Cystic Fibrosis Case Study
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What is cystic fibrosis?
-multisystem, chronic disease with respiratory, gastrointestinal, endocrine, and reproductive involvement
-progressive lung dysfunction, pancreatic insufficiency
-most common in caucasians, but prevalence among other ethnic backgrounds is increasing and higher than previously estimated
what is the most common fatal life-shortening inherited disorder among Caucasians?
cystic fibrosis
how many people are affected by cystic fibrosis in the US?
>30,000
how many new cases of cystic fibrosis are diagnosed each year?
~1,000
what percentage of patients are diagnosed with cystic fibrosis by age 2?
~75% of patients
What percentage of the CF population is over 18?
>50%
how many carriers of cystic fibrosis are asymptomatic carriers?
> 10 million
what is the birth prevalence of cystic fibrosis in caucasians?
1 out of 3,000-3,500
what is the birth prevalence of cystic fibrosis in hispanics?
1 out of 8,000-9,500
what is the birth prevalence of cystic fibrosis in African Americans ?
1 out of 15,000-17,000
what is the birth prevalence of cystic fibrosis in Asian Americans?
1 out of 32,000
what is the inheritance pattern of cystic fibrosis?
autosomal recessive
what is the gene responsible for cystic fibrosis?
mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein on the long arm of chromosome 7
what does clinical disease of cystic fibrosis require?
two copies of mutated CFTR gene
What is the role of CFTR?
-Chloride channel protein found in the apical membranes of secretory epithelial cells in various organs
-regulates Cl- channel function which in turn affects the activity of Na+ channels
-Regulates the movement of salt and water in and out of cells
-Remember, the goal of Na+/Cl- channels is to maintain appropriate composition of secretions
what does a mutation in the CFTR gene disrupt?
-disrupts normal epithelial ion transport thereby altering the function of mucosal epithelial cells in the lungs, pancreatic ducts, biliary tree, intestines, vas deferens, and sweat glands
-results in thickened secretion which lead to organ dysfunction
What is the most common mutation in the CFTR gene?
-Delta F508
-deletion of phenylalanine at position 508
0presents in 70% of patients with CF
-different CFTR mutations result in various disease phenotypes and severity
what are characteristics of Classes I, II, III of cystic fibrosis?
-severe progressive pulmonary disease pancreatic insufficiency
-delta F508 class II
what are characteristics of classes IV, V, VI of cystic fibrosis?
milder symptoms
what accounts for the variable spectrum of severity in presentation of CF and correlates with degree of organ involvement and complications?
the wide variety of CFTR mutations
what is the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis in the sweat lumen?
CFTR regulates Cl- so in the sweat lumen if you can't regulate it, Cl can't go into the cell and then you have a lot of Cl on the skin and Na → excessive sweating→ salty sweat
what is the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis in the airway of the lung?
Cl can't go out so it stays in more Na goes in and H20 follows → dehydrated airway and thick mucus that is difficult to clear
what are clinical manifestations of cystic fibrosis?
-salty skin
-poor growth and weight gain
-excessive mucus production
-frequent respiratory infections
-persistent cough
-wheezing
what does defective chloride channels result in with cystic fibrosis?
-sodium and chloride ion imbalance and leads to abnormally thick, sticky mucus and failure to clear mucus secretions effectively
-thickening of airway debris and dry mucosal surface
-mucus plugging
-airway obstruction
-airway inflammation
-bacterial overgrowth/colonization
-chronic recurrent pulmonary infections
-progressive endobronchial destruction
-bronchiectasis
-loss of lung function
high prevalence of airway colonization is present with what bacteria?
-Staphylococcus aureus
-haemophilus influenzae
-pseudomonas aeruginosa (80% of patients, associated with clinical status deterioration)
-Burkholderia cepacia (associated with worsening lung function, poor overall outcome, increased mortality
What are clinical respiratory manifestations of cystic fibrosis?
-Shortness of breath
-Decreased pulmonary function
-Exercise intolerance
-Thickening of airway mucus
-Persistent productive coughing
-Frequent lung infections/pneumonia
-Wheezing
-Hypoxemia
-Mechanical obstruction of airways
-Ventilation perfusion mismatch
-Destruction of lung parenchyma
What are respiratory complications that present clinically in cystic fibrosis?
