chapters after midterm II
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
Countries engaged in international trade will specialize in production based on:
a. relative levels of gross domestic product (GDP)
b. comparative advantage
c. relative exchange rates
d. relative inflation rates
e. relative unemployment rates
comparative advantage
International trade and the associated increase in international competition has forced American businesses to:
a. raise production costs
b. redistribute income to workers
c. improve productivity
d. reduce productivity
e. be less efficient
improve productivity
While comparative advantage is the biggest reason many nations engage in trade, two other important reasons are:
a. economies of scale and increased competition
b. economies of scale and decreased competition
c. increased competition and increased production costs
d. increased production costs and access to smaller markets
e. decreased competition and access to smaller markets
economies of scale and increased competition
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), later replaced by USMCA, was intended to increase U.S. trade with which other countries?
a. China and Russia
b. Brazil and Panama
c. Argentina and Chile
d. Colombia and Venezuela
e. Mexico and China
Mexico and Canada
What are the effects on market equilibrium, domestic price, and quantity, of restrictions to trade such as tariffs, quotas, or other restrictions imposed by the government?
a. equilibrium price remains the same and equilibrium quantity sometimes increase because domestic producers produce more
b. equilibrium price falls because of a reduction in the supply of the good and the quantity remains the same
c. both equilibrium price and quantity increase
d. equilibrium price decreases and quantity will increase
e. there is an increase in the equilibrium price, but a reduction in the equilibrium quantity
There is an increase in the equilibrium price, but a reduction in the equilibrium quantity
A tariff is:
a. a tax on exports
b. a tax on imports
c. a trade agreement between two countries
d. a good allowed to be imported tax-free
e. a permit for the import of foreign goods
a tax on imports
A limit imposed on the volume of total imports of a particular good is known as a(n):
a. trade cap
b. import quota
c. tariff
d. exchange limit
e. seawall
import quota
When a country decides to begin importing a good that they already produce domestically, then there will be an increase in ______ and the market price will ______.
a. supply; increase
b. demand; increase
c. supply; decrease
d. supply and demand; decrease
e. demand; decrease
supply; decrease
When a country decides to impose a tariff on a good, they are already importing, we can expect the _____ to decrease and the price of the good to ______.
a. supply; increase
b. demand; increase
c. supply; decrease
d. supply and demand; decrease
e. demand; decrease
supply; increase
A quota:
a. imposes a tax on goods entering the country
b. limits the quantity of goods leaving the country
c. subsidizes the production of goods leaving the country
d. limits the quantity of goods entering the country
e. is a tax in an imported good
limits the quantity of good entering the country
An import quota:
a. limits the amount of a good that can be imported, thus increasing prices
b. is the same as a ban on imports
c. increases the amount of a good imported, thus increasing prices
d. increases the amount of a good imported, thus decreasing prices
limits the amount of a good that can be imported, thus increasing prices
Which of the following arguments is most likely used to protect a new developing industry?
a. a new developing industry will reduce employment in the nation
b. a new infant industry requires protection from foreign competition
c. a developing nation needs to protect all developing industries for them to grow
d. protection is needed to avoid predatory dumping from other nations
e. protection of a new developing industry is needed to achieve economic independence
A new infant industry requires protection from foreign competition
When a foreign supplier sells a good below the price it charges in its home country, this is called:
a. loss-leading
b. flooding
c. dumping
d. price fixing
e. lowballing
dumping
Why do politicians sometimes resist free trade and “globalization”?
a. free trade does not benefit the economy as a whole
b. special interest groups may not benefit from free trade
c. free trade does not benefit the global economy
d. free trade usually hurts consumers
e. only the rich benefit from free trade
Special interest groups may not benefit from free trade
A possible reason a nation might impose a restrictive policy such as a tariff is to:
a. help domestic firms increase market share relative to their foreign competition
b. increase the welfare of domestic consumers
c. increase the level of imports
d. reduce the welfare of domestic producers
e. give foreign consumers more options
help domestic firms increase market share relative to their foreign competition
If trade is balanced for a nation,
a. the sum of its exports and imports is zero
b. the value of its exports exceeds the value of its imports
c. the value of its exports is equal to the value of its imports
d. the difference between exports and imports for this nation is greater than zero
e. net exports are positive always for this nation
the value of its exports is equal to the value of its imports
If a country imposed a tariff on imported beef, what would be the effects on the country’s market for beef?
After the tariff, the price of beef will increase and quantity of beef will decrease. Imports of beef will decrease. Domestic producers will benefit because they produce more and can charge a higher price.
