial end of the clavicle attach too?
1. Lateral
2. The acromial end articulates with the acromion process of the
scapula
2. The acromial end articulates with the acromion process of the
scapula
64
New cards
What does the sternal end of the clavicle attach too?
1. Medial
2. The sternal end attaches to the manubrium of the sternum
2. The sternal end attaches to the manubrium of the sternum
65
New cards
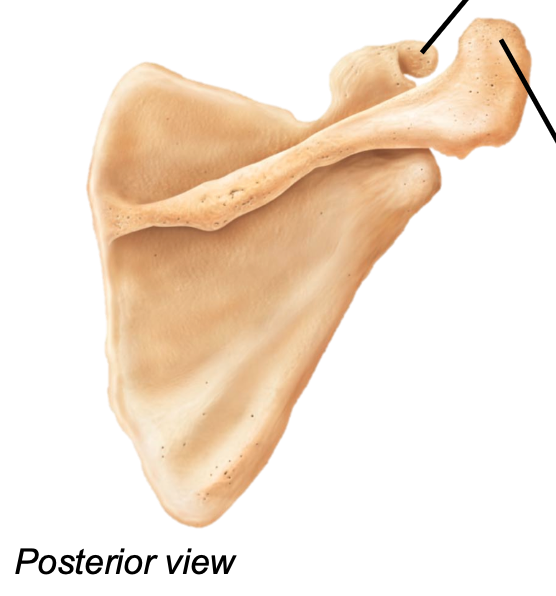
Scapula
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Located in pectoral girdle
3. Located on the posterior surface of the rib cage
4. Scapular spine is on posterior side of the scapula
5. Contains
- Gelnoid cavity
- Supraspinous/infraspinous fossae
- Subscapular fossa
- Coracoid process
- Acromion
2. Located in pectoral girdle
3. Located on the posterior surface of the rib cage
4. Scapular spine is on posterior side of the scapula
5. Contains
- Gelnoid cavity
- Supraspinous/infraspinous fossae
- Subscapular fossa
- Coracoid process
- Acromion
66
New cards
Glenoid Cavity
1. AKA glenoid fossa
2. Appendicular skeleton
3. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
4. Where the humerus articulates
5. Forms shoulder joint
2. Appendicular skeleton
3. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
4. Where the humerus articulates
5. Forms shoulder joint
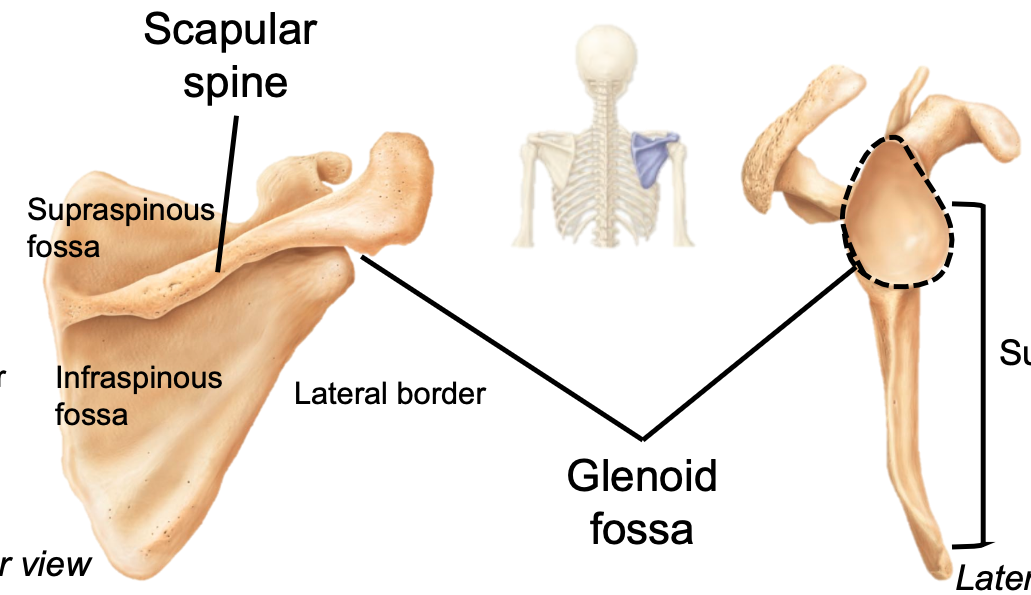
67
New cards
Supraspinous/infraspinous Fossae
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
3. Attachment sites for muscles
2. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
3. Attachment sites for muscles
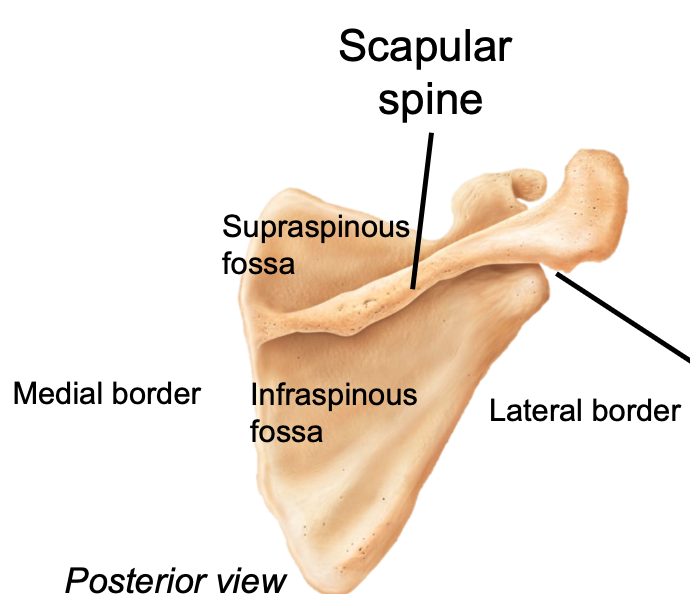
68
New cards
Subscapular Fossa
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
3. Anterior site for muscle attachment
2. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
3. Anterior site for muscle attachment
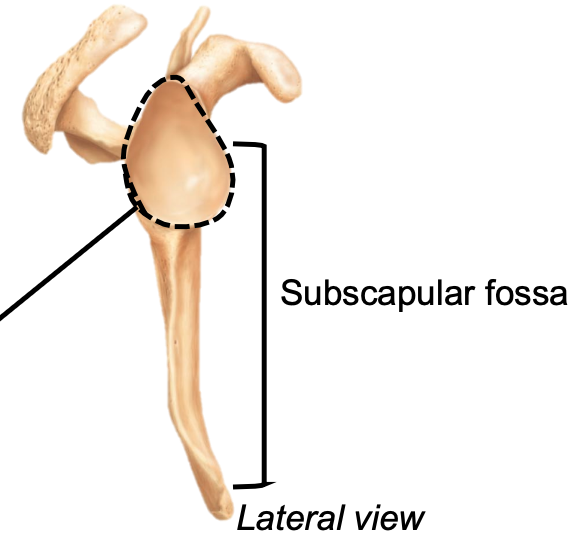
69
New cards
Coracoid Process
