Long Bones & Bone Tissue
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
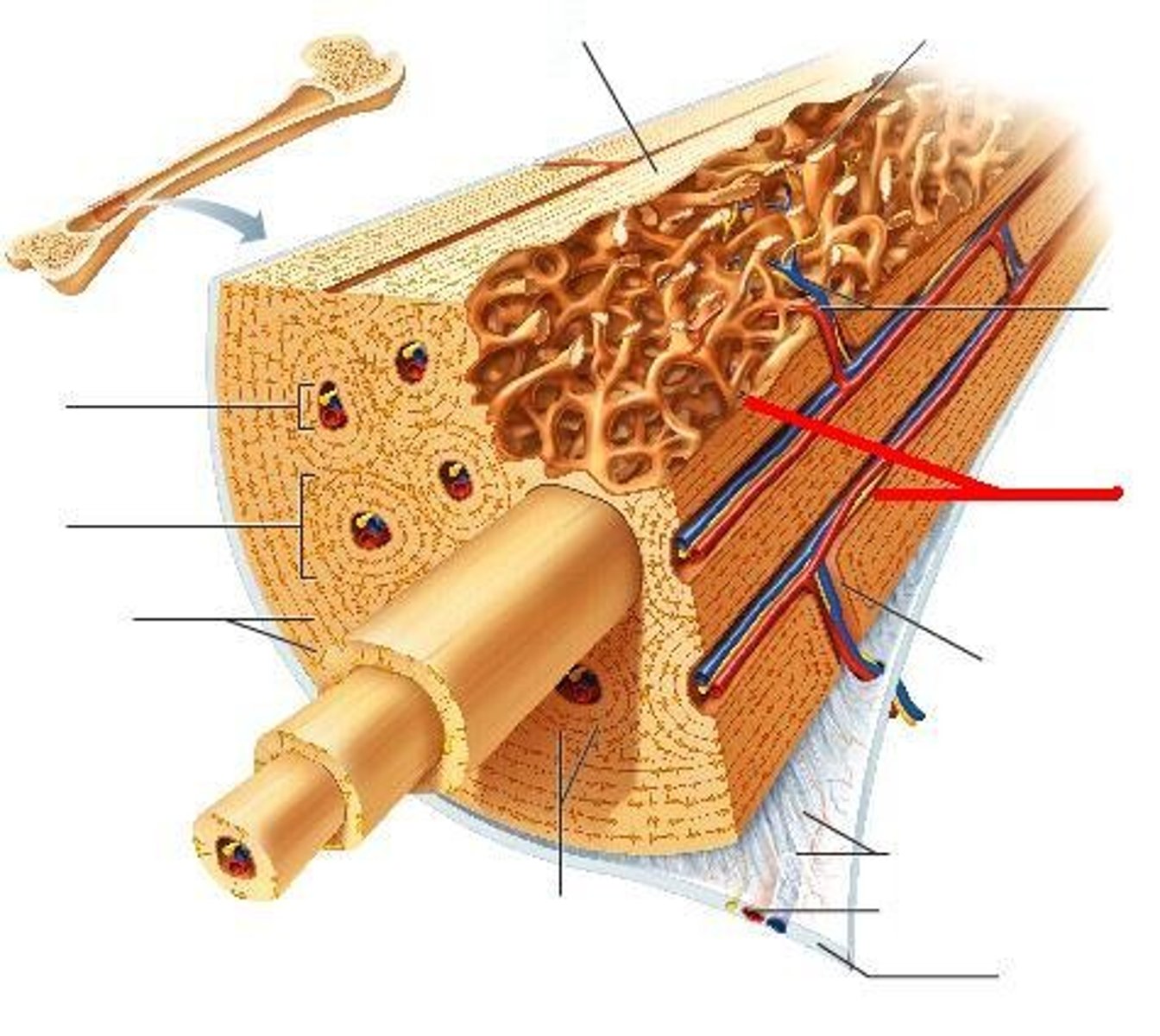
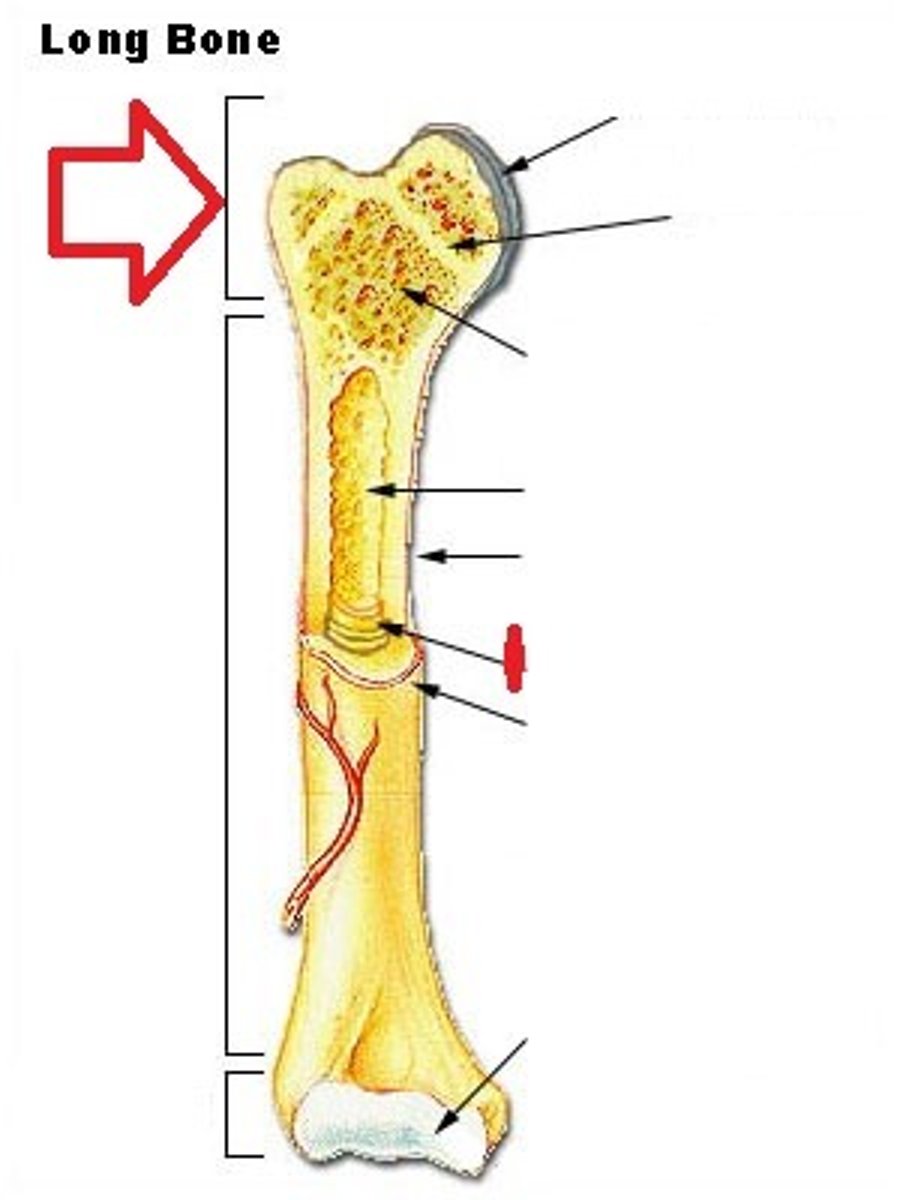
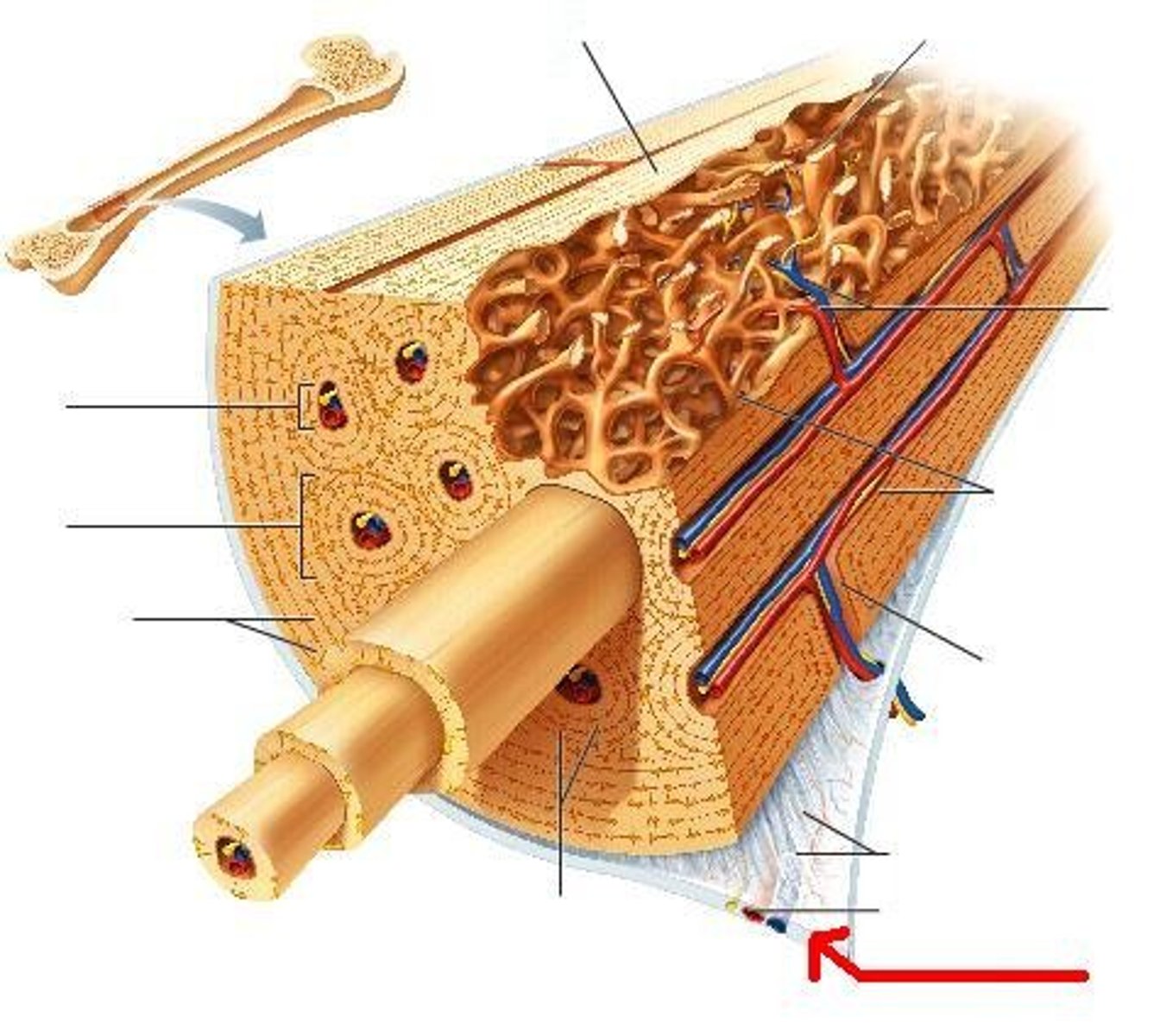
Diaphysis
Shaft of a long bone
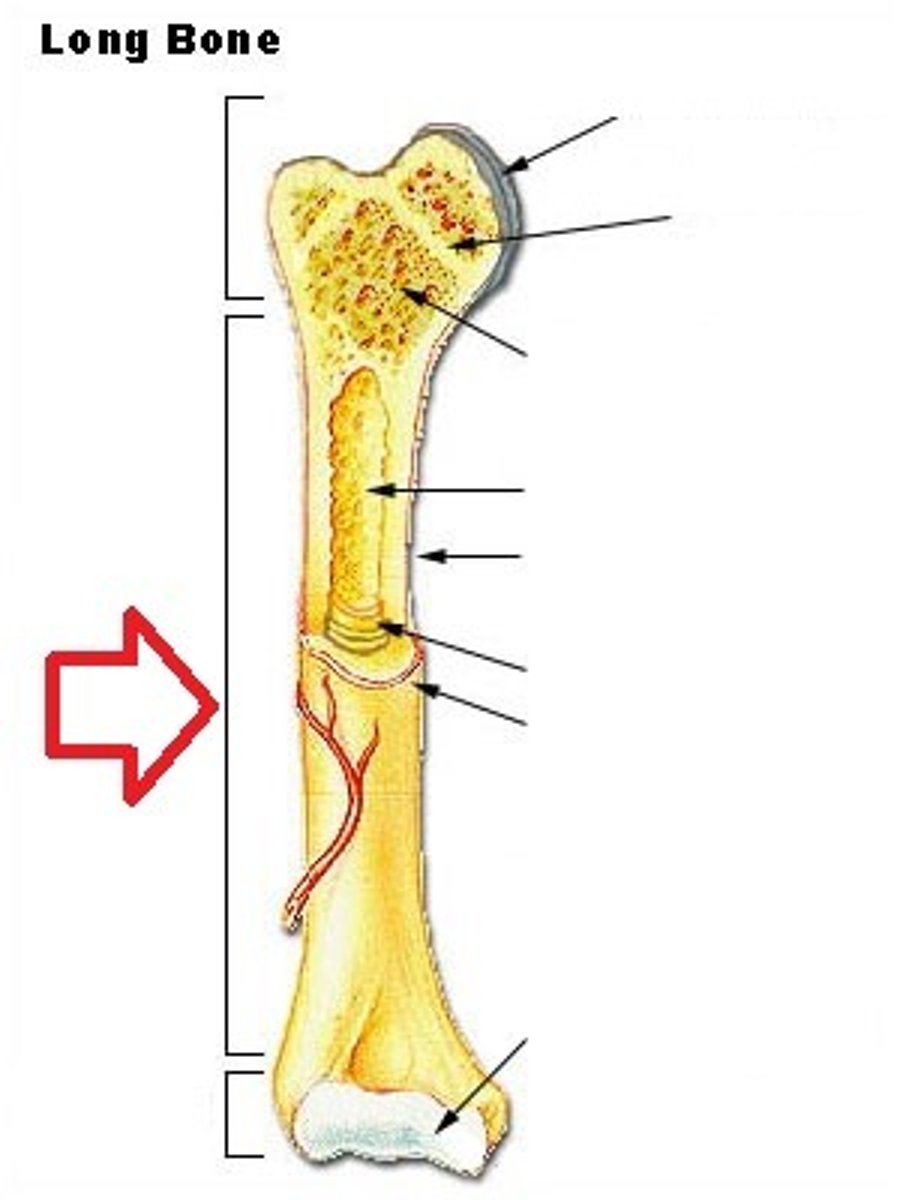
Epiphysis
End of a long bone