The cost of producing a bushel of wheat in Country A is $5, and the price at which Country A sells a bushel of wheat abroad is $4. This is an example of:
a. import quota
b. import tariffs
c. dumping
d. economies of scale
e. export tariffs
dumping
Specialization and _____ make it possible to achieve gains from trade between nations.
a. a strong central government
b. a high literacy rate
c. a stable population size
d. comparative advantage
e. sharing of technology
comparative advantage
Use the following scenario to answer the next two questions.
Suppose Canada, an industrialized nation, and Mexico, a developing nations, both produce clothes and cars. The real wage in Mexico is lower than in Canada. The countries have a free trade agreement. Each nation will produce according to its comparative advantage.
Which one of these statements correctly describes the benefits both countries receive from trade?
Both nations benefit from trade because they are able to produce a combined larger output and exchange it between them at a lower cost than their respective domestic opportunity costs.
Which country’s consumers will benefit from the free trade agreement?
both countries
The ability of one person or nation to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another is called a(n) _____ advantage.
a. positional
b. absolute
c. comparative
d. structural
e. relative
comparative
In general, a nation can enjoy a higher standard of living by _____ than by being self-sufficient.
a. increasing its versatility
b. avoiding trade with other nations
c. specializing and trading
d. taxing imported goods
e. producing on the PPF curve
specializing and trading
Which of the following statements describes a trade deficit?
a. the total value of a nation’s exports and imports
b. the difference between a nation’s total exports and total imports
c. a nation’s exports are greater than its imports
d. a nation’s imports are greater than its exports
e. a nation’s exports are exactly equal to its imports
a nation’s imports are greater than its exports
If the reserve ratio is 25%, what is the simple deposit multiplier?
a. 0.25
b. 25
c. 4
d. 50
e. 5
4
Federal funds are the
a. deposits that private banks hold on reserve at the Federal Reserve (Fed)
b. loans between private banks
c. loans from the Fed to private banks
d. income generated by the Fed through discount loans
e. portion of bank deposits that are set aside and not loaned out
loans between private banks
If the reserve ratio is 8%, what is the simple deposit multiplier?
a. 0.08
b. 24
c. 8
d. 48
e. 12.5
12.5
To decrease the money supply, the Federal Reserve could
a. increase the discount rate
b. decrease the reserve ratio
c. forbid the reselling of U.S. Treasury securities
d. encourage banks to lend money to borrowers
e. conduct an open market purchase of U.S Treasury securities
increase the discount rate
The sale of existing US Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve will
a. have no effect on the money supply
b. increase the money supply
c. increase the reserves at banks
d. decrease the amount of U.S. Treasury securities held at banks
e. decrease the money supply
decrease the money supply
Currency is
paper bills and coins used to buy goods and services
Fiat money is money that
a. is declared to have a certain value below its intrinsic value
b. can be exchange for a commodity at a fixed rate; there is no inherent value
c. is inherently valuable; its value as a medium of exchange is in addition to its inherent value
d. has no value except as a medium of exchange; there is no inherent intrinsic value
e. an intrinsic value to its value as a medium of exchange
has no value except as a medium of exchange; there is no inherent intrinsic value
A bank's assets are the
a. financial obligations the bank owes to others
b. items of value the banks owns
c. portion of bank deposits that are set aside and not loaned out
d. currency deposited in the bank’s accounts
e. property the bank underwrites as the loan source
items of value the bank owns
A bank's liabilities are the
a. financial obligations the bank owes to others
b. items of value the bank owns
c. portion of bank deposits that are set aside and not loaned out
d. currency deposited in the bank’s accounts
e. property the bank underwrites as the loan source
financial obligations the bank owes to others
A bank owner's equity is the
a. financial obligations the bank owes to others
b. items of value the bank owns
c. portion of bank deposits that are set aside and not loaned out
d. difference between a bank’s assets and its liabilities
e. property the bank underwrites as the loan source
difference between a bank's assets and its liabilities
Bank reserves are the
a. financial obligations the bank owes to others
b. items that the bank owns
c. property the bank underwrites as the loan source
d. currency deposited in a bank’s accounts
e. portion of banks deposits that are set aside and not loaned out
portion of bank deposits that are set aside and not loaned out
The discount rate is the
a. rate at which loans are issued between banks and the Federal Reserve (Fed)
b. interest rate charged by banks on interbank loans
c. difference between the interest paid for deposits and the interest gained from loans
d. percentage of deposits that must be held back and not loaned out
e. interest rate on the loans made by the Fed to private banks
interest rate on the loans made by the Fed to private banks
Open market operations involve the
a. purchase or sale of bonds by a central bank
b. Federal reserve (Fed) dictating the discount rate to influence the money supply
c. purchase of securities from the U.S. Treasury
d. loaning of deposits between private banks
e. sale of Fed notes
purchase or sale of bonds by a central bank
What does it mean for the Federal Reserve Bank (Fed) to be the "lender of last resort?"
a. it will make loans to individuals when no bank will do so
b. it will make loans to a bank when no other bank will do so
c. it will buy Treasury bonds when no private entity will do so
d. a loan from the Fed is the least desirable kind of loan
e. a loan from the Fed is normally the last step on the way to bank failure
it will make loans to a bank when no other bank will do so
What is the difference between commodity money and commodity-backed money?