-Bronchiolitis
-Bronchitis
-Bronchiectasis
-Pneumonia
-Hemoptysis
-Atelectasis
-Pneumothorax
-Cor pulmonale
-Pulmonary hemorrhage
-End stage lung disease or respiratory failure
what is digital clubbing?
-hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
-enlargement and swelling of the nail beds
-usually due to chronic respiratory problems of cyanotic heart conditions
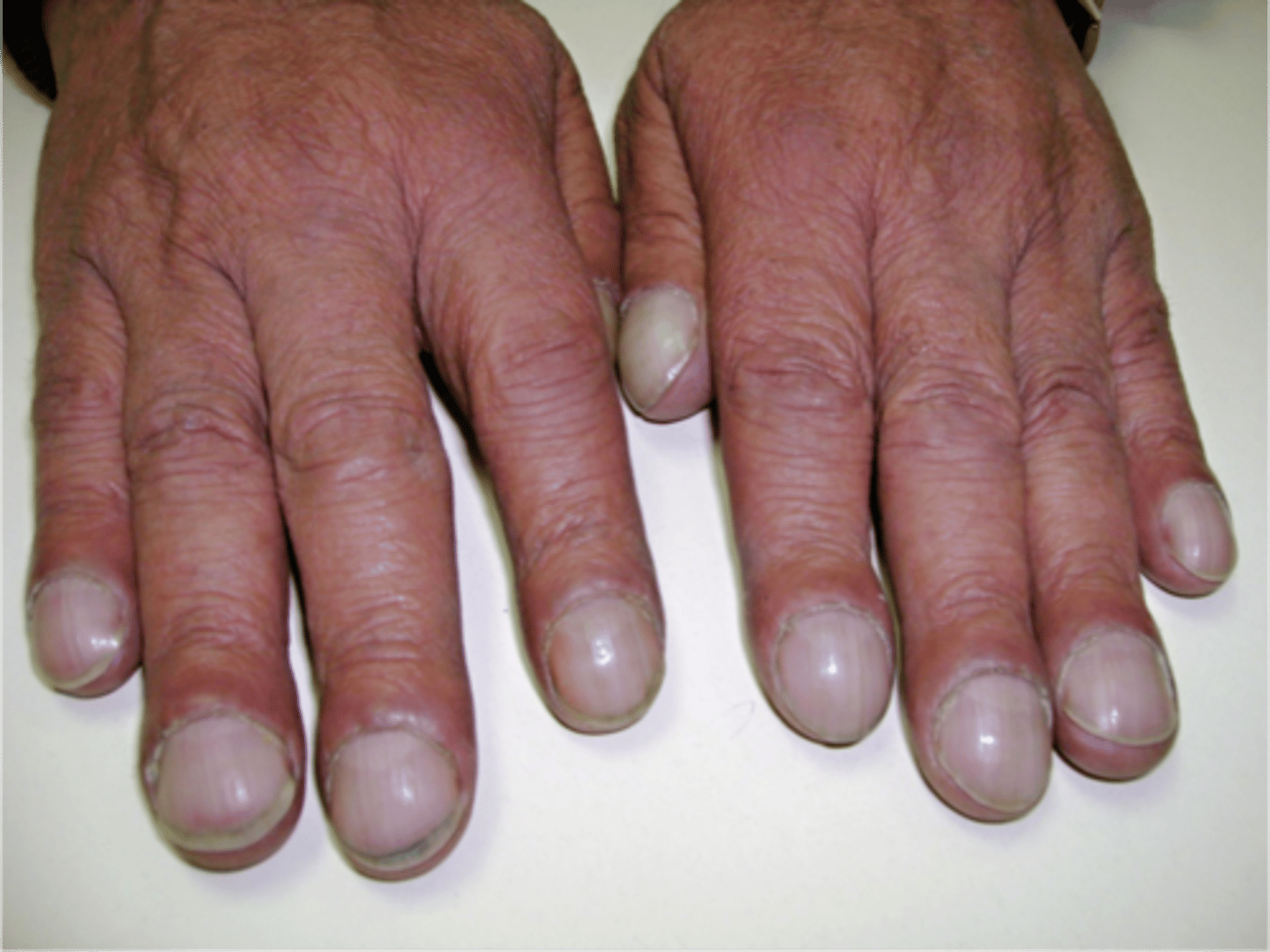
what symptoms in an otherwise healthy child may raise suspicion for CF?