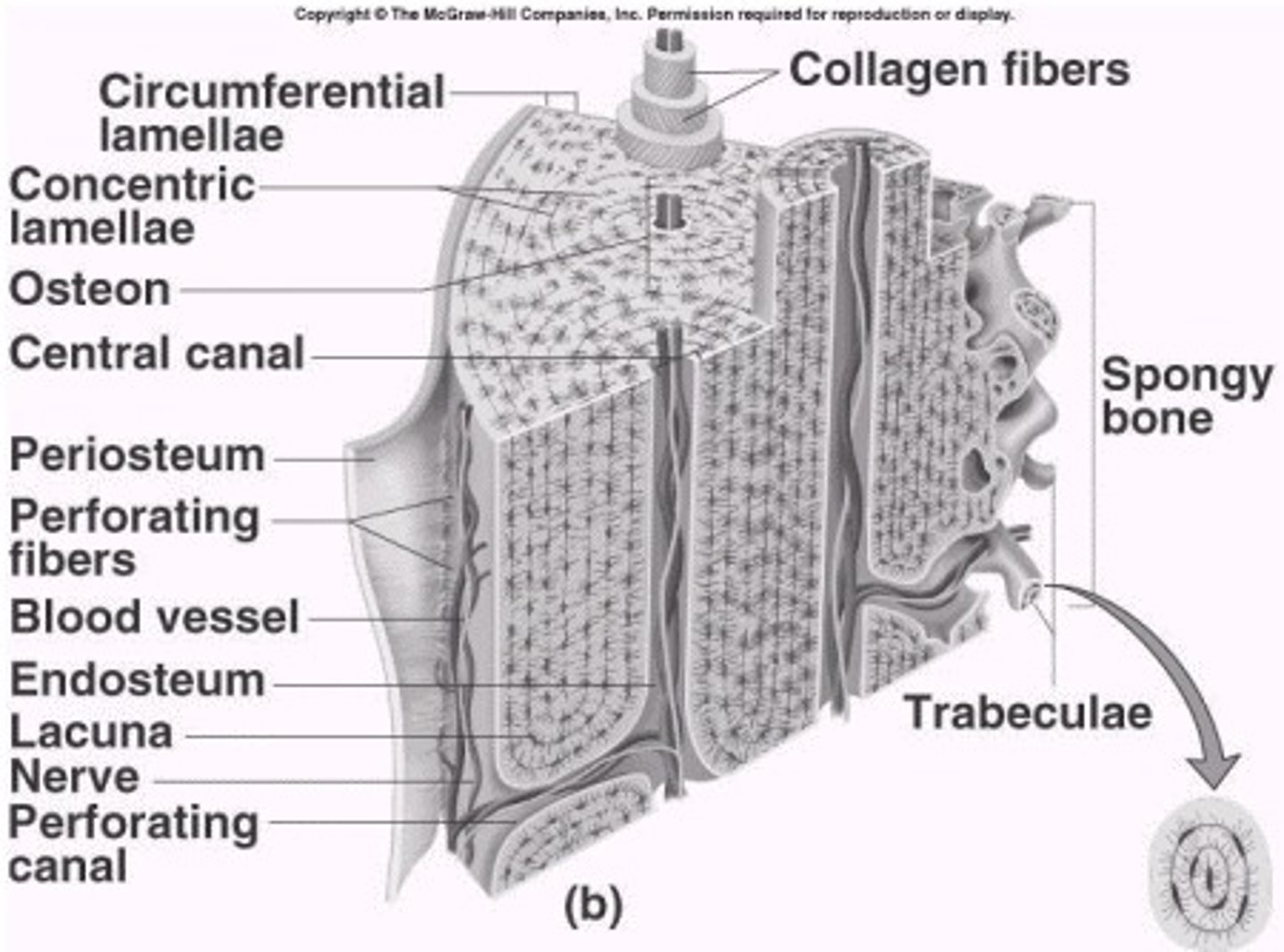
Endosteum
Tissue that lines the medullary cavity
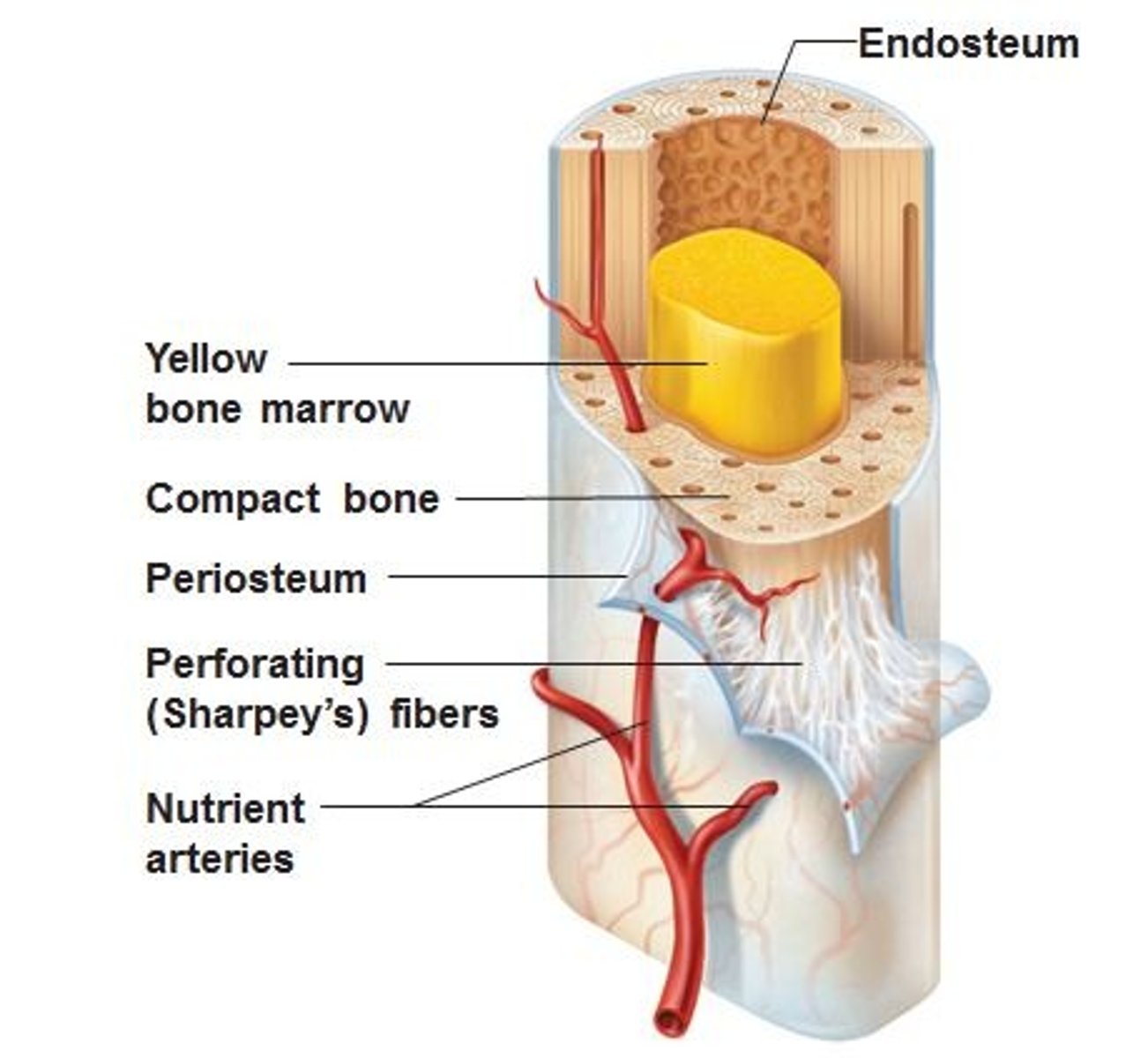
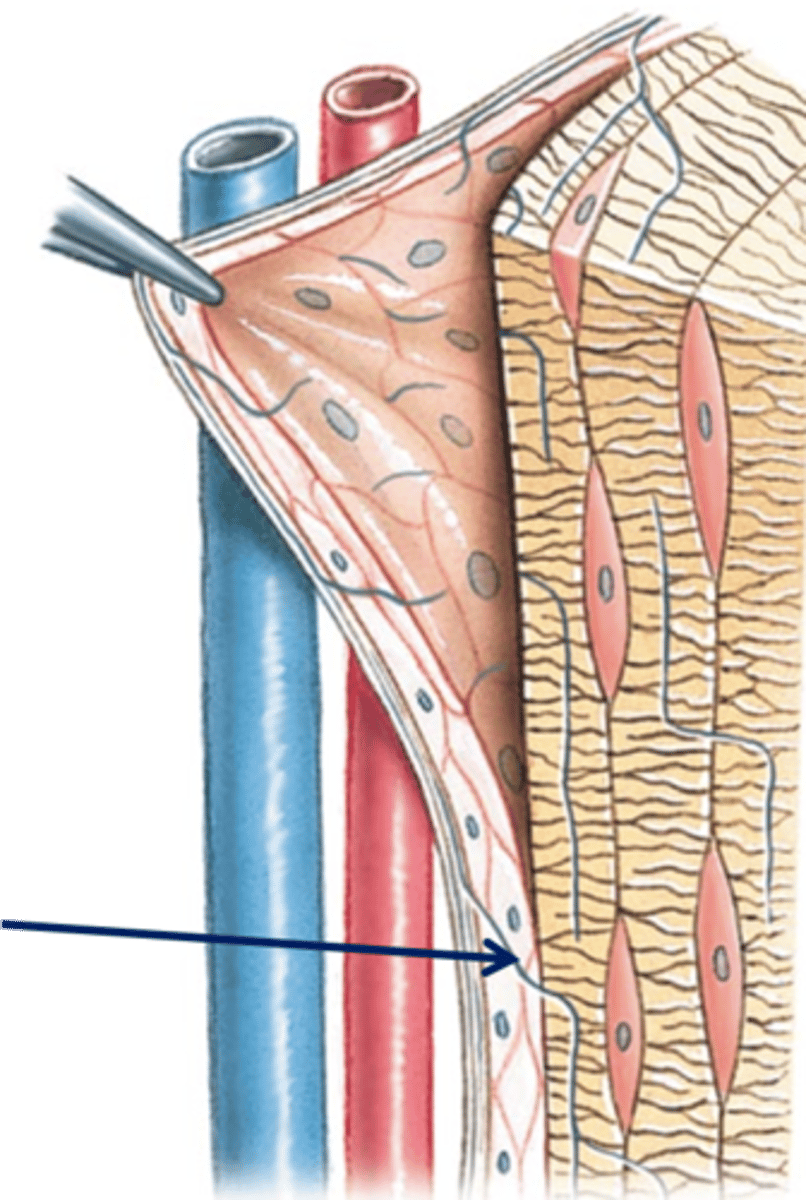
Periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
Epiphyseal Plate
Growth plate, made of cartilage, gradually ossifies