Commodity money is an actual good, whereas commodity-backed money is only exchangeable for an actual good.
Which of the following is a component of M1?
a. checking accounts
b. credit card debt
c. money market mutual funds
d. certificates of deposit
e. U.S. Treasury securities
checking accounts
What function of money is highlighted when the price of one product is compared to another?
a. means of bartering
b. medium of exchange
c. store of value
d. commodity backing
e. unit of account
unit of account
Craig has a savings account at the local bank, and his sister has home mortgage loan at the same bank. How does each of these appear on the bank's balance sheet?
The savings account is a liability, and the mortgage is an asset.
Which of the following would NOT be an asset for a commercial bank?
a. loans
b. U.S. Treasury securities
c. cash in the vault
d. checkable deposits
e. investment
checkable deposits
How is owner's equity calculated?
a. reserves - borrowings
b. assets - liabilities
c. reserves - liabilities
d. assets - borrowings
e. owners equity cannot be calculated from the information on a banks balance sheet
assets - liabilities
A fractional reserve banking system is a system where banks:
a. show only a fraction of deposits on their balance sheets
b. accept only a fraction of loan requests
c. accept only a fraction of the deposits individuals try to make
d. keep a fraction of deposits on hand as reserves
e. maintain a fixed ratio between savings deposits and checking deposits
keep a fraction of deposits on hand as reserves
If a bank has a reserve ratio of 25% and holds $5,300,000 in deposits, what is the desired reserve level?
a. $25,000
b. $2,275,000
c. $280,000
d. $5,005,000
e. $1,325,000
1,325,000
If Bank of Mateer maintains a reserve ratio of 15% and there is $100,000 in deposits, what is the desired reserve level?
a. $100,000
b. $60,000
c. $15,000
d. $0
e. $40,000
$15,000
Which of the following claims is true?
the US has a trade deficit in goods trade, but a surplus in service trade
Which is true with regard to US trade?
the US has run a trade deficit since 1975
In the US, imports and exports:
have both risen in the last 50 years
How would you characterize world trade in goods over the past 40 years?
it has grown dramatically
When economists are using the phrase "economic growth" what are they referring to?
Percentage changes in real GDP per capita
The time period in which per capita GDP for the world started to increase faster than it had in the rest of history began during what years?
1800s
If the annual growth rate of an economy is 7%, how long will it take for income to double?
10 years
Rule of 70: 70/7%= 10
Land, labor, and capital are considered
a. resources
b. technology
c. institutions
d. investments
Resources
Why is technological advancements important for economic growth?
It allows us to produce more output while using fewer resources.
Why do institutions, such as private property rights, promote economic growth?
a. private property rights guarantees that the economy is stable in the short run, which encourages investment
b. private property rights are usually forced on a country, whereas collective ownership is voluntarily adopted
c. Private property rights create an incentive to maximize the value of one's property, e\which is not true when property is collectively owned
d. private property rights guarantee that everyone will have equal amounts of property
e. private property rights are not established by governments but rather by private individuals
Private property rights create an incentive to maximize the value of one's property, e\which is not true when property is collectively owned
Which of the following factors is positively correlated with economic growth?
a. collectively owned resources
b. political stability and rule of law
c. high barriers to international trade
d. high rates of inflation
e. restrictions on immigration
political stability and rule of law
Economic growth is defined as the percentage change in
a. nominal gross domestic product (GDP)
b. population
c. real per capita GDP
d. price level
e. GDP deflator
real per capita GDP
Resources are also known as
a. factors of productivity
b. factors of input
c. factors of production
d. elements of growth
e. elements of productivity
factors of production
Competitive markets contribute significantly to economic growth because
a. they encourage firms to exploit consumers via high prices
b. people who want to participate don't face barriers to entry
c. they employ high levels of government regulations
d. they prevent foreign firms (with better ideas) from entering markets
e. they create an incentive for firms to differentiate their products
people who want to participate don't face barriers to entry
If your income increases at a rate of 6% per year, about how long will it take to double your income?