-recurrent sinusitis
-nasal polyps
why might cystic fibrosis patients experience gastrointestinal problems?
intestinal abnormality due to thickened secretions
what are some gastrointestinal problems that may present with CF?
-meconium ileus
-distal intestinal obstruction syndrome (DIOS): Liquid stool may become firm and accumulate in the distal small intestine
-rectal prolapse
what is meconium ileus?
-in CF, meconium plug obstructs intestine, preventing stool passage at birth
-obstruction of terminal ileum by meconium in infants
-failure to pass meconium in the first 24-48 hours of life (highly suspicious for CF)
-first symptom in 15-20% of infants with CF
-abdominal distension and bilious emesis
what do the thickened secretions that result from CF cause in GI tract?
-cause impaired flow of bile and pancreatic secretions
-cholestasis adn malabsorption of fat and protein, liver and pancreatic disease
what is hepatobiliary disease seen with CF?
-focal biliary cirrhosis
-multilobular cirrhosis
-gallstones
what are examples of pancreatic dysfunction present in cystic fibrosis?
-pancreatic insufficiency
-cystic fibrosis related diabetes
what is pancreatic insufficiency that occurs as a result of cystic fibrosis?
-Thick, sticky mucus obstructs the pancreas and prevents digestive enzymes from reaching the intestine to help break down and absorb food
-Impedes not only the excretion of pancreatic enzymes but also the bicarbonate rich solution necessary for optimal pancreatic enzyme function
-results from absent pancreatic enzyme activity
what percentage of patients with cystic fibrosis are affected with pancreatic insufficiency?
85-95% of patients
how are pancreatic enzyme activity related to pulmonary issues in CF?
those with normal or subnormal pancreatic enzyme activity have fewer pulmonary issues and lower mortality
what kind of malabsorption is present with pancreatic insufficiency?
-fat malabsorption
-protein malabsorption
what are characteristics of fat malabsorption in pancreatic insufficiency?
-steatorrhea
-fat soluble vitamin deficiencies (A,D,E,K)
-symptomatic deficiency can occur before diagnosis or as later complication of the disease
What are manifestations of pancreatic insufficiency that results from cystic fibrosis?
-frequent, abnormal BM
-bulky, greasy, foul smelling stools
-increased flatulence
-abdominal distension and cramping
-colicky pain after feeding
-poor weight gain/FTT
what are nutritional guidelines for cystic fibrosis?
-research suggests a close correlation between opimizing nutritional status and maintenance of lung function
-routine use of pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy prior to meals can improve digestion and intestinal absorption of dietary protein and fat
what are reproductive problems that may occur in males with cystic fibrosis?
-absent or incomplete vas deferens
-congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (97-98%)
-Azoospermia
what are reproductive problems that may occur in females with cystic fibrosis?
may have difficulty with becoming pregnant, however many successful pregnancies have been reported
what are diagnostic studies used to diagnose CF?
-newborn screen
-DNA or genetic testing (prenatal and postnatal)
-sweat test
-Nasal Potential Difference test
What are benefits of newborn screen testing for CF?
-Patients are identified before onset of clinical manifestations
-Slow progression of lung disease and malnutrition
-Avoids 15-month setback between initial symptoms and diagnosis
-Alleviates anxiety, frustration, and emotional distress that comes along with delay in diagnosis
-Reduces expenses with tedious work-ups for FTT
-Long term benefits from early nutritional treatment
What is an IRT assay (newborn screening for CF)?
-measures the amount of Immunoreactive Trypsinogen (IRT)
-pancreatic protein typically elevated in patients with CF
-~80% sensitive, not diagnostic and false positive occurs
what is a trypsinogen (newborn screening for CF)?
-produced in the pancreas and transported to the intestine, where it is activated to form the enzyme trypsin, a key digestive enzyme that breaks down proteins
-In CF, thick mucus plugs obstruct pancreatic duct and prevent s this from reaching the intestine (Blood IRT levels will be elevated in newborns with CF)
what does the presence of an elevated IRT level indicate?
the need for a second tier of testing, either IRT or DNA
what are the types of second tier testing?
-IRT/repeat IRT
-IRT/DNA
-State dependent
-PCPs notified of the +NBS and further definitive testing can be done
What is the sweat chloride test?