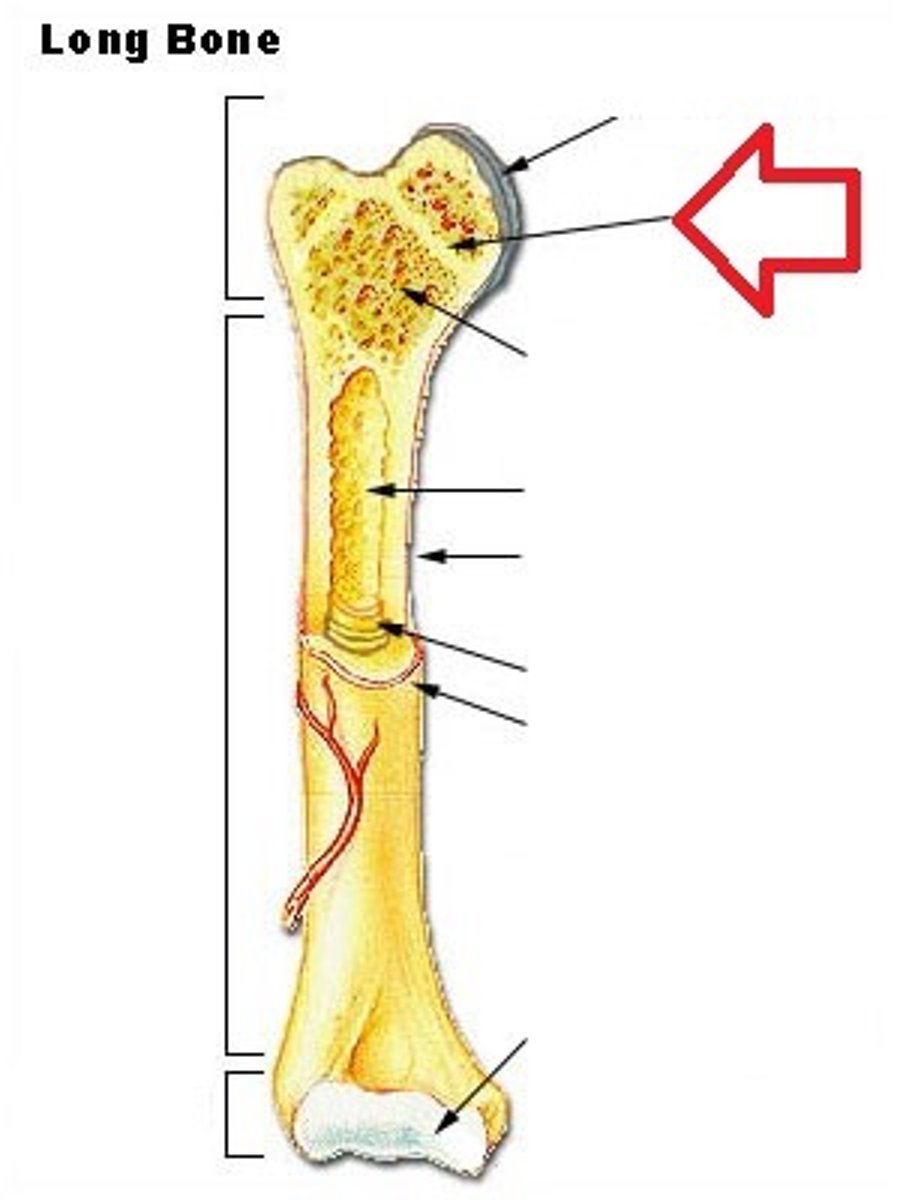
Epiphyseal Line
The appearance of this structure signals the end of bone growth
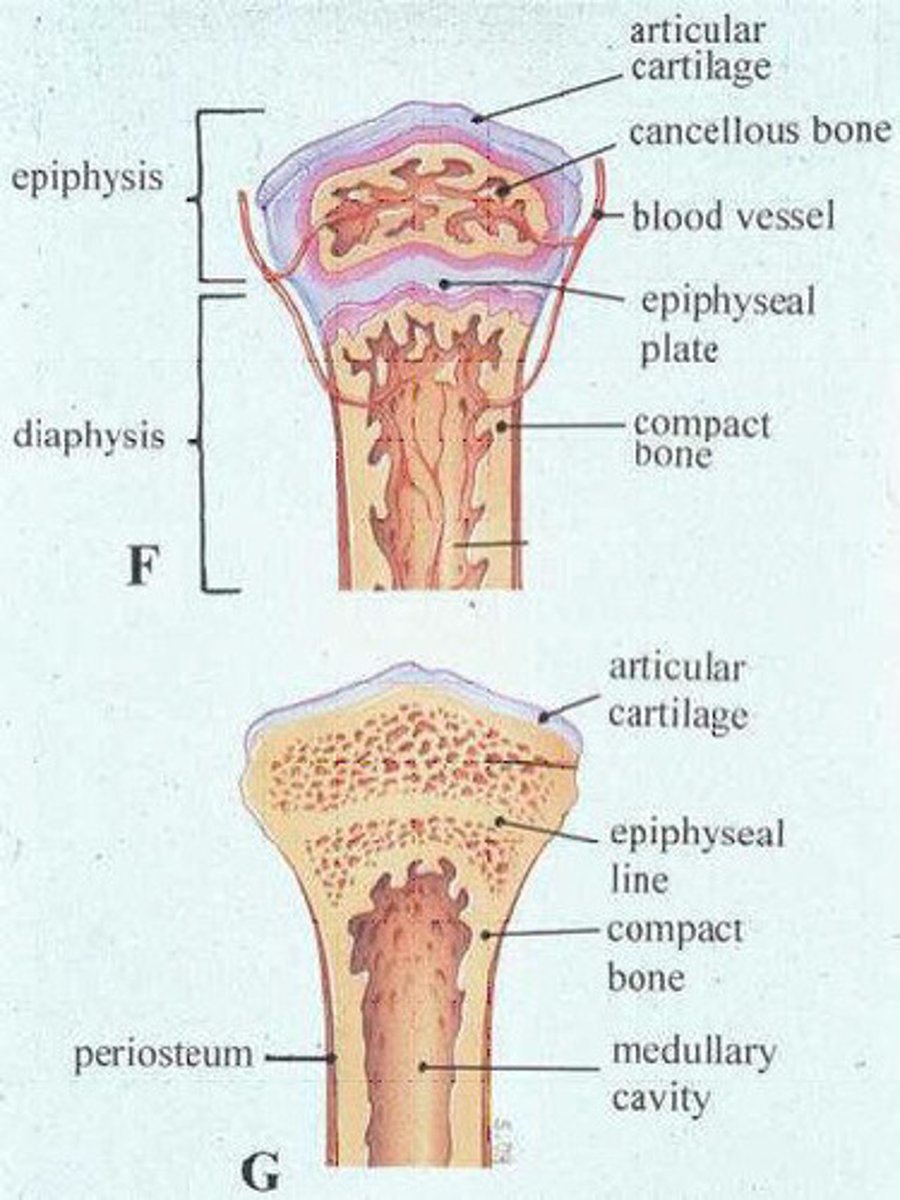
Articular Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage attached to articular bone surfaces
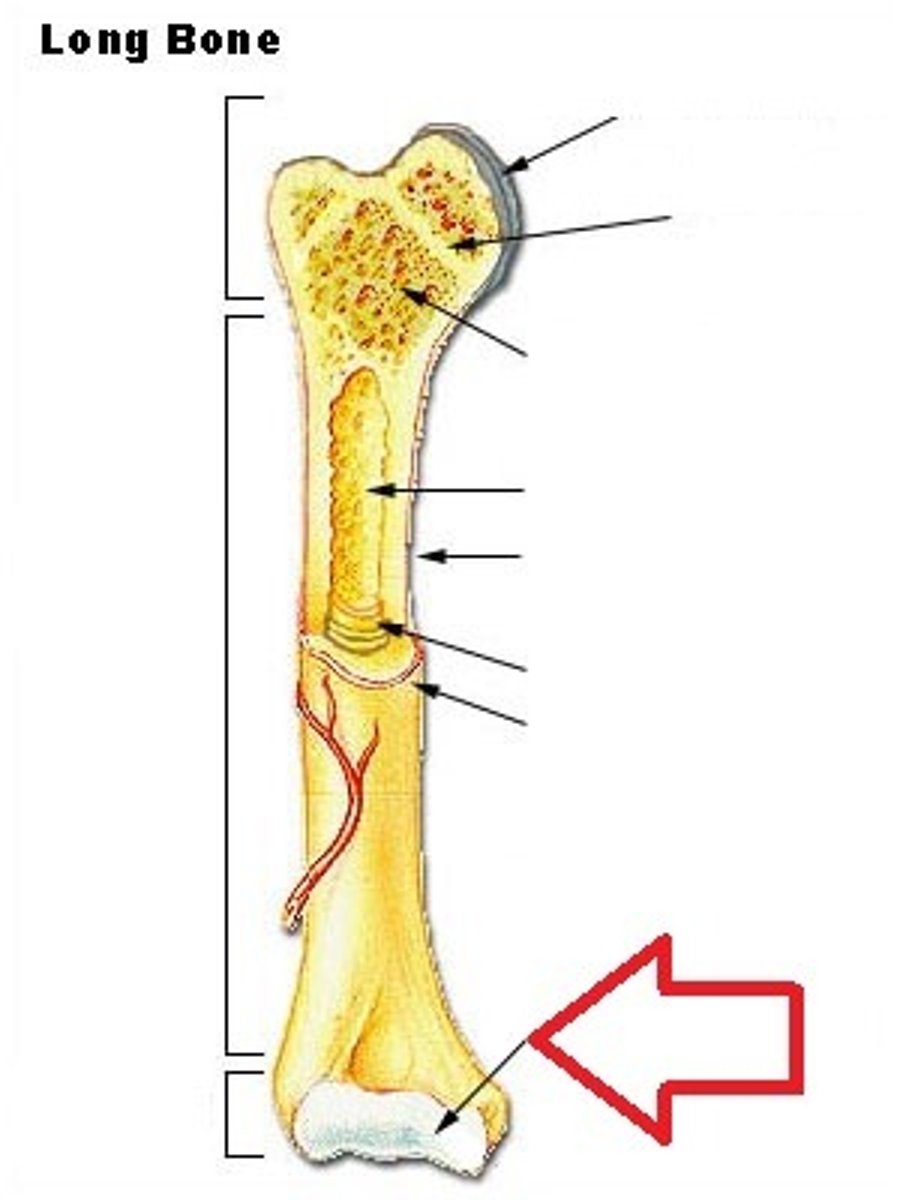
