Biology 2024
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Receptor
specialised cell that can detect changes in an organism's environment.
(the change = the stimulus)
Temperature receptors
respond to changes in temperature. (touch)
Photoreceptors
respond to light energy (sight)
Mechanoreceptors
respond to mechanical stimuli such as touch, pressure or vibrations. (touch)
Sound receptors
respond to vibrations (sound)
Chemoreceptors
respond to specific chemicals (smell and taste)
effector examples
glands and muscles
Effector
cause a response to the stimulus (muscles contract, glands release hormones)
types of nervous action
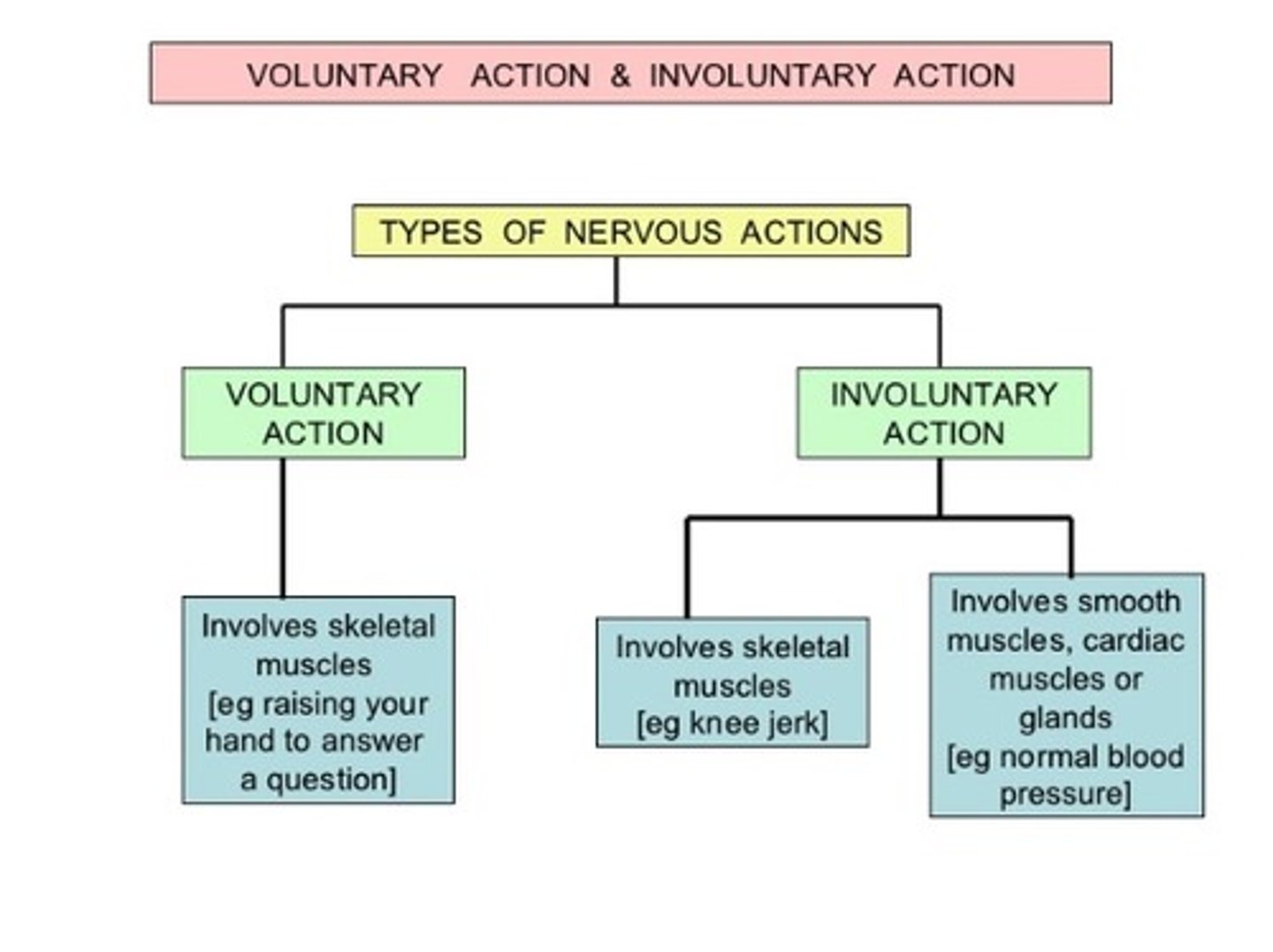
Voluntary actions
The decision starts in the brain that coordinates a response in many different parts of the body.
Involuntary actions
Processes constantly occurring in our bodies
We cannot make these things happen, and cannot choose to we stop them.
Some activities, such as breathing and blinking are partly voluntary and partly involuntary: we breathe automatically without thinking about it, and yet we can alter the rate of our breathing if we want to.
reflex arc
The nervous system communicates information via a stimulus-response model:
Stimuli (internal or external) are converted into electrical signals by receptors
Effectors (muscles or glands) convert the electrical signals into a response