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
3. Attachment point of the biceps muscle
4. Located anteriorly
2. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
3. Attachment point of the biceps muscle
4. Located anteriorly
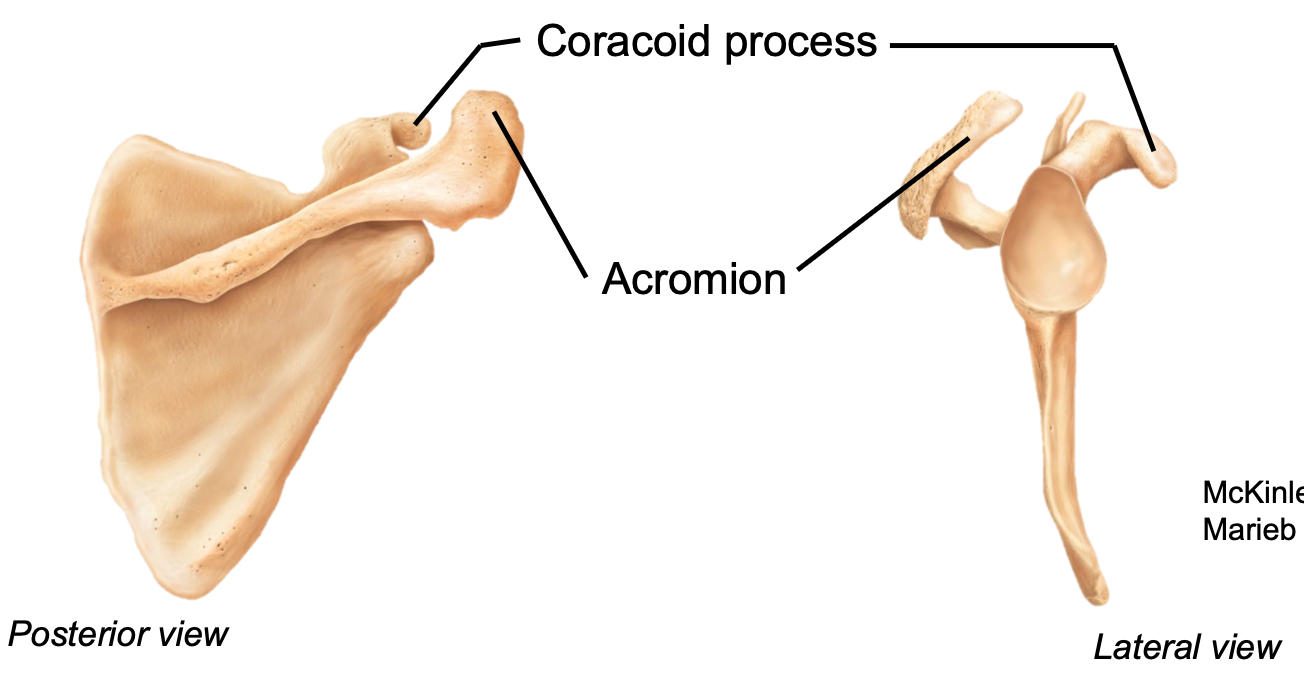
70
New cards
Acromion
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
3. Articulates with the acromial end of clavicle
4. Located posteriorly
2. Located in pectoral girdle on scapula
3. Articulates with the acromial end of clavicle
4. Located posteriorly
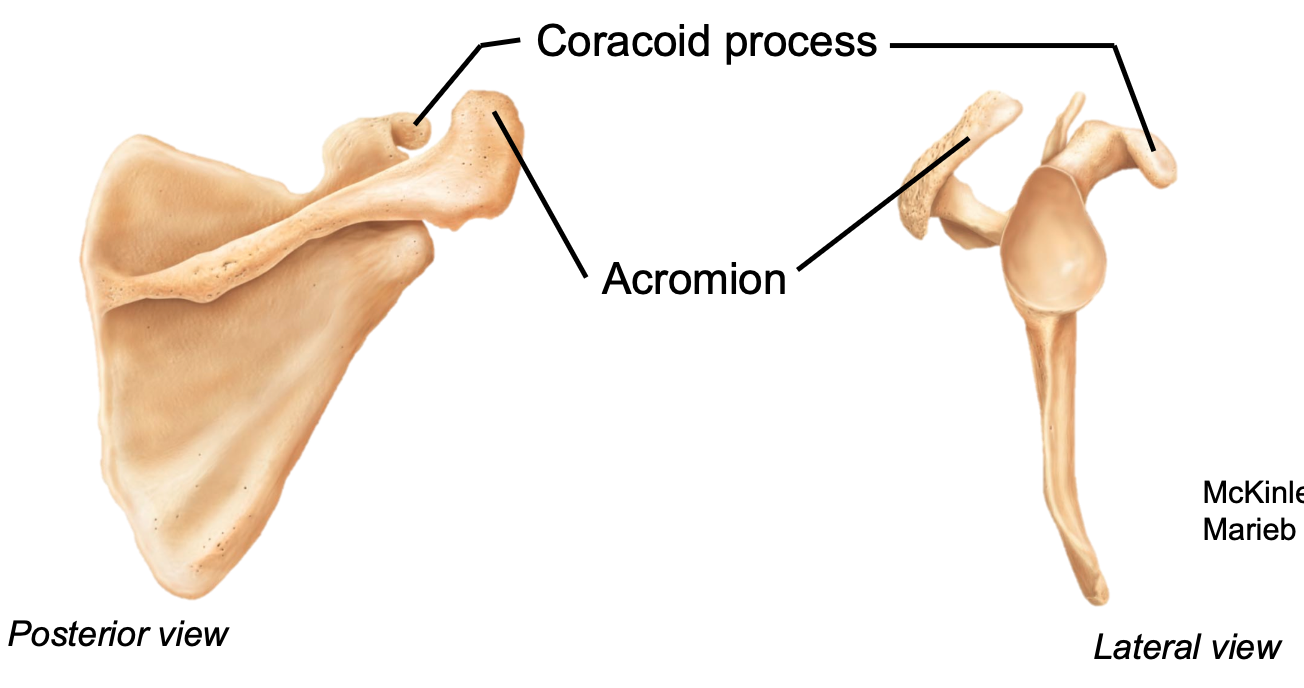
71
New cards
Upper Limb
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. 30 bones
3. Arm
4. Forearm
5. Hand
2. 30 bones
3. Arm
4. Forearm
5. Hand
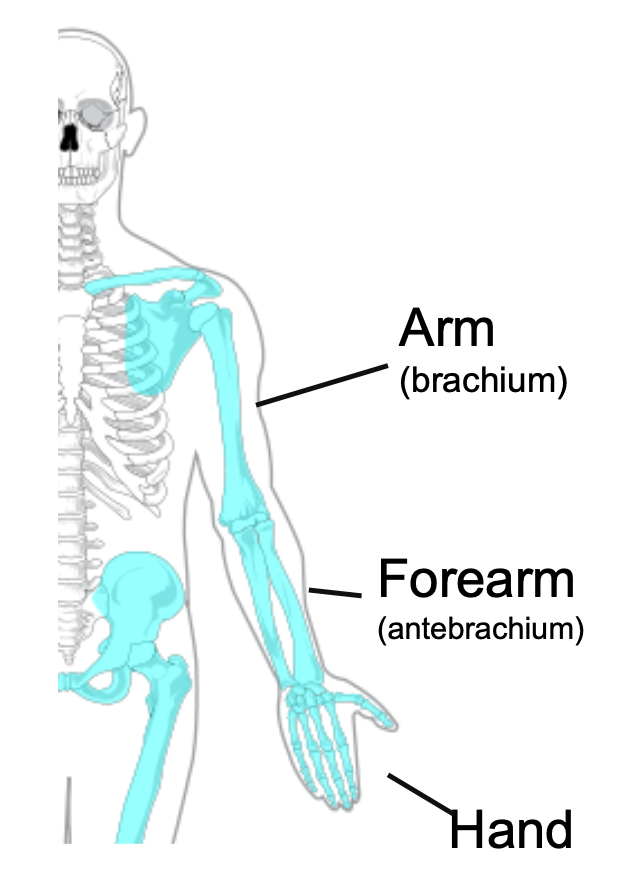
72
New cards
Arm
1. AKA Brachium
2. Upper arm
3. One bone
- Humerus
2. Upper arm
3. One bone
- Humerus
73
New cards
Forearm
1. AKA antebrachium
2. Lower arm
3. Two bones
- Radius
- Ulna
2. Lower arm
3. Two bones
- Radius
- Ulna
74
New cards
Hand
1. Includes the wrist
2. 27 bones
- Carpal bones
- Metacarpals
- Phalanges
2. 27 bones
- Carpal bones
- Metacarpals
- Phalanges
75
New cards
Humerus
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Head articulates with scapula at the glenoid cavity
4. Distal end articulates with radius and ulna (elbow)
5. Greater and lesser tubercles are sites of muscle attachment
- Deltoid tuberosity is attachment for deltoid muscle
6. Most frequently fractures at the surgical neck
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Head articulates with scapula at the glenoid cavity
4. Distal end articulates with radius and ulna (elbow)
5. Greater and lesser tubercles are sites of muscle attachment
- Deltoid tuberosity is attachment for deltoid muscle
6. Most frequently fractures at the surgical neck
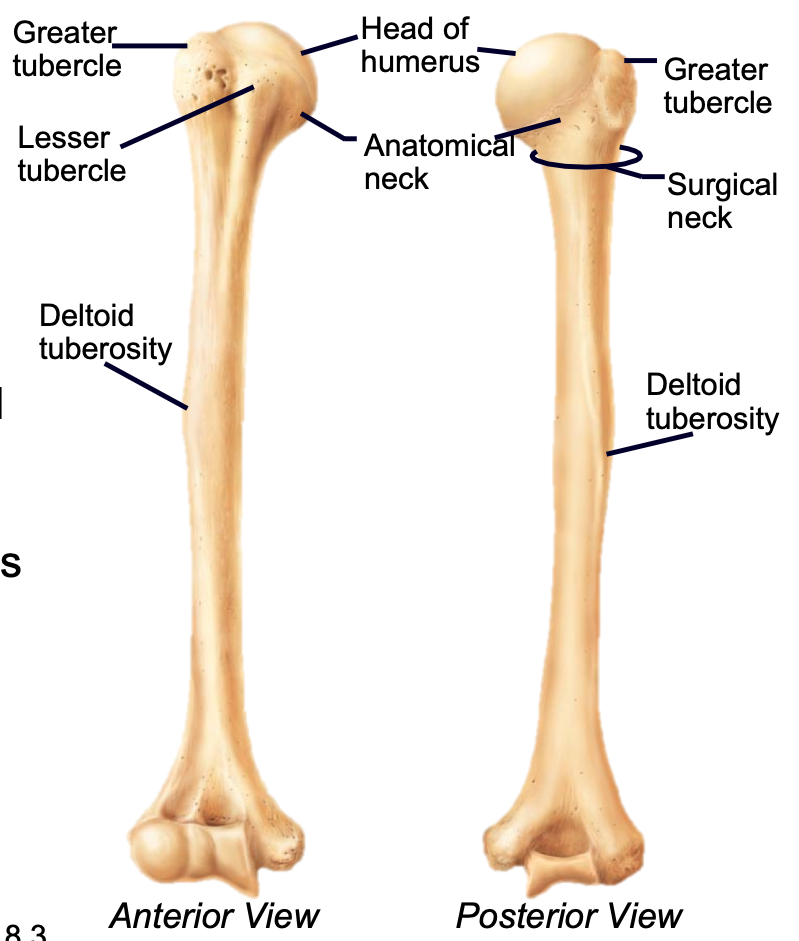
76
New cards
What are common fractures of the humerus?