Medullary Cavity (Yellow Marrow)
The center portion of the shaft of a long bone containing the yellow marrow
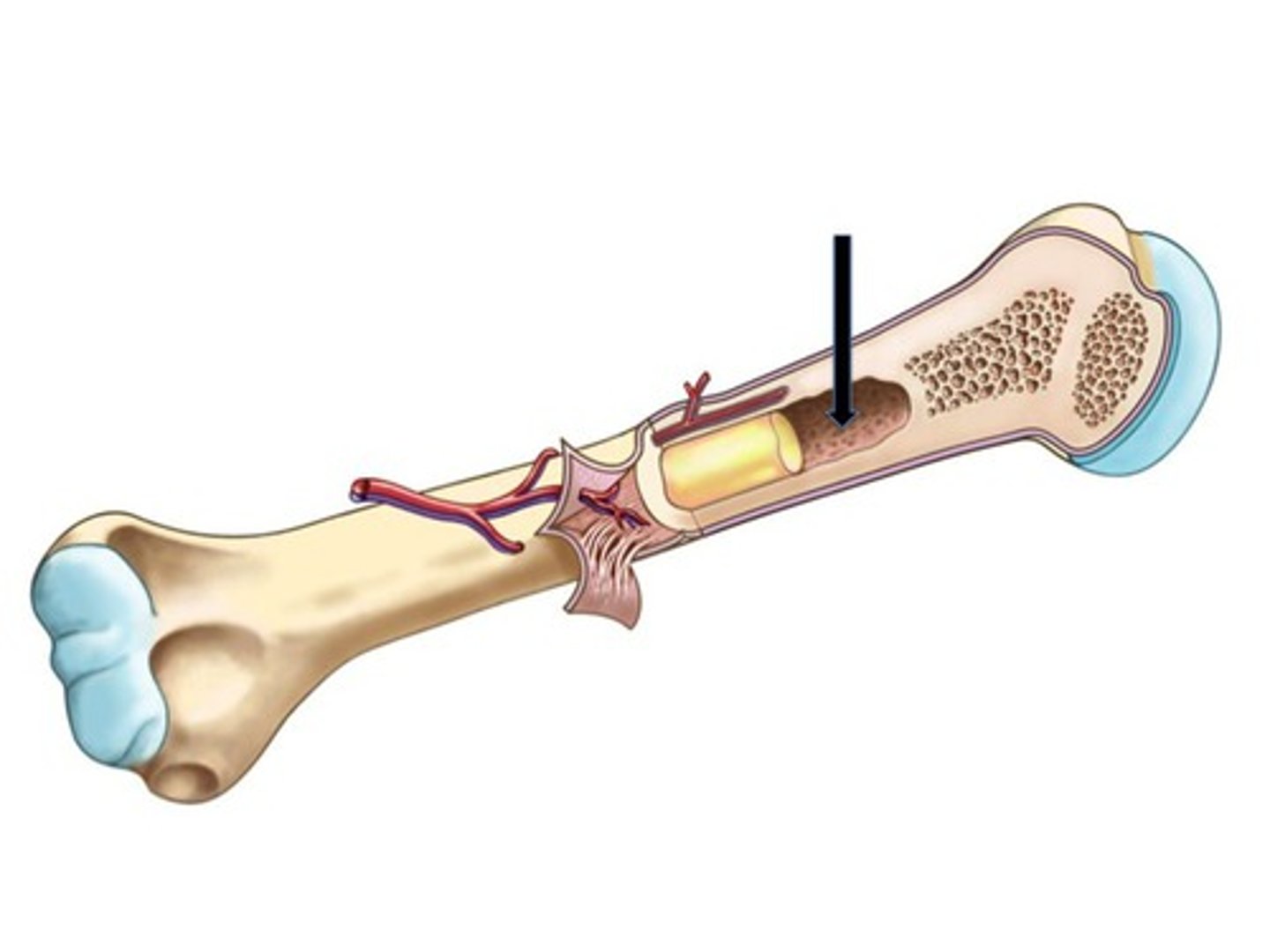
Compact Bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
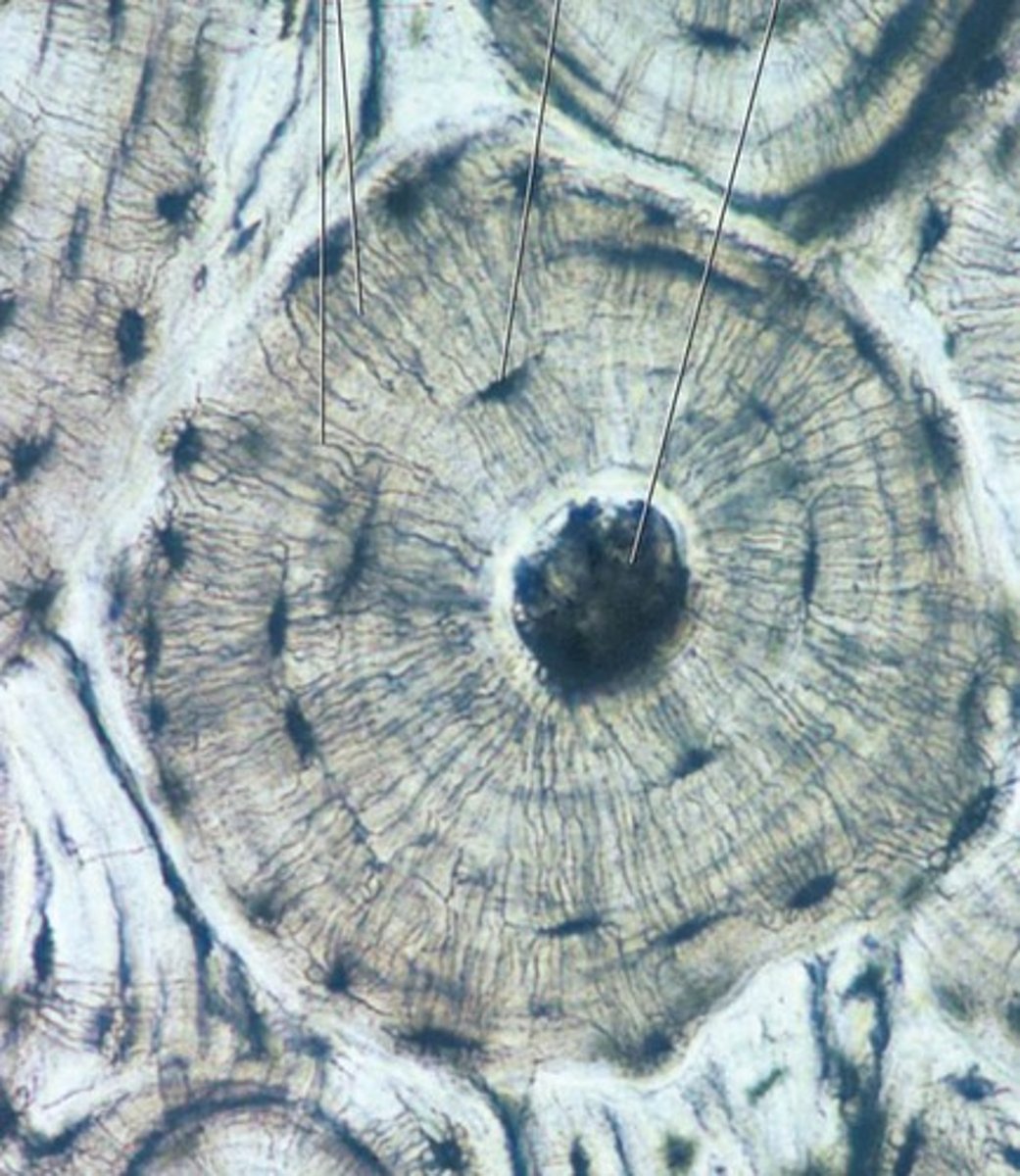
Osteon (Haversian System)
Structural unit of compact bone