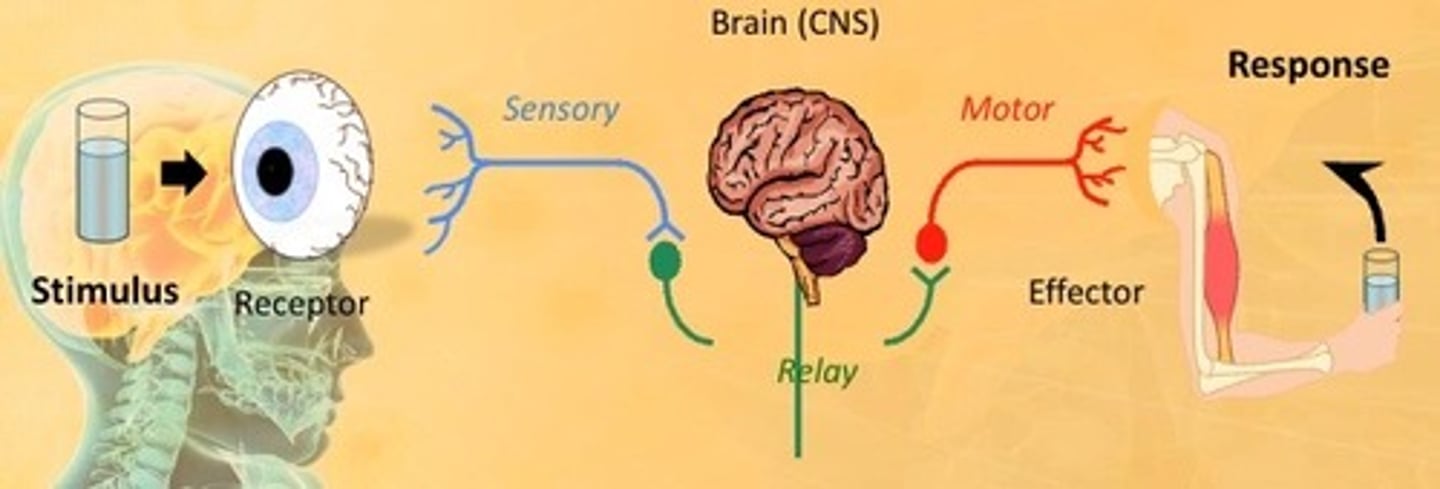
describe the process of a reflex arc

What carries the electrical signals around your nervous system?
NEURONES
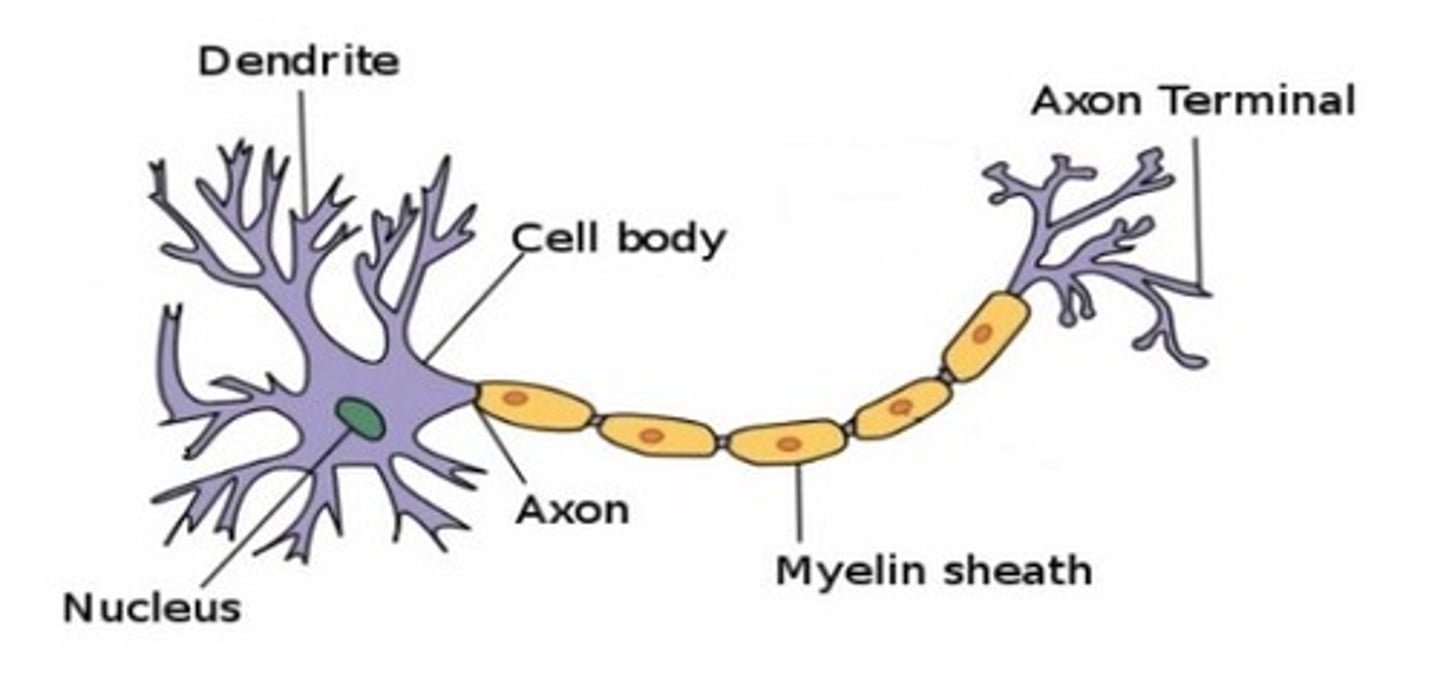
How does a signal travel across a neuron?
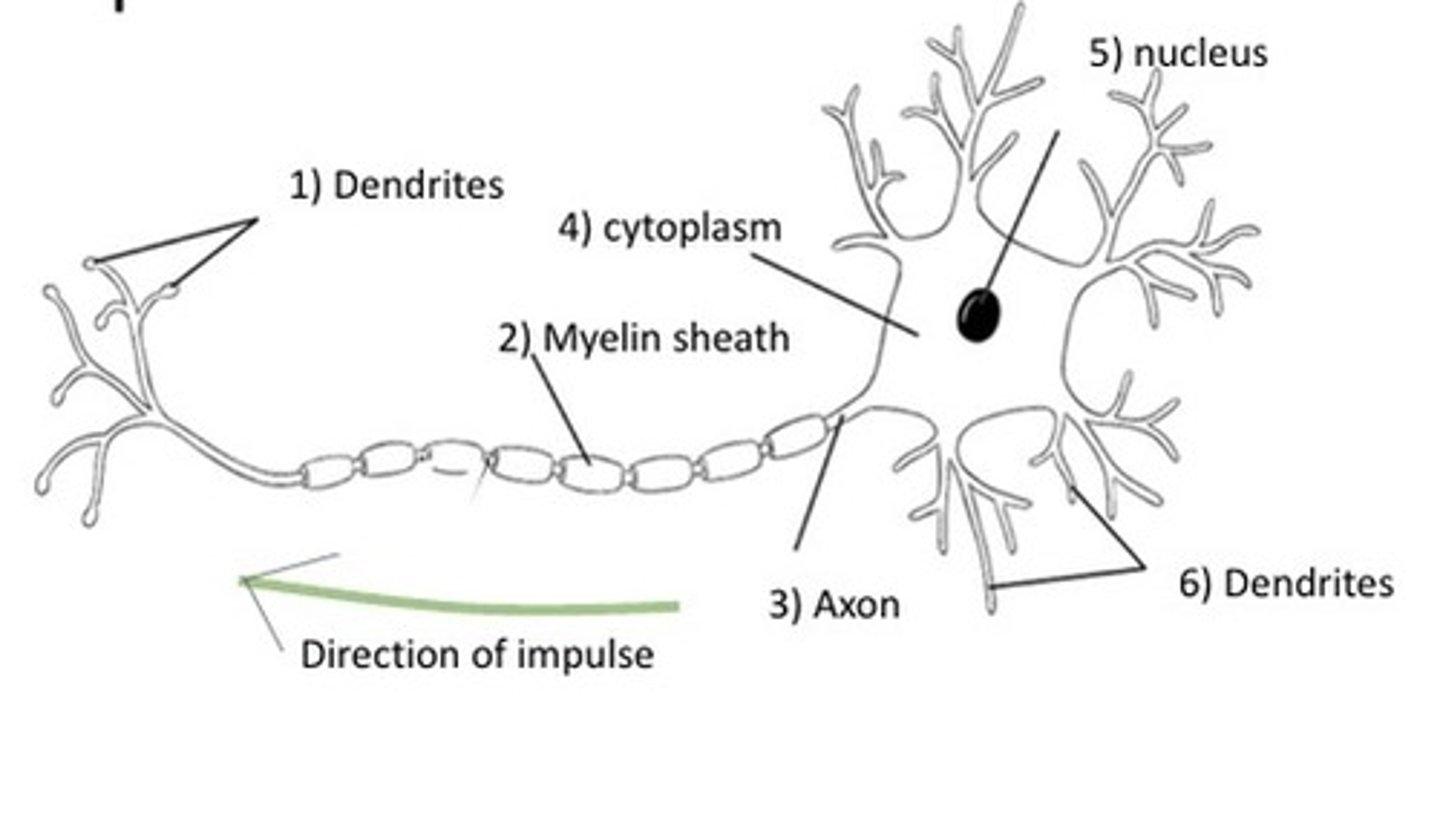
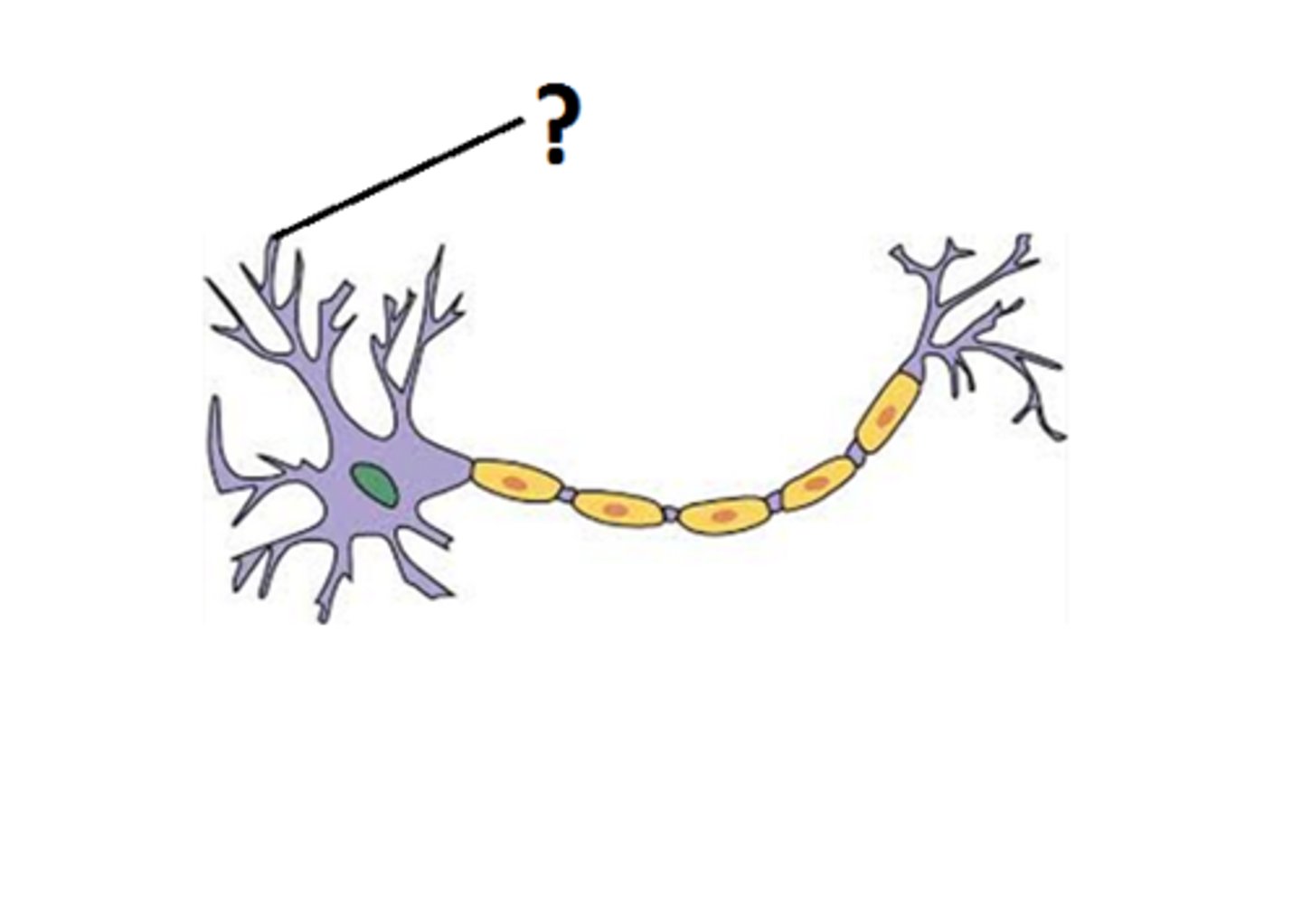
Dendrites pick up electrical signals from other neurons nearby. (nerve signals)
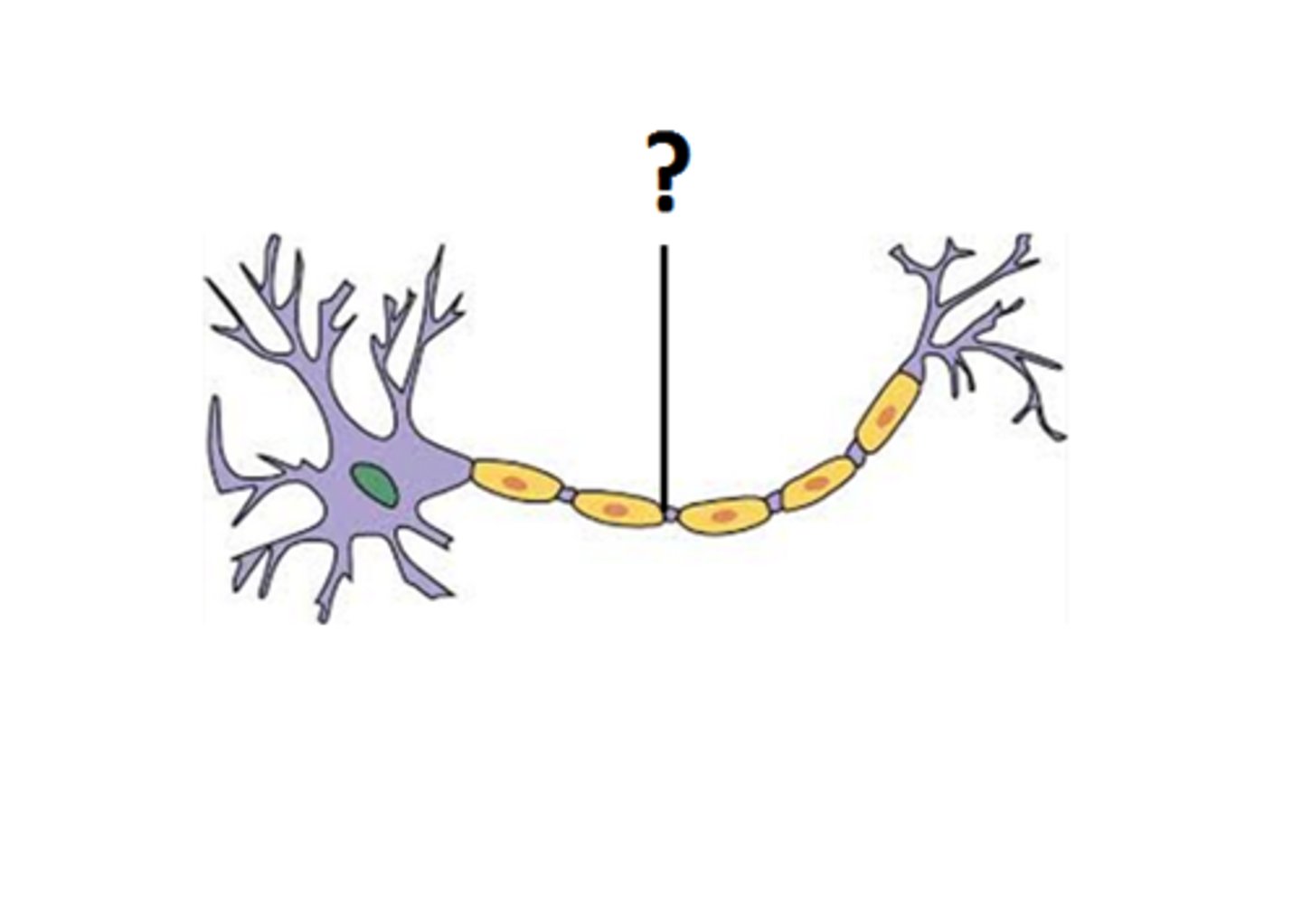
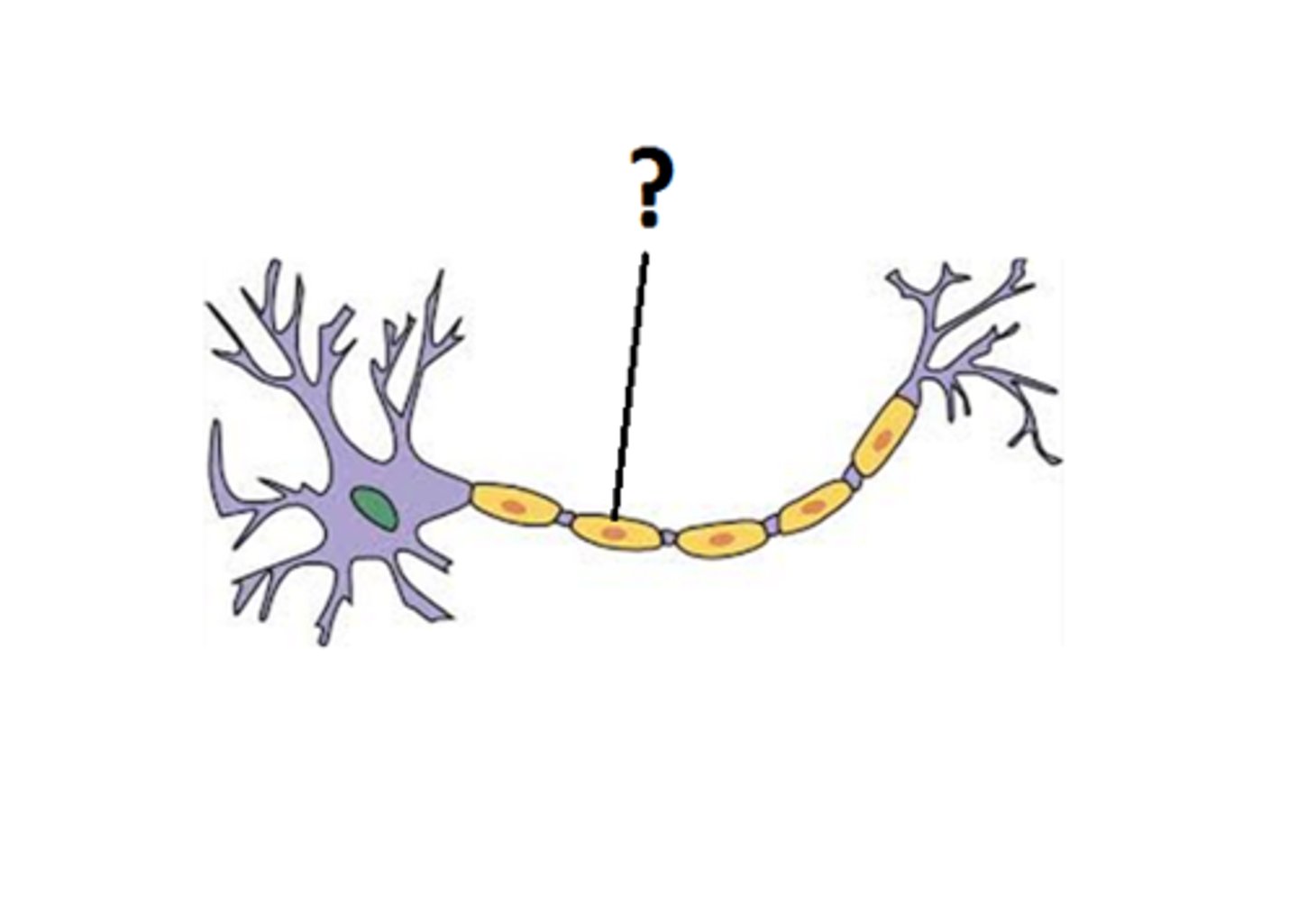
Myelin insulates the nerve fibres, so they carry the impulses much faster.
The nerve signal passes to the cell body, then along the axon, where it might be passed onto another neuron/effector.
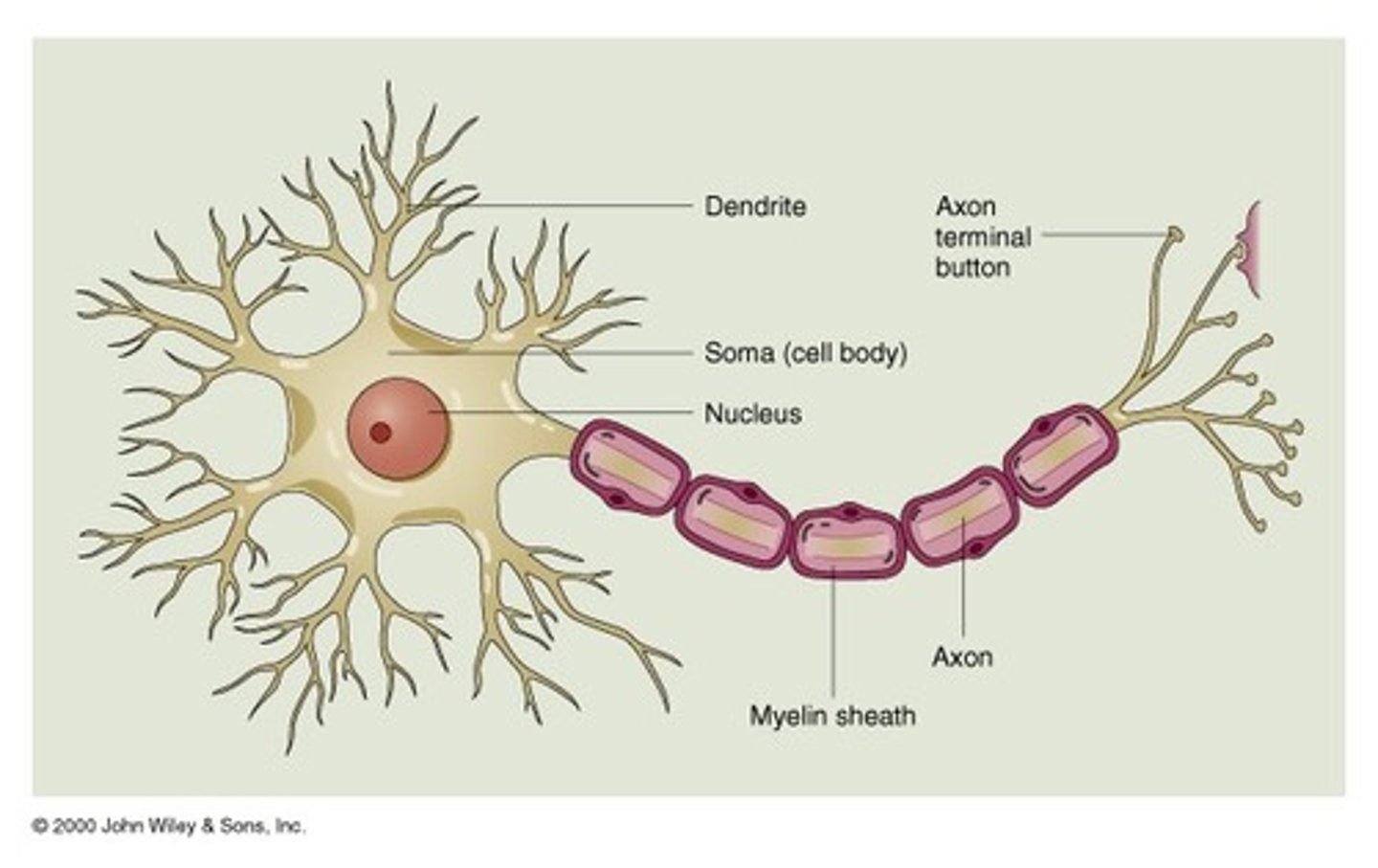
types of nerve cells
sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons
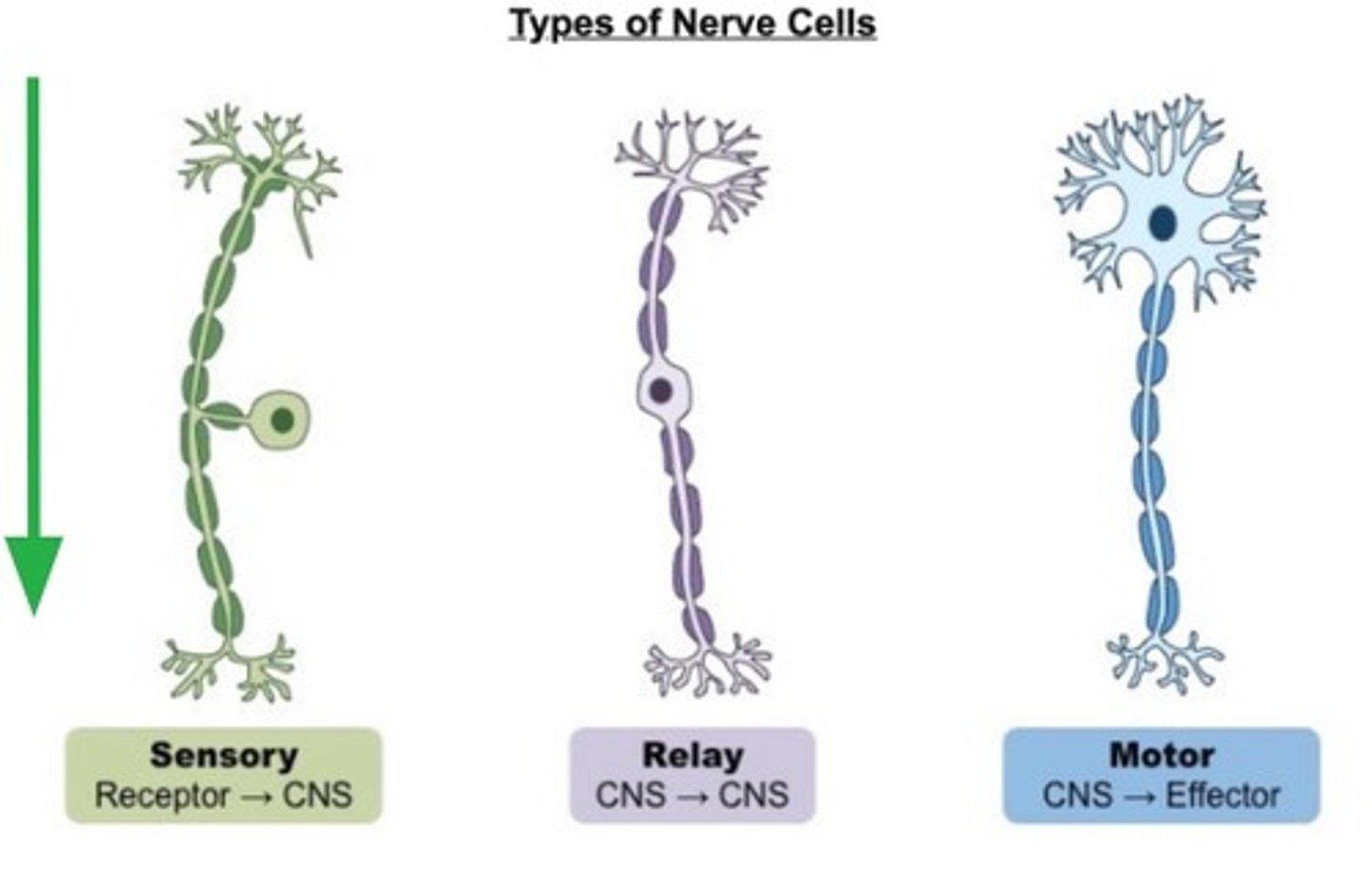
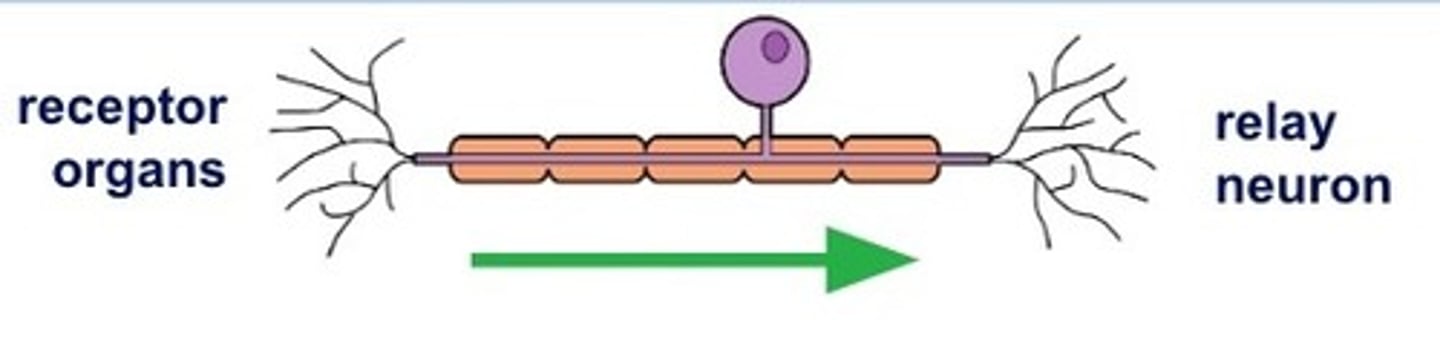
sensory neurons
pick up an impulse from a receptor cell and carry it to the spinal cord
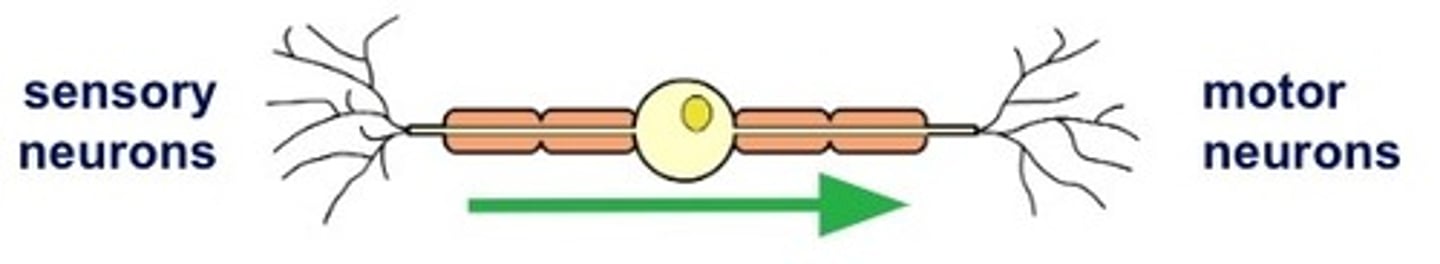
Relay neuron
picks up impulse from the sensory neuron then relays it to other neurons. Pass the impulse to the brain or to a motor neuron.
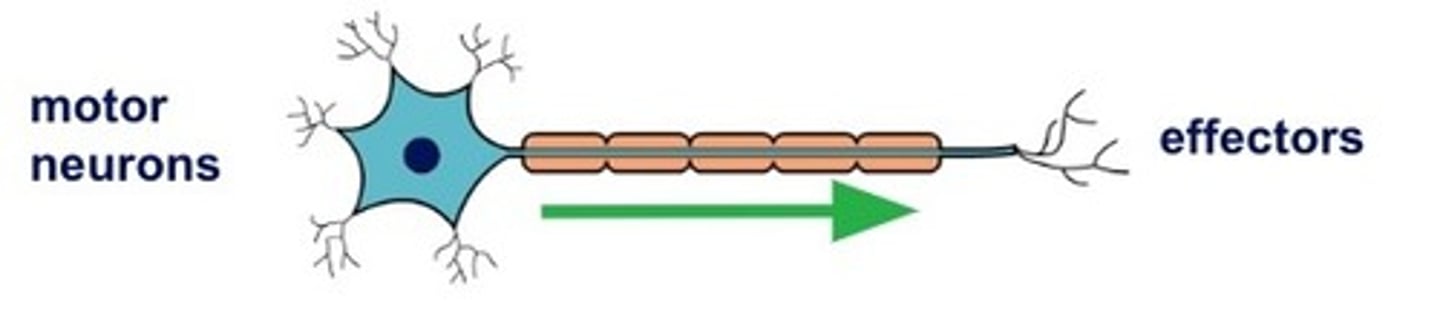
Motor neurons
pass the impulse to an effector
draw and label a neuron diagram
Sensitivity
ability to detect and process information
The sensitivity homunculus