1. Surgical neck (1)
2. Midshaft spiral fractures (2)
3. Nerves (in yellow) pass along the bone and can be damaged by these two fractures
4. MAY lead to permanent upper limb dysfunction
2. Midshaft spiral fractures (2)
3. Nerves (in yellow) pass along the bone and can be damaged by these two fractures
4. MAY lead to permanent upper limb dysfunction
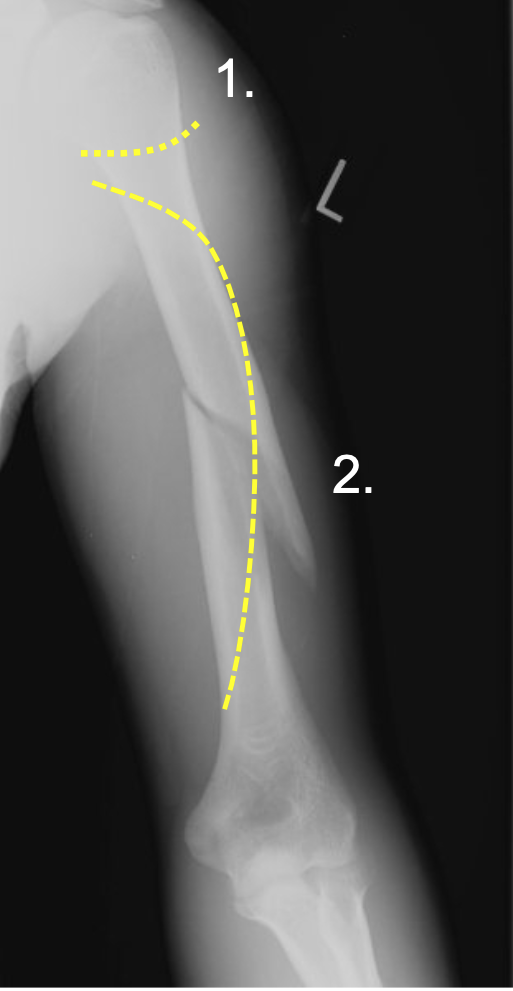
77
New cards
Distal Humerus
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Articulates with the radius and ulna
4. Capitulum
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Articulates with the radius and ulna
4. Capitulum
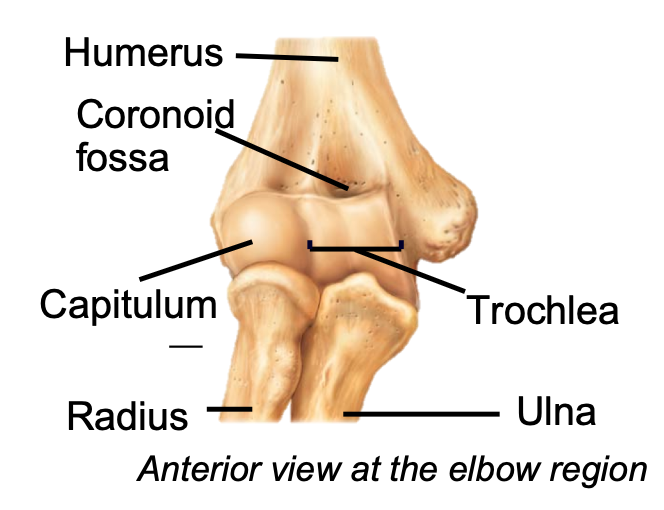
78
New cards
Trochlea (Upper Limb)
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Trochlea of the humerus articulates with trochlear notch of ulna
4. Trochlear notch fits over trochlea to create a hinge
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Trochlea of the humerus articulates with trochlear notch of ulna
4. Trochlear notch fits over trochlea to create a hinge
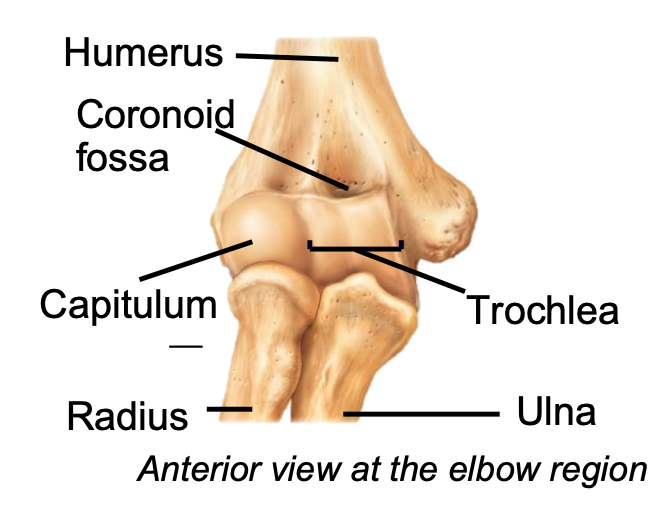
79
New cards
Coronoid (Upper Limb)
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Coronoid process of ulna fits into coronoid fossa when forearm bends
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Coronoid process of ulna fits into coronoid fossa when forearm bends
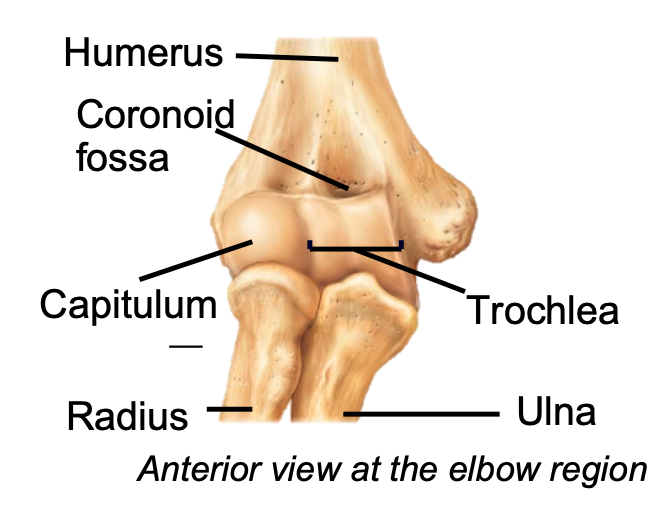
80
New cards
Olecranon Process (Upper Limb)
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Olecranon process of ulna fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus when forearm extends
4. Sharp edge of elbow
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Olecranon process of ulna fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus when forearm extends
4. Sharp edge of elbow
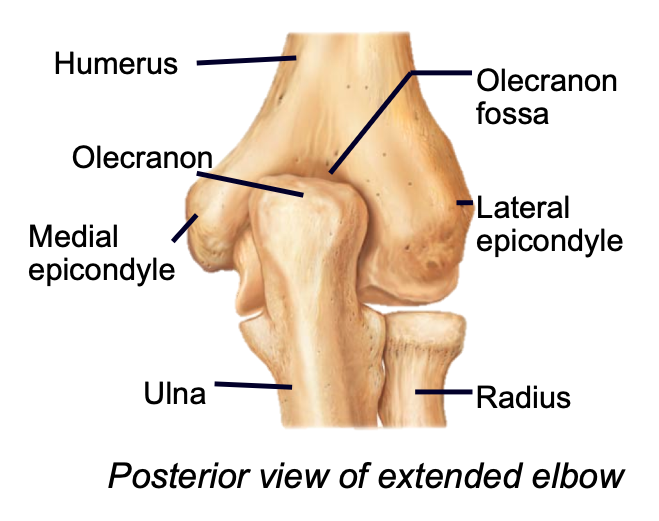
81
New cards
Lateral/Medial Epicondyles (Upper Limb)
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Lateral and medial epicondyles on humerus are attachment sites for forearm muscles
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Lateral and medial epicondyles on humerus are attachment sites for forearm muscles
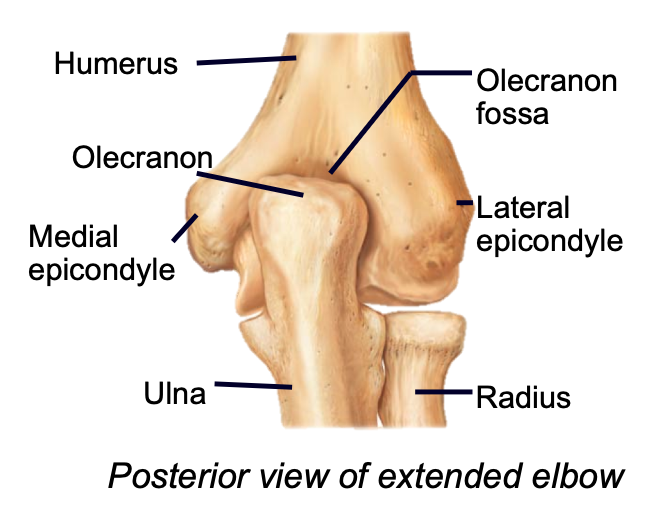
82
New cards
Capitulum
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Distal humerus
4. Articulates with head of the radius
2. Found in arm of upper limb
3. Distal humerus
4. Articulates with head of the radius
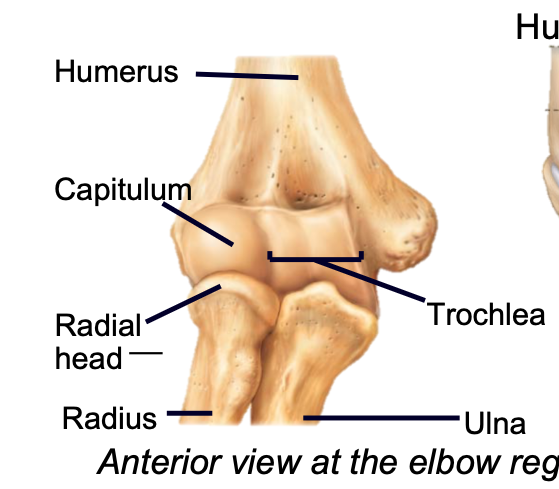
83
New cards
What is the major articulation at the elbow?