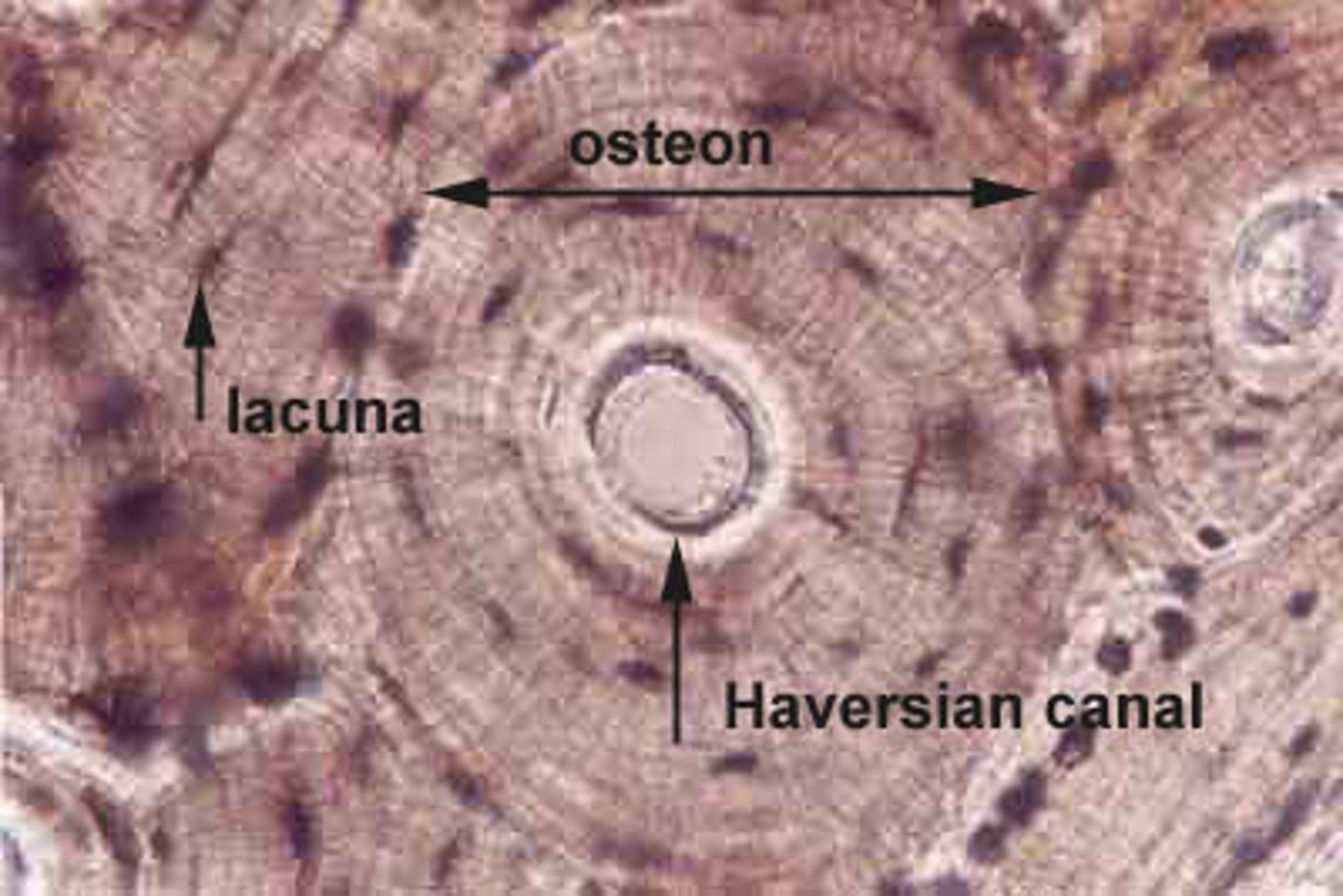
Central Canal
The hollow center of an osteon, also known as a Haversian canal. The central canal contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. Bone is laid down around the central canal in concentric rings called lamellae.
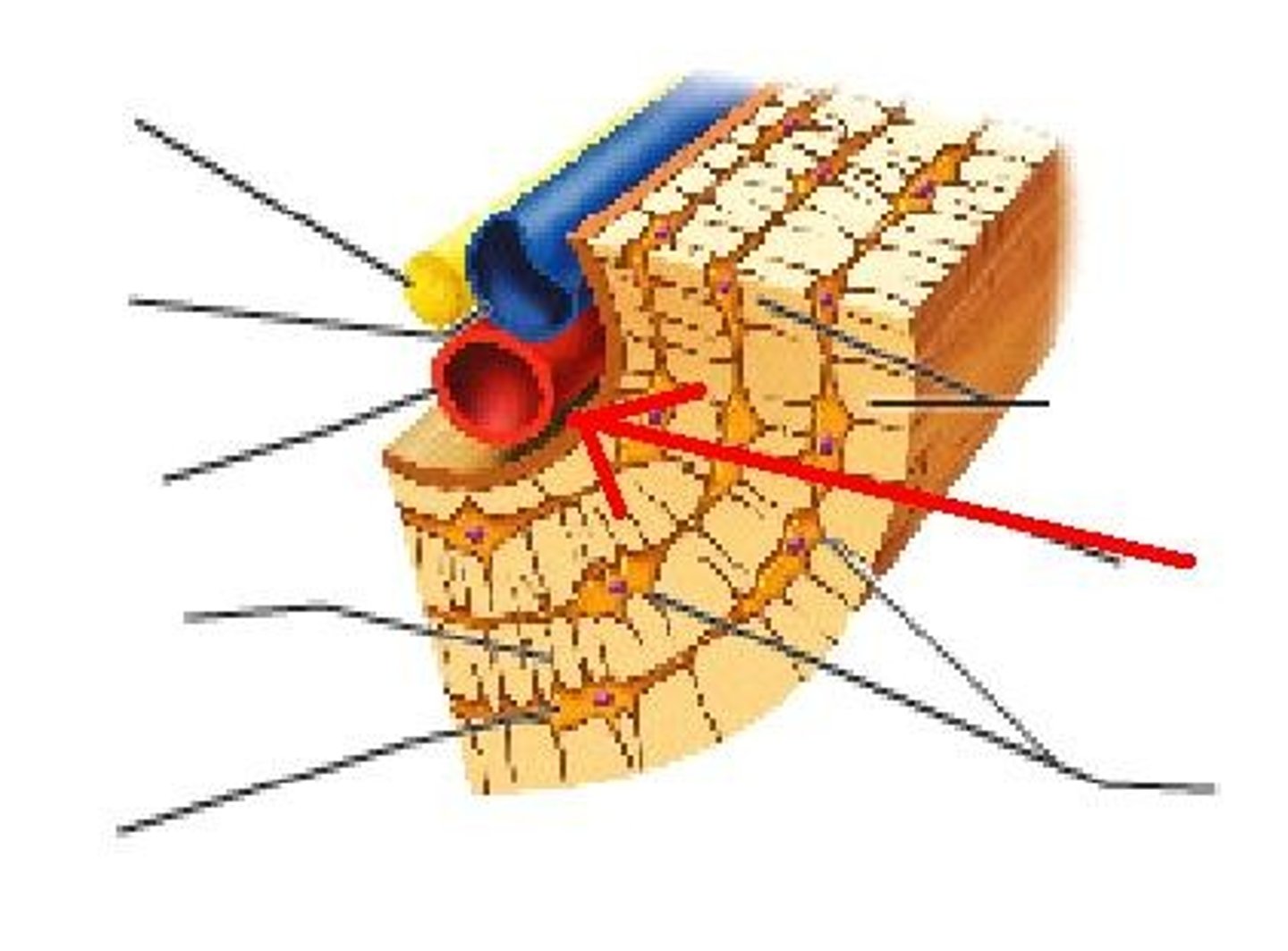