concept in neuroscience
represents the sensory distribution of the body on the cerebral cortex (brain)
way to visualize how different parts of the body are mapped in the brain
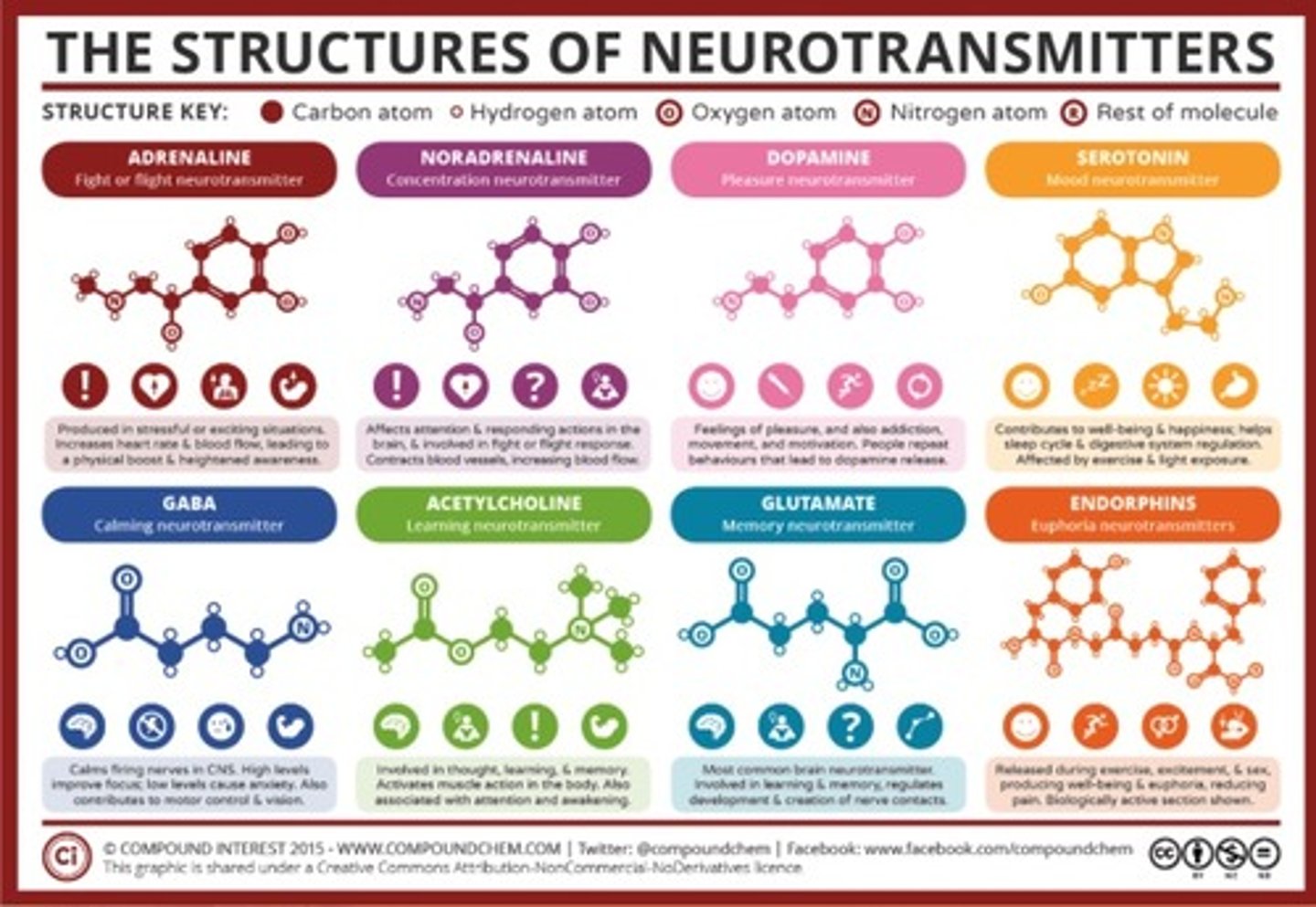
Neurotransmitters
Dopamine
Adrenaline
Noradrenaline
Serotonin
GABA
Acetylcholine
Endorphins
Excitatory
“excite” the neuron and cause it to “fire off the message,” → the message continues to be passed along to the next cell. E.g. glutamate, epinephrine and norepinephrine
Inhibitory
block or prevent the chemical message from being passed along any farther
Modulatory
influence the effects of other chemical messengers. They “tweak” or adjust how cells communicate at the synapse. They also affect a larger number of neurons at the same time. E.g. dopamine
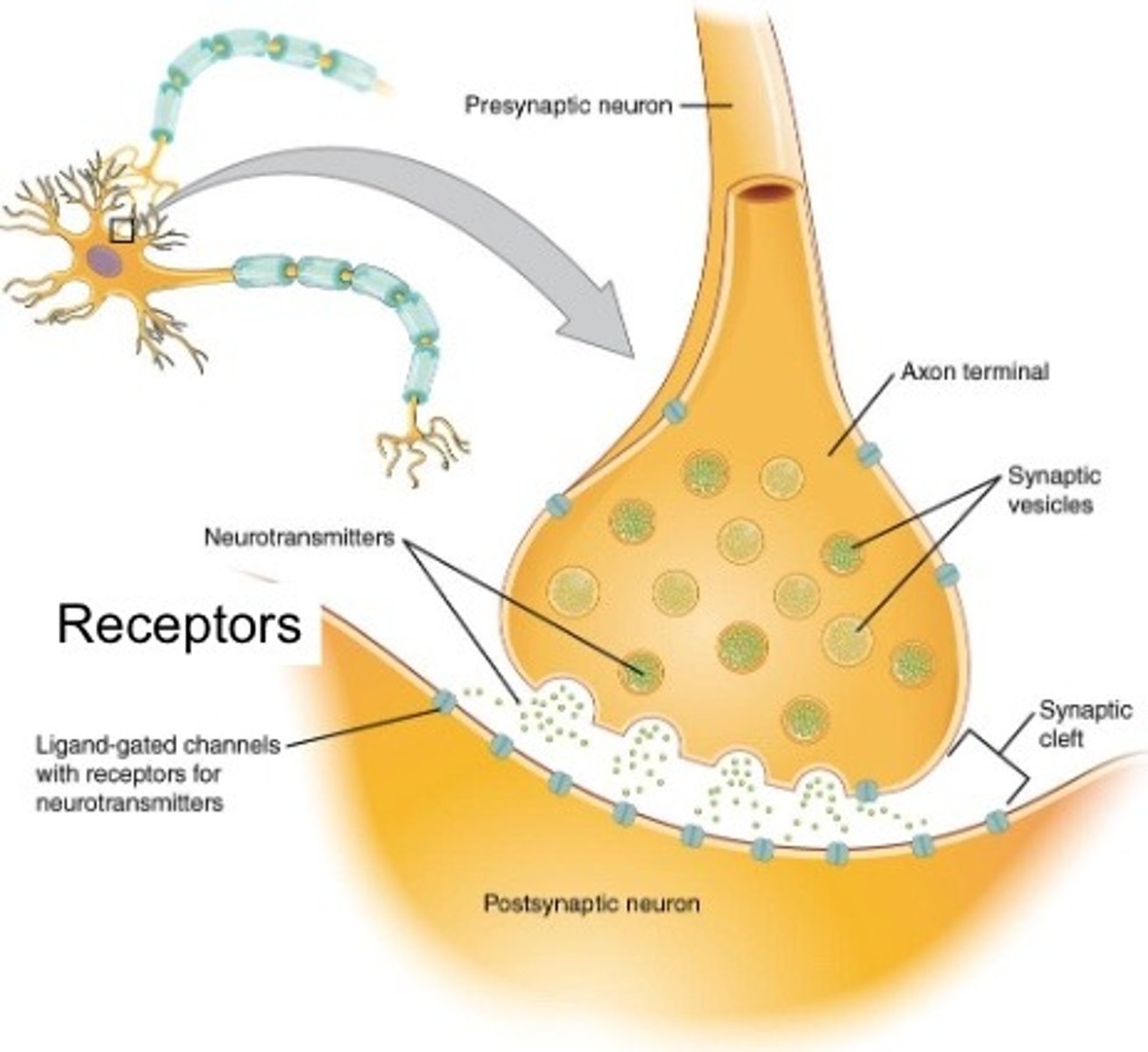
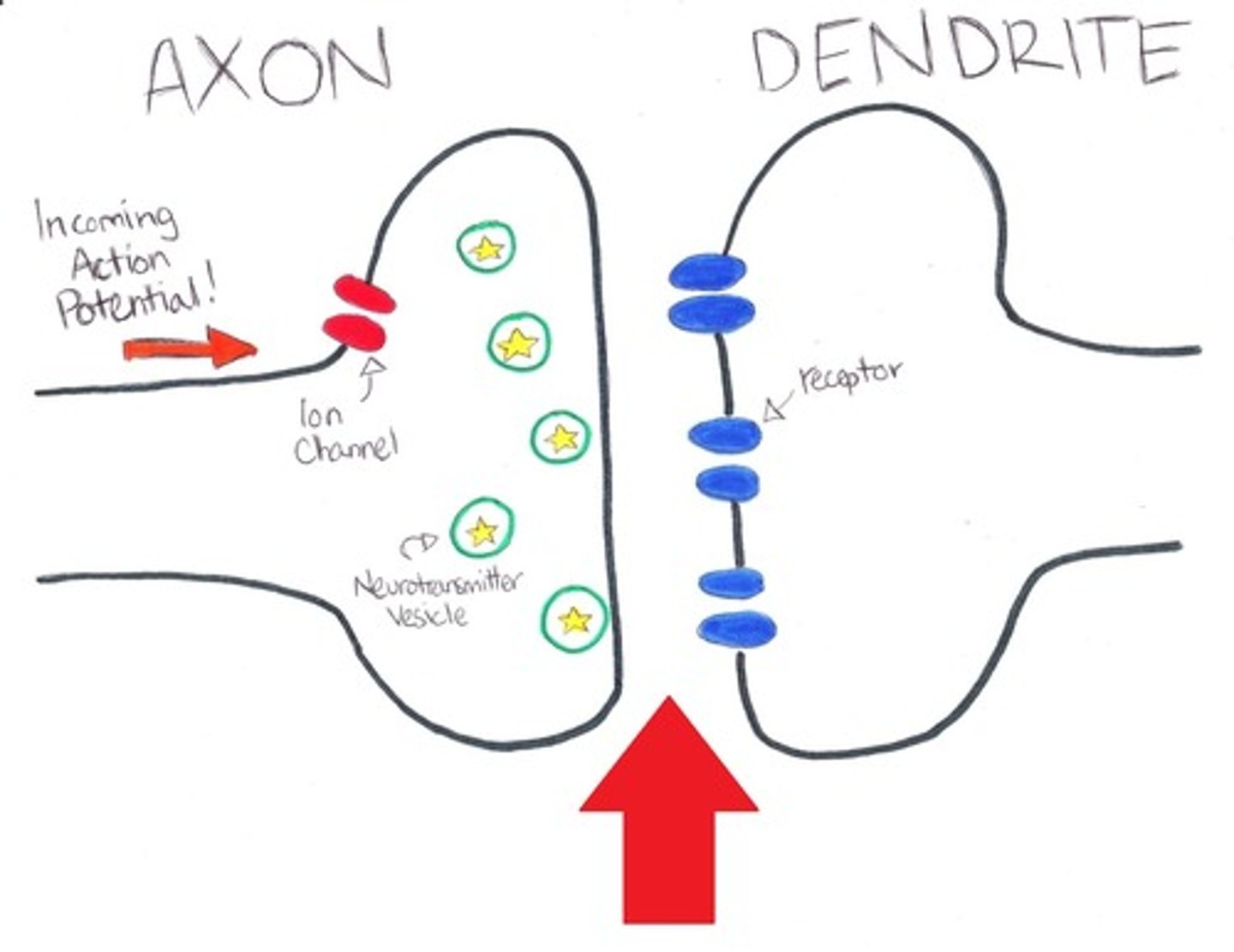
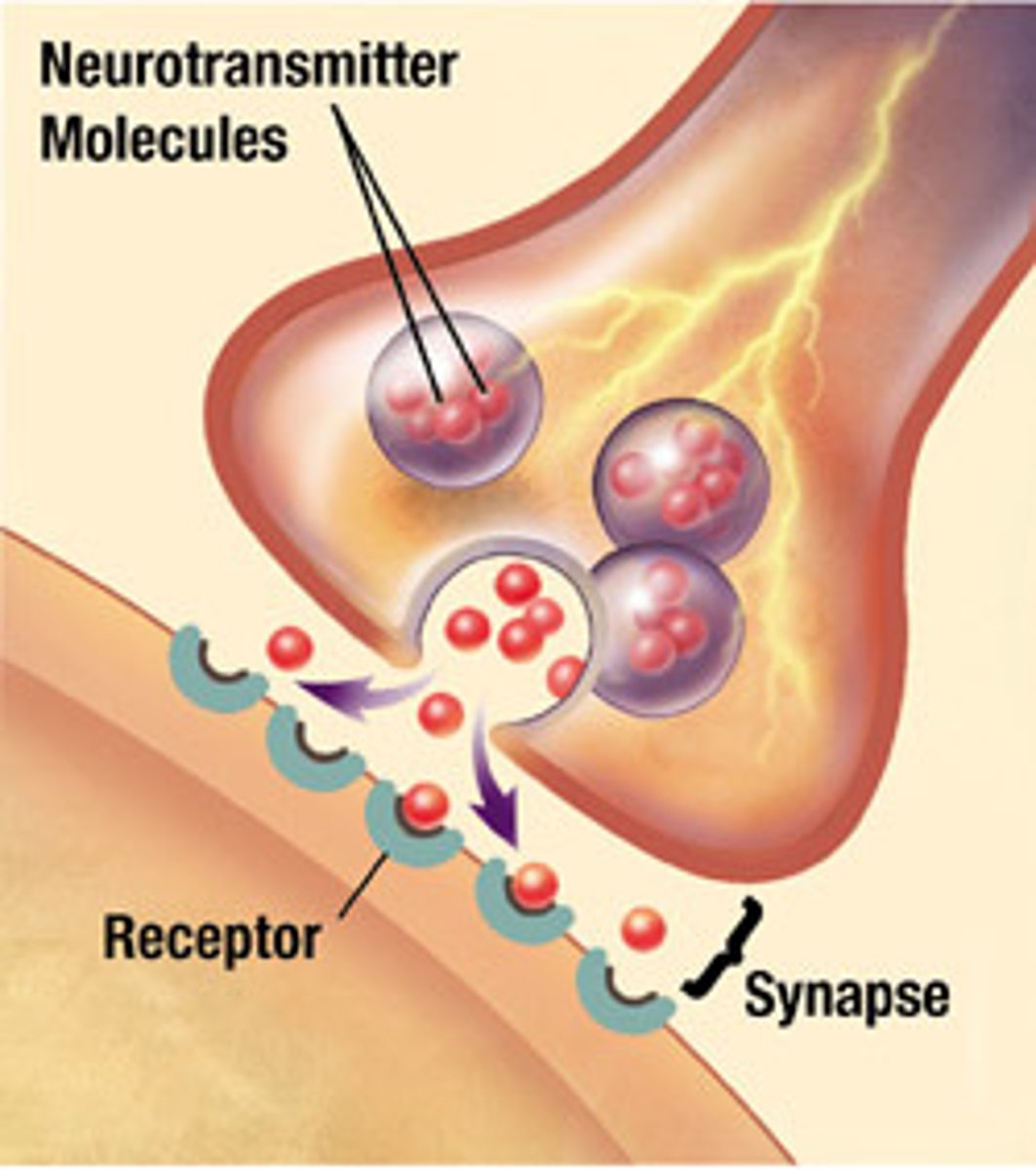
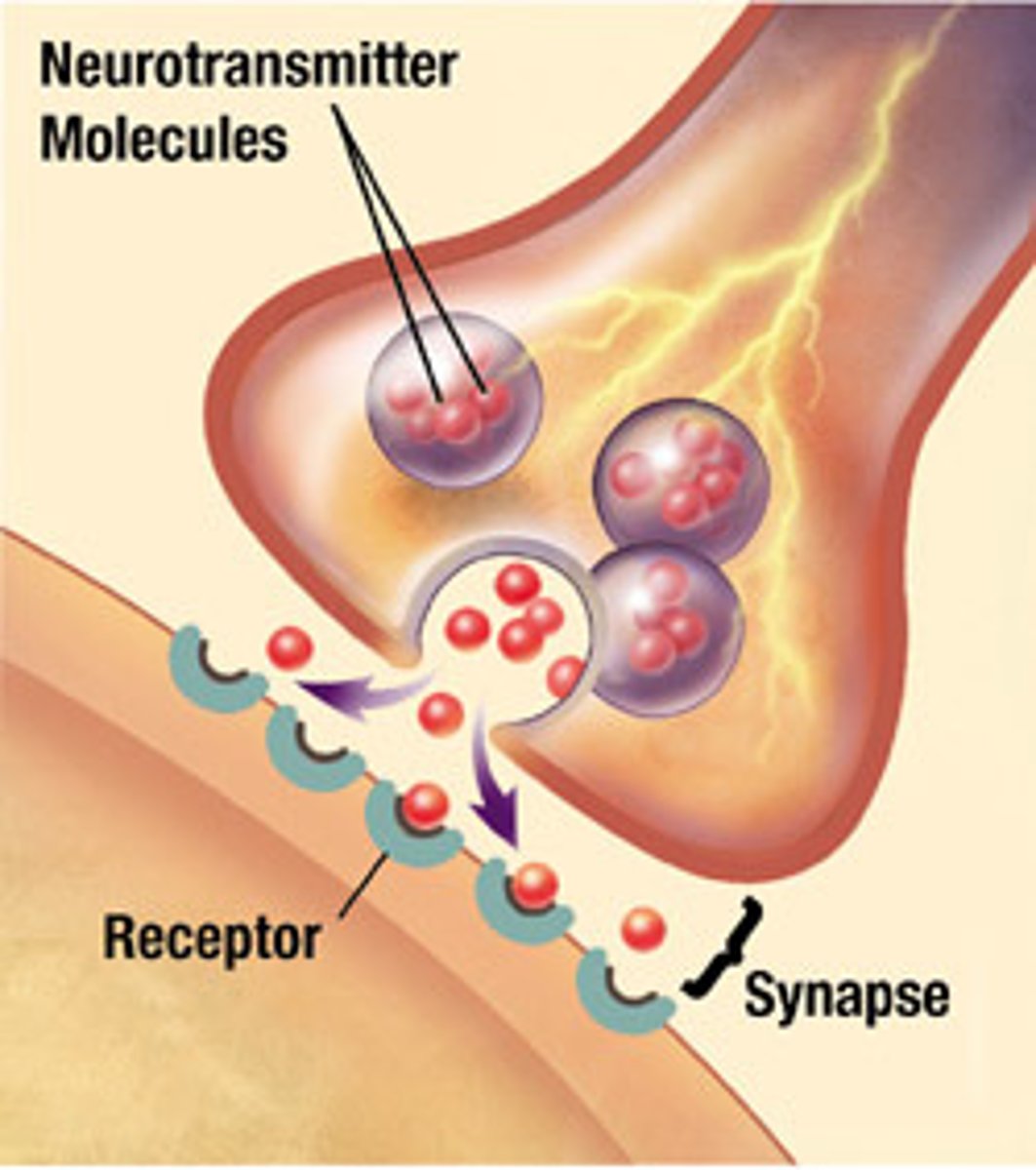
What is a synapse?
A synapse is a junction between two neurons across which messages pass.
form of messages
1)across neurons
2)between
1)electrical
2)chemical
draw a synapse
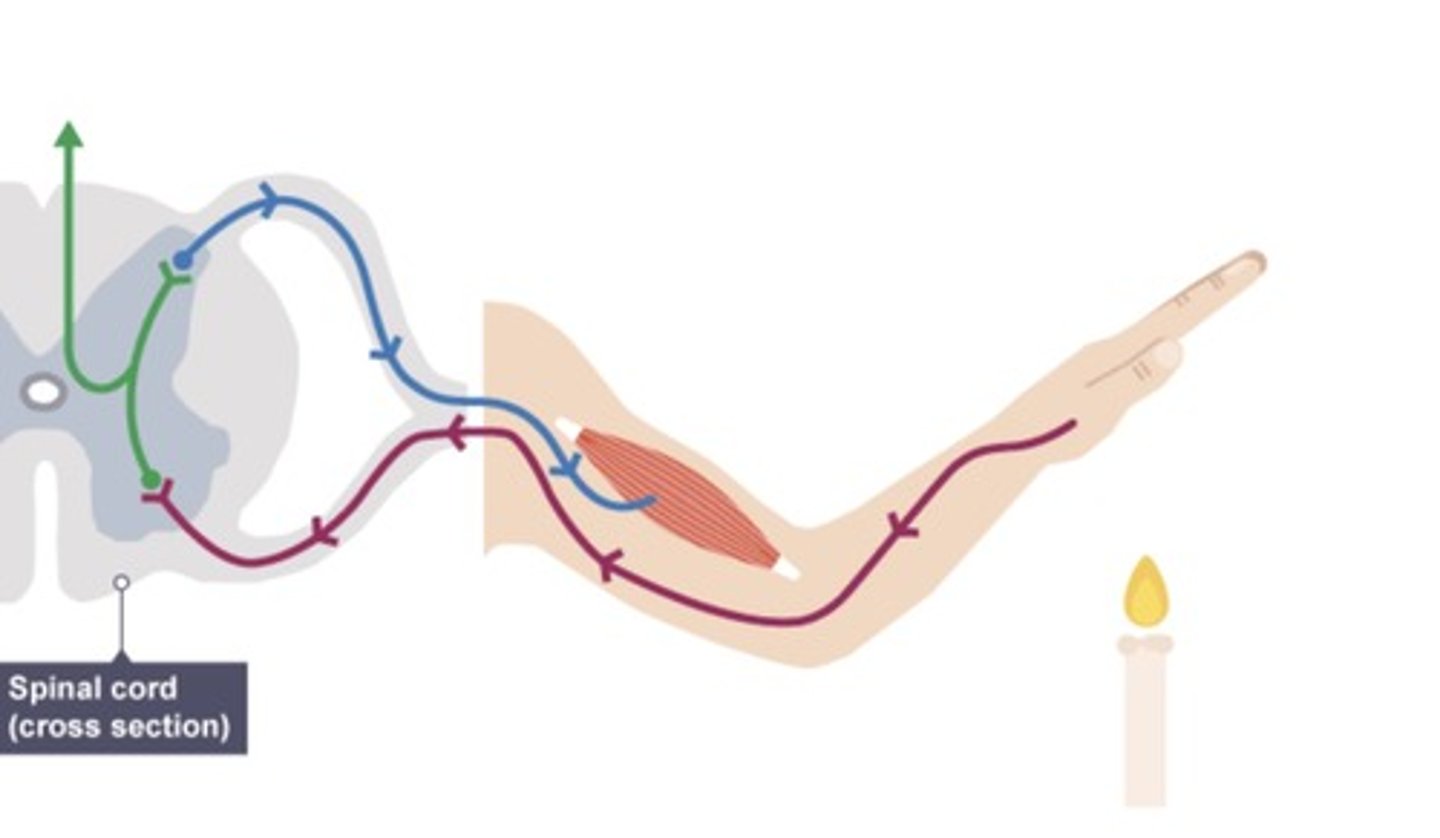
basic format of a reflex arc
stimulus → receptors → sensory neuron → relay neuron → motor neuron → effector → response
synaptic vesicle
storage site for neurotransmitters
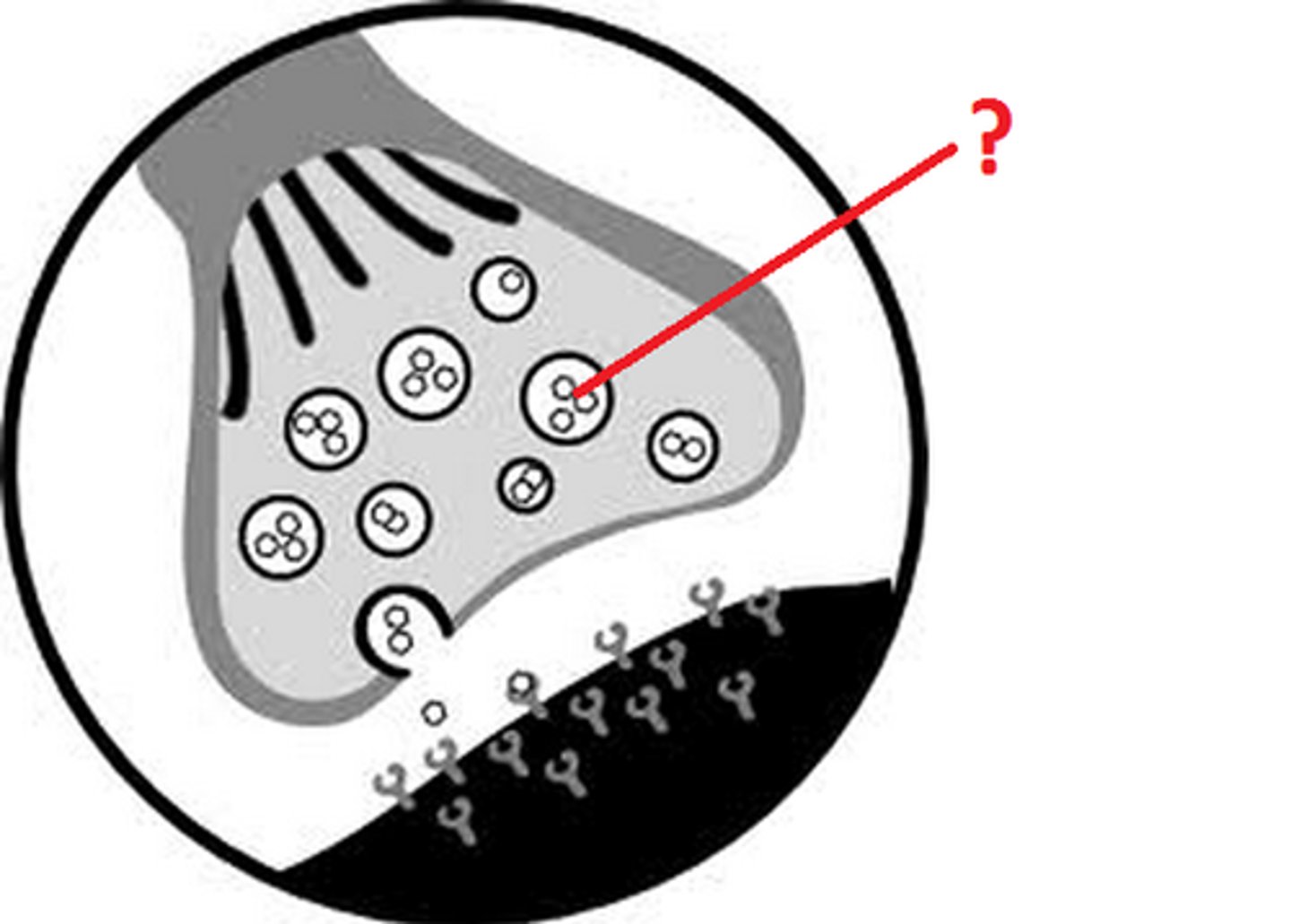