Radial head articulates with the radial notch of the ulna (proximal
radioulnar joint) to form a pivot joint
radioulnar joint) to form a pivot joint
84
New cards
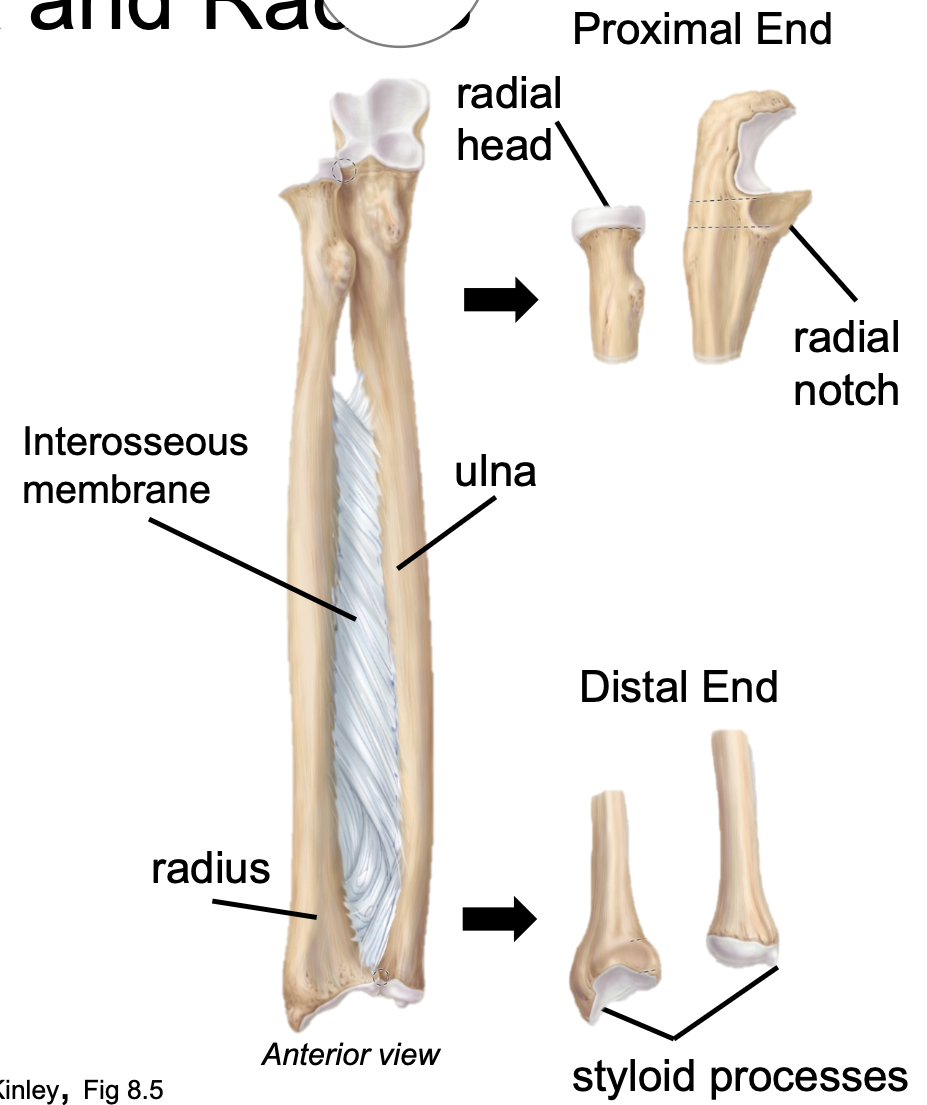
Ulna
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in forearm
3. Medial
4. Connected to the radius by interosseous membrane to keep bones a fixed distance and allow rotation
5. Radial head articulates with radial notch on ulna (proximal)
6. Has a styloid process (distal)
2. Found in forearm
3. Medial
4. Connected to the radius by interosseous membrane to keep bones a fixed distance and allow rotation
5. Radial head articulates with radial notch on ulna (proximal)
6. Has a styloid process (distal)
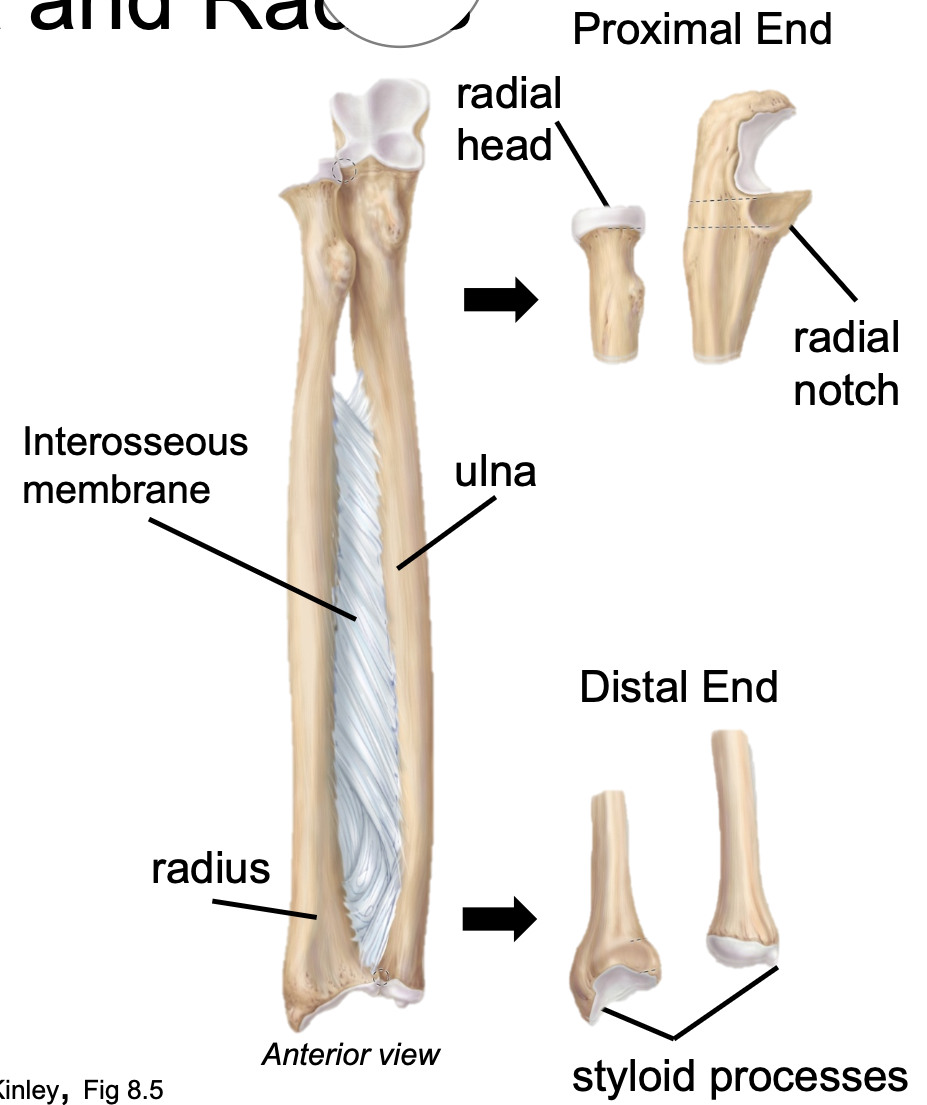
85
New cards
Radius
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in forearm
3. Lateral
4. Connected to the ulna by interosseous membrane to keep bones a fixed distance and allow rotation
5. Radial head articulates with radial notch on ulna (proximal)
6. Has a styloid process (distal)
2. Found in forearm
3. Lateral
4. Connected to the ulna by interosseous membrane to keep bones a fixed distance and allow rotation
5. Radial head articulates with radial notch on ulna (proximal)
6. Has a styloid process (distal)
86