12 years
Rule of 70: 70/6% = 11.67
Jayme has worked for the same company her entire life. Her current income is $90,000 per year. When she was hired, she made $45,000 per year. The company has given Jayme a consistent raise of 5% every year. How long has Jayme been with the company?
14 years
Rule of 70: 70/5% = 14
From 2017 to 2018 real per capita gross domestic product (GDP) in the United States grew by 2.2%. If this growth rate is sustained, according to the rule of 70, in roughly how many years will real per capita GDP double?
32 years
Rule of 70: 70/2.2% = 31.8
Resources are
a. the output that firms produce
b. inputs used to produce goods and services
c. the technology that firms use to make things
d. the institutions that encourage efficiency
e. the cost of producing goods and services
inputs used to produce goods and services
A(n) _____ in capital goods should _____ worker productivity.
a. decrease; increase
b. increase; increase
c. increase; have not effect on
d. increase; decrease
e. decrease; have no effect on
increase; increase
An example of physical capital is
a computer
Saudi Arabia is an oil-rich country in the Middle East. The oil in Saudi Arabia is _____ for the country.
natural resource
Which of the following are the 3 major categories of resources?
natural resources, physical capital, human capital
From 1960 to 1990, real per capita gross domestic product (GDP) in South Korea grew an average of 8% per year. At that rate, according to the rule of 70, it takes about ________ years for South Korea's economy to double in size.
9 years
Rule of 70: 70/8% = 8.75
What is the primary benefit of taxes with regard to economic growth?
a. taxes make the economy fairer by redistributing income from the rich to the poor
b. taxes improve the efficiency of markets by changing producer decisions
c. taxes increase worker productivity by increasing the amount of work one needs to do
d. Taxes provide the revenue to pay for government services
e. taxes create stable price levels, which incentivizes investment
Taxes provide the revenue to pay for government services.
_____ is a mandated federal program that funds health care for retired persons.
a. medicare
b. social security
c. medicaid
d. food stamps
e. unemployment compensation
medicare
_____ is/are a government-administered program.
social security
reforming entitlement programs is difficult because:
a. reforms require changes to existing law, which take time
b. there is a very little interest in the problem of rising national debt
c. the proposed reforms all require tax increases, which are politically unpopular
d. all the reforms proposed are only short-term solutions
e. there are no good ideas for effective reform
reforms require changes to existing law, which take time.
what is considered discretionary government spending?
a. retirement checks to former government employees
b. medicare payments
c. payments to food stamp recipients
d. funding for federal highway repairs
e. interest on Treasury bonds held by foreign owners
funding for federal highway repairs
the largest source of tax revenue for the government is ____ taxes.
a. individual income
b. estate
c. corporate income
d. excise
e. social insurance
individual income
mandatory outlays are another name for what?
another name for discretionary outlays
which type of tax is progressive in the US?
a. property
b. income
c. sales
d. excise
e. social insurance
income tax
mandatory outlays are different from discretionary outlays because:
discretionary outlays can be changed during the annual budget process, whereas mandatory outlays cannot.
taxes on wages:
a. are paid only by individuals who are self-employed
b. generate revenues earmarked for mandatory spending purposes
c. generate revenues earmarked for discretionary spending purposes
d. rise as a percentage of income as income increases
e. are not paid by workers in the bottom income tax bracket
generate revenues earmarked for mandatory spending purposes
the largest portion of federal outlays is dedicated to:
a. discretionary spending
b. payroll taxes
c. income taxes
d. mandatory spending
e. interest payments
mandatory spending
a marginal tax rate is:
a. the tax rate paid on a worker's next dollar of income
b. equal to a worker’s income tax bracket
c. the total tax paid divided by the amount of taxable income
d. irrelevant for making decisions about earning extra income
e. applied only to high earners under a progressive income tax system
the tax rate paid on a worker's next dollar of income
A US federal government budget deficit occurs when
a. government revenue exceeds outlays
b. government outlays exceed revenue
c, government outlays equal revenue
d. the United States borrows money from foreign countries
e. the United States lends money to foreign countries
government outlays exceed revenue
a US federal government budget surplus occurs when:
a. a government revenue exceeds outlays
b. government outlays exceed revenue
c. government outlays equal revenue
d. the United States borrows money from foreign countries
e. the United States lends money to foreign countries
a government revenue exceeds outlays
the US government could reduce its budget deficit by:
a. borrowing funds from abroad
b. raising the eligible retirement age to receive social security benefits
c. expanding the income assistance programs
d. increasing discretionary spending
e. decreasing the level of means-testing for Medicare eligibility
raising the eligible retirement age to receive social security benefits.
the federal budget deficit has grown so quickly in the past decade because of:
a. increased tax revenue
b. increased spending on entitlement programs
c. lower income tax rates on the top 1% of households
d. economic expansion
e. higher interest payments on current government debt
increased spending on entitlement programs
why does the federal debt tend to increase during periods of recession?
economic activity decreases, which decreases revenues and increases outlays.