Transverse (Volksmann's Canal)
Perpendicular to the haversian canals and connect the blood and nerve supply from the periosteum to the central canal
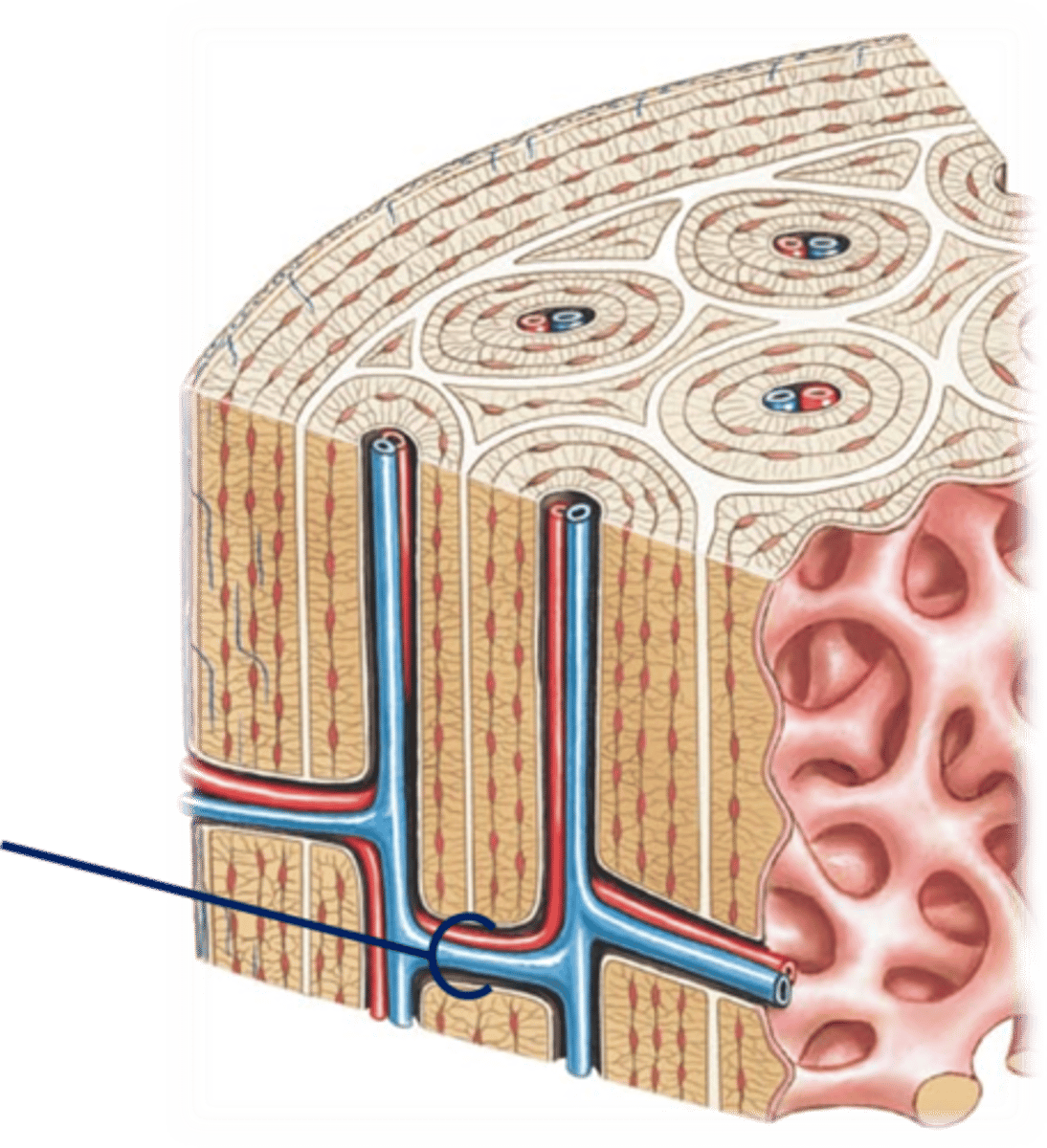
Perforating Fibers (Sharpey's)
Strong fibers that anchor the periosteum to the bone
Lamelle