New cards
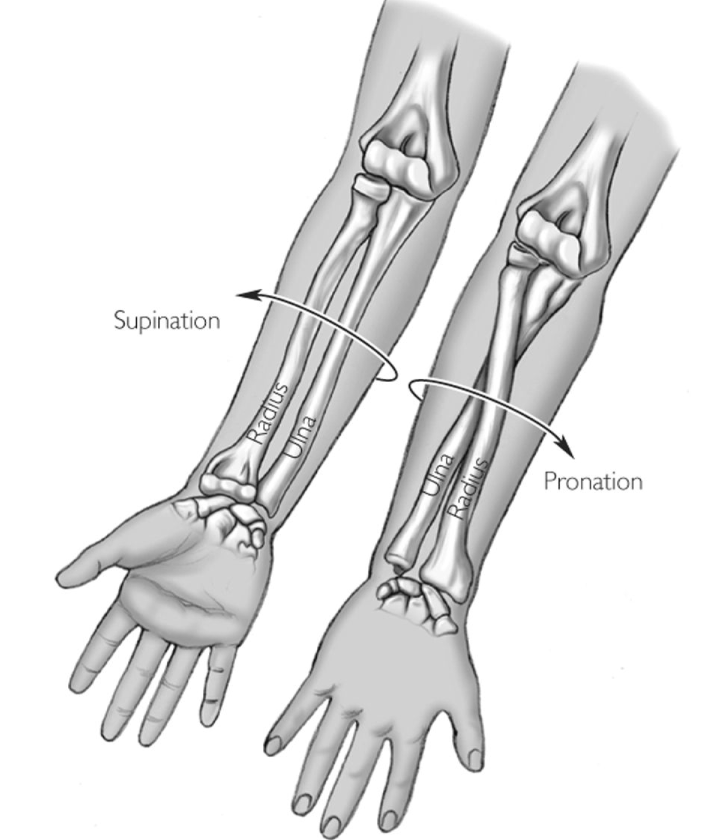
Pronation (Upper Limb)
1. Radius crosses over ulna
2. When palm faces posteriorly
- Bones cross and form an X
2. When palm faces posteriorly
- Bones cross and form an X
87
New cards
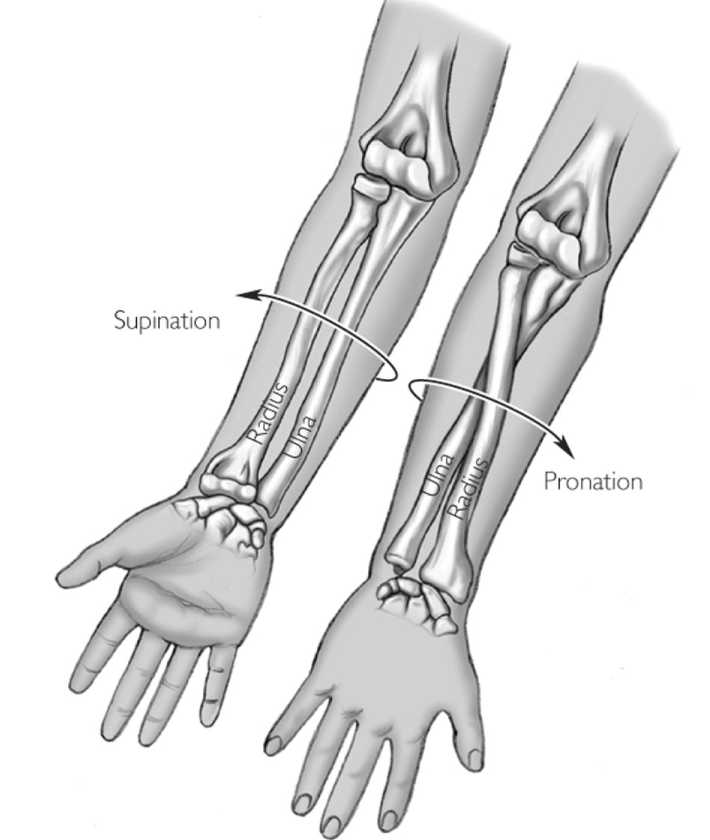
Supination (Upper Limb)
1. Radius parallel to ulna
2. In standard anatomical position
- Radius is lateral and ulna is medial
2. In standard anatomical position
- Radius is lateral and ulna is medial
88
New cards
Where do the ligaments that anchor to the wrist attach?
Ligaments that anchor the the wrist attach to the radial and
ulnar styloid processes
ulnar styloid processes
89
New cards
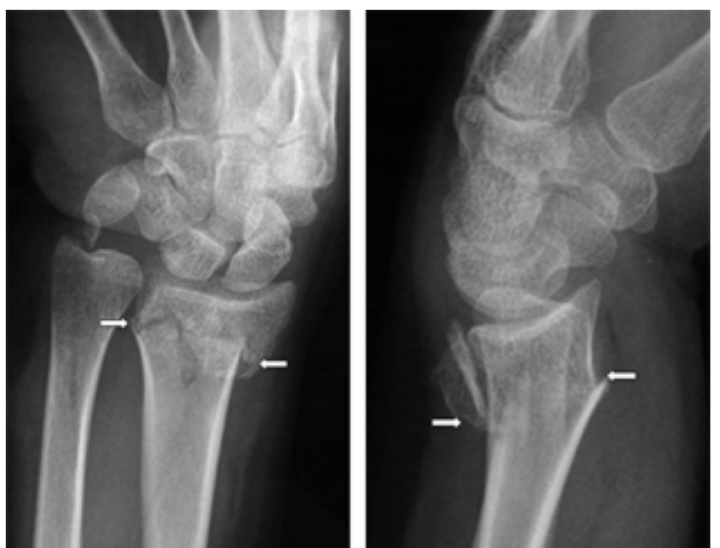
Wrist Fractures
1. Typically fracture distal radius while catching yourself during a fall
2. Common in older females
3. “Dinner-fork ” presentation
4. Can lead to nerve damage and dysfunction
2. Common in older females
3. “Dinner-fork ” presentation
4. Can lead to nerve damage and dysfunction
90
New cards
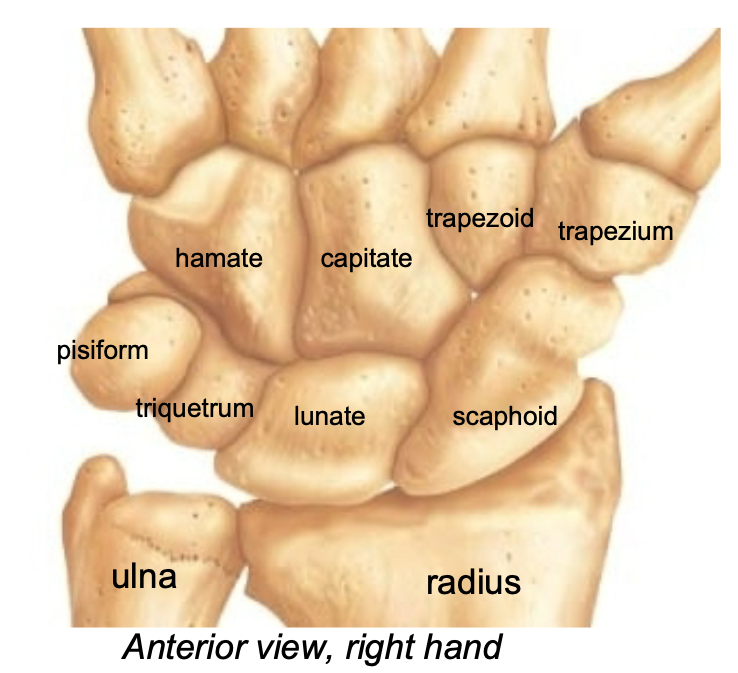
Carpals
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in wrist
3. 8 carpal bones make up wrist
4. Proximal end of hand
5. Arranged (roughly) in 2 rows
- Straight Line To Pinky, Here Comes The Thumb