____ are payments made to groups or individuals when no good or service is received in return.
a. unilateral payments
b. entitlements
c. endorsements
d. transfer payments
e. exempt payments
transfer payments
mandatory outlays are sometimes referred to as ______ programs
a. entitlement
b. expansionary
c. endorsement
d. obligatory
e. means-tested
entitlement
_____ outlays include spending that can be changes when the government is setting its annual budget.
a. government
b. mandatory
c. discretionary
d. perpetual
e. penetrable
discretionary
an important consequence of foreign-held debt is the _____ of the supply of loanable funds in the United States, which helps keep interest rates ____.
a. decrease; high
b. increase; low
c. decrease; low
d. velocity; stable
e. increase; high
increase ; low
which of the following is an example of an excise tax?
a. tax on imports
b. state sales tax
c. gasoline tax
d. property tax
e. inheritance tax
gasoline tax
Suppose there is a plunge in stock market values. In the short run, we would expect the price level to ____ and the unemployment rate to ____.
a. increase; decrease
b. decrease; decrease
c. increase; increase
d. remain unchanged; decrease
e. decrease; increase
decrease; increase
The US and Canada are trading partners. If wealth increases in Canada, in the short run, equilibrium output in the US will ___ and the price level will ___
increase; increase
Based on the graph, a positive supply shock best represents by a movement from
LRSA1 to LRSA2 or SRAS1 to SRAS2 (pick one on exam)
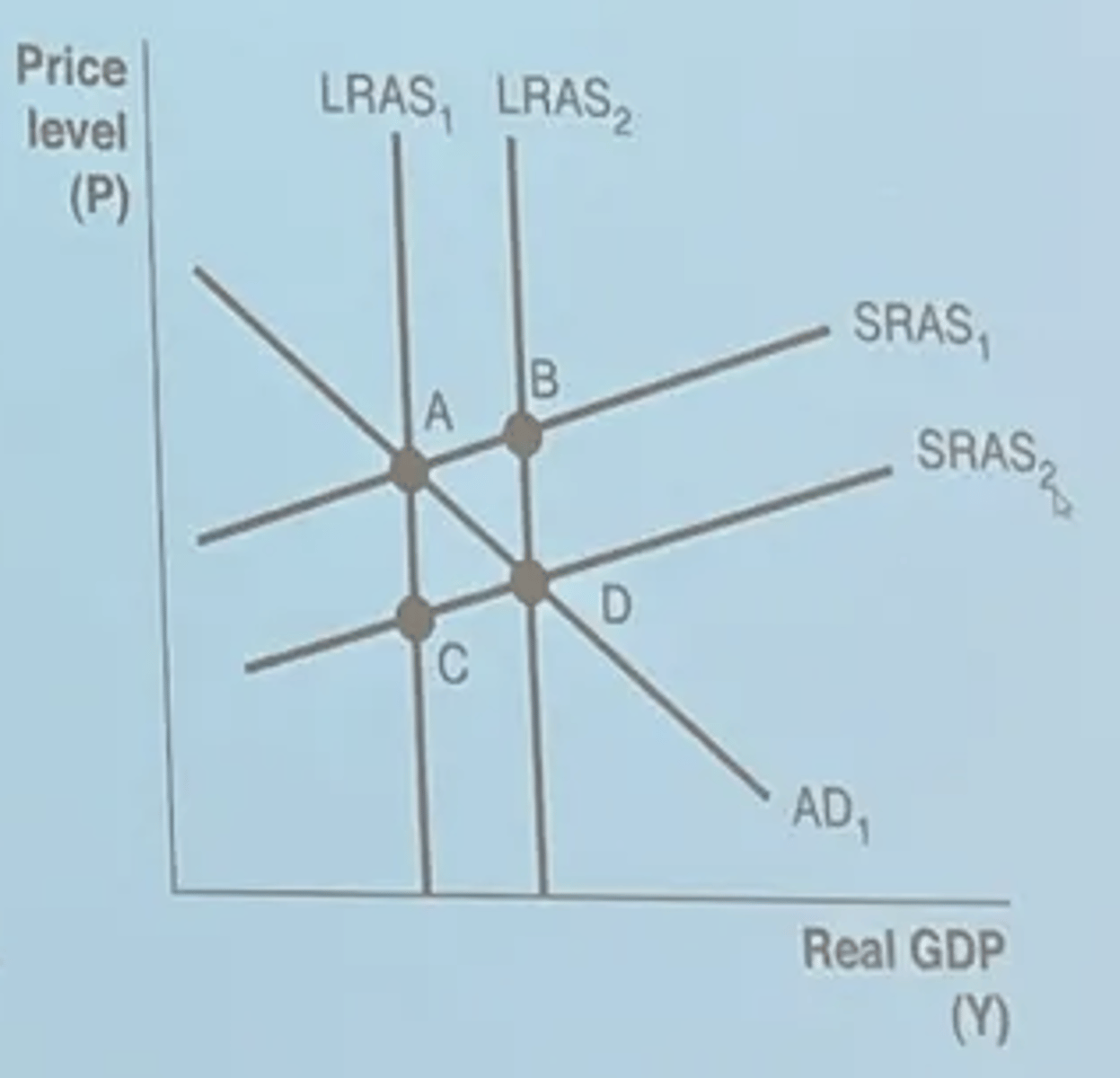
Based on the graph, which of the following would cause the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve to shift from SRAS2 to SRAS1?