The many thin layers of compact bone with no spaces
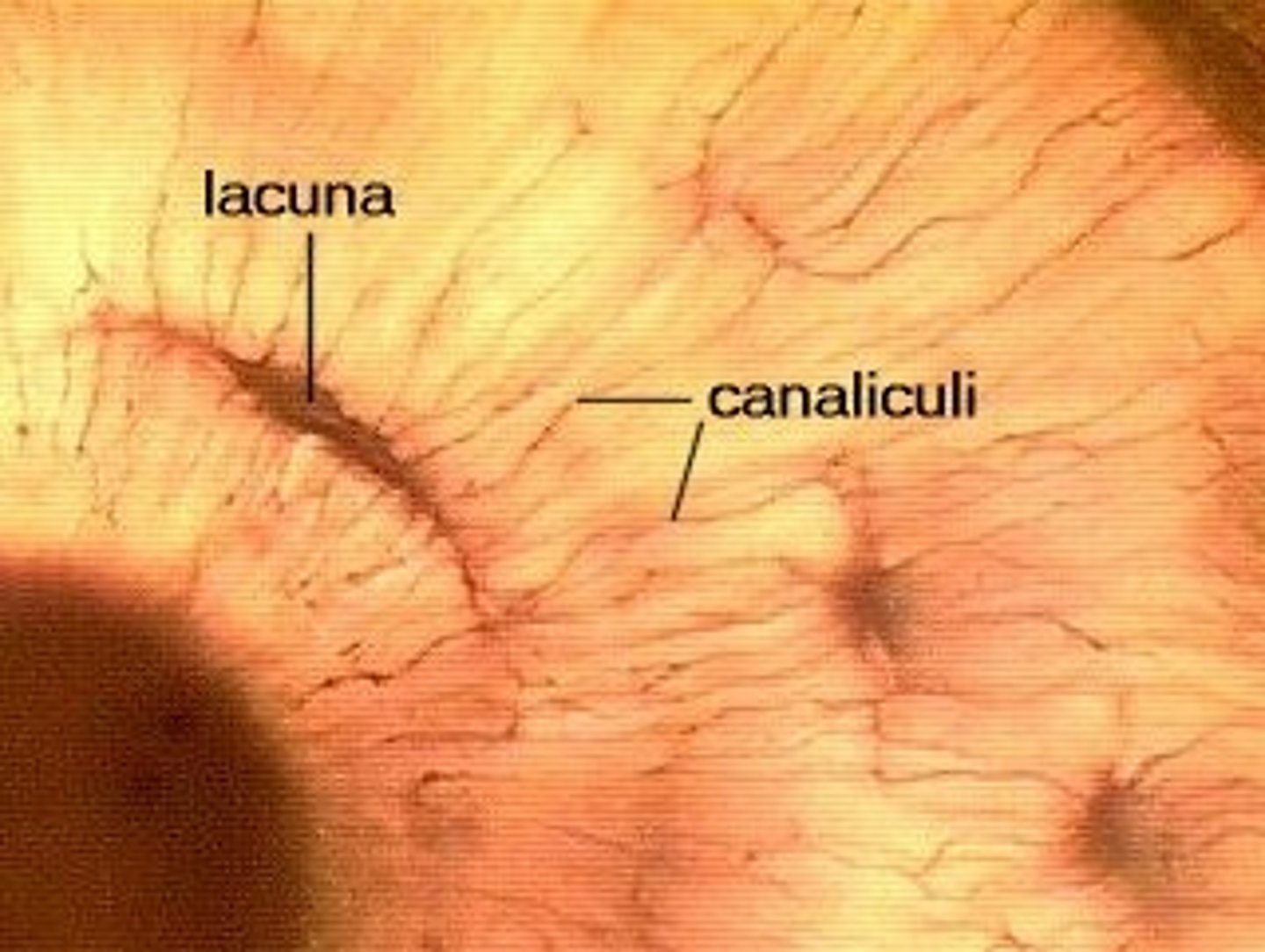
Osteocytes in Lacunae
Mature bone cell (usually trapped in lacunae)
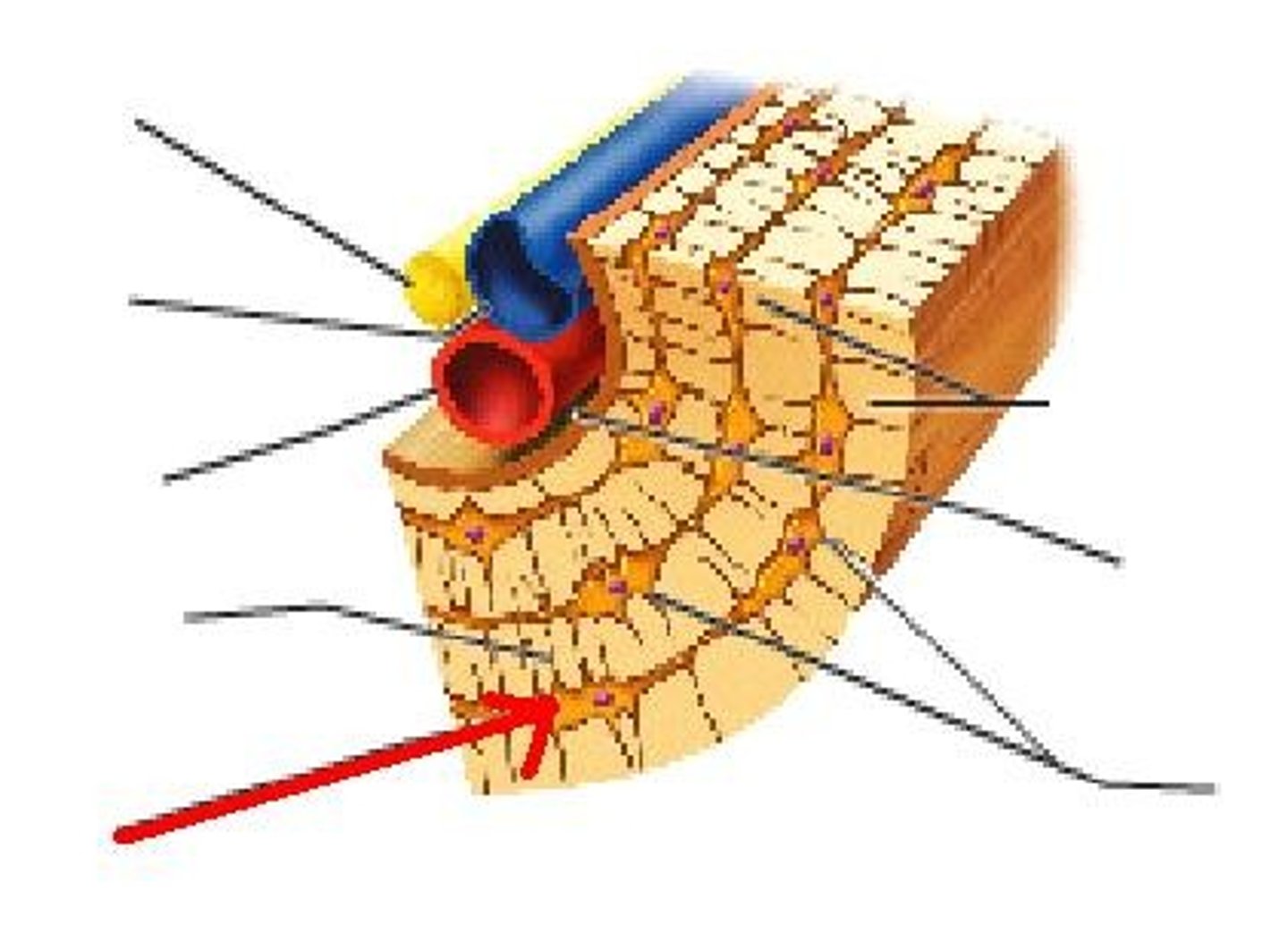
Canaliculi
Hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
Spongy Bone