synaptic clef
a gap into which neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal
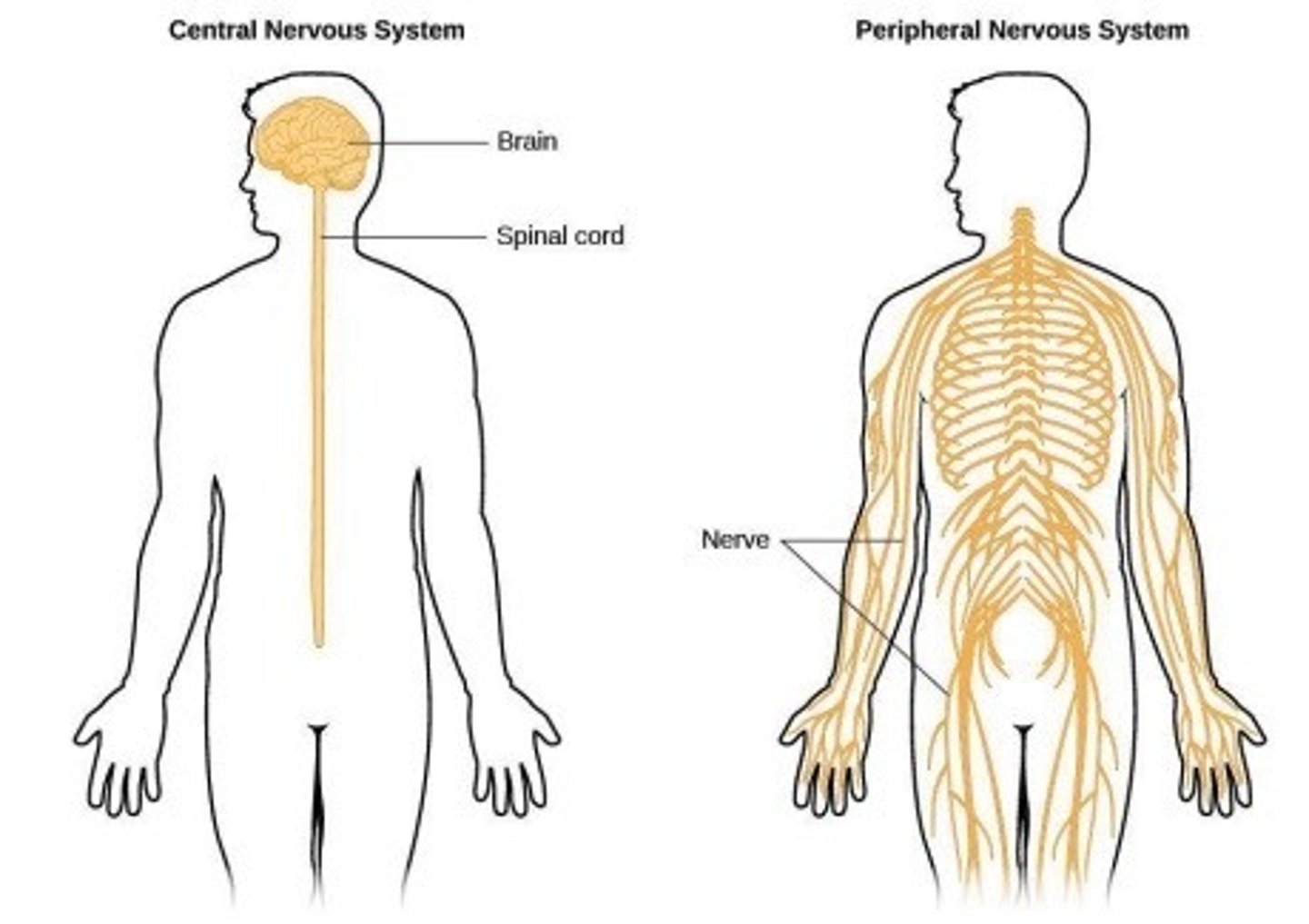
Nervous system
The main job of the nervous system is to transmit messages from one part of the body to another.
Nerve impulses are tiny pulses of electricity which travel rapidly through the CNS and along the nerves.
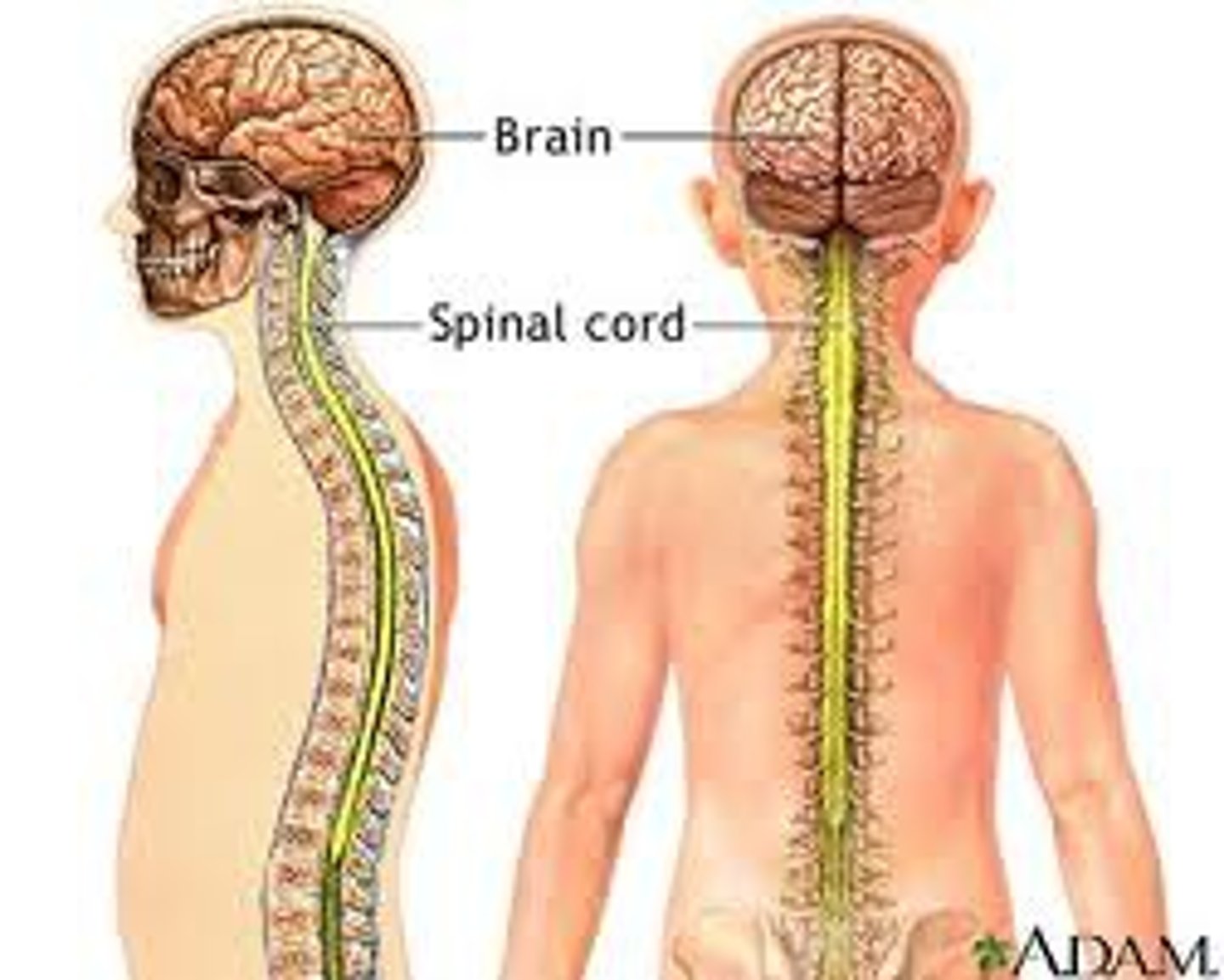
CNS vs PNS
glands
type of effector that produces chemicals such as hormones as a response

muscles
type of effector that causes movement (most of the time) as a response
Reflexes
Reflexes are automatic responses that do not need the involvement of the brain and are a lot faster because of it.
Receptor
specialised cell that can detect changes in an organism's environment.
(the change = the stimulus)
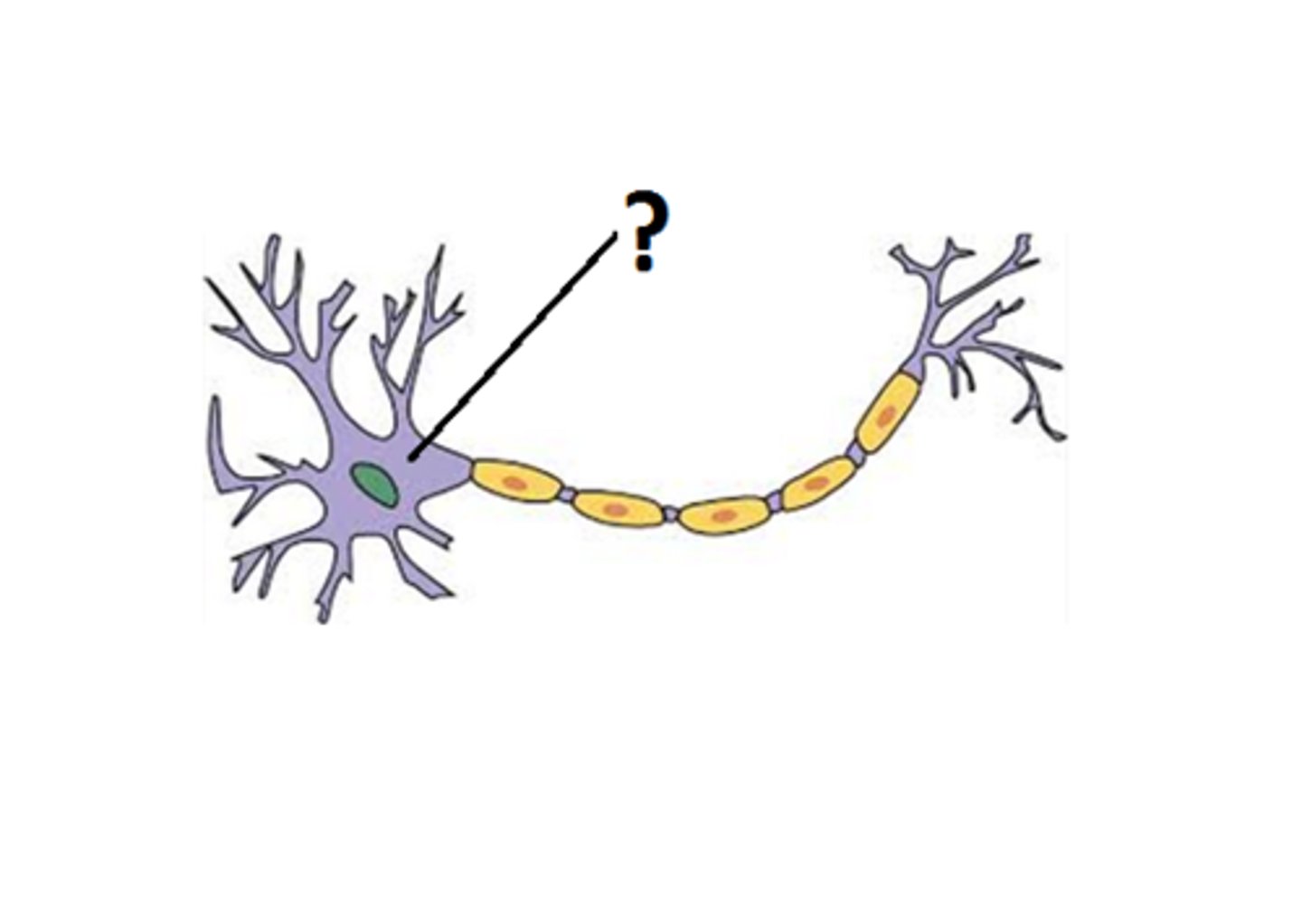
Axon
portion of a nerve cell that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body
cell body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
central nevous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord
coordinator
controls and coordinates all involuntary and voluntary functions of the body
Dendrite
branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
Effector
An organ (a gland or muscle) that becomes active in response to nerve impulses. (stimulus)
Interneuron
neurons that internally communicate between the sensory inputs and motor neurons
involuntary response
A response to a stimulus that occurs without someone making a conscious choice. They are automatic, such as reflexes.
motor neurons
neurons that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce movement and all voluntary responses, such as speaking and breathing.
myelin sheath
insulating layer around nerves, made of proteins and fatty substances
Neurotrasmitters
chemical found in the synaptic vesicles that, when released, has an effect on the next cell
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
receptor
protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response
reflex arc
the nerve pathway involved in a reflex action including at its simplest a sensory nerve and a motor nerve with a synapse between.
response
a reaction to a stimulus
senses
systems we have throughout our bodies that allow us to detect information and transform energy into neural impulses
sensory neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
Stimulus
any event or situation that evokes a response
Synapse
A junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
Variation
differences between individuals of the same species.

Genetic Variation
Differences caused because individuals have different genotypes
→ slight differences in certain genes in the chromosomes.
