5c: Change of state
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:24 AM on 11/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
3 states of matter
solid, liquid, gas
2
New cards
solid
definite shape and volume
3
New cards
solid - particle arrangement
- closely packed
- vibrate about fixed positions
- vibrate about fixed positions
4
New cards
liquid
- indefinite shape
- definite volume
- definite volume
5
New cards
liquid - particle arrangement
- closely packed
- flow over one another
- flow over one another
6
New cards
gases
indefinite shape and volume
7
New cards
gases - particle arrangement
- far apart
- move randomly
- move randomly
8
New cards
why are gases highly compressible
- large gaps between particles
- easier to push particles closer together
- easier to push particles closer together
9
New cards
are changes of state reversible
yes
10
New cards
change of state
- number of molecules and mass doesn't change
- energy changes
- energy changes
11
New cards
changes of state
- melting
- boiling
- condensing
- freezing
- subliming
- boiling
- condensing
- freezing
- subliming
12
New cards
melting
solid to liquid
13
New cards
boiling
liquid to gas
14
New cards
condensing
gas to liquid
15
New cards
freezing
liquid to solid
16
New cards
subliming
solid to gas
17
New cards
heating a system
- increased kinetic energy
- temperature increases
- change of state
- temperature increases
- change of state
18
New cards
factors affecting increase in system temperature
- mass
- type of material
- amount of energy (thermal)
- type of material
- amount of energy (thermal)
19
New cards
specific heat capacity
amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1 C
20
New cards
substance with a low specific heat capacity
heats up and cools down quickly (less energy required)
21
New cards
substance with a high specific heat capacity
heats up and cools down slowly (more energy required)
22
New cards
formula for change in thermal energy
mass x specific heat capacity x change in temperature
23
New cards
investigating changes of state - aim
investigate how the temperature of ice varies when it changes state from a solid to a liquid
24
New cards
investigating changes of state - equipment
- thermometer
- ice cubes
- beaker
- tripod and gauze
- bunsen burner
- stopwatch
- ice cubes
- beaker
- tripod and gauze
- bunsen burner
- stopwatch
25
New cards
investigating changes of state - method
- place ice cubes and thermometer in beaker
- place beaker on tripod and gauze
- heat beaker
- take regular temperature measurements
- place beaker on tripod and gauze
- heat beaker
- take regular temperature measurements
26
New cards
investigating changes of state - systematic errors