A looser, more porous type of bone tissue found at the inner core of the epiphyses in long bones and all other bone types. Spongy gone is filed with red bone marrow, important in blood cell formation.
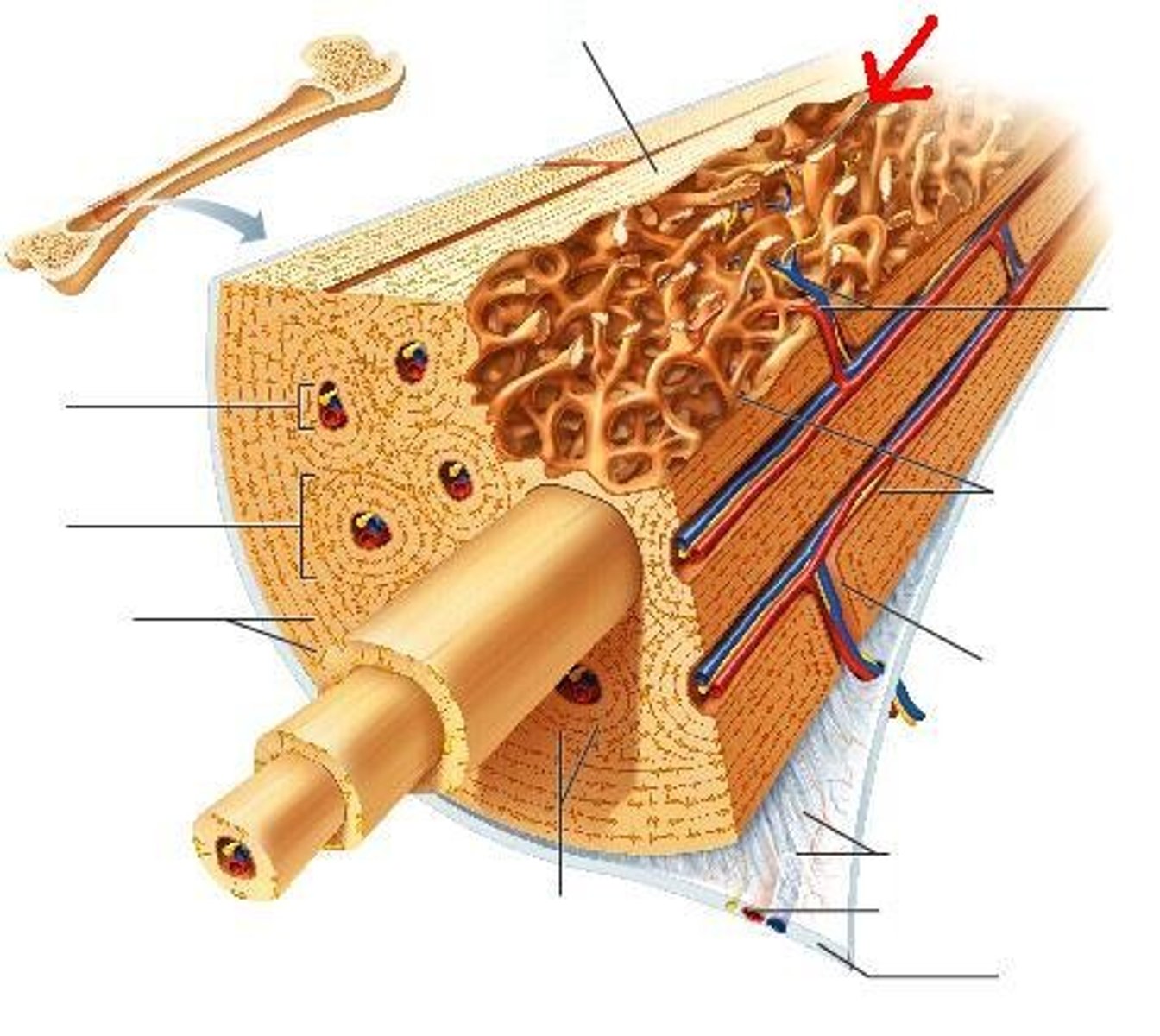
Trabeculae
The interconnecting tiny arches of bone tissue found in spongy bone are called