a. congress votes to decrease the minimum wage
b. there is an increase in spending and firms
c. wages and input prices rise as the economy responds to inflation expectations
d. the number of people in the workforce increases
e. a temporary fall in the price of oil results in lower gasoline prices
wages and input prices rise as the economy responds to inflation expectations
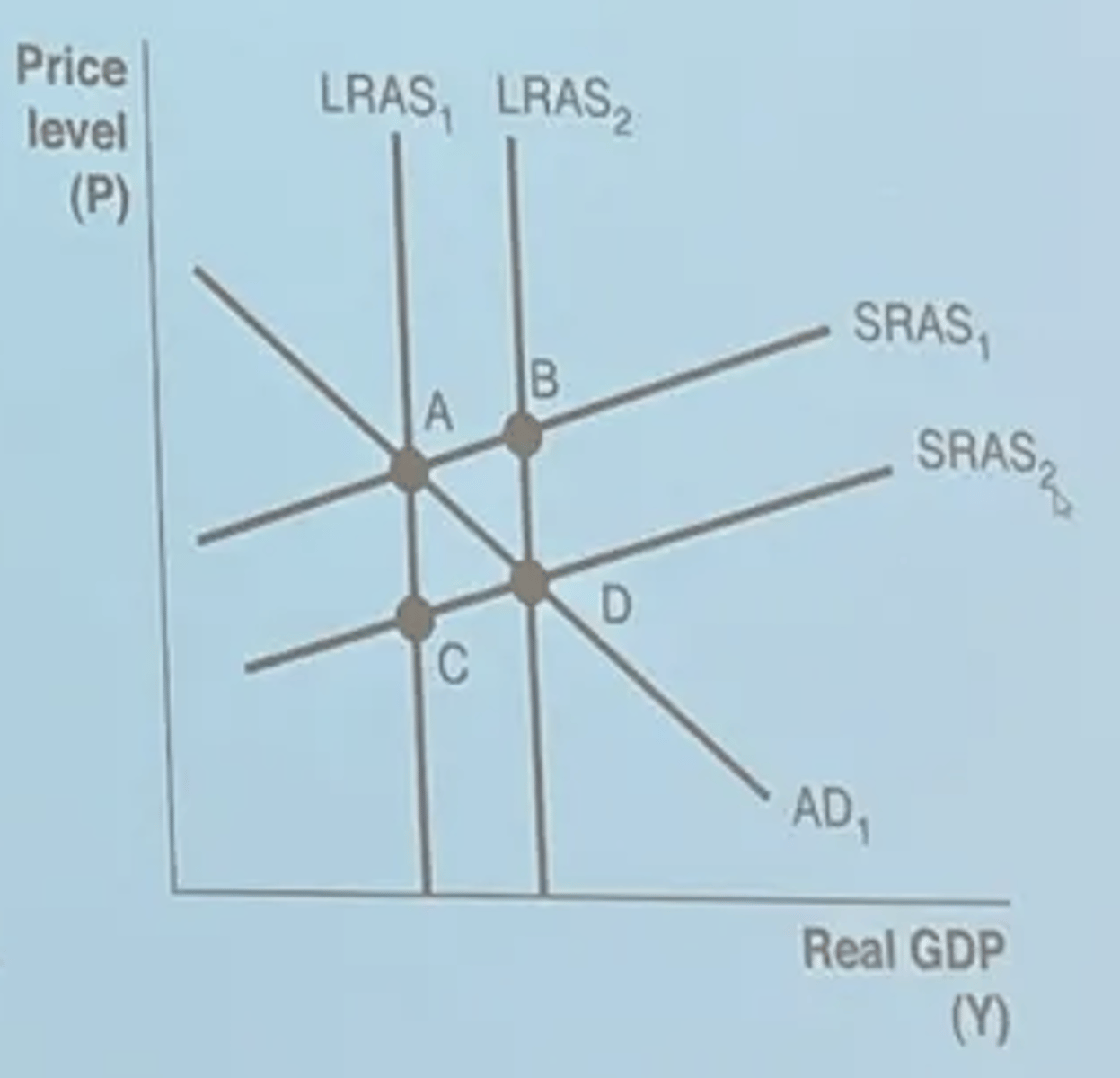
What would cause a shift of LRAS1 to LRAS 2
Improvement in tech
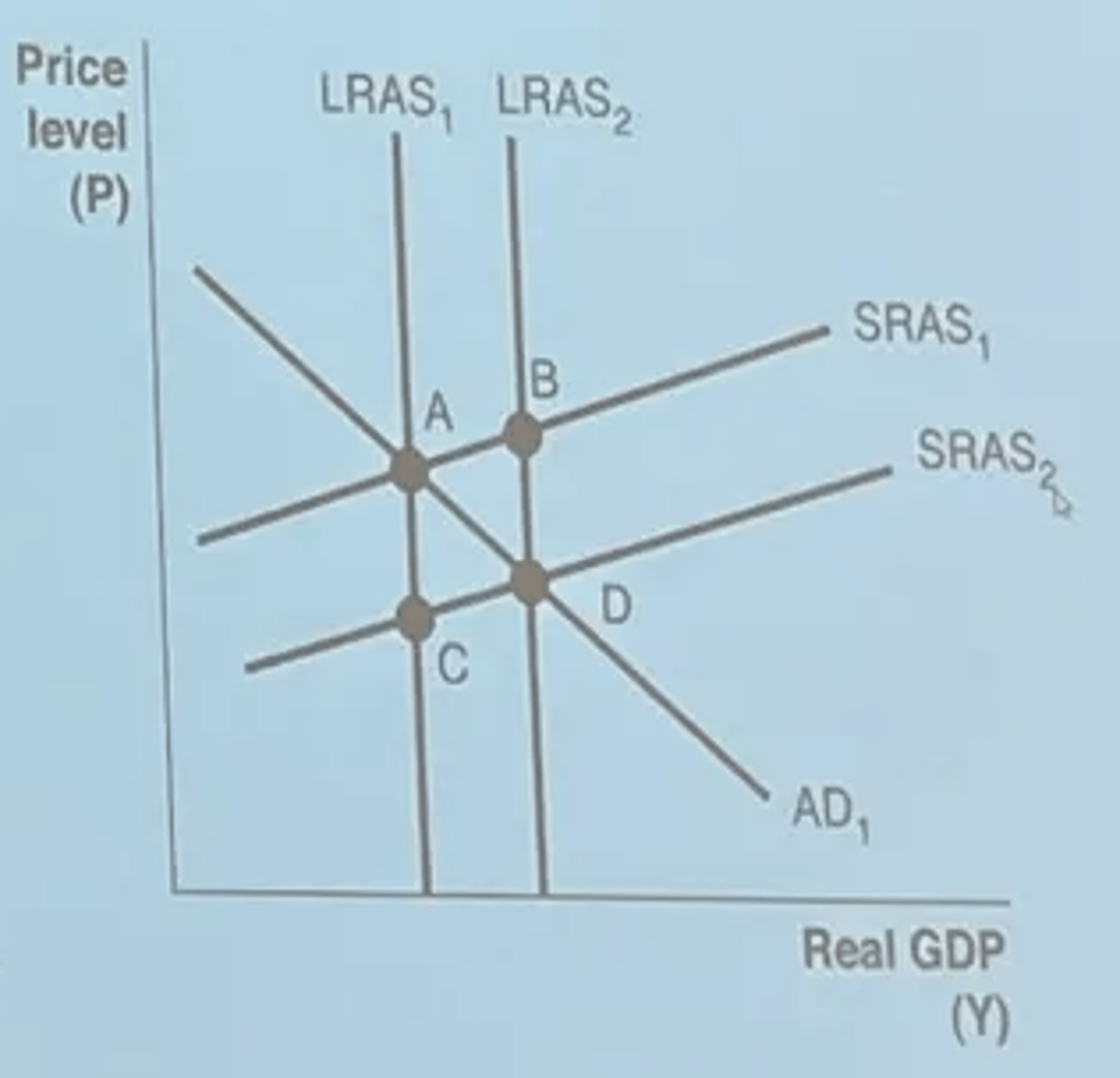
People are worried about losing their job, the short run will
increase Aggregate Demand (AD)
What would cause a shift of SRAS1 to SRAS2?