-Quantitative pilocarpine iontophoresis sweat chloride test: gold standard
-measures the chloride in the sweat which is increased in CF patients.
-Pilocarpine stimulates localized sweating for the sweat glands
-a weak electrical current is applied to the area to stimulate sweating
-careful collection of sweat on gauze pads or filter paper, weighed and analyzed for chloride content
what are parameters for positive sweat chloride?
>60 mmol/L, confirmed by a second elevated sweat test result is diagnostic
how is genetic testing used to identify CF?
-helpful if indeterminate sweat tests
-identifies about 95% of patients with this disease
-must have disease causing mutation of BOTH the CFTR genes to be positive
what does one CFTR gene mutations indicate?
carrier of CF
what do two CFTR gene mutations indicate?
disease
what is a nasal potential differencce?
-used if patients has clinical featured of CF and indeterminate sweat chloride testing
-used primarily in older children and adults needing a definitive diagnosis
-performed at specialized research centers
-measures the electrgical potential difference across the nasal epithelium and detects biochemical abnormalities caused by the CFTR defect
-abnormal transport of sodium and chloride ions results in a more negative potential difference across the cell- seen in patients with CF
what are treatments of CF?
-require visits to specialized clinic a few times a year
-pulmonary clearance 20-30 mins BID and more often for acute exacerbations
-techniques used to clear secretions thereby improving lung function
-above techniques used in conjunction with inhaled therapies for mucus thinning (mucolytics)
what are some techniques used to clear secretions to improve lung function in CF?
-postural drainage: placed in a downward position allowing drainage with gravity
-chest physiotherapy/percussion: clapping on the chest with a cupped hand
-airway clearance vest: high frequency chest wall oscillation
-Active cycle breathing (huff coughs): take a depe breath, hold it in, and actively exhale
-positive expiratory pressure (PEP valve, oscillating PEP, acapella): prevents airway closure, increases lung ventilation
-exercise: increase chest muscle strength
what other techniques can be used in conjunction with inhaled therapies for mucous thinning?
-inhaled DNase (Dornase Alfa, Pulmozyme): breaks down the DNA in the airway from bacteria
-hypertonic saline: draws water from airway cells into the mucus
what are treatments of chronic pulmonary infections?
-bronchodilators
-anti inflammatories
-routine respiratory cultures for surveillance and during flairs
-nebulized antibiotics (Tobramycin, Aztreonam) typically used every other month
-corticosteroids inhaled/ oral not routinely recommended
-lung transplants
what are some anti-inflammatories used in chronic pulmonary infections?
-high dose ibuprofen: shown to slow the decline in pulmonary function but not widely used due to small increased risk for GI bleed and need to monitor drug levels
-PO Azithromycin: dosed three times/week decreases exacerbation as long as not colonized with P.Aeruginosa
what is an exception when corticostreroids may recommend?
allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) or concurrent asthma
What is treatment for other symptoms associated with CF?
-pancreatic enzyme supplements
-replacement of fat soluble vitamins (ADEK)
-high fat, high calorie diet
-nutritional supplements
-insulin therapy for CF related diabetes
-Ursodiol: decreases bile duct clogging and helps bile flow from the liver
-liver transplantation
-disease modifying therapy: several new ones are in clinical trials, Ivacaftor
what is Ivacaftor (Kalydeco)?
-activates defective CFTR at the cellular level
-first FDA approved CF disease modifying medication
-for ages 6+ with G551D mutation
-shown to improve lung function, weight, quality of life, and reduce exacerbations
What is the prognosis of CF?
-CF still remains a life-limiting disorder and shortens life span
-Survival has greatly improved in the past 30 to 40 years due to advances in technology and research
-Males > females survival
-More than 30 potential ongoing therapies are in various stages of preclinical development and clinical trials
-median age for survival is now >37 years
-90% CF patients have completed high school
->60% have attended college
-since NBS, the chancces of improved health quality nad longevity are even greater
why is screening for CF so beneficial?
allows treatment to start even before symptoms occur- enhance nutrition and minimize or delay complications
what does CF PANCREAS stand for?