eye level to avoid parallax errors
27
New cards
investigating changes of state - random errors
- begin experiment when temp is below 0
- enough ice cubes to surround the thermometer
- enough ice cubes to surround the thermometer
28
New cards
investigating changes of state - safety considerations
- wear goggles
- bunsen burner on heat proof mat
- react to spills
- bunsen burner on heat proof mat
- react to spills
29
New cards
investigating changes of state - graph
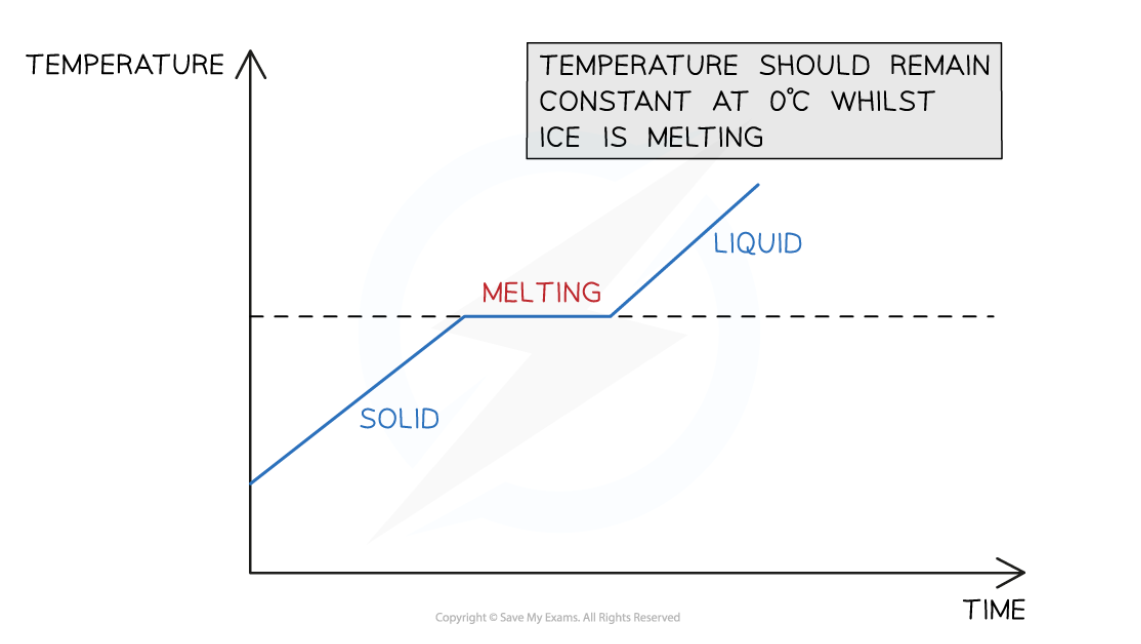
30
New cards
investigating specific heat capacity - aim
determine the specific heat capacity of a solid and of water by measuring the energy required to increase the temperature of a known amount by one degree
31
New cards
investigating specific heat capacity - apparatus
- thermometer
- block of aluminium
- beaker of water
- immersion heater
- voltmeter
- ammeter
- power supply
- digital balance
- stopwatch
- block of aluminium
- beaker of water
- immersion heater
- voltmeter
- ammeter
- power supply
- digital balance
- stopwatch
32
New cards
investigating specific heat capacity - method
- place beaker on digital balance
- add 250ml water and record mass
- place immersion heater and thermometer in water
- connect up circuit
- record initial temperature at 0 s
- turn on power supply and start stopwatch
- record voltage and current every 60 secibds
- repeat but replace beaker of water with solid block of aluminium
- add 250ml water and record mass
- place immersion heater and thermometer in water
- connect up circuit
- record initial temperature at 0 s
- turn on power supply and start stopwatch
- record voltage and current every 60 secibds
- repeat but replace beaker of water with solid block of aluminium
33
New cards
investigating specific heat capacity - analysis
- energy = current x voltage x time
- ΔQ = m x c x ΔT
- ΔQ = m x c x ΔT
34
New cards
investigating specific heat capacity - systematic errors
- digital balance set to 0
- water lost to surroundings
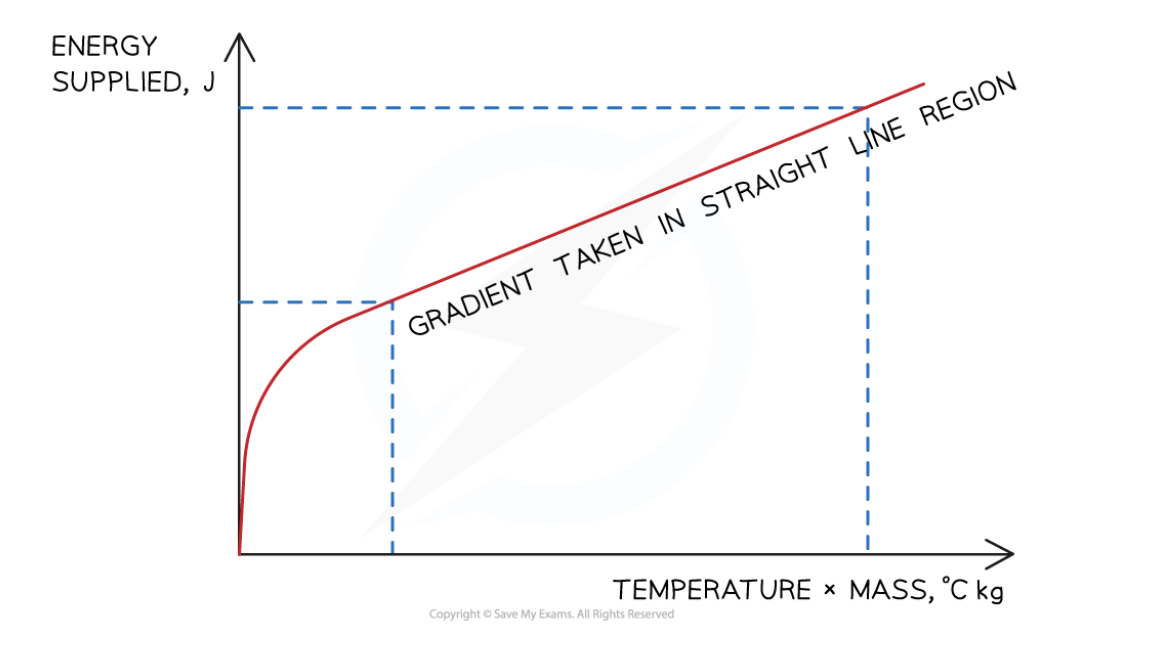
- gradient on straight-line region
- water lost to surroundings
- gradient on straight-line region
35
New cards
investigating specific heat capacity - random errors
- stir constantly with thermometer
- choose higher value if they change constantly
- choose higher value if they change constantly
36
New cards
investigating specific heat capacity - safety considerations
- use a heatproof mat as immersion heater is hot
- immersion heater connected to DC supply
- use clamp stand to hold beaker
- wear goggles
- react quickly to spills
- immersion heater connected to DC supply
- use clamp stand to hold beaker
- wear goggles
- react quickly to spills
37
New cards
investigating specific heat capacity - graph