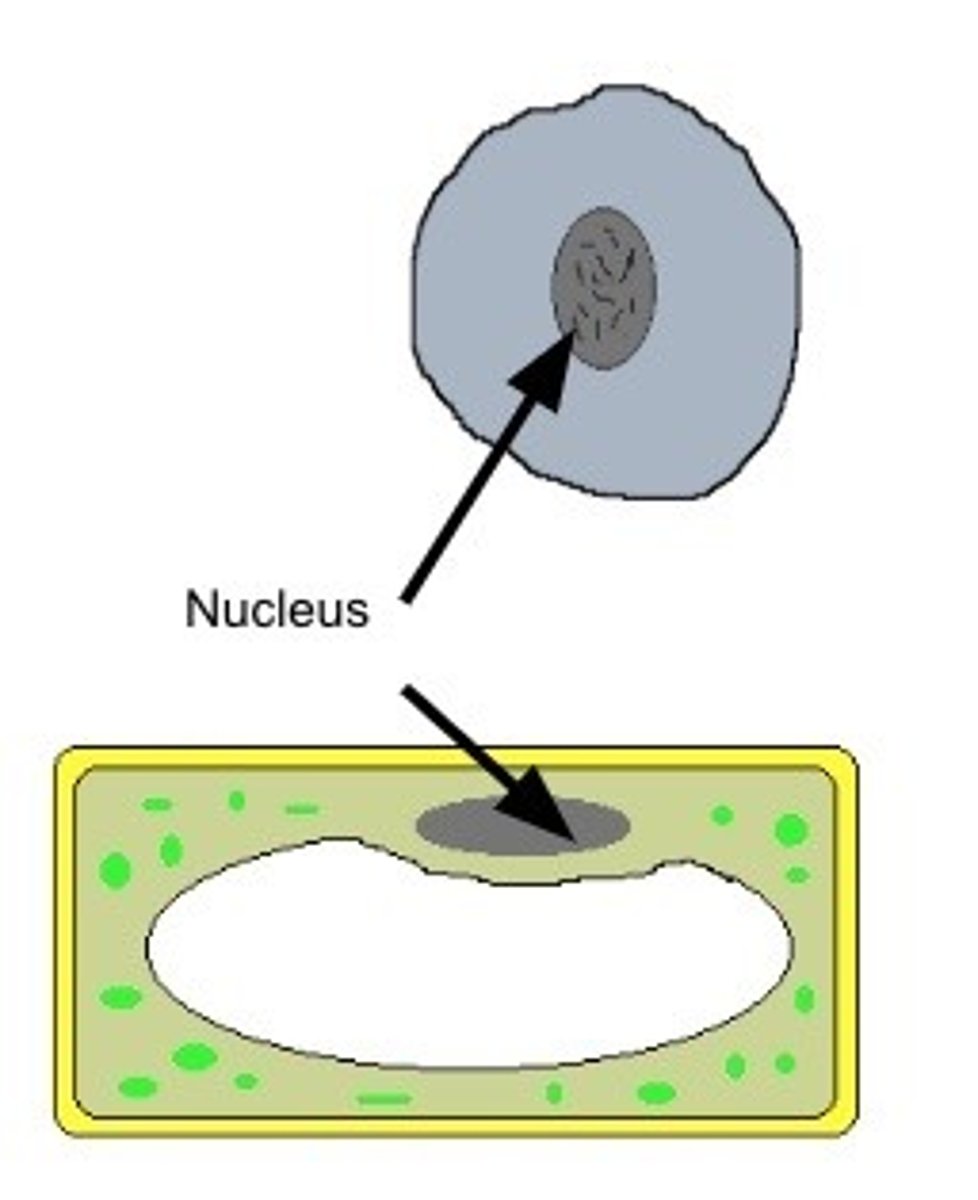
Where is DNA stored?
chromosomes
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 (23 pairs)
Environmental Variation
Variation caused by an individual's surroundings (environment).
Characteristics of animal and plant species can be affected by factors such as climate, diet, accidents, culture and lifestyle.
Discontinuous variation
inheritance pattern in which traits are distinct and are transmitted independently of one another
Always caused by genes.
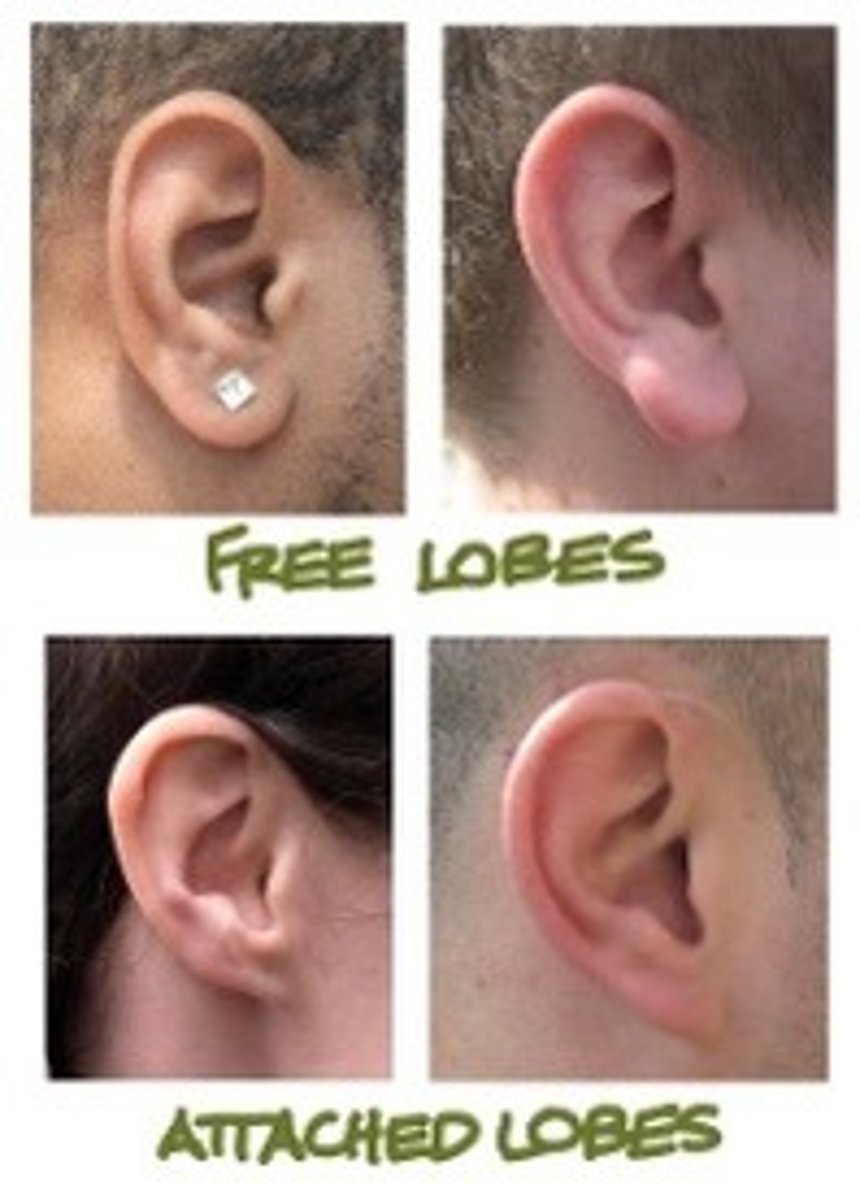
Examples: natural hair colour, blood groups, free/attached earlobes
Continuous Variation
Gradual variation
Generally caused by genes and the environment.
E.g. mass, leaf length, height, skin colour.
Inheritance
the transmission of genetic information from generation to generation.
DNA
the molecular blueprint for inheritance
DNA is the universal genetic code!
ALL organisms have DNA made up of the same structure.
What is the only difference between species or individuals of the same species, regarding their DNA?
the sequence (order) of the nitrogen bases. – The A, T, C and G’s are just arranged differently.
why aren't fruits of the same plant identical?
they are fertilised by different plants
A segment of DNA is called ....
a gene
genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission. Each gene controls a trait.
How do we inherit traits?
Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in each body cell.
Half from each parent – carried in the sperm and egg. So, sex cells only carry 23 chromosomes.
The 1st 22 pairs do NOT determine your sex – they carry genes for other traits.
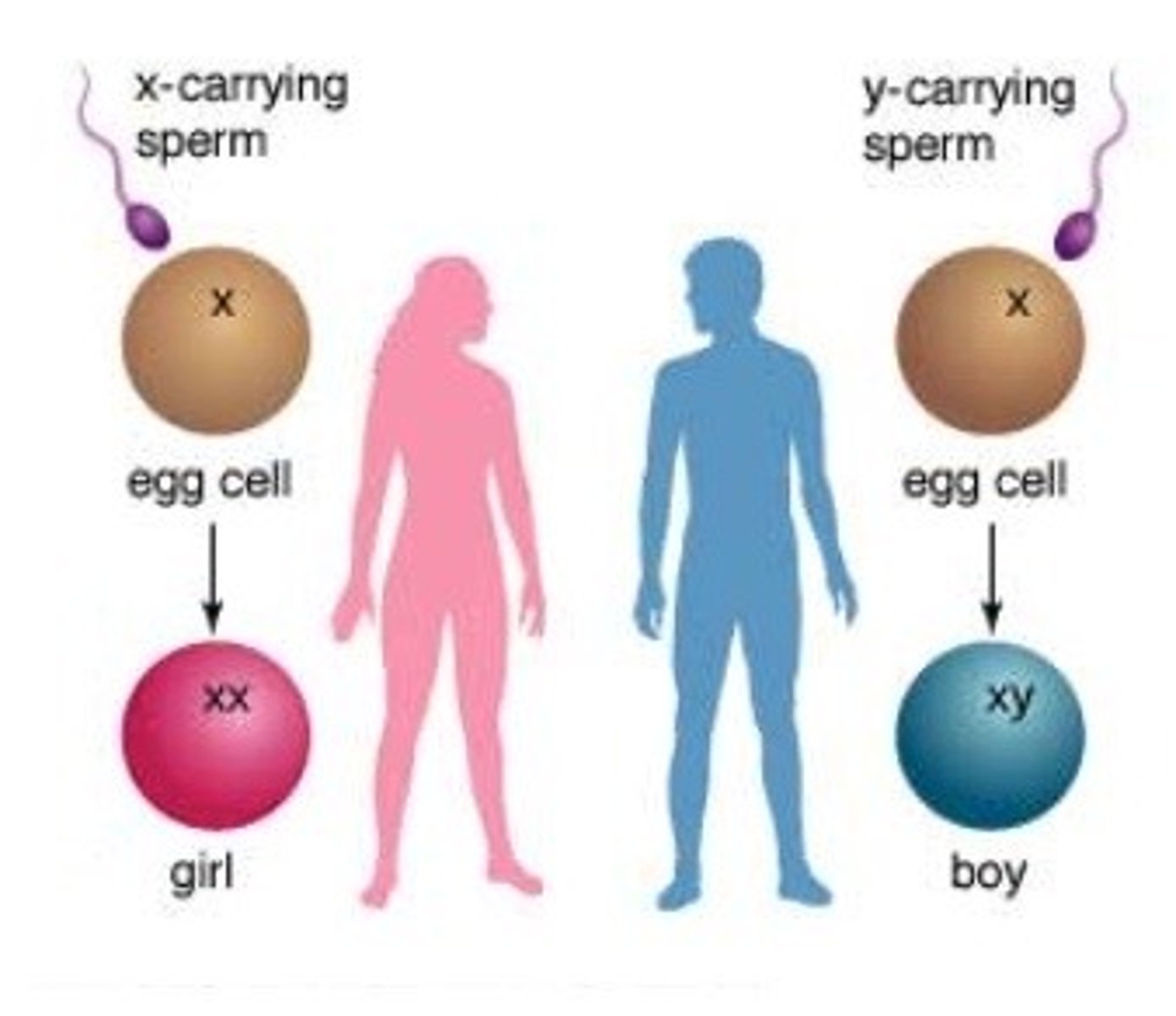
The 23rd pair are the sex chromosomes
XX = female, XY = male
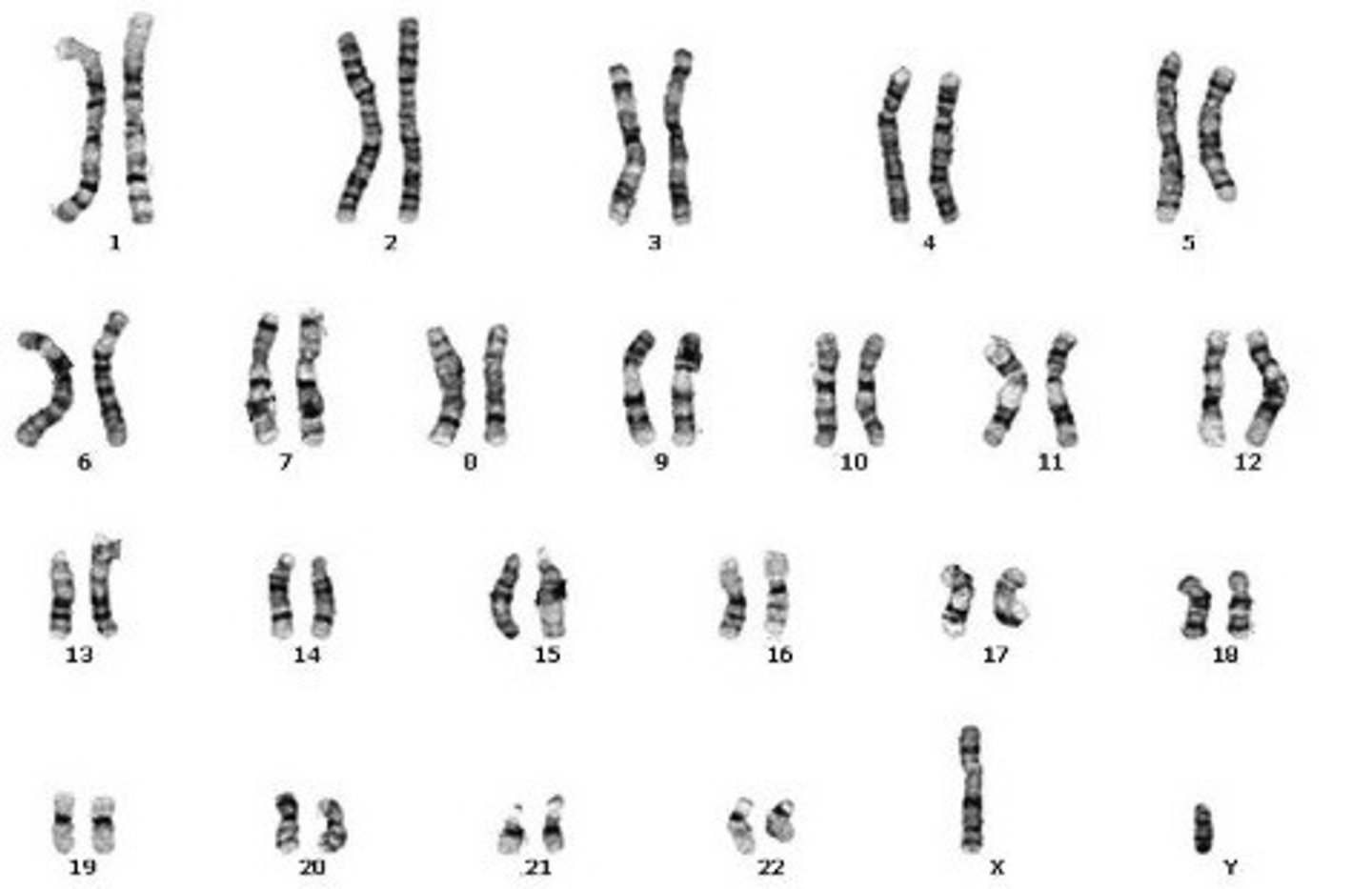
male chromosomes
XY - If the 23rd pair of chromosomes are the different sizes, XY, then the organism is a male.