-C Chronic respiratory disease – chronic cough and wheezing
-F Failure to thrive
-P Pancreatic insufficiency, Polyps
-A Alkalosis, metabolic
-N Neonatal intestinal obstruction, Nasal Polyps
-C Clubbing of fingers
-R Rectal prolapse
-E Electrolyte elevation in sweat
-A Aspermia , Absent vas deferens
-S Sputum – S.aureus/P.aeruginosa
what is the inheritance pattern for cystic fibrosis?
autosomal recessive disorder of epithelial ion transport caused by variation in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator gene (CFTR)
what group is most commonly affected by cystic fibrosis?
most common in individuals of northern European ancestry, but is observes in all ancestral backgrounds
what is the live birth incidence of CF?
-ranges from 1 in 313 among Hutterites of southern Alberta, Canada
-1 in 90,000 among the Asian population of hawaii
-1 in 3200 among white people in US
what is CFTR?
-anion channel that conducts chloride and bicarbonate
-regulated by ATP and by phosphorylation by cAMP dependent kinase
-facilitates the maintenance of hydration of airway secretions through the transport of chloride and inhibition of sodium uptake
what does dysfunction of CFTR lead to?
can affect many different organs, particularly those that secrete mucus, including the upper and lower respiratory tracts, pancreas, biliary system, male genitalia, intestine, and sweat glands
what does dehydrated and viscous secretions in the lungs of individuals with CF interfere with?
mucociliary clearance, inhibit the function of naturally occurring antimicrobial peptides, provide a medium for growth of pathogenic organism, and obstruct airflow
what happens in the first months of life in patients with CF?
viscous secretions and bacteria colonizing them initiate an inflammatory reaction
What damages the bronchioles in CF?
the release of inflammatory cytokines, host antibacterial enzymes, and bacterial enzymes
what decreases the amount of functional lungs and eventually leads to respiratory failure in CF patients?
recurrent cycles of infection, inflammation, and tissue destruction
What happens if there is a loss of CFTR chloride into the pancreatic duct?
-impairs the hydration of secretions and leads to the retention of exocrine enzymes in the pancreas
-damage from these retained enzymes eventually causes fibrosis of the pancreas
what does CFTR regulate with sweat?
regulates the uptake of sodium chloride from this as it moves through the sweat duct
what happens to sweat in the absence of functional CFTR?
it has an increased sodium chloride content and this is the basis of the historical "salty baby syndrome" and the diagnostic sweat chloride test
what contributes to airway obstruction and infection with pseudomonas aeruginosa (two traits that define lung disease) in CF?
genetic modifiers and nongenetic factors both contribute
what is the primary determinant of the degree of pancreatic exocrine dysfunction?
CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) genotypes
what is the presence of CFTR variants associated with severe pancreatic exocrine dysfunction a prerequisite for?
development of diabetes and intestinal obstruction
what determines if diabetes occurs and whether neonatal intestinal obstruction occurs in severe endocrine dysfunction?
genetic modifiers
When does CF classically manifest?
in early childhood, although approximately 4% of patients are diagnosed in adulthood
What are variants within CFTR associated with?
a spectrum of disease, including isolated obstructive azoospermia, idiopathic pancreatitis, disseminated bronchiectasis, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, atypical sinopulmonary disease, and asthma
for what does a correlation between specific CFTR variant alleles, their resulting level of CFTR dysfunction, and CF disease severity exist for?
pancreatic insufficiency of splicing or protein maturation, thereby expansing the spectrum of disease associated with some variants
what is the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis usually based on?
clinical criteria and sweat chloride concentration, though a genetic diagnosis following identification of two CF-causing variants in trans is permitted as long as sweat chloride concentration is used as a confirmatory measure
what therapy might be helpful in the rise of life expectancy?
widespread use of newly developed small molecule therapies (termed CFTR modulators) that target the basic defect causing CF, by correcting or enhancing the function of CFTR protein-bearing specific variants
what are the objectives of medical therapy if an individual is ineligible for modulator interventions?
-clearance of pulmonary secretions
-control of pulmonary infection
-pancreatic enzyme replacement
-adequate nutrition
-prevention of intestinal obstruction
what is the ONLY effective treatment of respiratory failure in CF?
lung transplant
what treats malabsorption in CF effectively?
pancreatic enzyme replacement and supplementation of fat-soluble vitamins, but some patients also require caloric supplements
What do many CF newborn screening protocols utilize?
IRT- a pancreatic enzyme precursor measured from dried blood spot- as the first tier test and progress to another IRT measurement and/or screening for specific CFTR variants as a second tear
what is the probability of having a child with CF for couples who already have an affected child?
1 in 4