6. Very flexible because of the gliding motions at articulations
7. Scaphoid is fractured most frequently
2. Found in wrist
3. 8 carpal bones make up wrist
4. Proximal end of hand
5. Arranged (roughly) in 2 rows
- Straight Line To Pinky, Here Comes The Thumb
6. Very flexible because of the gliding motions at articulations
7. Scaphoid is fractured most frequently
91
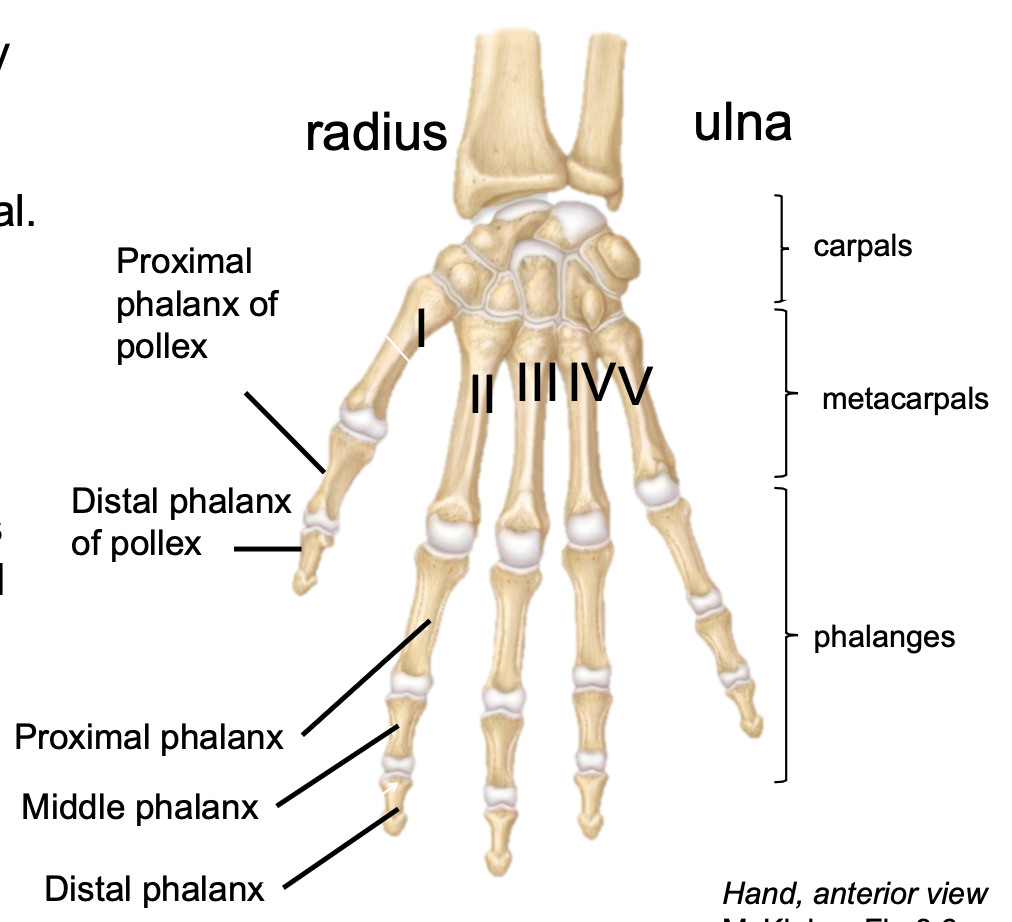
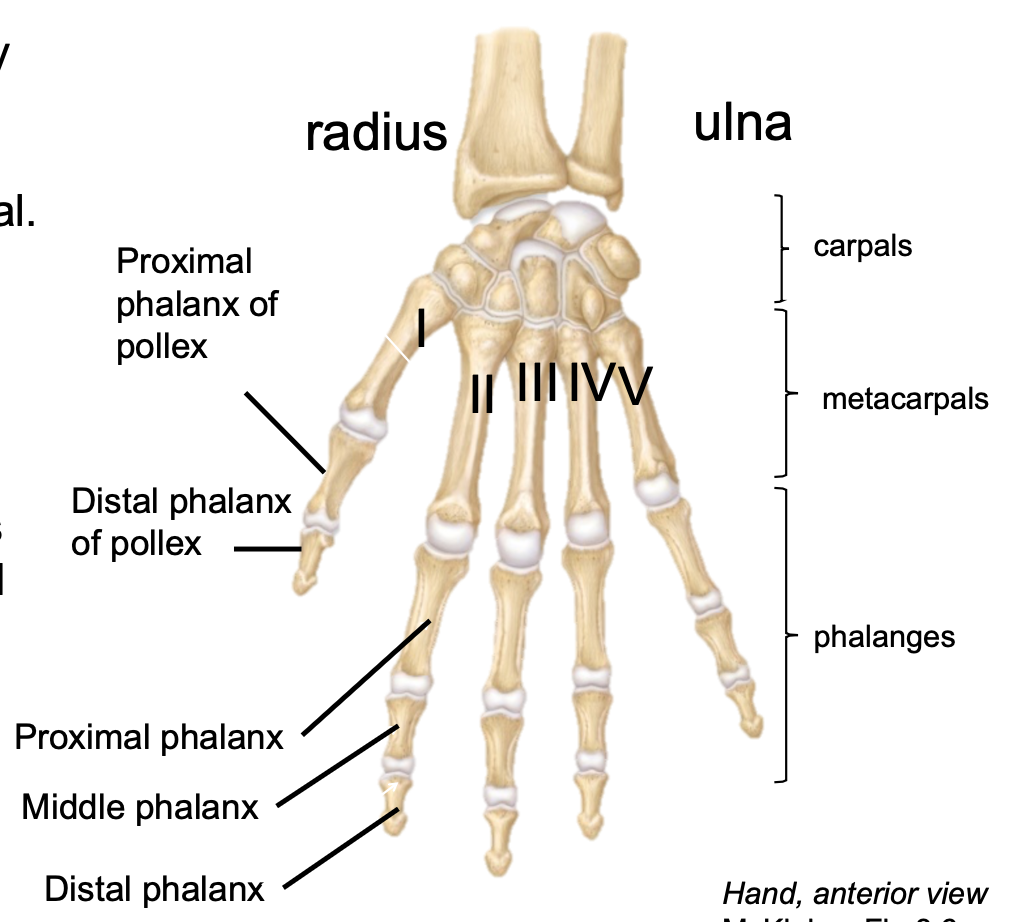
New cards
Metacarpals
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in hand
3. Each digit has one metacarpal
2. Found in hand
3. Each digit has one metacarpal
92
New cards
Phalanges (Upper Limb)
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Found in hand
3. Digits II-V have three phalanges
- Proximal, middle and distal
4. Digit I (Pollex or Thumb) has two phalanges
- Proximal and distal
2. Found in hand
3. Digits II-V have three phalanges
- Proximal, middle and distal
4. Digit I (Pollex or Thumb) has two phalanges
- Proximal and distal
93
New cards
How are the digits in the hand labeled?
1. There are 5 digits in each hand
2. They are labeled I-V starting at the thumb and ending at the pinky
2. They are labeled I-V starting at the thumb and ending at the pinky
94
New cards
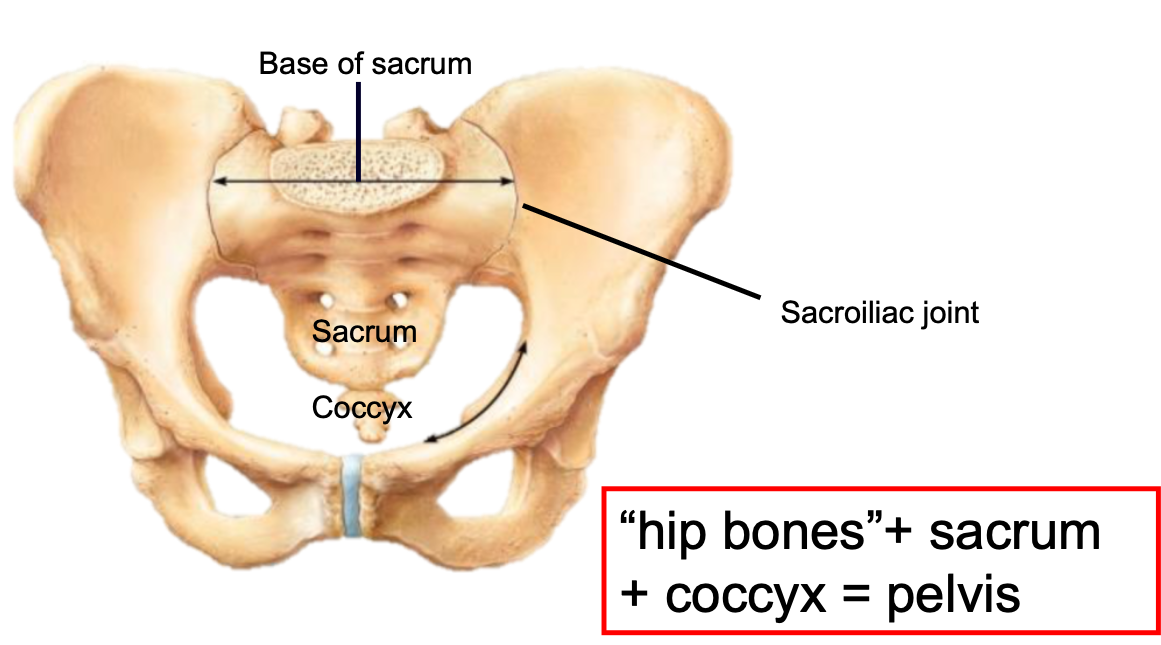
Pelvis