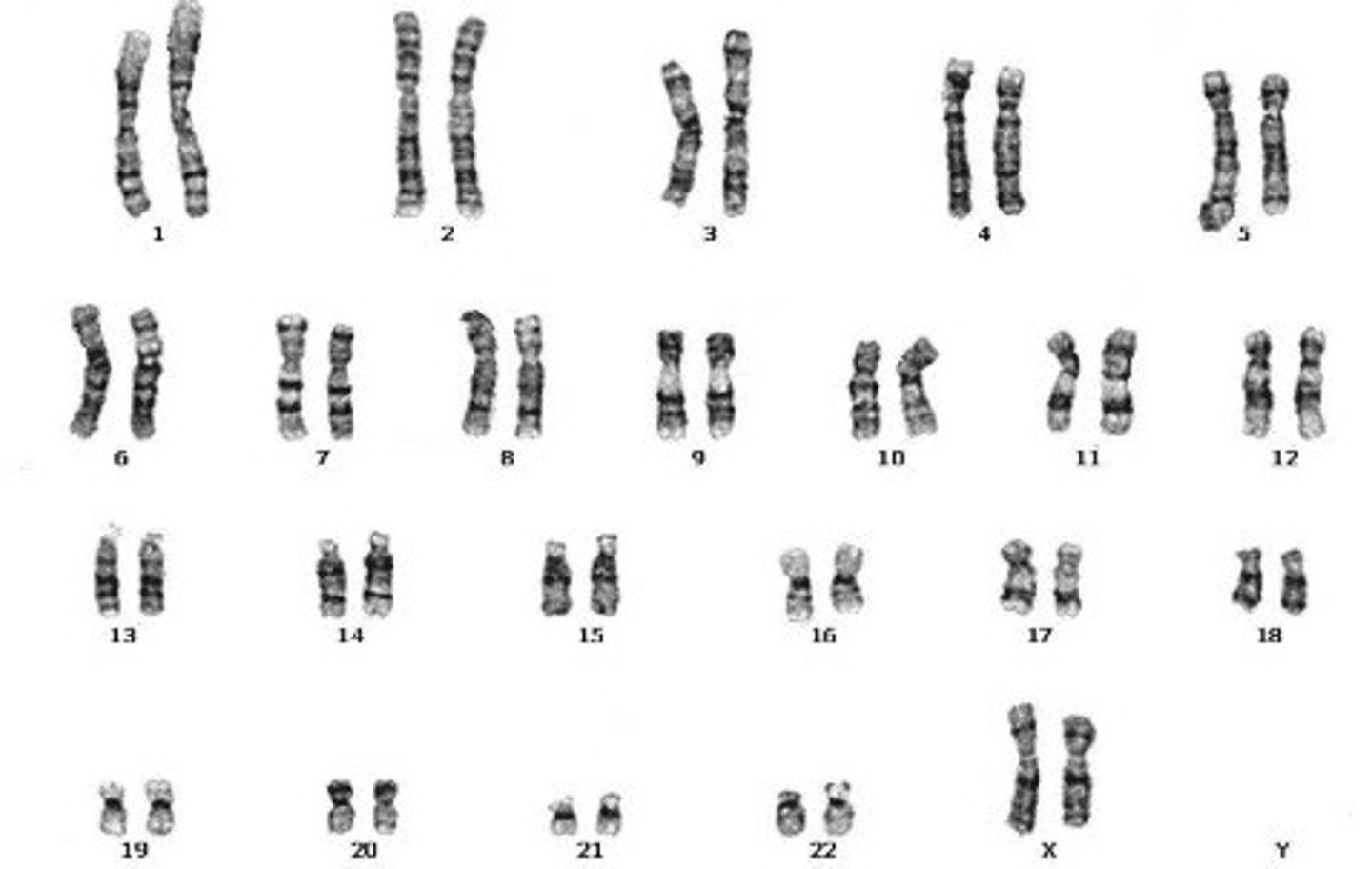
Female chromosomes
XX - If the 23rd pair of chromosomes are the same size, XX, then the organism is a female.
autosomes
Chromosomes that are not directly involved in determining the sex of an individual.
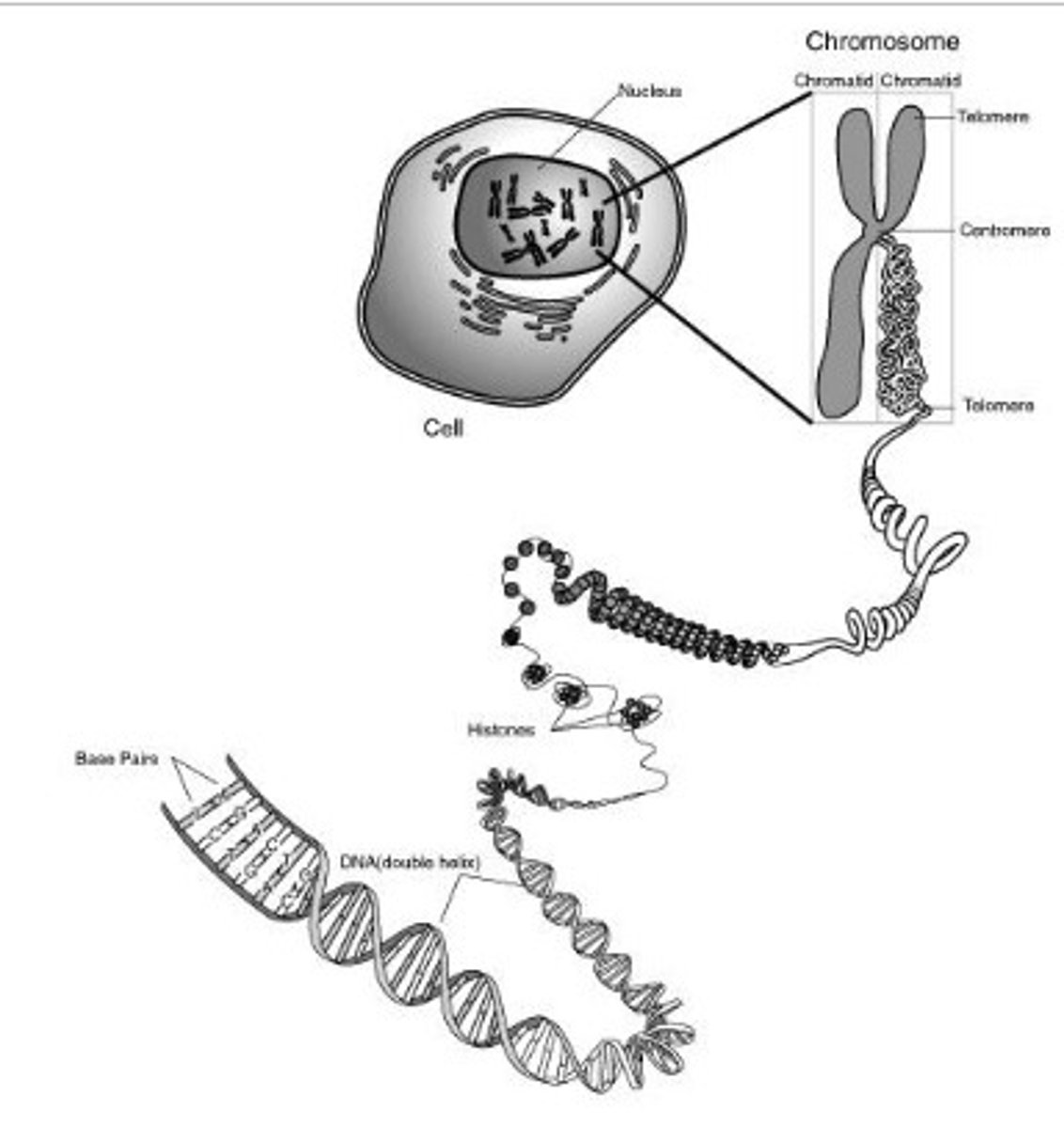
Organise these structures in order of size (smallest → largest):
Cell
DNA
Chromosome
Nucleus
DNA
Chromosome
Nucleus
Cell
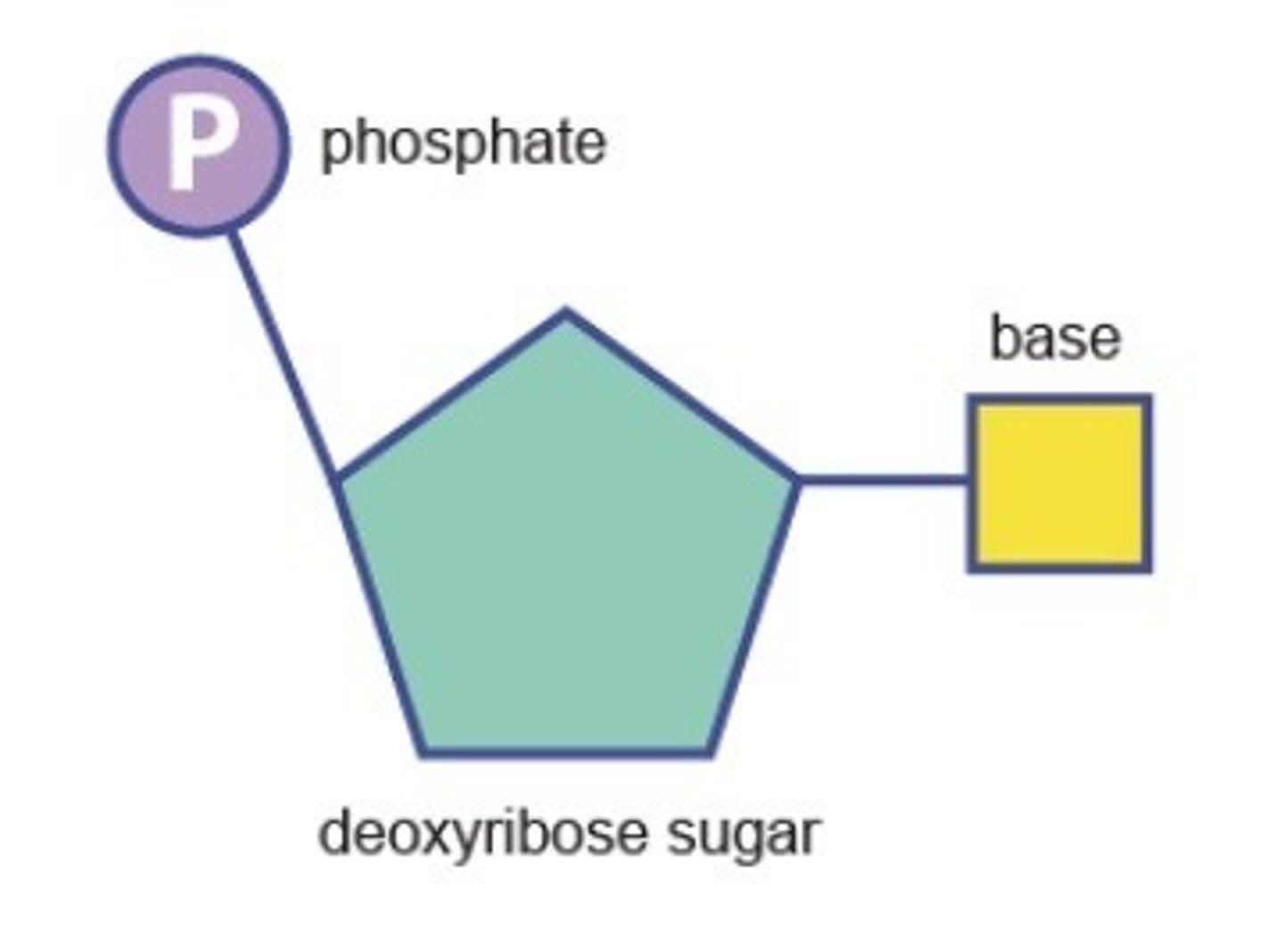
nucleotide
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
DNA is made of ...
nucleotides
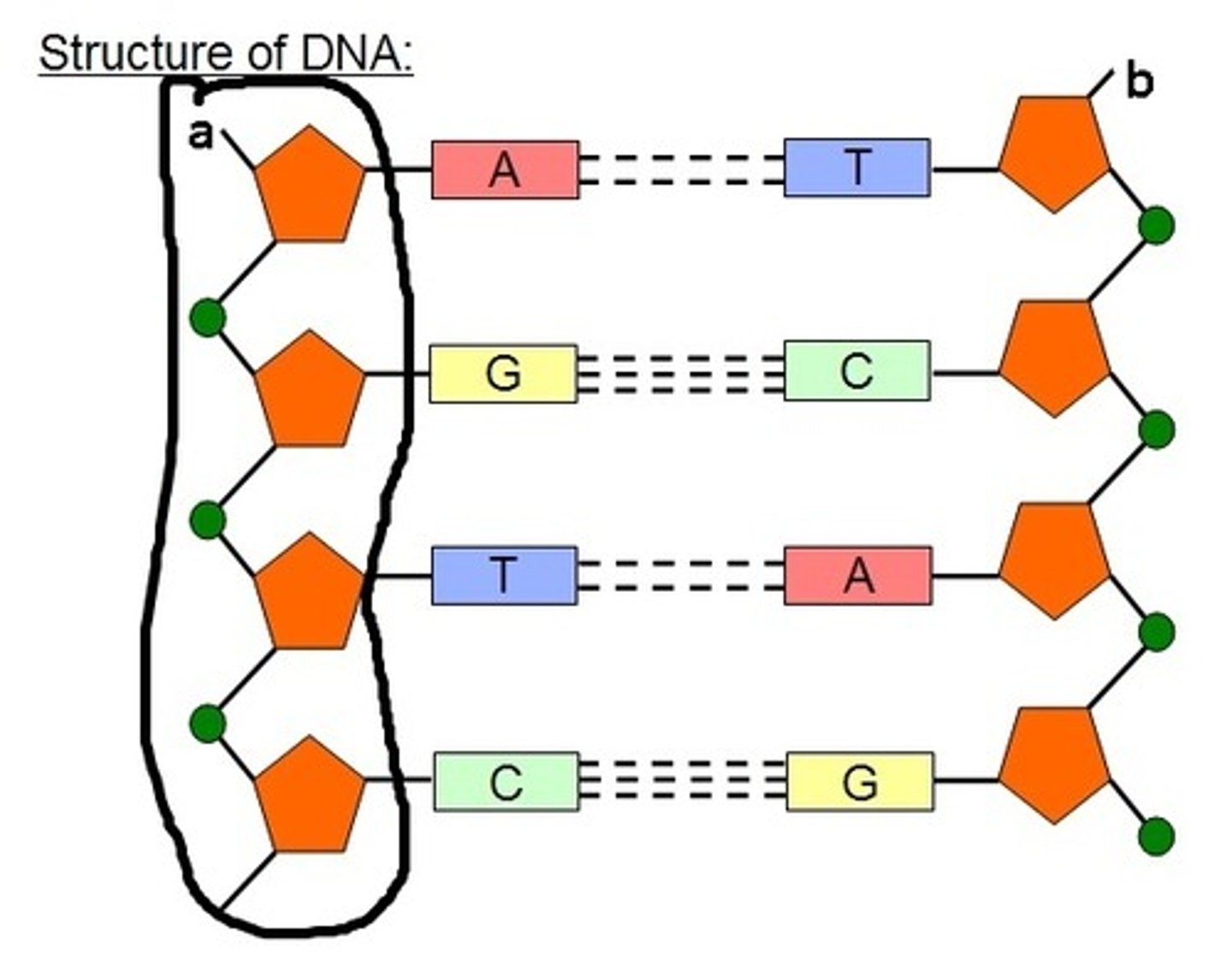
DNA structure
Along the backbone of the structure is a Phosphate molecule bonded to a sugar called Deoxyribose.
There are two lines of phosphate-sugars like a ladder called a double helix. Connecting the two lines of the ladder together are bases.