a. a negative supply shock
b. a decrease in the price level
c. a change in menu costs
d. a decrease in the price of labor
e. a situation with less money illusion
decrease in price of labor
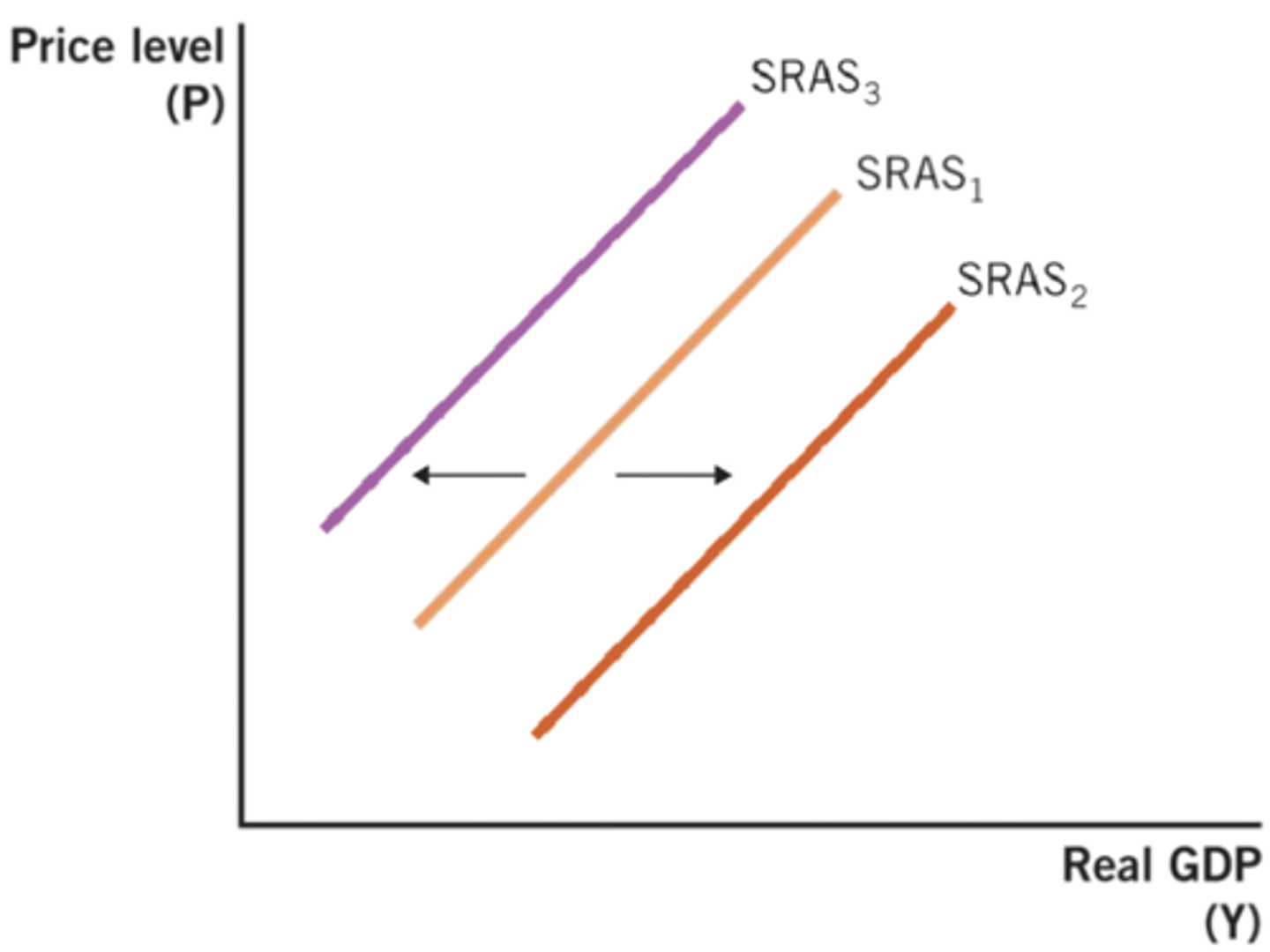
An increase in government spending will primarily affect which curve?
a. aggregate demand (AD)
b. short-run aggregate supply (SRAS)
c. long-run aggregate supply (LRAS)
d. AD and SRAS
e. AD and LRAS
aggregate demand (AD)