1. Part of both the appendicular and axial skeleton
2. Consists of
- Hip bones
- Sacrum
- Coccyx
3. Attaches the lower limbs to the trunk
- Body weight passes through pelvis to the lower limbs
4. Supports viscera
5. Strong attachment to axial skeleton at the sacroiliac joint (very stable)
6. Less freedom of movement compared to pectoral girdle
2. Consists of
- Hip bones
- Sacrum
- Coccyx
3. Attaches the lower limbs to the trunk
- Body weight passes through pelvis to the lower limbs
4. Supports viscera
5. Strong attachment to axial skeleton at the sacroiliac joint (very stable)
6. Less freedom of movement compared to pectoral girdle
95
New cards
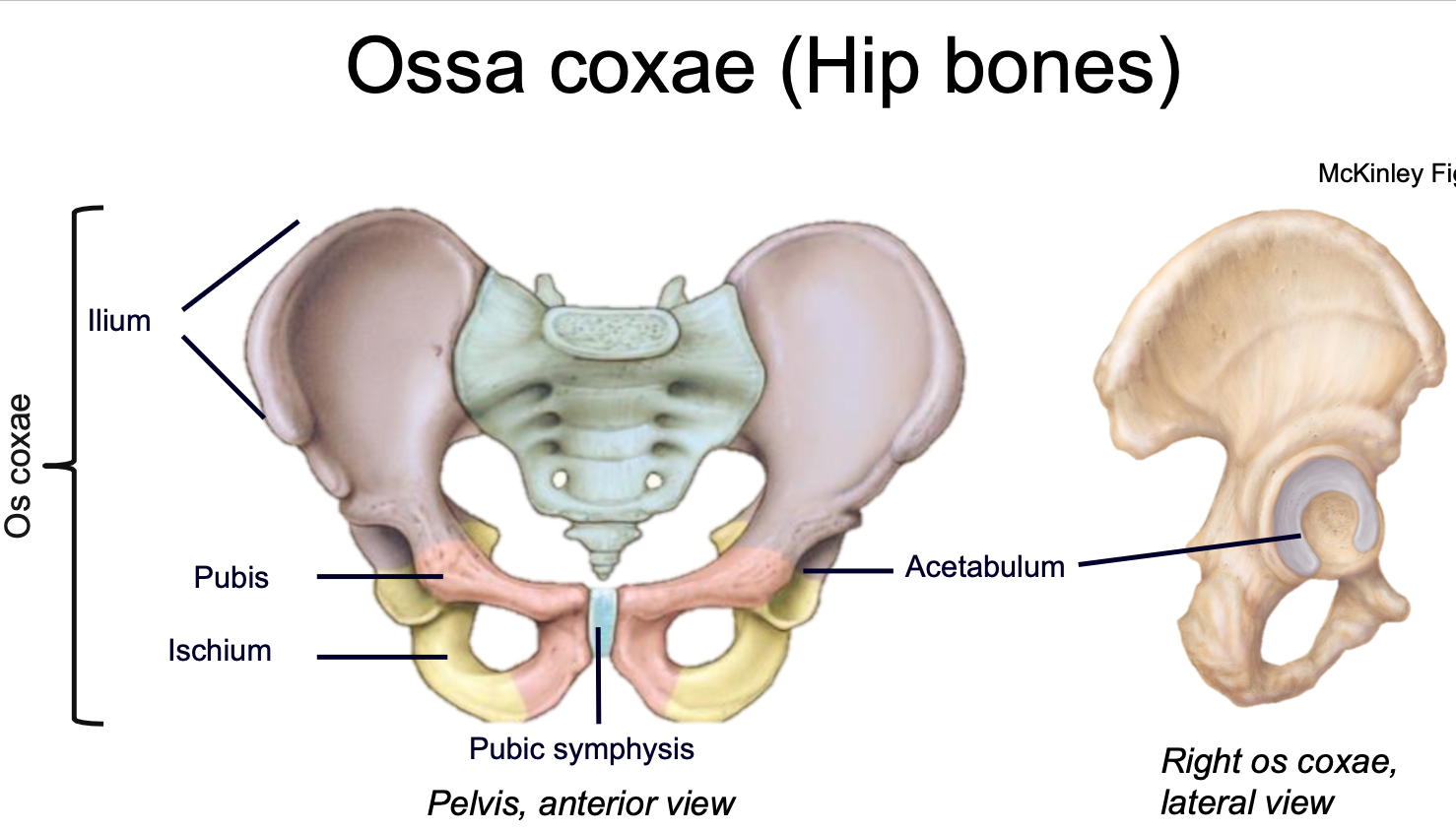
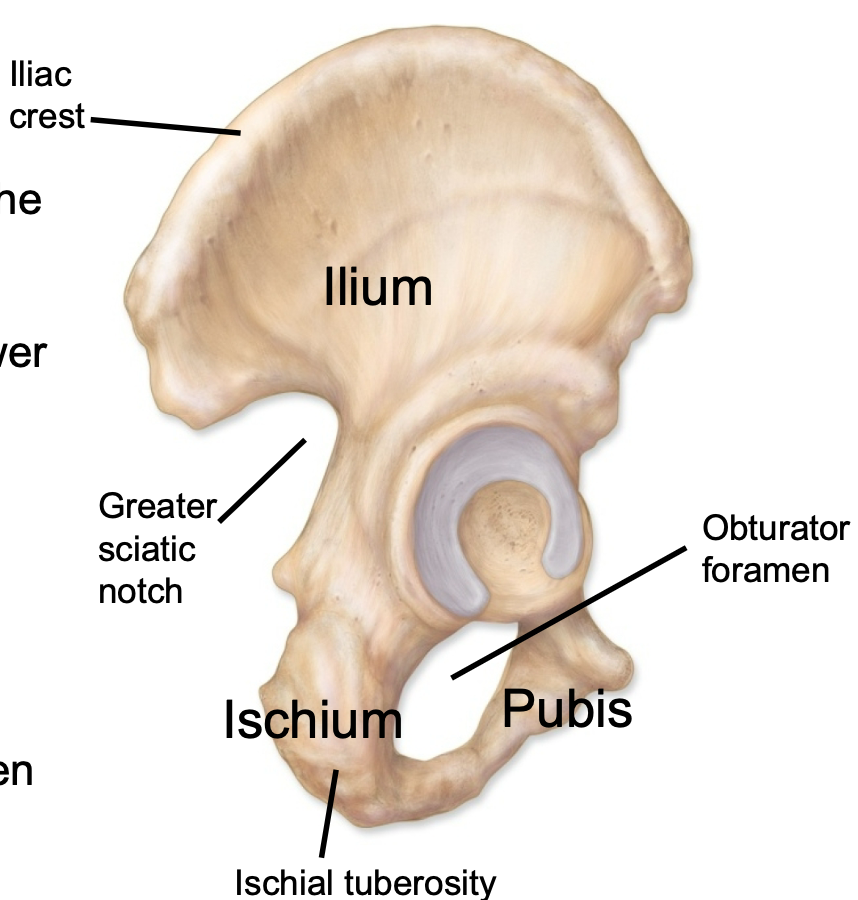
Ossa Coxae
1. AKA Hip bones
2. Appendicular skeleton
3. Found in pelvis
4. Consists of three bones that fuse by adulthood
- Ilium
- Ischium
- Pubis
2. Appendicular skeleton
3. Found in pelvis
4. Consists of three bones that fuse by adulthood
- Ilium
- Ischium
- Pubis
96
New cards
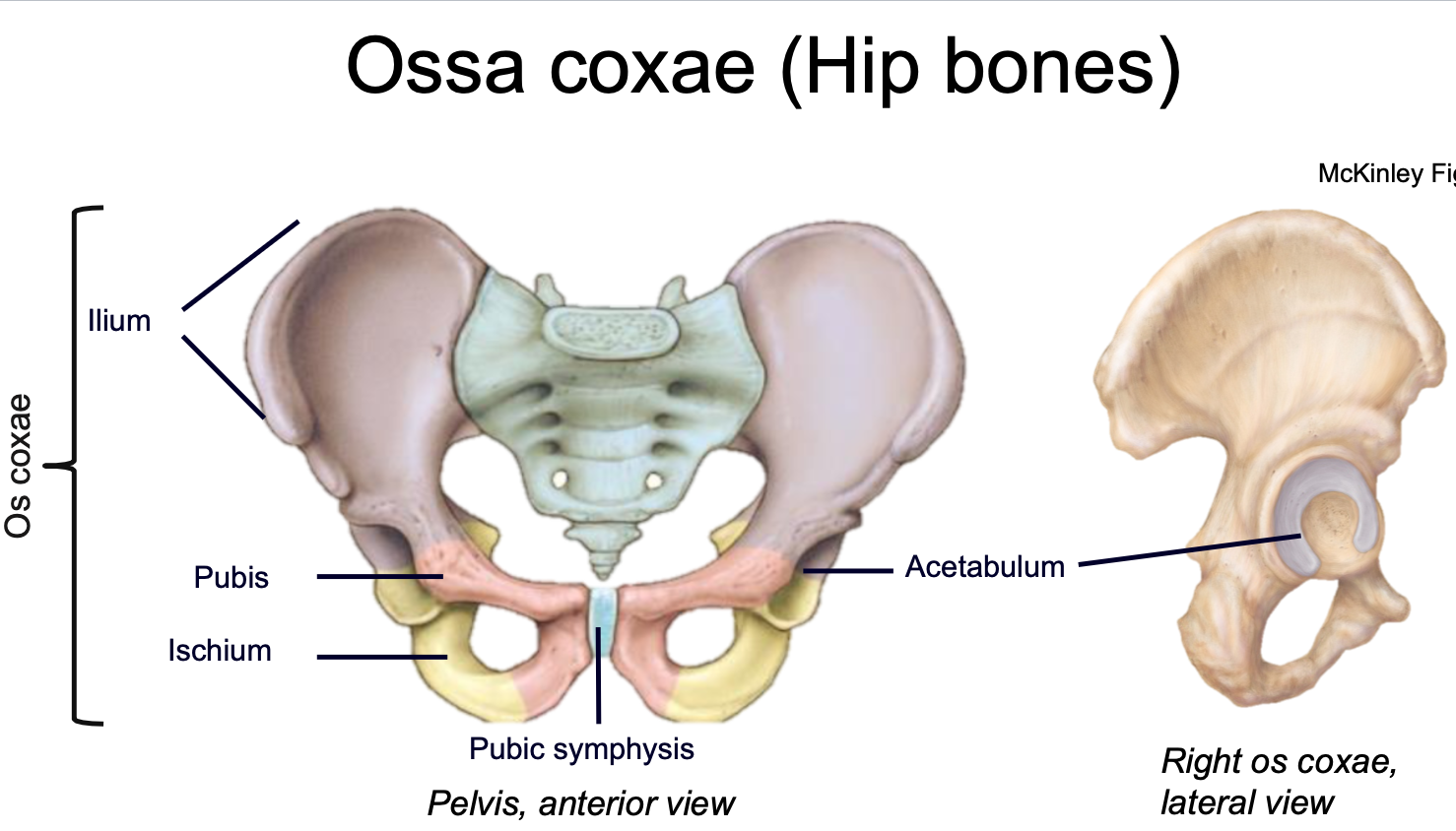
Acetabulum
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Where the ilium, ischium, and pubis fuse
3. Found in hipbone in pelvis
4. Cup-shaped lateral socket where head of the femur articulates
5. Composed of all three pelvic bones