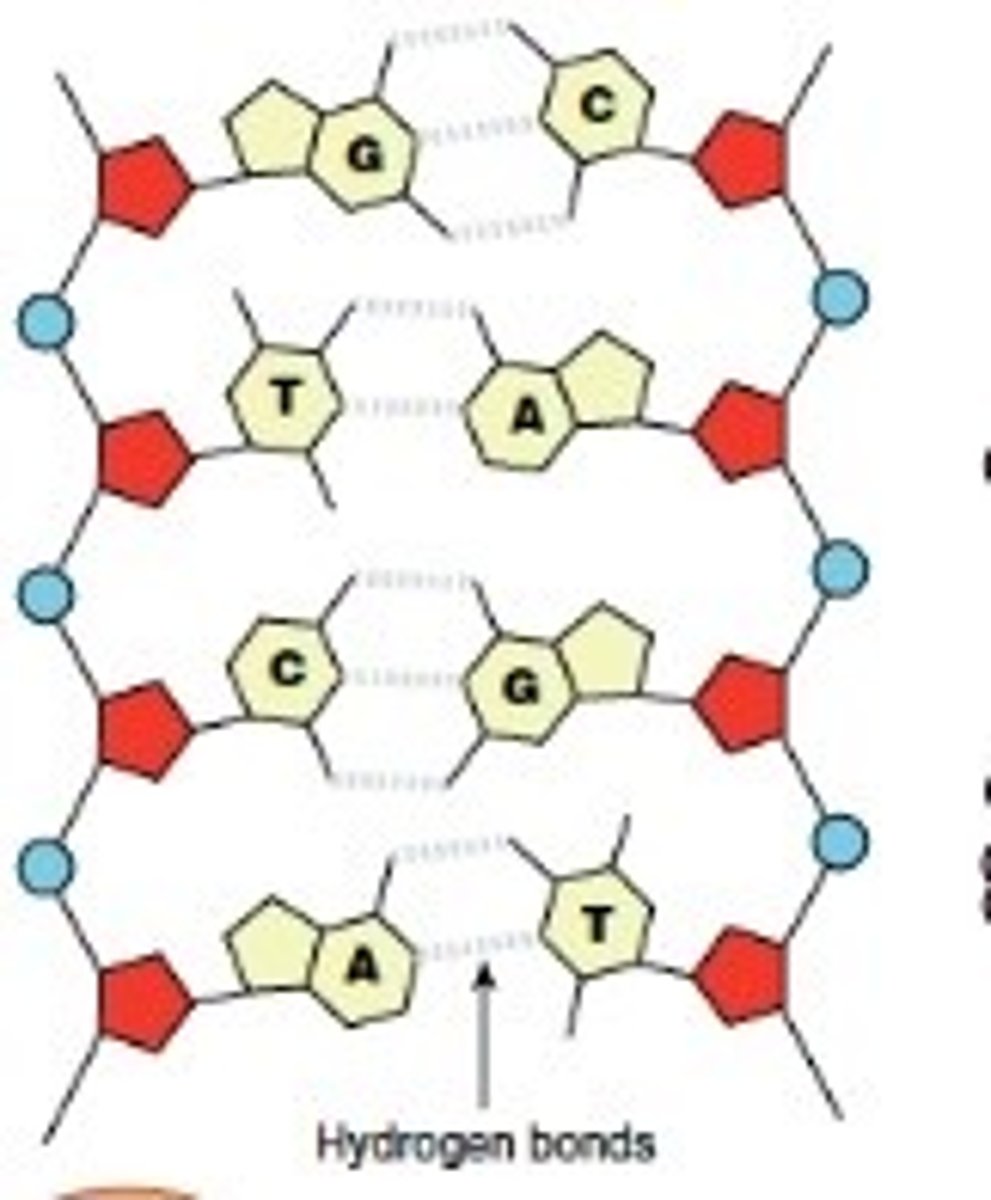
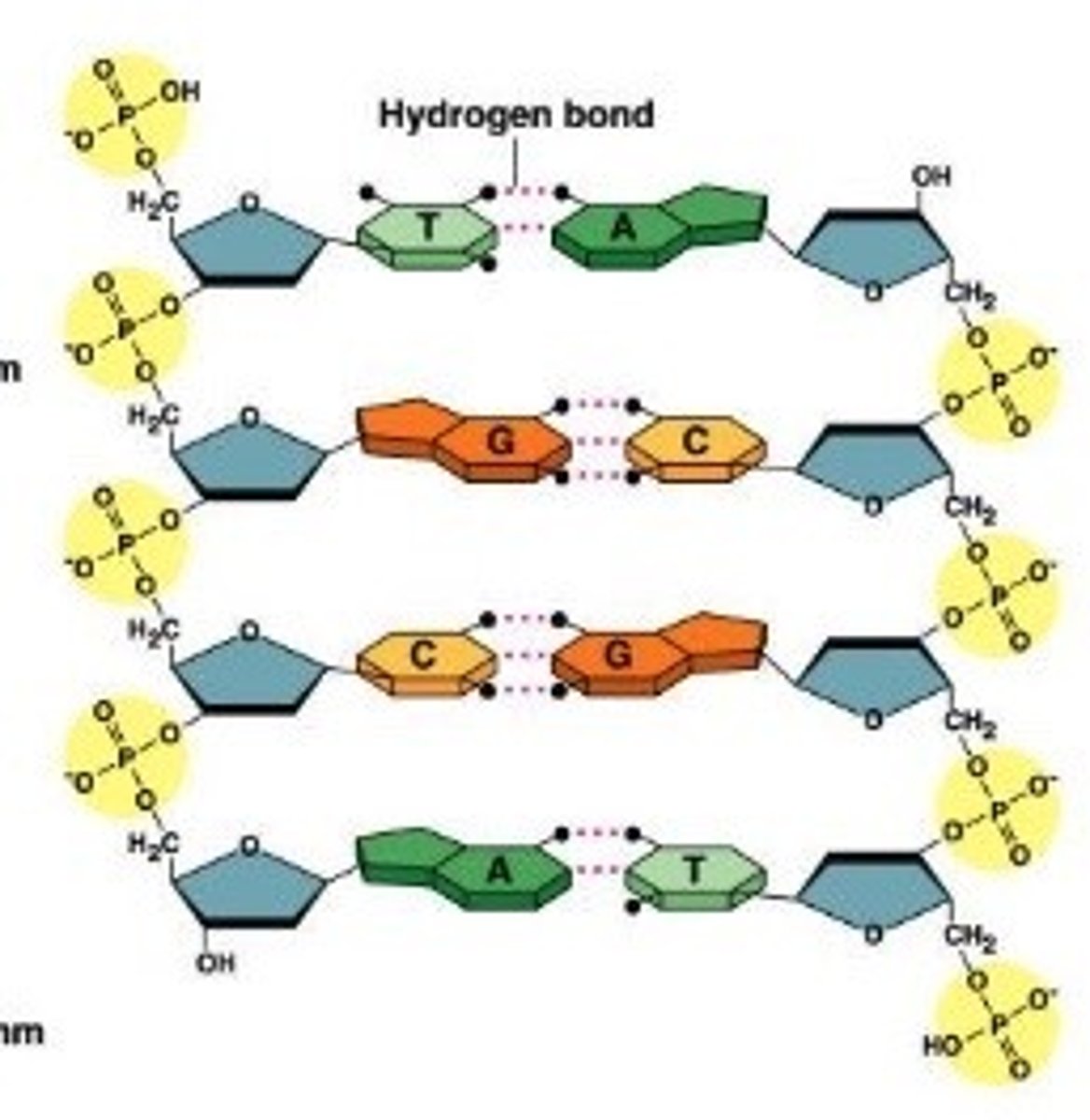
Bases of DNA
There are four bases Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine
complementary base pairs
A (Adenine) will always form weak hydrogen bonds with T (Thymine)
G (Guanine) will always form weak bonds with C (Cytosine)
Where is DNA found in eukaryotes?
nucleus
Where is DNA found in prokaryotes?
cytoplasm
DNA is an abbreviation for
deoxyribonucleic acid
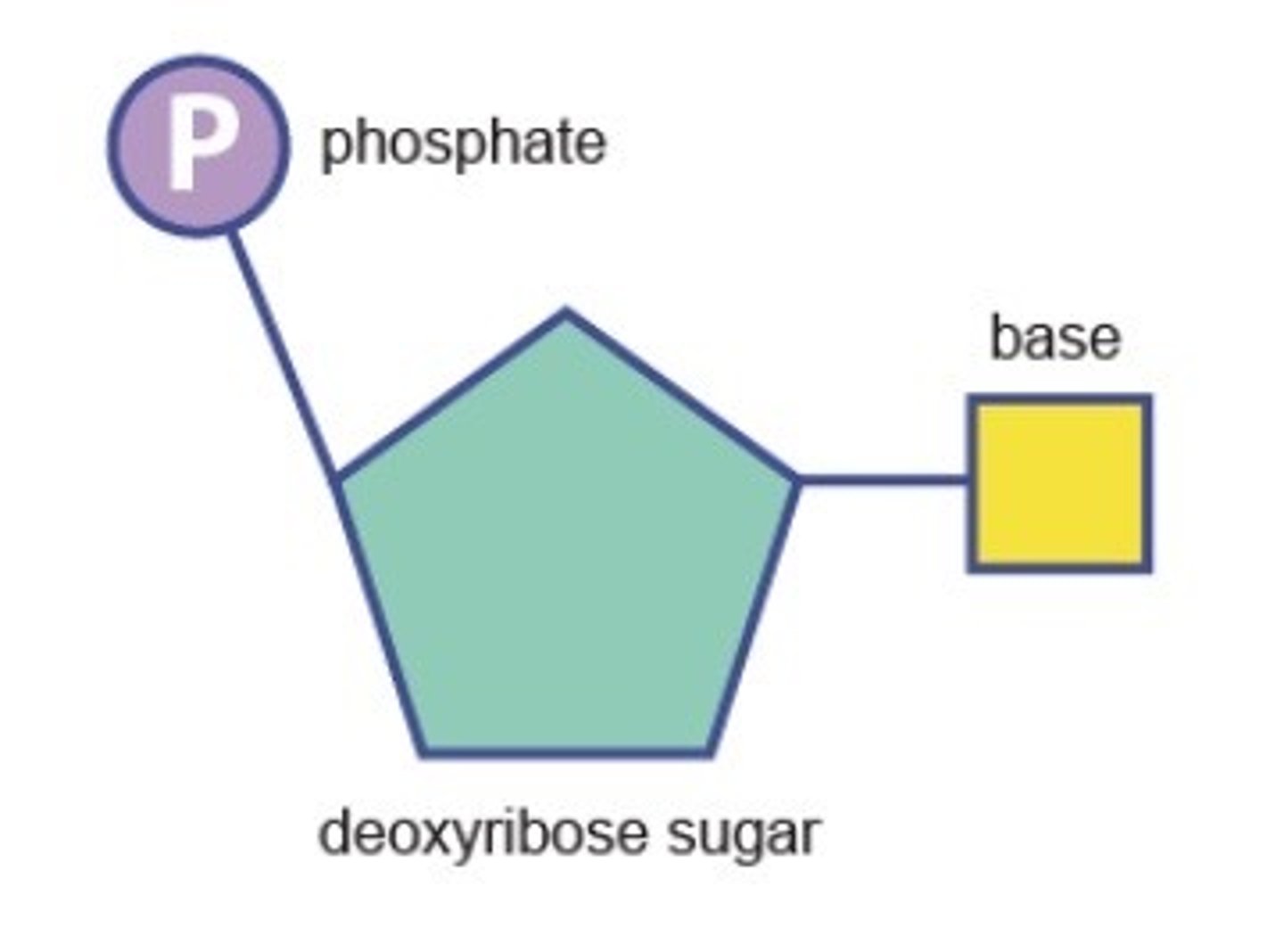
3 parts to a nucleotide
Deoxyribose sugar (5 carbons - pentagon shaped)
Phosphate group
Nitrogen base
Draw a Nucleotide Structure
Mutation
a change in a gene or chromosome.
A change in a gene creates new alleles.
alleles
Alleles are all the different versions of the same gene.
Once scientists have the genome of an organism they can ....
→ figure out what the bases code for
→ then, it is possible to edit its genetic information.
Genetic Modification
Changing the genetic material of an organism by removing, changing or inserting genes.
- This can include inserting a gene from one species into an entirely different species.
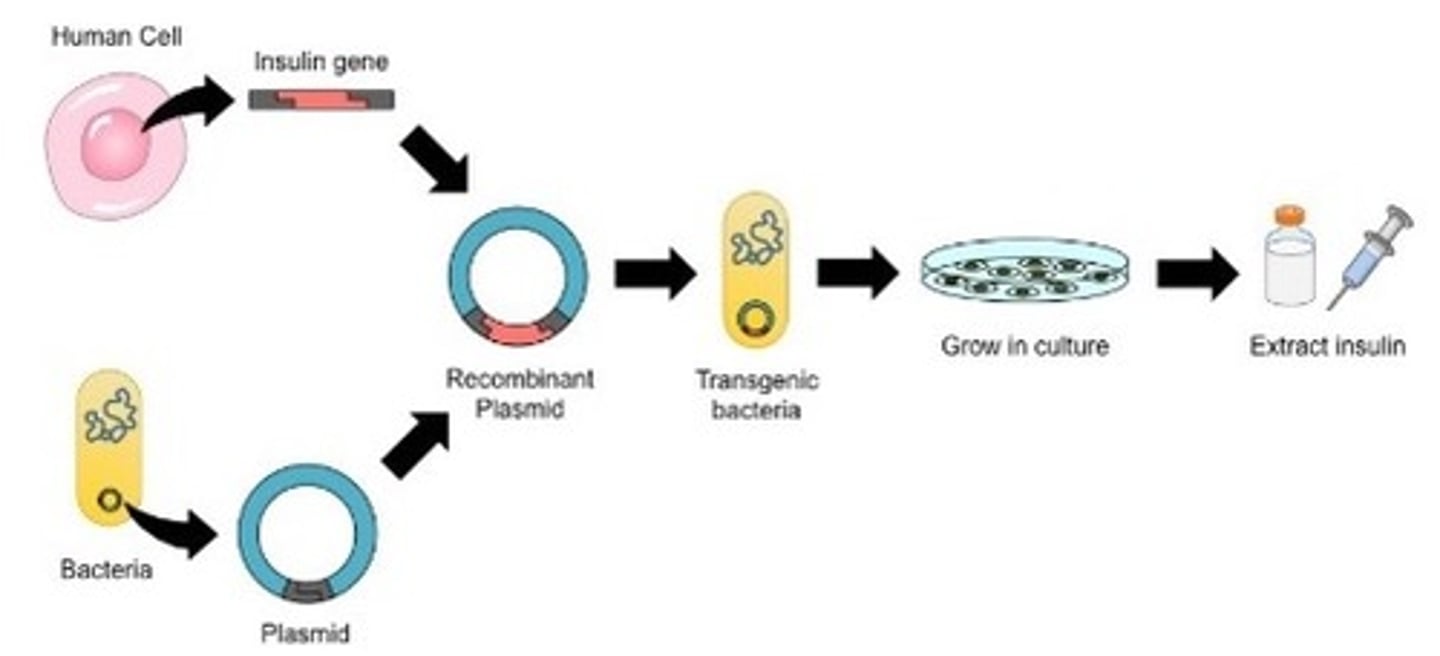
Recombinant DNA - Using bacteria to produce insulin
sugar phosphate bonding
Allele
An alternative form of a gene.
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
complementary base pairs
the standard arrangement of bases in nucleotides in relation to their opposite pairing, such as cytosine paired with guanine and adenine with thymine.
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
DNA profile
A distinctive pattern of DNA fragments that can be used to identify individuals
DNA double helix
twisted ladder shape of DNA
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
genetically modified organisms
An organism whose genetic material has been altered through some genetic engineering technology or technique.