cognitive psychology - behaviourism + attention
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
who introduced the first psychological lab
wilhelm wundt
1879
what is structuralism
the analysis of the mind in terms of it’s basic elements - introspection
who was structuralism introduced by
wundt & titchener
what is psychoanalysis
analysis of internal, mostly unconscious psychological forces
who was psychoanalysis introduced by
freud
what is functionalism
to study functions (of consciousness) rather than structure
what is behaviourism
environmental control of behaviour through learning
humans are products of their learning experiences
who introduced behaviourism
john b (broadus) watson
what are features of classical conditioning
unconditioned stimulus
unconditioned response
conditioned stimulus
conditioned response
examples of classical conditioning in everyday life
phobias
avoiding harmful food
music
smells
advertising
what is the idea of the ‘horse that could count’/clever hans
the idea that the horse was not counting to a specific number, but instead noticed subtle cues in body language in order to stop tapping his hoof
neobehaviourism 1930-1960
skinners box
reward and punishment
what is positive reinforcement
giving something positive
increasing a behavioural response to a stimulus because it elicits a reward
what is negative reinforcement
taking something negative
increasing a behaviour response to a stimulus because it stops an averse stimulus
what is positive punishment
giving something negative
decrease a behavioural response to a stimulus by presenting an aversive stimulus
what is negative punishment
taking something positive
decrease a behavioural response to a stimulus by taking away a positive stimulus
what is operant conditioning
shaping
reward for behaviour that is closer to a desired outcome
reinforcement schedules for operant conditioning
ratio - after a certain amount of times the behaviour has been presented
interval - after a certain amount of time
fixed - after every behaviour
variable - more difficult to extinct
operant vs classical
classical - association of one stimulus with the automatic response to another stimulus
operant - association of a behaviour with a stimulus - reward/punishment
who is tabula rasa
suggests that humans learn behaviour from environmental stimuli
issues with behaviourism
thought and consciousness
complexity of behaviour
what is verbal behaviour
language learnt through shaping
who is noah chomsky
father of modern linguistics
poverty of stimulus
innate component
language can not be explained through reinforcement
what is vigilance in terms of attention
sustained attention
what are the types of attention
vigilance (sustained)
selective (focused)
divided
what is a disjunctive task
target has a unique feature - not shared by others
quicker to spot
parallel processing - pre-attentive, fast
what processing does a disjunctive task use
parallel
what is a conjunctive task
target group have unique combinations - shared with each other
hard to spot which one
serial processing - slow, RT depends on array size
what processing does a conjunctive task use
serial
what is the theory of feature integration
targets defined by a unique feature pop out easily regardless of number of distractors
treisman and gelade - 1980
wickens 3 dimensional structure of human processing
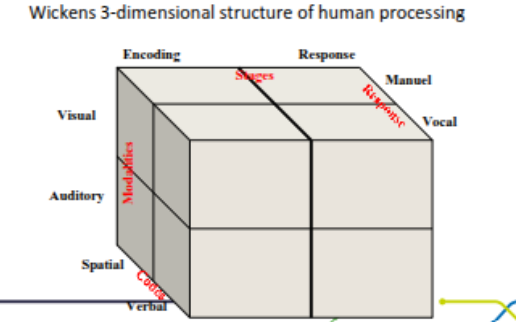
what did cherry - 1953 suggest
we perceive information from unattended channels
what is inattentional blindness
the failure to notice an unexpected or unexplored stimulus that is in our visual field when other tasks are being performed
what is attention capture
salience of a stimulus results in attention shift
for focused and selective attention we are monitoring task irrelevant info less - unless it pops up
explanations for inattentional blindness
visual perception of unattended objects is incomplete or limited
attention capture
external factors that can affect perception efficiency/attention
distractors, salience of stimulus, semantic category, distance
internal factors that can affect perception efficiency/attention
practice, expertise/interests, fears
what is cognitive insight
choice requires awareness of decision making
people are often unable to report causes of decisions
people are often unaware of the influence of a cause - nisbett and wilson 1977
decision making diagram - wegner 2002
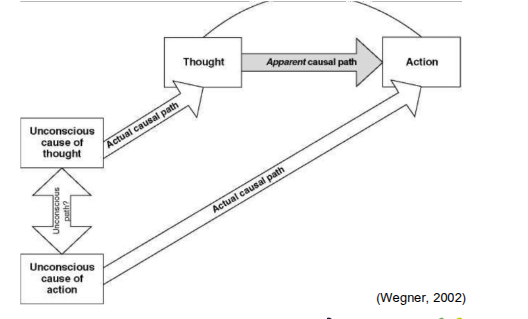
what influences decisions
salience
heuristics
priming
what is salience
when particular objects in the environment attract our attention more than other objects
attentional capture
what is gleitmans theory
the way options are described has an influence on our decision making
what is framing
the way options are described has an influence of our decision making - gleitman
our decision is influenced by the way information is phrased
what are heuristics
a strategy for making judgements quickly at the price of occasional mistakes
mental shortcuts
what is availability bias
items that are more readily available in memory are judged as having occurred more frequently
what is priming
when exposure to one stimuli influences the response to a later one