2. Where the ilium, ischium, and pubis fuse
3. Found in hipbone in pelvis
4. Cup-shaped lateral socket where head of the femur articulates
5. Composed of all three pelvic bones
97
New cards
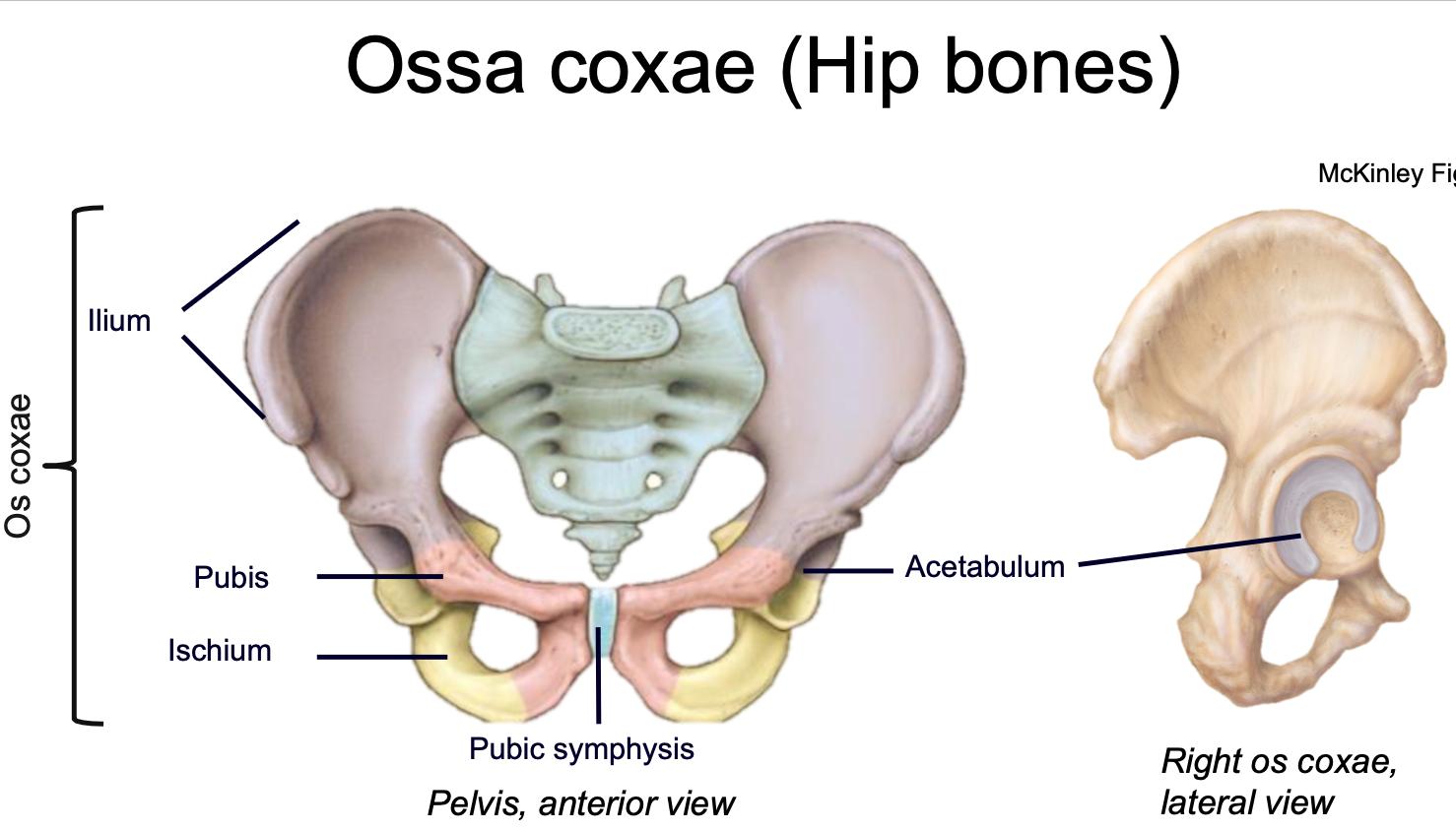
Pubic Symphysis
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Where the two hip bones articulate (join) anteriorly
2. Where the two hip bones articulate (join) anteriorly
98
New cards
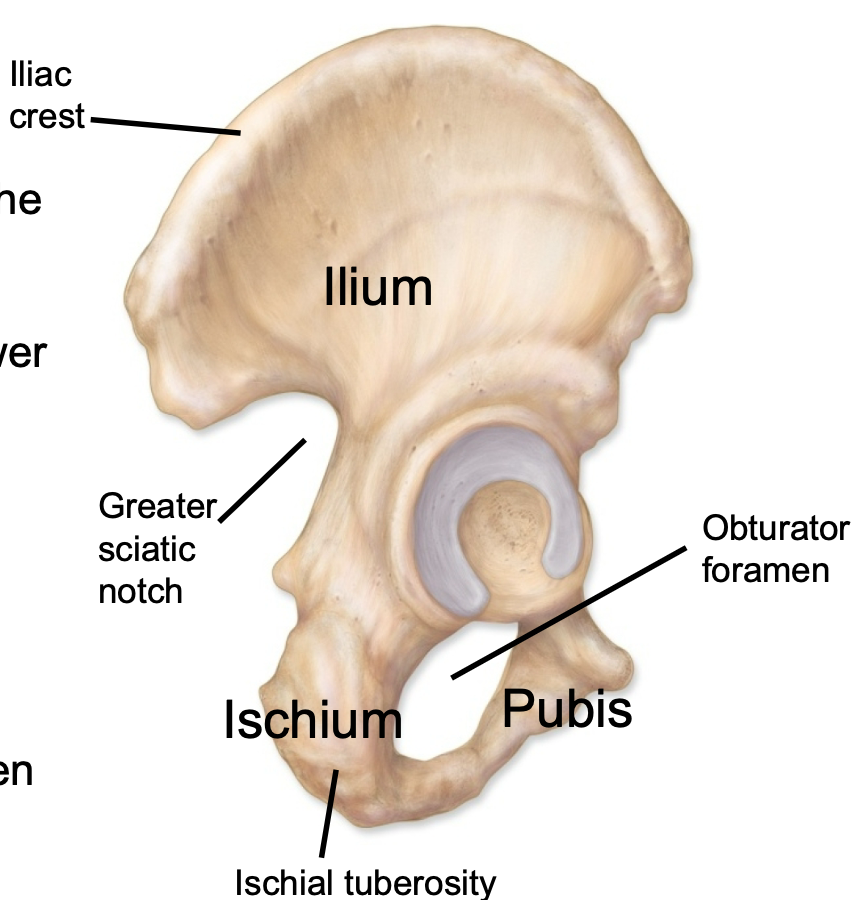
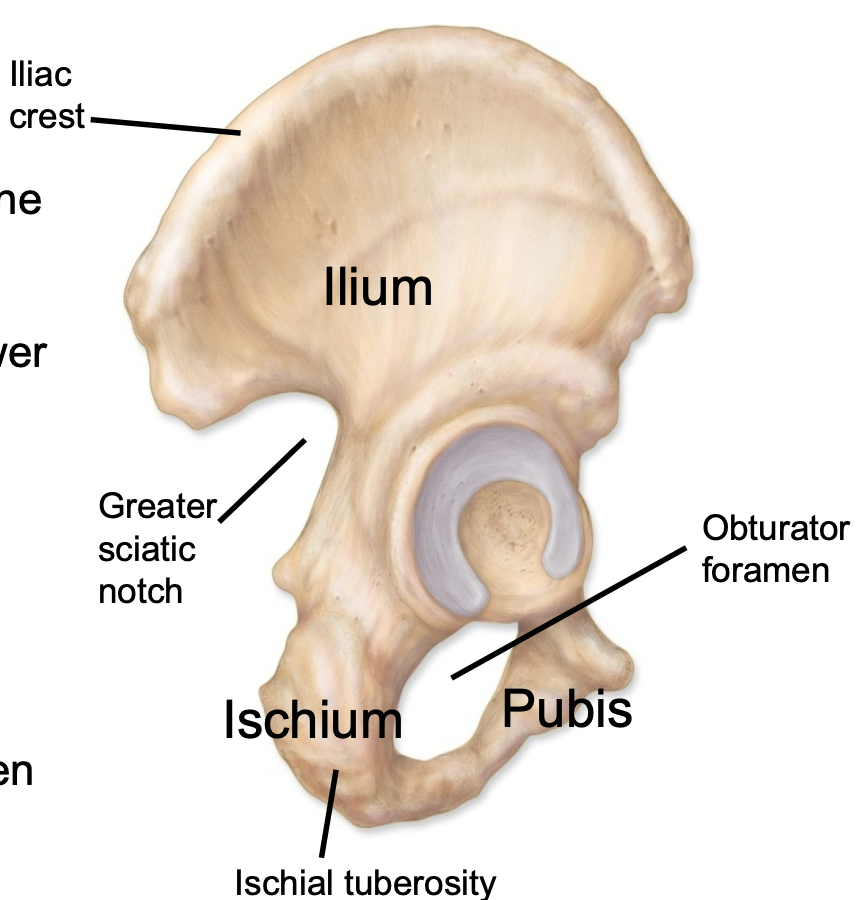
Ilium
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Hip bone found in pelvis
3. Iliac crest is superior ridge of the bone
4. Greater sciatic notch allows passage of sciatic nerve to lower limb
2. Hip bone found in pelvis
3. Iliac crest is superior ridge of the bone
4. Greater sciatic notch allows passage of sciatic nerve to lower limb
99
New cards
Ischium
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Hip bone found in pelvis
3. Ischial tuberosities are the “sit bones"
2. Hip bone found in pelvis
3. Ischial tuberosities are the “sit bones"
100
New cards
Pubis
1. Appendicular skeleton
2. Hip bone found in pelvis
3. Along with the ischium contributes to obturator foramen
2. Hip bone found in pelvis
3. Along with the ischium contributes to obturator foramen